Unlocking Precision Agriculture: How Topographic Mapping Revolutionizes Crop Yield Optimization
“3D mapping tools can analyze up to 5 key topographic factors: slope, elevation, aspect, curvature, and roughness.”
In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, we at Farmonaut are at the forefront of a revolution that’s transforming the way we grow our food. Today, we’re diving deep into the fascinating realm of topography in agriculture and how it’s reshaping the landscape of precision farming. As we unravel the complexities of 3D mapping for farming and digital elevation models in agriculture, we’ll discover how these cutting-edge technologies are not just changing the game – they’re redefining it.
Topography, the study of land surface features, has long been a crucial factor in agricultural practices. However, with the advent of precision agriculture tools and advanced remote sensing techniques, we’re now able to harness this information like never before. From optimizing irrigation systems to implementing sustainable farming practices, the applications are as vast as the fields we cultivate.
At Farmonaut, we’re passionate about making these groundbreaking technologies accessible to farmers worldwide. Our satellite-based farm management solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with traditional farming methods, providing real-time insights that can dramatically improve crop yields and resource management.
The Fundamentals of Topography in Agriculture
Before we delve into the high-tech world of precision agriculture, let’s establish a solid understanding of what topography means in the context of farming. Topography refers to the arrangement of natural and artificial physical features of an area. In agriculture, this encompasses several key elements:
- Elevation: The height of land above sea level
- Slope: The steepness or gradient of the land
- Aspect: The direction a slope faces (e.g., north-facing, south-facing)
- Curvature: The shape of the land surface (convex or concave)
- Roughness: The variability of the terrain at a small scale
Each of these topographic factors plays a crucial role in determining how water moves across the land, how soil develops, and ultimately, how crops grow. For instance, steep slopes can lead to increased erosion and water runoff, while flat areas might be prone to waterlogging. South-facing slopes in the Northern Hemisphere typically receive more sunlight, affecting plant growth and soil temperature.
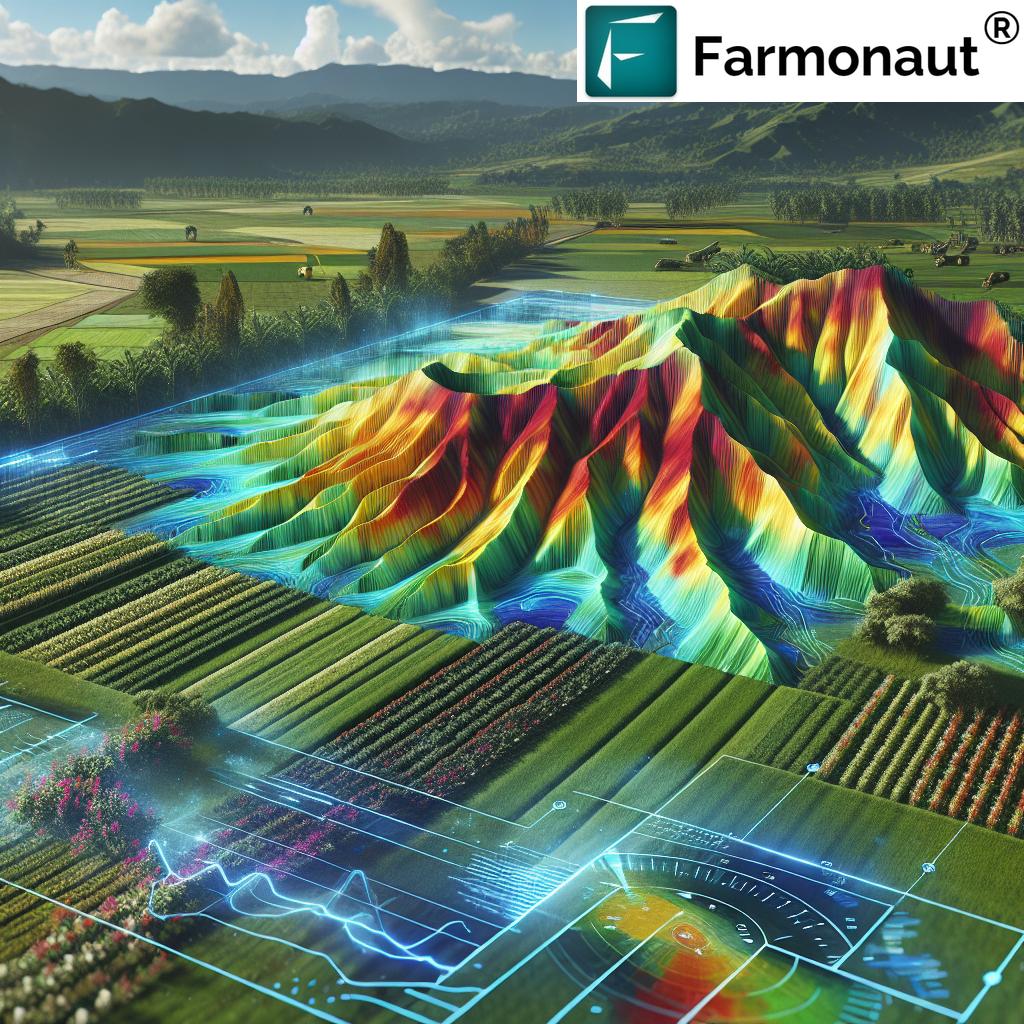
The Revolution of 3D Mapping in Agriculture
Now, let’s explore how modern technology is taking our understanding of topography to new heights – quite literally. 3D mapping for farming has revolutionized the way we visualize and analyze agricultural landscapes.
These advanced mapping techniques use a combination of technologies:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Uses laser pulses to measure distances and create highly accurate 3D models of the Earth’s surface.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Provides precise location data for mapping and machinery guidance.
- Satellite Imagery: Offers broad coverage and regular updates of land surfaces.
- Drone Surveys: Provides high-resolution imagery and can access hard-to-reach areas.
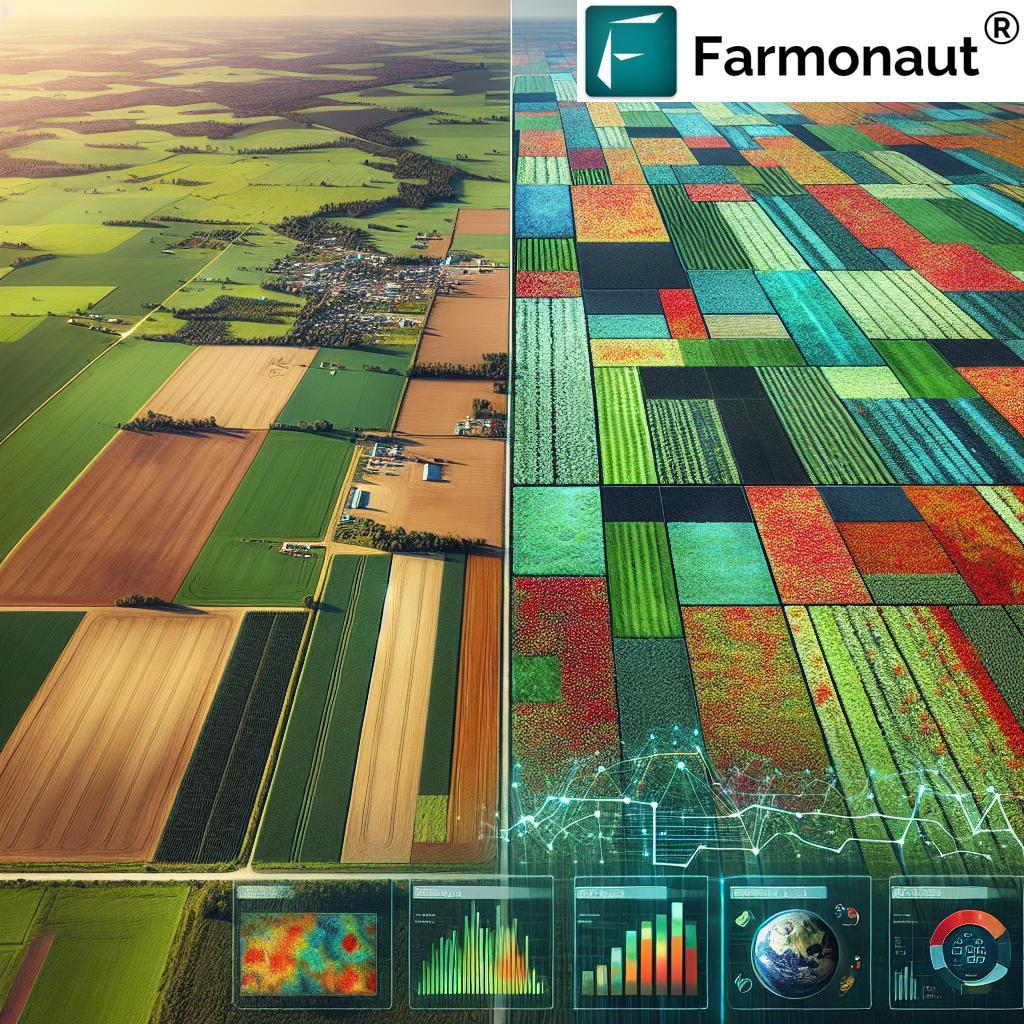
At Farmonaut, we harness the power of satellite imagery and AI to create detailed digital elevation models (DEMs) of agricultural lands. These models serve as the foundation for a wide range of precision agriculture tools, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions about their crops and land management strategies.
Digital Elevation Models: The Backbone of Precision Agriculture
Digital elevation models (DEMs) are the cornerstone of modern topographic analysis in agriculture. These 3D representations of the terrain surface provide invaluable information about the land’s contours, slopes, and drainage patterns. Here’s how DEMs are transforming farming practices:
- Water Management: By understanding how water flows across their fields, farmers can optimize irrigation systems and prevent waterlogging or drought stress.
- Erosion Control: Identifying areas prone to erosion allows for targeted soil conservation measures.
- Precision Planting: DEMs help in planning the most efficient planting patterns, taking into account sunlight exposure and soil conditions.
- Nutrient Management: Topographic data can reveal how nutrients are likely to be distributed across a field, enabling more precise fertilizer application.
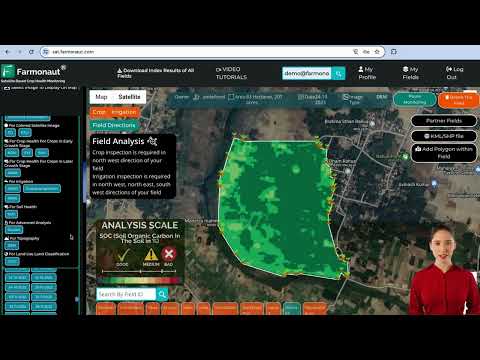
Our Farmonaut platform integrates DEM data with real-time satellite imagery to provide farmers with a comprehensive view of their land. This integration allows for dynamic monitoring of crop health in relation to topographic features, a powerful tool for optimizing yields.
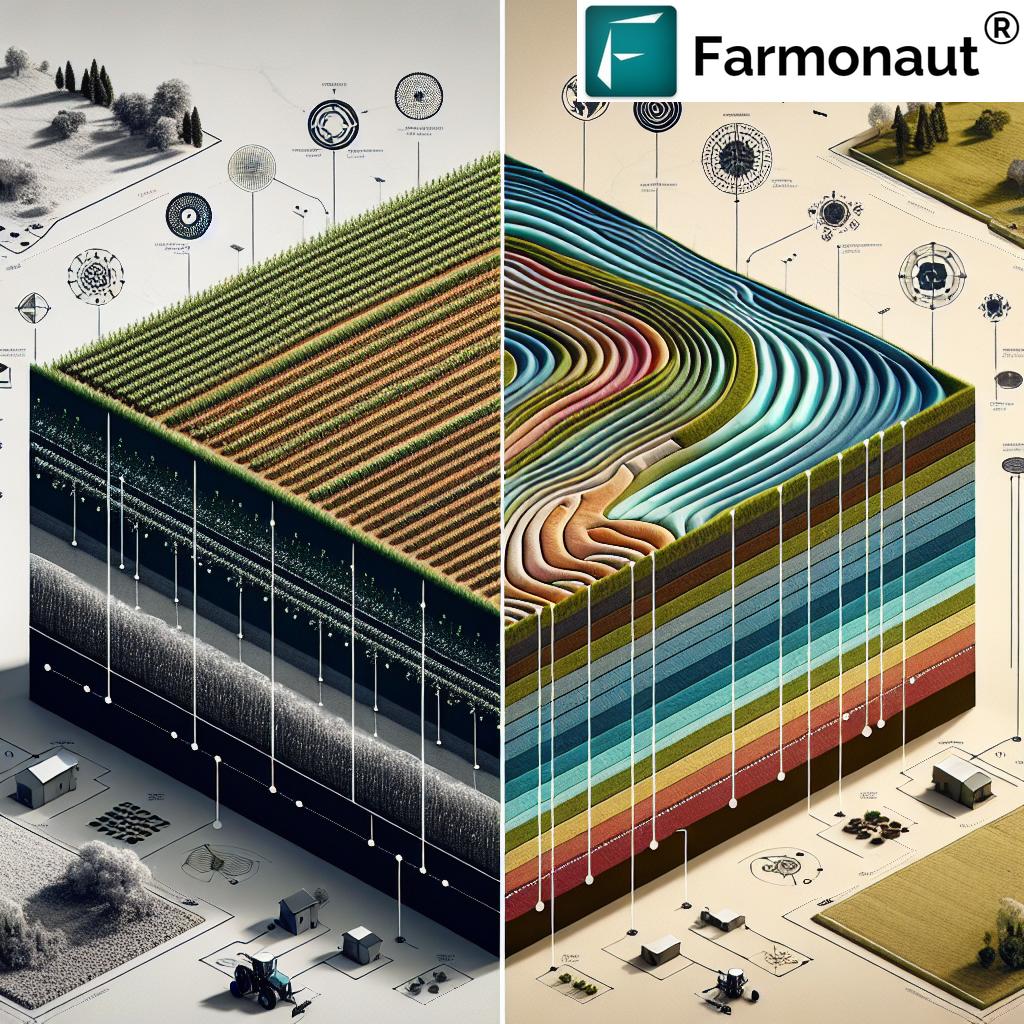
Topographic Factors Affecting Crop Growth
Understanding how topography influences crop growth is essential for maximizing agricultural productivity. Let’s explore some key topographic factors and their impacts:
| Topographic Factor | Impact on Agriculture | Precision Agriculture Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Slope | Affects water runoff, soil erosion, and machinery operation | Farmonaut’s 3D mapping for optimized contour plowing and terrace farming |
| Elevation | Influences temperature, precipitation, and growing season length | Crop selection advice based on elevation-specific climate data |
| Aspect | Determines sunlight exposure and microclimate conditions | Customized planting schedules and crop variety recommendations |
| Drainage Patterns | Affects soil moisture levels and nutrient distribution | Precision irrigation planning using Farmonaut’s soil moisture analytics |
By leveraging these topographic insights, farmers can make informed decisions about crop selection, planting strategies, and resource allocation. For instance, north-facing slopes in the Northern Hemisphere may be better suited for cold-hardy crops, while south-facing slopes could be ideal for sun-loving varieties.
Soil Management Techniques Informed by Topography
Topography plays a crucial role in soil formation and characteristics. Understanding this relationship allows for more effective soil management techniques:
- Soil Texture Mapping: Topographic data can help predict soil texture variations across a field, informing tillage practices and water management.
- Erosion Prevention: By identifying areas prone to erosion, farmers can implement targeted conservation measures like cover cropping or contour plowing.
- Nutrient Distribution: Topography influences how nutrients move through the soil. This knowledge enables precision fertilizer application, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Organic Matter Management: Low-lying areas often have higher organic matter content due to accumulation. This information can guide soil amendment strategies.
At Farmonaut, our soil fertility mapping tools incorporate topographic data to provide a comprehensive view of soil health across agricultural lands. This integration allows farmers to tailor their soil management practices to the specific needs of each area within their fields.
Precision Irrigation Systems: Harnessing Topography for Water Efficiency
Water management is one of the most critical aspects of agriculture, and topography plays a pivotal role in determining how water moves across the landscape. Precision irrigation systems that take topography into account can dramatically improve water use efficiency:
- Variable Rate Irrigation: By mapping field elevation and slope, irrigation systems can adjust water application rates to ensure uniform soil moisture across undulating terrain.
- Drainage Optimization: Understanding the natural drainage patterns informed by topography allows for strategic placement of drainage infrastructure, preventing waterlogging in low-lying areas.
- Runoff Management: Topographic data helps in designing water catchment systems and erosion control measures to capture and utilize runoff effectively.
Our Farmonaut platform integrates topographic data with real-time soil moisture measurements to provide farmers with actionable insights for irrigation management. This combination of historical topographic information and current soil conditions enables precise, timely irrigation decisions.
“Topographic mapping can improve crop yields by up to 20% through optimized water and nutrient management.”
Crop Yield Optimization Through Topographic Analysis
The ultimate goal of precision agriculture is to optimize crop yields while minimizing resource inputs. Topographic analysis plays a crucial role in achieving this balance:
- Yield Mapping: By overlaying yield data with topographic information, farmers can identify areas of consistently high or low productivity and investigate the underlying causes.
- Variable Rate Technology: Topography-informed variable rate application of seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides ensures that inputs are used most effectively across different field zones.
- Microclimate Management: Understanding how topography creates microclimates within a field allows for tailored crop management strategies, such as frost protection in low-lying areas.
Farmonaut’s crop yield optimization tools leverage advanced AI algorithms to analyze topographic data alongside satellite imagery, weather information, and historical yield records. This comprehensive approach provides farmers with actionable insights to maximize their crop productivity.
Sustainable Farming Practices Enhanced by Topographic Insights
As we face increasing pressure to produce more food with fewer resources, sustainable farming practices are more important than ever. Topographic analysis can contribute significantly to sustainability efforts:
- Precision Conservation: By identifying areas prone to erosion or nutrient leaching, farmers can implement targeted conservation measures where they’re most needed.
- Carbon Sequestration: Topographic data can help identify areas suitable for agroforestry or other carbon sequestration practices.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Understanding the diverse habitats created by topographic variations allows for strategic placement of wildlife corridors and natural areas within agricultural landscapes.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to promoting sustainable agriculture. Our platform includes tools for carbon footprint tracking and environmental impact assessment, helping farmers align their practices with global sustainability goals.
The Future of Topography in Precision Agriculture
As technology continues to advance, the role of topography in precision agriculture is set to become even more significant. Here are some exciting developments on the horizon:
- AI-Powered Predictive Models: Machine learning algorithms will increasingly be able to predict crop performance based on topographic features and historical data.
- Real-Time Topographic Monitoring: Advances in satellite and drone technology will enable more frequent and detailed topographic mapping, allowing for dynamic land management strategies.
- Integration with IoT Devices: Topographic data will be seamlessly integrated with a network of soil sensors, weather stations, and farm machinery to create a holistic precision farming ecosystem.
At Farmonaut, we’re constantly innovating to stay at the forefront of these technological advancements. Our commitment to research and development ensures that our farmers have access to the most cutting-edge precision agriculture tools available.
Empowering Farmers with Farmonaut’s Topography-Based Solutions
As we’ve explored throughout this article, topography plays a crucial role in modern precision agriculture. At Farmonaut, we’re dedicated to making these advanced technologies accessible to farmers of all scales. Our platform offers a range of tools that leverage topographic data to optimize farming practices:
- 3D Field Mapping: Create detailed digital elevation models of your farmland.
- Soil Fertility Analysis: Understand how topography influences soil health and nutrient distribution.
- Precision Irrigation Planning: Optimize water use based on topographic features and real-time soil moisture data.
- Crop Health Monitoring: Track vegetation health indices in relation to topographic factors.
- Yield Forecasting: Predict crop yields using AI models that incorporate topographic data.
We invite you to explore how Farmonaut can transform your farming operations. Our user-friendly platform is accessible via web, Android, and iOS applications, ensuring you have the insights you need at your fingertips, wherever you are.
Ready to revolutionize your farming practices? Access Farmonaut’s cutting-edge solutions today:
For developers and businesses looking to integrate our powerful satellite and weather data into their own systems, we offer a robust API solution. Learn more about our API capabilities and access our developer documentation:
Conclusion: Embracing the Topographic Revolution in Agriculture
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive guide, topography in agriculture is far more than just understanding the lay of the land. It’s about harnessing the power of advanced technologies to unlock the full potential of every acre, every plant, and every drop of water. From 3D mapping for farming to sophisticated digital elevation models in agriculture, these precision agriculture tools are transforming the way we grow our food and manage our natural resources.
At Farmonaut, we’re proud to be at the forefront of this agricultural revolution. Our mission is to make these powerful technologies accessible to farmers worldwide, enabling them to make data-driven decisions that boost productivity, enhance sustainability, and ensure food security for generations to come.
As we look to the future, the integration of topographic analysis with AI, IoT, and remote sensing will continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in agriculture. By embracing these innovations, we can create a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable food system that meets the challenges of the 21st century and beyond.
We invite you to join us on this exciting journey. Whether you’re a small-scale farmer looking to optimize your operations or a large agribusiness seeking to implement cutting-edge precision agriculture techniques, Farmonaut has the tools and expertise to help you succeed. Together, we can unlock the full potential of your land and contribute to a more sustainable and prosperous agricultural future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is topography in agriculture?
Topography in agriculture refers to the study and analysis of land surface features such as elevation, slope, and aspect, and how they impact farming practices, soil health, and crop growth. - How does topography affect crop growth?
Topography influences factors like water drainage, soil erosion, sunlight exposure, and microclimate conditions, all of which directly impact crop growth and yield. - What are digital elevation models (DEMs) in agriculture?
DEMs are 3D representations of the terrain surface used in precision agriculture to analyze land features, plan irrigation systems, and optimize crop management strategies. - How can farmers use topographic mapping to improve their practices?
Farmers can use topographic mapping to optimize irrigation, prevent soil erosion, plan precision planting, and implement targeted nutrient management strategies. - What technologies are used for creating topographic maps in agriculture?
Technologies like LiDAR, GPS, satellite imagery, and drone surveys are commonly used to create detailed topographic maps for agricultural purposes. - How does Farmonaut incorporate topographic data into its platform?
Farmonaut integrates satellite imagery and AI algorithms to create digital elevation models and provide topography-based insights for crop health monitoring, irrigation planning, and yield optimization. - Can small-scale farmers benefit from topographic analysis in agriculture?
Yes, Farmonaut’s platform makes topographic analysis accessible to farmers of all scales, helping even small-scale farmers optimize their practices and improve yields. - How does topography influence soil management in agriculture?
Topography affects soil formation, erosion patterns, and nutrient distribution. Understanding these relationships allows for more effective soil conservation and fertility management practices. - What is the role of topography in sustainable farming practices?
Topographic insights help implement precision conservation measures, optimize resource use, and enhance biodiversity, contributing to more sustainable farming practices. - How can I access Farmonaut’s topography-based agricultural solutions?
You can access Farmonaut’s solutions through our web application, Android app, or iOS app. For developers, we also offer API access to our satellite and weather data.