Iowa’s Cedar River Crisis: How Farmonaut’s Technology Can Combat Agricultural Nitrate Pollution and Protect Drinking Water
“The Cedar River in Iowa faces EPA reclassification as an impaired waterway due to nitrate levels exceeding safe limits.”
In the heartland of America, a crisis is unfolding that threatens the very essence of life – clean water. The Cedar River, a vital source of drinking water for nearly 130,000 residents in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, is at the center of a growing environmental and public health concern. As experts in agricultural technology and environmental monitoring, we at Farmonaut are deeply invested in understanding and addressing the challenges posed by agricultural nitrate pollution. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the complexities of the Cedar River crisis and how innovative technologies can play a crucial role in safeguarding our water resources.
Understanding the Cedar River Crisis
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has recently reclassified the Cedar River as an impaired water body due to alarmingly high nitrate levels that exceed federal standards. This decision has sent ripples through the agricultural and environmental communities, reigniting discussions about the impact of agricultural runoff on water quality and the urgent need for more stringent state regulations.
The Iowa Department of Natural Resources (DNR) had previously removed the Cedar River from the impaired waters list, a move that drew criticism from the EPA. The federal agency argued that the DNR’s assessment was based on flawed reasoning and neglected crucial public data, including contributions from the U.S. Geological Survey and the University of Iowa. This federal intervention is a rare occurrence, underscoring the gravity of the water quality issues at hand.
The Nitrate Conundrum
At the heart of this environmental crisis lies a familiar culprit: nitrates. These compounds, primarily stemming from agricultural sources such as fertilizers and manure, are the main pollutant affecting the Cedar River. While the city’s water treatment facilities employ advanced filtration systems to ensure that drinking water meets the EPA’s threshold for nitrates, concerns about long-term exposure persist.
Roy Hesemann, the utilities director, has assured residents of the safety of tap water. However, environmental experts like Michael Schmidt from the Iowa Environmental Council warn that prolonged exposure to even low levels of nitrates can pose significant health risks, including potential links to cancer and birth defects.
The Agricultural Impact
Iowa’s agricultural sector bears a significant responsibility for nitrate pollution in waterways. A 2012 nutrient reduction strategy indicated that agriculture accounts for a staggering 92% of the nitrates found in the state’s waters. Despite regulations targeting point sources like municipal wastewater, the agricultural sector has largely escaped similar scrutiny or requirements for reduction.
This disparity in regulation highlights a critical gap in water quality management strategies. While municipal and industrial sources are heavily regulated, non-point sources like agricultural runoff remain challenging to control and monitor effectively.
The Call for Change
State Representative Sami Scheetz has highlighted the flaws in Iowa’s measurement and management of water quality, emphasizing that adherence to federal standards is crucial for public health. The EPA’s decision to reclassify the Cedar River underscores the need for more effective measures to manage agricultural runoff and protect water resources.
While city officials maintain that Cedar Rapids’ filtration systems ensure water safety, there’s a growing consensus among state lawmakers and environmental advocates that more proactive steps must be taken to tackle nitrate pollution at its source. This includes maintaining the Cedar River’s total maximum daily load (TMDL), which serves as a critical pollution control measure.
Farmonaut’s Innovative Approach to Water Quality Management
At Farmonaut, we recognize the urgent need for innovative solutions to address agricultural pollution and protect our water resources. Our cutting-edge technology offers a range of tools and services designed to help farmers, policymakers, and environmental agencies combat nitrate pollution effectively.
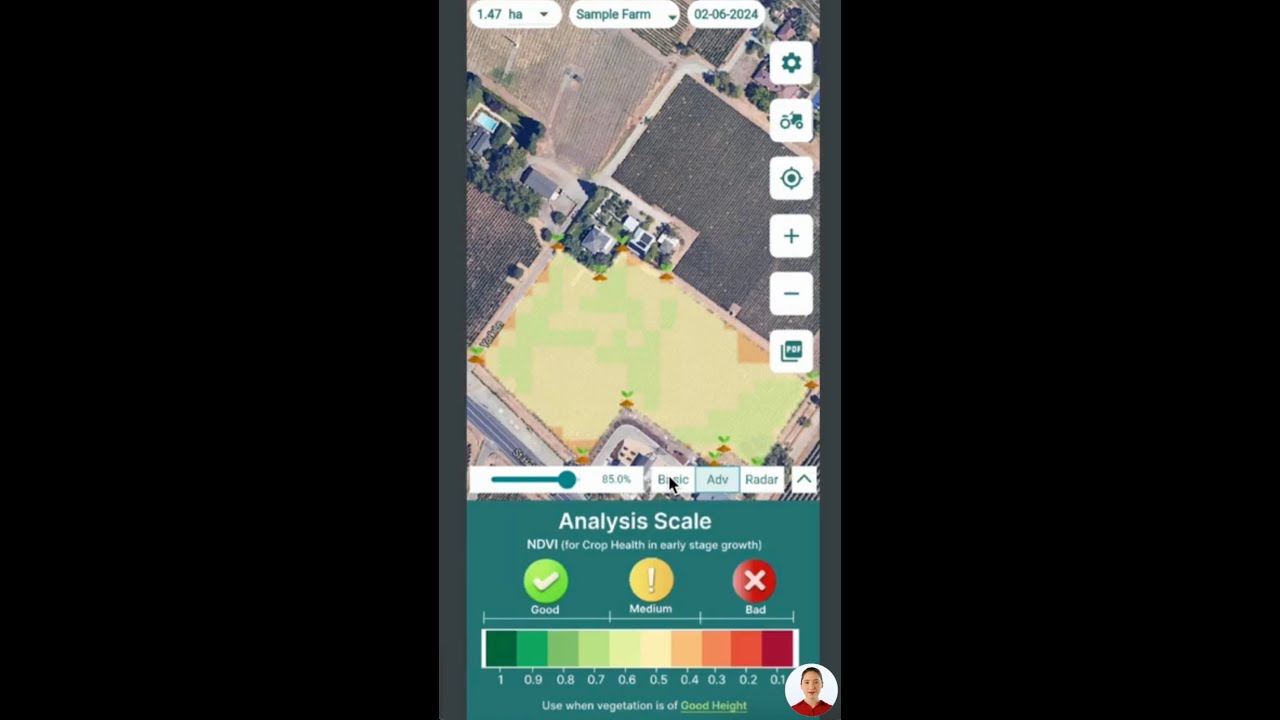
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Our advanced satellite imagery technology allows for real-time monitoring of crop health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This data is invaluable for optimizing fertilizer usage and reducing excess nitrate runoff.
AI-Driven Advisory System: Our Jeevn AI system provides personalized farm advisory services, delivering real-time insights and expert crop management strategies. By helping farmers make informed decisions about fertilizer application and irrigation, we can significantly reduce the risk of nitrate pollution.
Blockchain-Based Traceability: Our blockchain technology enables comprehensive traceability solutions, ensuring transparency and accountability in agricultural practices. This can be crucial for implementing and monitoring nitrate reduction strategies across the agricultural supply chain.
Implementing Sustainable Farming Practices
To address the nitrate pollution crisis effectively, we must focus on implementing sustainable farming practices that minimize environmental impact while maintaining agricultural productivity. Farmonaut’s technology plays a crucial role in this transition:
- Precision Fertilizer Application: Our satellite data and AI recommendations enable farmers to apply fertilizers precisely where and when they’re needed, reducing excess runoff.
- Cover Crop Monitoring: We provide tools to track the effectiveness of cover crops in reducing soil erosion and nutrient leaching.
- Water Management: Our hydrologic monitoring capabilities help in optimizing irrigation practices, reducing water waste and minimizing nutrient transport.
- Soil Health Assessment: Regular soil health monitoring through our platform allows for better nutrient management and reduced reliance on chemical fertilizers.
The Role of Data in Water Quality Monitoring
Effective water quality management relies heavily on accurate and timely data. Farmonaut’s platform integrates various data sources, including satellite imagery, ground sensors, and historical records, to provide a comprehensive view of water quality trends and potential pollution hotspots.
Real-Time Monitoring: Our system allows for continuous monitoring of water bodies, enabling quick detection of nitrate level spikes and other pollutants.
Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical data and current agricultural practices, we can predict potential pollution events and take preventive measures.
Collaborative Data Sharing: Our platform facilitates data sharing between farmers, researchers, and regulatory bodies, fostering a collaborative approach to water quality management.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced data integration
Addressing the Challenges of Agricultural Runoff Management
Managing agricultural runoff is a complex challenge that requires a multi-faceted approach. Farmonaut’s technology contributes to this effort in several key ways:
- Watershed Mapping: Our satellite imagery allows for detailed mapping of watersheds, identifying critical areas for runoff management.
- Buffer Zone Optimization: We provide tools to design and monitor the effectiveness of buffer zones in trapping nutrients before they reach waterways.
- Drainage System Analysis: Our technology can assess the efficiency of drainage systems and identify areas prone to nutrient leaching.
- Seasonal Risk Assessment: By analyzing weather patterns and soil conditions, we help farmers anticipate high-risk periods for runoff and adjust their practices accordingly.

Balancing Agricultural Productivity and Environmental Protection
One of the greatest challenges in addressing nitrate pollution is balancing the need for agricultural productivity with environmental protection. Farmonaut’s approach focuses on maximizing efficiency to achieve this balance:
- Yield Optimization: By providing detailed crop health data, we help farmers maximize yields while minimizing input use.
- Resource Efficiency: Our AI-driven recommendations help optimize water and fertilizer use, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Sustainable Intensification: We support practices that increase productivity on existing agricultural land, reducing the need for expansion into natural habitats.
- Economic Incentives: By demonstrating the economic benefits of sustainable practices, we encourage wider adoption of environmentally friendly farming methods.
The Importance of Drinking Water Filtration Systems
While addressing nitrate pollution at its source is crucial, effective drinking water filtration systems remain an essential safeguard for public health. Farmonaut’s technology can support water treatment facilities in several ways:
- Pollutant Forecasting: Our predictive analytics can help treatment plants anticipate periods of high nitrate levels and adjust their filtration processes accordingly.
- Treatment Efficiency Monitoring: By providing real-time data on water quality in source waters, we help treatment facilities optimize their processes and resource allocation.
- Long-term Planning: Our historical data and trend analysis support long-term planning for water treatment infrastructure improvements.
“Long-term exposure to high nitrate levels in drinking water can pose significant health risks to local populations.”
Nutrient Reduction Strategies: A Collaborative Approach
Effective nutrient reduction requires collaboration between farmers, policymakers, and technology providers. Farmonaut’s platform facilitates this collaborative approach:
- Data-Driven Policy Making: Our comprehensive data analytics support evidence-based policy development for nutrient management.
- Farmer Education: We provide educational resources and training on best practices for nutrient management and water quality protection.
- Community Engagement: Our platform can be used to engage local communities in water quality monitoring and conservation efforts.
- Research Support: We collaborate with academic institutions to advance the science of agricultural pollution control and water quality management.
Access our API Developer Docs for advanced integration options
The Future of Agricultural Pollution Control
As we look to the future, the role of technology in agricultural pollution control will only grow. Farmonaut is at the forefront of this technological revolution, continually developing new tools and methodologies to address emerging challenges:
- Machine Learning Advancements: We’re developing more sophisticated machine learning models to improve the accuracy of our pollution predictions and mitigation recommendations.
- IoT Integration: We’re exploring ways to integrate Internet of Things (IoT) devices with our satellite data for even more precise monitoring and control.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Our platform is evolving to help farmers adapt to changing climate conditions while minimizing their environmental impact.
- Ecosystem Services Valuation: We’re working on tools to help quantify the economic value of ecosystem services provided by sustainable farming practices, incentivizing their adoption.
Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs. Farmonaut-Enabled Approaches
| Strategy | Traditional Approach | Farmonaut-Enabled Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Fertilizer Application | Uniform application based on general guidelines | Precision application using satellite imagery and AI-driven recommendations |
| Water Quality Monitoring | Periodic manual sampling and testing | Continuous real-time monitoring through satellite and sensor integration |
| Runoff Management | Generic best practices applied uniformly | Tailored strategies based on site-specific data and predictive analytics |
| Soil Health Assessment | Annual or seasonal soil testing | Ongoing monitoring with satellite-based soil health indicators |
| Data-Driven Decision Making | Reliance on historical trends and general knowledge | AI-powered insights combining real-time data with historical patterns |
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The reclassification of the Cedar River as an impaired water body serves as a wake-up call for state authorities and underscores the pressing need to address agricultural runoff as a leading contributor to water quality issues. The health and safety of our communities’ drinking water depend on sustained efforts to monitor, regulate, and improve the management of pollutants, particularly from farming practices.
At Farmonaut, we are committed to providing the tools and technologies necessary to tackle these complex environmental challenges. By leveraging satellite imagery, AI, and blockchain technology, we empower farmers, policymakers, and environmental agencies to make data-driven decisions that protect our water resources while maintaining agricultural productivity.
The path forward requires a collaborative effort from all stakeholders. We invite farmers, researchers, policymakers, and environmentalists to join us in this crucial mission. Together, we can develop and implement innovative solutions that safeguard our water resources for generations to come.
Farmonaut Subscriptions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the main cause of nitrate pollution in the Cedar River?
The primary source of nitrate pollution in the Cedar River is agricultural runoff, particularly from fertilizers and manure used in farming practices. - How does Farmonaut’s technology help reduce nitrate pollution?
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring and AI-driven advisory system help farmers optimize fertilizer use, reducing excess application that leads to runoff. - Are there health risks associated with high nitrate levels in drinking water?
Yes, long-term exposure to high nitrate levels in drinking water can pose health risks, including potential links to cancer and birth defects. - How can farmers benefit from using Farmonaut’s platform?
Farmers can benefit through improved crop yields, reduced input costs, and more sustainable farming practices that comply with environmental regulations. - What role does blockchain technology play in addressing water quality issues?
Blockchain technology enables transparent and secure tracking of agricultural practices and supply chains, supporting accountability in nutrient management efforts.
By addressing the Cedar River crisis and implementing innovative solutions like those offered by Farmonaut, we can work towards a future where clean water and sustainable agriculture coexist harmoniously. The challenge is significant, but with the right tools and collective effort, we can protect our vital water resources while supporting a thriving agricultural sector.