Advancing Sustainable Agriculture: Farmonaut’s Guide to Soil Science Education and Precision Farming in America

“Soil science education programs can increase crop yields by up to 25% through improved soil management techniques.”
Welcome to Farmonaut’s comprehensive guide on advancing sustainable agriculture through soil science education and precision farming in America. As pioneers in agricultural technology, we at Farmonaut are committed to making precision agriculture accessible and affordable for farmers across the United States. In this blog post, we’ll explore the intricate world of soil science, its impact on sustainable farming practices, and how precision agriculture technology is revolutionizing the way we approach food production in America.
The Importance of Soil Science in Modern Agriculture
Soil science forms the bedrock of sustainable agriculture. It’s a multidisciplinary field that combines elements of biology, chemistry, and physics to understand the complex ecosystem beneath our feet. In America, where agriculture plays a crucial role in the economy and food security, the study of soil science has never been more critical.
- Soil health management
- Nutrient cycling
- Water retention and conservation
- Carbon sequestration
- Erosion control
These aspects of soil science directly impact crop yield, environmental sustainability, and the long-term viability of farming operations. As we face challenges like climate change and increasing food demand, understanding and applying soil science principles becomes paramount.
Soil Science Education: Paving the Way for Future Agronomists
The field of soil science offers diverse educational pathways for aspiring professionals. From undergraduate degrees to specialized certifications, there are numerous opportunities to gain expertise in this critical area.
| Education Level | Certifications/Programs | Career Opportunities | Estimated Salary Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| High School | FFA Soil Science Program | Entry-level Lab Assistant | $25,000 – $35,000 |
| Associate’s Degree | Soil Science Technician Certification | Soil Sampling Technician | $35,000 – $50,000 |
| Bachelor’s Degree | Certified Professional Soil Scientist (CPSS) | Soil Conservationist, Agronomist | $50,000 – $80,000 |
| Master’s Degree | Certified Crop Advisor (CCA) | Research Scientist, Agricultural Consultant | $70,000 – $100,000 |
| Ph.D. | USDA Soil Science Researcher Certification | University Professor, Senior Researcher | $90,000 – $150,000+ |
Soil science education in America is robust, with numerous prestigious institutions offering programs that combine classroom learning with hands-on field experience. These programs cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Soil physics and chemistry
- Soil microbiology and ecology
- Soil fertility and plant nutrition
- Soil conservation and management
- Precision agriculture techniques
For professionals looking to enhance their skills or transition into the field, agronomy certification programs offer specialized training. These certifications, such as the Certified Crop Adviser (CCA) program, provide in-depth knowledge of soil science and its practical applications in agriculture.
Precision Agriculture Technology: Farmonaut’s Contribution
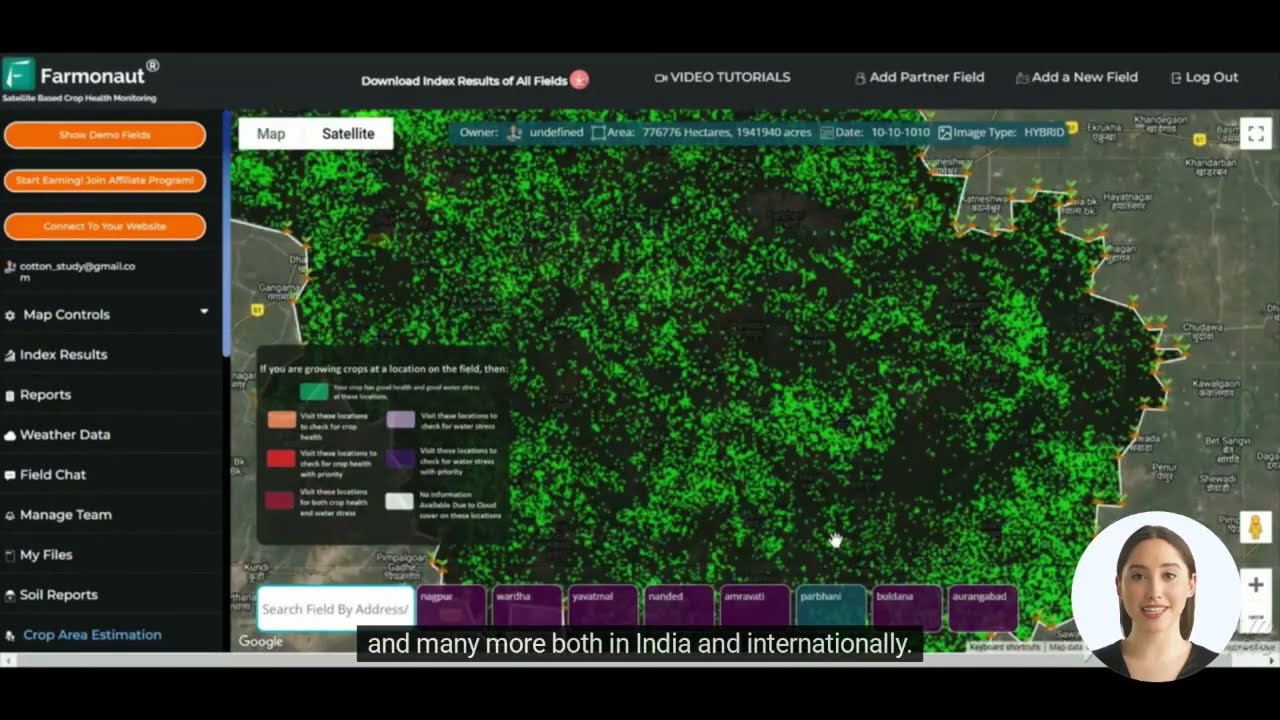
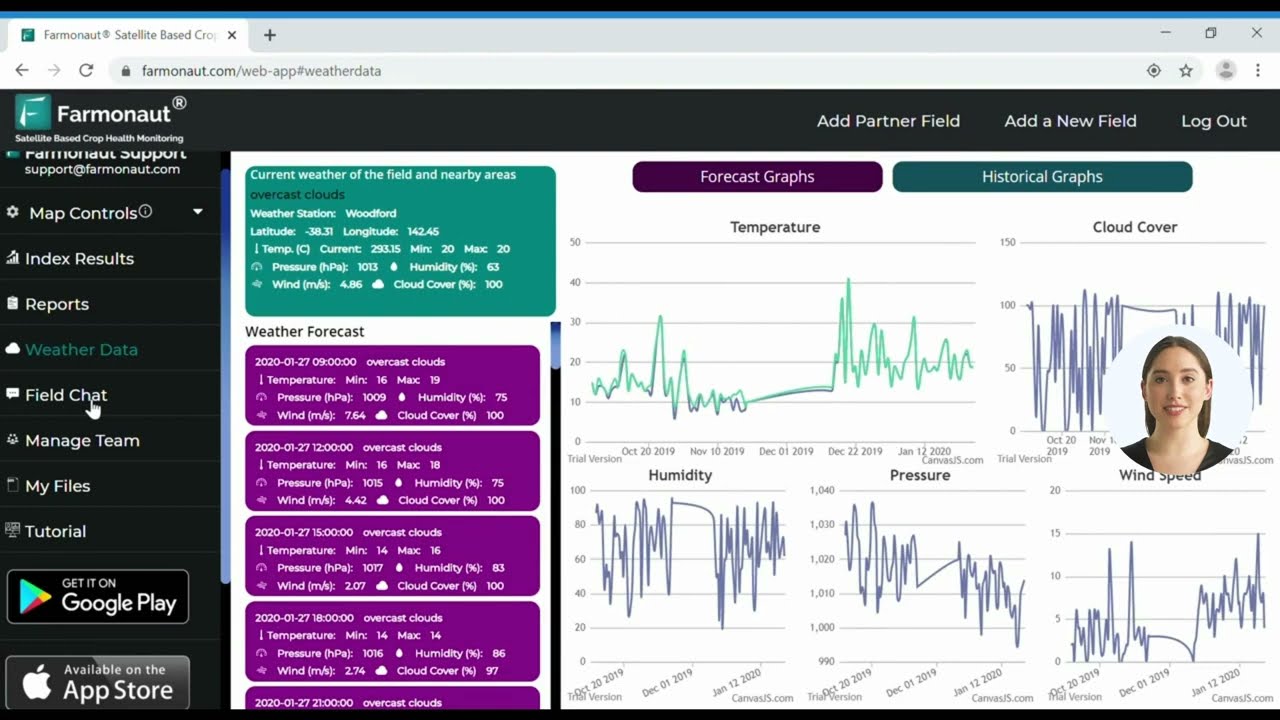
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of integrating precision agriculture technology with soil science principles. Our satellite-based farm management solutions provide farmers with real-time data and insights, enabling them to make informed decisions about their soil and crop management strategies.

Key features of our technology include:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring
- AI-driven advisory systems for personalized farm management
- Soil moisture analysis and irrigation planning
- Precision fertilizer application recommendations
- Carbon footprint tracking for sustainable farming practices
By leveraging these technologies, farmers can optimize their soil management practices, leading to improved crop yields and more sustainable farming operations.
Agricultural Research and Development: Driving Innovation
The field of agricultural research and development (R&D) is crucial for advancing soil science and precision farming techniques. In America, numerous institutions and organizations are dedicated to pushing the boundaries of our understanding and developing new technologies to address the challenges faced by modern agriculture.
Key areas of focus in agricultural R&D include:
- Development of drought-resistant crop varieties
- Innovative soil analysis techniques
- Bioengineering for improved plant nutrient uptake
- Advanced irrigation systems for water conservation
- AI and machine learning applications in agriculture
These research efforts are essential for developing sustainable farming practices that can meet the growing global demand for food while minimizing environmental impact.
Climate Change and Agriculture: Adapting Through Soil Science
Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture, but soil science offers powerful tools for adaptation and mitigation. By understanding the role of soil in carbon sequestration and implementing climate-smart agricultural practices, farmers can contribute to both food security and climate change mitigation.
“Sustainable farming practices can reduce water usage in agriculture by 30-50% while maintaining productivity levels.”
Some key strategies include:
- Cover cropping to improve soil health and reduce erosion
- No-till farming to preserve soil structure and increase carbon storage
- Precision irrigation to conserve water resources
- Agroforestry practices to enhance biodiversity and soil quality
- Use of organic amendments to boost soil organic matter content
Farmonaut’s technology supports these efforts by providing farmers with the data and insights needed to implement these practices effectively.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for Developers
Water Conservation in Farming: A Soil Science Approach
Water scarcity is a growing concern in many parts of America, making water conservation in agriculture a top priority. Soil science plays a crucial role in developing and implementing effective water management strategies.
Key approaches include:
- Soil moisture monitoring and precision irrigation
- Improving soil structure to enhance water retention
- Implementing drought-tolerant crop varieties
- Using mulches and cover crops to reduce evaporation
- Adopting deficit irrigation techniques in water-stressed regions
Farmonaut’s satellite-based soil moisture analysis helps farmers optimize their irrigation practices, ensuring that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time.
Crop Yield Optimization: The Role of Soil Analysis
Maximizing crop yields while maintaining soil health is a delicate balance that requires in-depth soil analysis and management. Advanced soil analysis techniques provide farmers with detailed information about their soil’s composition, nutrient levels, and biological activity.
Key aspects of soil analysis for crop yield optimization include:
- Macro and micronutrient testing
- Soil pH and electrical conductivity measurements
- Organic matter content analysis
- Soil microbial activity assessment
- Soil structure and compaction evaluation
By leveraging this information, farmers can make informed decisions about fertilizer application, crop rotation, and soil amendment strategies to optimize yields sustainably.
Access Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs
Sustainable Farming Practices: Integrating Soil Science and Technology
Sustainable farming practices are essential for ensuring long-term food security and environmental health. By integrating soil science principles with advanced technology, farmers can implement practices that promote soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience.
Key sustainable farming practices include:
- Crop rotation and diversification
- Integrated pest management
- Precision nutrient management
- Conservation tillage
- Agroecological approaches to farming
Farmonaut’s platform supports these practices by providing farmers with data-driven insights and recommendations tailored to their specific soil and environmental conditions.
The Future of Soil Science and Precision Agriculture
As we look to the future, the integration of soil science and precision agriculture technology holds immense promise for addressing global challenges in food production and environmental sustainability. Emerging trends and technologies include:
- Advanced remote sensing technologies for soil analysis
- AI-powered predictive models for crop management
- Blockchain-based traceability systems for sustainable sourcing
- Robotics and automation in soil sampling and analysis
- Gene editing for improved crop-soil interactions
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these developments, continuously improving our platform to provide farmers with the most advanced and effective tools for sustainable agriculture.
Conclusion: Empowering Farmers Through Knowledge and Technology
The advancement of sustainable agriculture through soil science education and precision farming is crucial for meeting the challenges of the 21st century. By combining scientific knowledge with cutting-edge technology, we can create a more resilient, productive, and environmentally friendly agricultural system.
At Farmonaut, we’re proud to be part of this journey, providing farmers with the tools and insights they need to implement sustainable practices and optimize their operations. We invite you to explore our platform and join us in shaping the future of agriculture in America and beyond.
Download Farmonaut’s Mobile Apps:


Farmonaut Subscriptions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is precision agriculture, and how does it relate to soil science?
A: Precision agriculture is an approach that uses technology to optimize crop management and resource use. It relies heavily on soil science principles to make data-driven decisions about planting, fertilization, irrigation, and harvesting, tailored to specific soil conditions within a field.
Q: How can farmers benefit from Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring provides real-time insights into crop health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This allows farmers to make timely decisions about irrigation, fertilizer application, and pest management, leading to improved crop yields and resource efficiency.
Q: What career opportunities are available in soil science?
A: Soil science offers diverse career paths, including soil conservationist, agronomist, environmental consultant, research scientist, and agricultural policy advisor. With the growing emphasis on sustainable agriculture, the demand for soil science professionals is expected to increase.
Q: How does climate change impact soil health, and what can farmers do to adapt?
A: Climate change can affect soil health through increased erosion, changes in soil moisture, and alterations in soil microbial communities. Farmers can adapt by implementing practices such as cover cropping, reduced tillage, and precision irrigation, which improve soil resilience and water retention.
Q: What are some key soil analysis techniques used in modern agriculture?
A: Modern soil analysis techniques include spectroscopy for rapid nutrient assessment, electrical conductivity mapping for soil texture analysis, and DNA sequencing for soil microbial community analysis. These advanced methods provide detailed insights into soil health and fertility.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the world of soil science, sustainable agriculture, and precision farming. By embracing these principles and technologies, we can work together to create a more sustainable and productive agricultural future for America and the world.