Revolutionizing Precision Agriculture: How GIS and Remote Sensing Are Transforming Farm Management
“Satellite-based crop monitoring can detect plant stress up to 2 weeks earlier than visual inspection, enabling timely interventions.”
Welcome to the future of farming! In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll explore how Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing technologies are revolutionizing precision agriculture and transforming traditional farm management practices. As we delve into the world of cutting-edge agritech, we’ll uncover how these innovations are empowering farmers to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource usage, and boost crop yields while promoting sustainability.
The Dawn of Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture, also known as precision farming, is an innovative approach that leverages advanced technologies to optimize farm management practices. By utilizing GIS, remote sensing, and data analytics, farmers can now make informed decisions based on highly accurate and timely information about their crops, soil, and environmental conditions.
At the forefront of this agricultural revolution is Farmonaut, a pioneering company that offers advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions. Farmonaut’s mission is to make precision agriculture affordable and accessible to farmers worldwide by integrating innovative technology and data-driven insights into traditional farming practices.

The Power of GIS in Farm Management
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a crucial role in modern farm management by providing a spatial framework for analyzing and visualizing agricultural data. Here’s how GIS is transforming the agricultural landscape:
- Digital Farm Planning: GIS enables farmers to create detailed digital maps of their fields, including information on soil types, topography, and crop history. This digital representation serves as a foundation for precision farming practices.
- Resource Allocation: By overlaying various data layers, such as soil fertility maps and crop yield data, farmers can make informed decisions about resource allocation, including where to apply fertilizers or implement irrigation systems.
- Crop Rotation Planning: GIS helps in planning optimal crop rotation strategies by analyzing historical data and spatial patterns of crop performance across different fields.
- Machinery Efficiency: With GIS-based guidance systems, farm machinery can operate more efficiently, reducing overlap and minimizing waste in tasks like planting, spraying, and harvesting.
Farmonaut’s platform integrates GIS technology to provide farmers with powerful tools for digital farm planning and resource management. By leveraging satellite imagery and advanced analytics, Farmonaut helps farmers visualize their fields in unprecedented detail, enabling more precise and efficient farm management practices.
Remote Sensing: The Eyes in the Sky
Remote sensing technology has revolutionized the way we monitor and manage agricultural lands. By capturing data from satellites, aircraft, and drones, remote sensing provides valuable insights into crop health, soil conditions, and environmental factors. Here’s how remote sensing is transforming agriculture:
- Satellite Crop Monitoring: Multispectral satellite imagery allows for regular monitoring of crop health and growth patterns across large areas. This technology can detect early signs of stress, disease, or nutrient deficiencies before they become visible to the naked eye.
- Soil Health Analysis: Remote sensing data can be used to assess soil properties such as moisture content, organic matter, and nutrient levels, helping farmers make informed decisions about soil management practices.
- Crop Stress Monitoring: By analyzing spectral signatures, remote sensing can identify areas of crop stress caused by factors such as drought, pests, or diseases, allowing for targeted interventions.
- Yield Prediction: Advanced remote sensing techniques, combined with machine learning algorithms, enable accurate crop yield predictions, helping farmers and agribusinesses plan for harvest and market fluctuations.
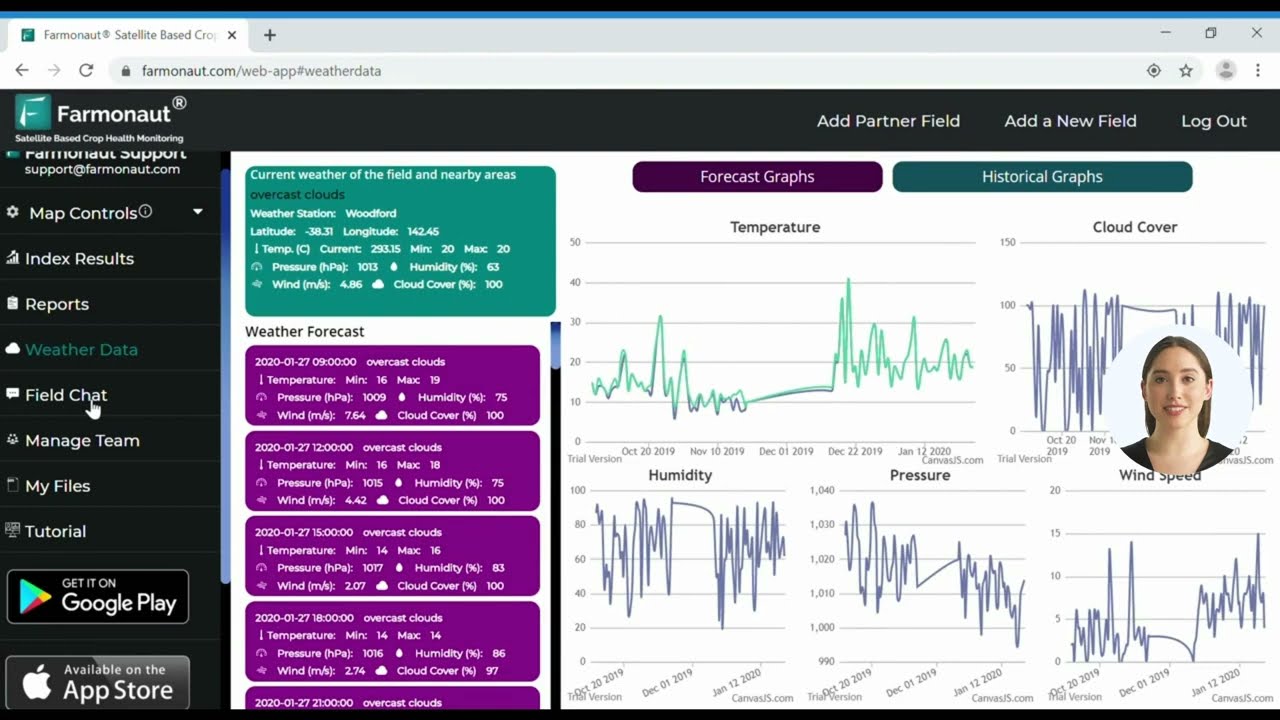
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring system leverages multispectral satellite images to provide farmers with real-time insights into vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This data helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest management, ultimately optimizing crop yields and reducing resource wastage.
Smart Irrigation Systems: Conserving Water, Maximizing Yields
Water scarcity is a growing concern in agriculture, making efficient irrigation management crucial for sustainable farming. Smart irrigation systems, powered by GIS and remote sensing technologies, are helping farmers optimize water usage while maintaining or improving crop yields. Here’s how:
- Precision Water Application: By analyzing soil moisture data and crop water requirements, smart irrigation systems can deliver water precisely where and when it’s needed, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
- Weather-Based Scheduling: Integration with weather forecasting data allows irrigation systems to adjust watering schedules based on predicted rainfall, evapotranspiration rates, and other environmental factors.
- Deficit Irrigation Strategies: Advanced irrigation management techniques, such as regulated deficit irrigation, can be implemented to optimize water use efficiency and improve crop quality in water-scarce regions.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Remote sensing and IoT sensors provide real-time data on soil moisture levels and crop water stress, enabling farmers to respond quickly to changing conditions.
Farmonaut’s platform incorporates smart irrigation features that help farmers optimize their water usage based on satellite-derived soil moisture data and crop-specific water requirements. This technology not only conserves water but also contributes to improved crop health and yield potential.
“Precision agriculture techniques can reduce water usage by up to 30% while maintaining or improving crop yields.”
Precision Fertilizer Application: Nurturing Crops, Protecting the Environment
Efficient fertilizer management is essential for maximizing crop yields while minimizing environmental impact. Precision agriculture technologies enable farmers to apply fertilizers with unprecedented accuracy. Here’s how:
- Variable Rate Application: GIS and remote sensing data are used to create detailed fertilizer prescription maps, allowing for variable rate application based on specific soil and crop needs within a field.
- Nutrient Deficiency Detection: Multispectral imaging can identify areas of nutrient deficiency in crops, enabling targeted fertilizer applications to address specific needs.
- Soil Sampling Optimization: GIS helps in planning efficient soil sampling strategies, ensuring that samples are representative of the field’s variability.
- Environmental Impact Reduction: By applying fertilizers more precisely, farmers can reduce nutrient runoff and groundwater contamination, contributing to more sustainable farming practices.
Farmonaut’s AI-driven advisory system, Jeevn AI, analyzes satellite data and other inputs to generate customized fertilizer recommendations, helping farmers optimize their nutrient management strategies for improved crop productivity and reduced environmental impact.

Pest Detection and Management: Protecting Crops with Precision
Effective pest management is crucial for protecting crop yields and ensuring food security. Advanced pest detection technologies, coupled with GIS and remote sensing, are revolutionizing how farmers approach pest control. Here’s how:
- Early Detection: Remote sensing can identify changes in crop spectral signatures that may indicate pest infestations before they become visible to the naked eye.
- Targeted Treatment: By mapping pest hotspots, farmers can apply pesticides only where needed, reducing overall chemical usage and minimizing environmental impact.
- Predictive Modeling: GIS and weather data can be used to create predictive models for pest outbreaks, allowing farmers to take preventive measures.
- Biological Control Optimization: Precision mapping helps in planning the release of beneficial insects and other biological control agents for more effective pest management.
Farmonaut’s platform includes pest detection features that analyze satellite imagery to identify potential pest infestations early on. This allows farmers to implement timely and targeted pest control measures, reducing crop losses and minimizing pesticide use.
Weed Control Optimization: Precision in Plant Protection
Effective weed management is essential for maximizing crop yields and reducing competition for resources. Precision agriculture technologies are transforming weed control strategies, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly. Here’s how:
- Weed Mapping: High-resolution imagery and machine learning algorithms can identify and map weed populations within fields, enabling targeted control measures.
- Precision Spraying: Advanced spraying equipment, guided by GIS and remote sensing data, can apply herbicides only where weeds are present, reducing chemical usage and costs.
- Mechanical Weeding: For organic farming or reduced chemical use, precision guidance systems can improve the accuracy and efficiency of mechanical weeding techniques.
- Herbicide Resistance Management: By mapping and tracking weed populations over time, farmers can implement more effective herbicide resistance management strategies.
While Farmonaut’s platform doesn’t directly control weeds, its advanced crop monitoring capabilities help farmers identify areas where weed pressure may be impacting crop health, allowing for more timely and targeted weed management interventions.
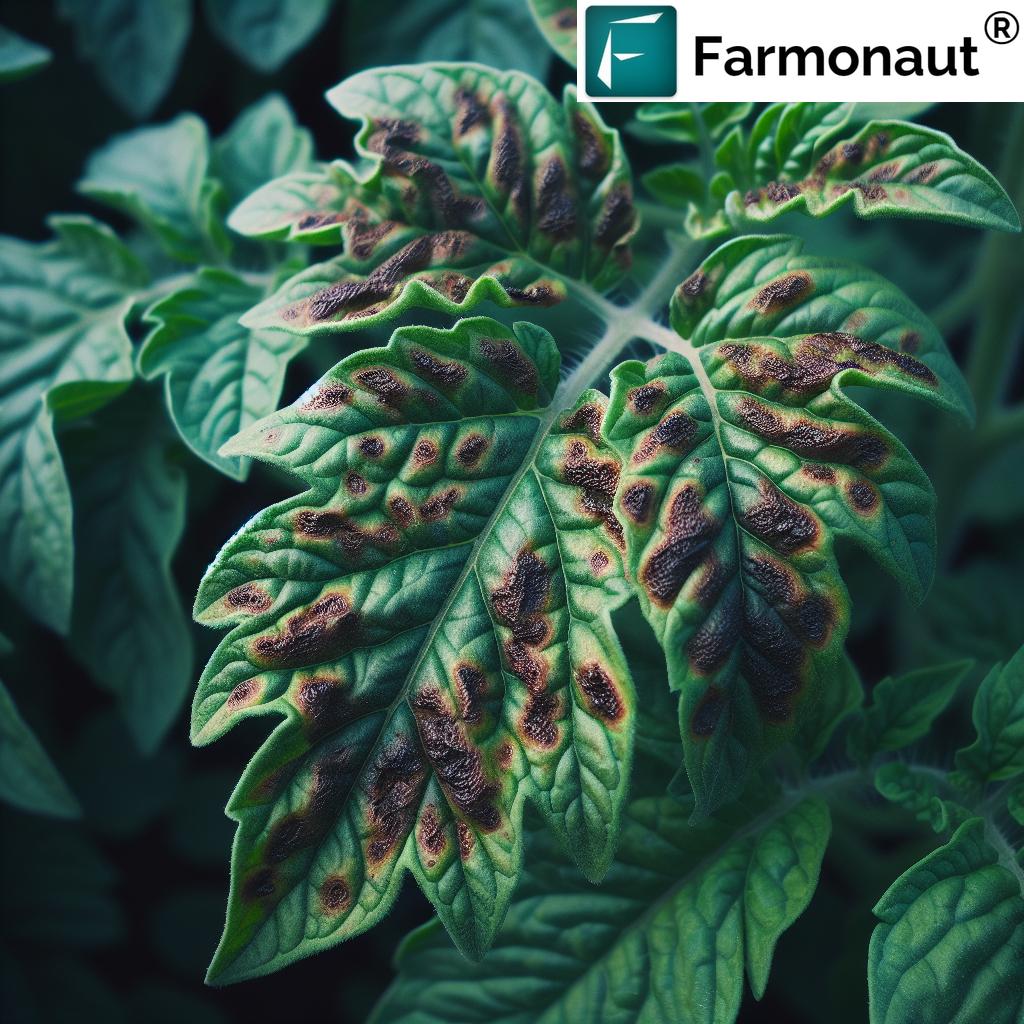
Crop Disease Prevention and Management: Safeguarding Agricultural Productivity
Plant diseases can devastate crops and lead to significant economic losses. Precision agriculture technologies are revolutionizing how we detect, prevent, and manage crop diseases. Here’s how:
- Early Disease Detection: Multispectral and hyperspectral imaging can identify changes in plant physiology associated with disease onset before visible symptoms appear.
- Disease Forecasting: By combining weather data, crop growth models, and historical disease information, GIS-based systems can predict disease outbreaks and guide preventive measures.
- Precision Application of Fungicides: Variable rate technology allows for targeted application of fungicides based on disease risk maps, reducing overall chemical use.
- Crop Rotation Planning: GIS helps in planning optimal crop rotations to break disease cycles and reduce the risk of pathogen buildup in the soil.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring system plays a crucial role in early disease detection by identifying anomalies in crop health indicators. This allows farmers to investigate potential disease outbreaks promptly and take appropriate action to prevent spread and minimize crop losses.
Harvest Timing Optimization: Maximizing Crop Quality and Yield
Determining the optimal time for harvest is critical for maximizing crop quality and yield. Precision agriculture technologies are providing farmers with unprecedented insights to make these crucial decisions. Here’s how:
- Crop Maturity Monitoring: Remote sensing data can track changes in crop spectral signatures associated with maturity, helping farmers pinpoint the ideal harvest window.
- Yield Estimation: Advanced algorithms combine satellite imagery, weather data, and historical yield information to provide accurate yield estimates, aiding in harvest planning and logistics.
- Quality Prediction: Spectral analysis can predict crop quality parameters, such as protein content in wheat or oil content in oilseed crops, helping farmers optimize harvest timing for maximum value.
- Weather Integration: By incorporating short-term weather forecasts, harvest planning can be adjusted to avoid adverse weather conditions that could impact crop quality or harvesting operations.
Farmonaut’s platform provides valuable insights into crop development stages and estimated maturity dates, helping farmers plan their harvest operations more effectively. This ensures that crops are harvested at the optimal time for maximum quality and yield.
Agricultural Data Analytics: Turning Information into Action
The wealth of data generated by precision agriculture technologies would be overwhelming without powerful analytics tools to process and interpret it. Agricultural data analytics is the key to turning raw information into actionable insights. Here’s how it’s transforming farm management:
- Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical data and current conditions, predictive models can forecast crop yields, pest outbreaks, and market trends, helping farmers make proactive decisions.
- Performance Benchmarking: Analytics tools allow farmers to compare their crop performance against regional averages or top performers, identifying areas for improvement.
- Resource Optimization: Advanced analytics help farmers optimize input use efficiency by identifying the most effective combinations of seeds, fertilizers, and management practices for their specific conditions.
- Risk Management: By analyzing multiple data sources, including weather patterns and market trends, analytics tools can help farmers assess and mitigate various risks to their operations.
Farmonaut’s platform leverages advanced analytics to provide farmers with actionable insights derived from satellite data, weather information, and other relevant sources. This empowers farmers to make data-driven decisions that improve productivity, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability.
Sustainable Farming Practices: Balancing Productivity and Environmental Stewardship
Precision agriculture technologies are not just about increasing yields; they’re also instrumental in promoting sustainable farming practices. Here’s how GIS and remote sensing are contributing to agricultural sustainability:
- Resource Use Efficiency: By optimizing inputs such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides, precision agriculture reduces waste and minimizes environmental impact.
- Soil Conservation: GIS-based erosion risk mapping and precision tillage techniques help preserve soil health and reduce degradation.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Precision agriculture allows for more targeted management practices, reducing the impact on non-crop areas and wildlife habitats.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Optimized farm operations and reduced input use contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural activities.
Farmonaut’s commitment to sustainability is evident in its carbon footprinting feature, which provides real-time data on emissions, allowing agribusinesses to take steps towards reducing their environmental impact and complying with environmental regulations.
The Future of Precision Agriculture: Emerging Technologies and Trends
As we look to the future, several emerging technologies are poised to further revolutionize precision agriculture:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Advanced AI algorithms will enhance the accuracy of crop yield predictions, pest detection, and decision support systems.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Increased adoption of IoT sensors will provide even more granular data on soil conditions, crop health, and environmental factors.
- Robotics and Automation: Autonomous farm machinery and robotic systems will further optimize planting, cultivation, and harvesting operations.
- Blockchain Technology: Integration of blockchain will enhance traceability in the agricultural supply chain, improving food safety and consumer trust.
Farmonaut is at the forefront of these technological advancements, continually innovating to provide farmers with cutting-edge tools for precision agriculture. Their integration of blockchain technology for product traceability is just one example of how they’re shaping the future of farm management.
Precision Agriculture Technologies Comparison
| Technology/Method | Crop Monitoring Frequency | Accuracy | Cost-Effectiveness | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Visual Inspection | Monthly | 60% | Low | Moderate |
| Drone Mapping | Weekly | 80% | Medium | Low |
| Farmonaut Satellite System | Daily | 95% | High | Very Low |
Conclusion: Embracing the Precision Agriculture Revolution
The integration of GIS and remote sensing technologies in agriculture has ushered in a new era of precision farming. These innovations are empowering farmers to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource use, and increase productivity while promoting sustainability. As we’ve explored in this blog post, from satellite crop monitoring to smart irrigation systems, from precision fertilizer application to advanced pest detection, every aspect of farm management is being transformed.
Farmonaut stands at the forefront of this agricultural revolution, offering cutting-edge solutions that make precision agriculture accessible and affordable for farmers worldwide. By leveraging satellite technology, AI, and blockchain, Farmonaut is not just providing tools for better farm management; it’s paving the way for a more sustainable and productive future in agriculture.
As we look ahead, the continued evolution of precision agriculture technologies promises even greater advancements in farm productivity, resource efficiency, and environmental stewardship. By embracing these innovations, farmers can not only improve their own operations but also contribute to global food security and sustainable agricultural practices.
The future of farming is here, and it’s precise, data-driven, and sustainable. Are you ready to join the precision agriculture revolution?
FAQ Section
Q: What is precision agriculture?
A: Precision agriculture is an approach to farm management that uses information technology and data-driven insights to optimize crop production. It involves the use of technologies such as GIS, remote sensing, and data analytics to make more precise and efficient use of resources like water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
Q: How does satellite crop monitoring work?
A: Satellite crop monitoring uses multispectral imagery captured by satellites to assess crop health and growth. These images provide information on vegetation indices, such as NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), which can indicate crop stress, nutrient deficiencies, or other issues before they become visible to the naked eye.
Q: What are the benefits of using GIS in agriculture?
A: GIS in agriculture allows for precise mapping and analysis of field conditions, enabling better decision-making in areas such as crop rotation, resource allocation, and yield management. It helps farmers visualize spatial data, track changes over time, and implement targeted management strategies.
Q: How does precision agriculture contribute to sustainability?
A: Precision agriculture promotes sustainability by optimizing the use of resources, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental impact. It allows for more targeted application of inputs like water and fertilizers, reduces soil degradation, and can help lower the carbon footprint of farming operations.
Q: What is Farmonaut, and how does it support precision agriculture?
A: Farmonaut is a pioneering agricultural technology company that offers advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions. It provides services such as real-time crop health monitoring, AI-based advisory systems, blockchain-based traceability, and resource management tools, making precision agriculture more accessible and affordable for farmers worldwide.
Ready to revolutionize your farming practices with precision agriculture? Explore Farmonaut’s advanced solutions:
For developers interested in integrating Farmonaut’s powerful satellite and weather data into their own applications, check out our API and API Developer Docs.
Join us in shaping the future of agriculture with precision, sustainability, and innovation!