Smart Digital Farming: 7 Tech Secrets for Huge Yields
“Precision agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 20% using smart sensors and data analytics.”
Introduction to Smart Digital Farming
Smart digital farming—also called precision agriculture or digital agriculture—is revolutionizing the way we manage, cultivate, and monitor crops and livestock. Integrating advanced technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, drones, robotics, and blockchain into agricultural practices enables us to collect massive amounts of real-time data and transform it into actionable insights. This data-driven approach empowers us to optimize resource use, enhance productivity, minimize environmental impact, and boost crop yields sustainably.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the “7 Tech Secrets” behind successful smart digital farming, highlight their game-changing benefits, and show how leading-edge platforms—like Farmonaut—are making these technologies accessible for all farmers. Let’s uncover the digital tools transforming global agriculture, one field at a time.
Why Smart Digital Farming Matters
With the world’s population booming and climate change posing unpredictable challenges to food security, agricultural productivity and sustainability have never been more critical. Traditional farming methods often fall short in utilizing resources efficiently or responding quickly to emerging threats such as pests, diseases, or extreme weather conditions. With smart digital farming, we can bridge this gap, harnessing real-time data and advanced technologies to make informed decisions that elevate yields and efficiency, while reducing costs and environmental burden.
- Data-driven management: Instead of relying solely on visual cues, we use quantitative data from sensors, satellites, and predictive models.
- Optimized resource use: We apply inputs such as water and fertilizers **only** where needed.
- Timely intervention: Early detection of crop health issues enables rapid, targeted responses, reducing losses from pests, droughts, or diseases.
- Traceability and transparency: Technologies like blockchain ensure secure and transparent food supply chains from farm to fork.
This technological shift is shaping the future of food, making “digital” the new normal in farming.
Core Technologies: 7 Tech Secrets for Huge Yields
Let’s dive into the seven transformative technologies driving the smart digital farming revolution—each is a powerful secret for achieving huge yield improvements, efficiency, and environmental sustainability.
1. Internet of Things (IoT) in Agriculture
IoT in agriculture uses a network of connected devices—including sensors, weather stations, and smart equipment—to continuously collect data on key environmental parameters such as soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and crop health. This persistent data stream enables us to monitor field conditions in real-time, unlocking rapid responses to shifting situations—be it irrigation needs, pest threats, or drought stress.
- Smart soil sensors detect moisture levels and send updates to our mobile or web apps for optimal irrigation scheduling, reducing water wastage.
- Environmental sensors track air quality, humidity, and leaf temperature, providing early warnings of disease risks.
Through IoT integrations, farmers can remotely control equipment—like turning on irrigation pumps based on sensor triggers—maximizing efficiency while cutting input costs.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning in Farming
The role of artificial intelligence in farming is to convert complex agriculture data analytics into powerful predictions and action plans. AI and machine learning models analyze satellite and sensor data, detect plant diseases, identify nutrient deficiencies, and optimize seeding or fertilization patterns in real time.
- AI algorithms forecast crop yields, helping us plan for marketing or storage well in advance.
- Machine learning can identify “invisible” patterns in crops, such as subtle stress before it appears visually.
- Automation of routine processes like irrigation, pest detection, and resource allocation unlocks higher productivity and reduces manual errors.
Our software ecosystem can leverage these AI-drive systems—like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI advisory system—to provide actionable farm management recommendations, tailored to each field.
3. Drones for Crop Monitoring & Aerial Imaging
Drones for crop monitoring offer an unprecedented vantage point. Outfitted with multispectral cameras, they capture images of fields at regular intervals, providing aerial insights into crop health, pest infestations, and irrigation issues.
- We spot pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies early—saving both crops and resources.
- High-resolution aerial imaging aids in precision application of fertilizers and pesticides, ensuring the right dose in the right location.
- Detailed field maps enable efficient field management and task prioritization.
With drone technology, even large-scale farms benefit from rapid, regular, and non-invasive crop health monitoring systems, driving both sustainability and productivity.
4. Farm Automation and Robotics
Farm automation and robotics have transformed field operations. Autonomous tractors, robotic harvesters, and automated weeding machinery perform vital tasks with precision and at scale, drastically reducing labor costs and human error.
- Planting, spraying, harvesting, and even pruning can now be handled by robotic equipment, running day and night as needed.
- Computer vision and AI-driven controls ensure robots identify and act on plant-level needs—improving yields and resource efficiency.
We can now focus more on management, analysis, and planning—letting the robots handle repetitive, time-consuming, and even risky field work.
“Digital farming technologies can reduce water usage in agriculture by nearly 30% through targeted irrigation systems.”
5. GPS Mapping & Precision Planting
With GPS mapping and precision planting, we create field maps with sub-meter accuracy, identifying soil variability and tailoring seed distribution, fertilizer, or pesticide application for each plot.
- Variable rate technology (VRT) adjusts input rates across the field, optimizing both cost and environmental sustainability.
- Precision planting ensures robust, uniform plant emergence for maximum crop growth.
These technologies are the cornerstone of precision agriculture, reducing waste while increasing yields and profitability.
6. Blockchain in Agriculture Supply Chain
The role of blockchain in agriculture supply chain is to provide immutable, transparent traceability throughout food production, transportation, and processing.
- Every link in the supply chain is recorded and verified on a secure, tamper-proof ledger, from sowing to supermarket shelves.
- Consumers and retailers get detailed insights into product origin, safety, and ethics, building trust in agricultural brands.
- For us, blockchain reduces fraud, improves quality assurance, and streamlines compliance with food safety standards.
Smart contracts further automate payments, deliveries, and documentation, transforming food security and transparency.
Discover how Farmonaut enables full blockchain-based traceability for agricultural produce at every stage: Learn more about Farmonaut’s Product Traceability.
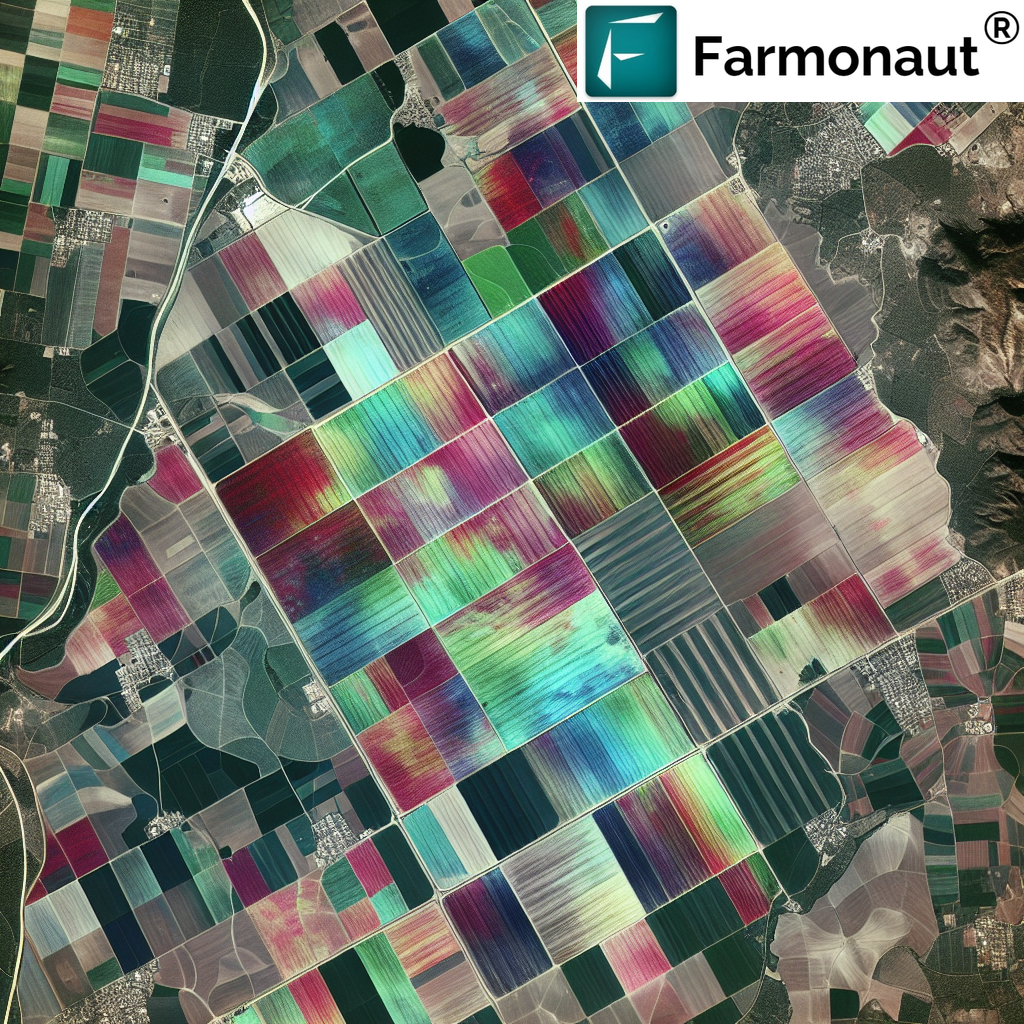
7. Satellite-Based Remote Sensing and Analysis
By leveraging satellite imagery and remote sensing technology, we gain consistent, large-scale monitoring of every hectare. This method provides detailed, multi-spectral analyses of crop vigor, soil moisture, and disease outbreaks.
- Farmonaut’s platform offers real-time, field-level data to identify growth trends, irrigation needs, and pest hotspots.
- Historical satellite data enable us to analyze long-term trends, predict yields, and schedule tasks more efficiently.
Satellite-based crop health monitoring and digital farm management are now affordable for all—without the need to invest in expensive hardware or sensor networks.
Comparative Technology Impact Table: Digital Farming’s Yield, Efficiency & Sustainability
To simplify complex choices in smart digital farming, here’s a comparative overview of top precision agriculture technologies, contrasting their yield, efficiency, and sustainability impacts:
| Technology Name | Main Function | Yield Improvement (%) | Cost Savings (%) | Sustainability Impact | Example Crops |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoT Sensors | Continuous soil & climate monitoring | +15–20 | –20–25 | Reduces water/fertilizer use by 30% | Wheat, maize, rice, vegetables |
| Drones (Aerial Imaging) | Crop health & pest detection | +10–15 | –10–15 | Minimizes pesticide use by 20% | Cotton, soy, vineyards |
| AI & ML Systems | Analytics & predictive modeling | +10–25 | –10–20 | Optimizes input timing/application | All major crops |
| Autonomous Machinery | Automated planting/harvesting | +5–10 | –25–30 | Cuts fuel & labor emissions | Sugarcane, grains |
| Remote Sensing (Satellites) | Large-scale crop/nutrient monitoring | +8–15 | –15–25 | Early detection, targeted resource use | Cotton, rice, forests |
| Blockchain | Supply chain traceability | Quality-driven | –5–10 | Reduces food fraud, increases consumer trust | All supply chains |
| GPS Mapping | Precision planting & VRT inputs | +5–12 | –8–15 | Reduces overuse of resources | Corn, soybean, orchards |
Precision Application and Integration: Making Tech Work for Real Farms
It’s no longer about choosing a single tool—it’s about integration. Combining satellite-based monitoring, IoT in agriculture, and AI-powered crop health monitoring systems enables us to oversee every step of farm management, from planting to harvest.
For example, using Farmonaut’s large scale farm management system (see product), agribusinesses can track multiple locations via satellite, receive instant health alerts, and plan logistics. For those focusing on transportation and equipment, fleet management (explore the service) streamlines vehicle use, reduces costs, and improves machine productivity.
Precision also extends to financing and sustainability. For crop loan and insurance verification, Farmonaut uses satellite data for crop loan & insurance validation. To monitor and improve our carbon footprinting, we use real-time emissions data (learn more) to comply with sustainability standards and minimize our environmental impact.
And for forestry, forest, or plantation advice, Farmonaut offers AI-driven insights—access forest, plantation, and advisory features—making precision, sustainable decision-making a reality.
Farmonaut: Transforming Digital Farming Globally
Farmonaut stands at the forefront of making precision agriculture affordable and scalable for every farmer, from smallholder to commercial. Our platform combines:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring: Multispectral analysis of NDVI, soil moisture, crop stress, and resource allocation, with historical data trends for season-on-season benchmarking.
- AI-based advisory solutions: Jeevn AI helps with real-time farm advisory, weather updates, irrigation and fertilizer planning, and expert crop management strategies.
- Blockchain-enabled traceability: Advanced supply chain transparency, from farm to shelf, to ensure food quality and safety for corporates and consumers.
- Fleet/resource management: Mobile- and web-based dashboards track all machinery, vehicles, and labor—reducing operational costs and maximizing productivity.
- Carbon footprinting features: Climate reporting tools summarize emissions, suggesting ways to improve sustainability and comply with regulations.
Our mission is to lower the cost barrier for global digital farming transformation—making high-impact data, precision AI, and supply chain trust available to every field, forest, and farmer worldwide.
For immediate integration into your systems, access the Farmonaut API and developer docs.
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
To make Digital Farming scalable and cost-effective, Farmonaut offers flexible, subscription-based plans for all sizes of landholding and agribusiness operations:
Key Benefits of Digital Farming
- Higher Productivity: By using data analytics, AI, and remote sensing, we manage each area of land for optimal yields. Early detection, precision input application, and continuous feedback increase output while minimizing loss.
- Resource Efficiency: IoT automation delivers water, fertilizers, and pesticides with pinpoint accuracy—leading to input cost savings of up to 30%.
- Sustainability: Minimizing overuse of resources protects ecosystems, reduces greenhouse emissions, and enables environmentally sustainable food production.
- Risk Management: Real-time monitoring and predictive models empower us to react immediately to weather variability, pest outbreaks, or diseases, reducing the risk of devastating crop losses.
- Transparency & Trust: Blockchain ensures farm-to-shelf traceability, improving food safety, brand reputation, and compliance with quality standards.
- Access to Financing: Satellite-based verification builds credibility when accessing crop loans and insurance, especially in emerging markets.
All these benefits democratize agricultural innovation, making high-impact tools widely available—not just for mega-farms, but for smallholders and cooperatives too.
Challenges and Considerations in Smart Digital Farming
While the advantages are significant, smart digital farming is not without hurdles:
- Data Privacy and Security: Collecting, storing, and sharing sensitive farm data raises concerns about ownership, security, and third-party misuse. Secure platforms and clear data policies are essential.
- High Initial Investment: Advanced technologies—while rapidly becoming more affordable—still require initial capital for adoption, which may be a barrier for very small farms.
- Technical Expertise: Deploying and maintaining digital systems demands certain technical skills. Training and support services are key to successful adoption.
- Data Integration: Combining data from different sources (satellite, drone, IoT, manual) into a unified, actionable dashboard may require robust, interoperable platforms like Farmonaut.
Despite these challenges, the rapid evolution of agri-tech platforms and falling technology costs are making advanced smart digital farming tools accessible and practical for more and more farmers every year.
Global Market Trends and Initiatives
Governments, NGOs, and global organizations increasingly recognize the power of digital farming to enhance food security and promote sustainable farming practices. Examples include China’s national “smart farming” transformation plan (2024–2028), which aims to scale up national agricultural big-data platforms by 2028.
According to a recent market report, the global digital farming market could reach USD 74.70 billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of over 13.5%. Key drivers include technology innovation, government policies, and demand for traceability, quality, and sustainability in food supply chains.
As climate and resource pressures intensify, precision-driven digital agriculture is set to reshape the world’s farms, forests, and supply networks, ensuring resilient food systems for generations to come.
FAQ: Understanding Digital Farming
- What is smart digital farming?
- Smart digital farming combines IoT, AI, drones, robotics, and blockchain technologies for real-time data collection, analysis, and actionable decision-making to increase yield, reduce waste, and promote sustainability in agriculture.
- How can IoT and AI improve my farm’s productivity?
- IoT sensors monitor soil, weather, and crop health continuously. AI analyzes this data, providing actionable recommendations on irrigation, fertilization, pest management, and predicting crop yields for optimal resource allocation.
- Are digital farming tools expensive?
- While some advanced tools require substantial initial investments, platforms like Farmonaut offer affordable, scalable subscription services, making digital farming accessible to smallholders, cooperatives, and large agribusinesses.
- How does digital farming support sustainability?
- By precisely applying water, fertilizers, and chemicals only where needed, digital farming minimizes resource waste and environmental impact, helping to maintain soil health and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- What is blockchain’s role in agriculture?
- Blockchain creates a secure, transparent record of every supply chain transaction, ensuring traceability, quality assurance, and food safety from farm to shelf.
- Can I get expert help with farm data analysis?
- Yes. AI-based advisory platforms like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI provide tailored recommendations and actionable insights for every stage of crop and resource management.
- Is there a free trial or demo for Farmonaut’s services?
- Visit Farmonaut’s app portal for more information on trials and feature options.
Conclusion: Smart Digital Farming for a Sustainable Tomorrow
The integration of advanced digital technologies into agriculture is transforming every aspect of food and fiber production—empowering us to make smarter, more sustainable choices that boost crop yields, reduce costs, and protect the environment. From IoT sensors and artificial intelligence to drones, automation, and blockchain, the tools of smart digital farming are revolutionizing how we plant, manage, harvest, and deliver our food—redefining what’s possible for the world’s farmers.
By leveraging these innovations—and platforms like Farmonaut—we are building a more productive, resilient, and sustainable agricultural system, fit for today and generations to come.
Ready to start your digital agriculture journey?