Manitowoc’s Urban Revival: Transforming Contaminated Factory Site into Workforce Housing
“Manitowoc’s urban renewal project will transform a contaminated factory site into 59 workforce housing units.”
In a bold move towards urban revitalization, we are excited to report on Manitowoc’s groundbreaking initiative to transform a long-abandoned factory site into a vibrant workforce housing development. This project, recently approved by city officials, marks a significant milestone in Manitowoc’s commitment to sustainable urban planning and community development. As we delve into the details of this transformative project, we’ll explore how it addresses both environmental concerns and local housing needs, setting a new standard for urban renewal projects across the nation.
The Genesis of Manitowoc’s Urban Revival
The city of Manitowoc has long grappled with the challenge of repurposing its industrial past for a more sustainable future. At the heart of this effort lies the former Mirro factory site, a symbol of the city’s rich manufacturing heritage that has stood vacant for years. Recognizing the potential of this brownfield site, Manitowoc’s city council has taken decisive action to breathe new life into this neglected area.
The approved project encompasses a comprehensive approach to site remediation and redevelopment. Key components include:
- Removal of contaminated soil
- Demolition of existing concrete structures and utility tunnels
- Introduction of fresh topsoil and fill
- Preparation for the construction of 59 workforce housing units
This multifaceted approach not only addresses the environmental challenges posed by the site but also paves the way for a development that promises to reinvigorate the local economy and provide much-needed housing options for Manitowoc’s workforce.
Federal Support for Local Innovation
“A federal infrastructure grant is funding the cleanup of a brownfield site, preparing it for future residential development.”
The project’s ambitious scope is made possible through a nearly $2 million grant provided by the federal infrastructure law. This substantial investment underscores the national commitment to supporting local initiatives that combine environmental remediation with economic development. By leveraging these federal funds, Manitowoc demonstrates how cities can tap into broader resources to drive meaningful change at the local level.
The grant’s allocation towards brownfield site cleanup is a critical first step in the redevelopment process. It addresses one of the primary barriers to urban renewal—the high costs associated with environmental remediation. By tackling this challenge head-on, Manitowoc is setting the stage for a development that not only enhances the city’s housing stock but also improves the overall environmental health of the community.
From Industrial Past to Residential Future
The transformation of the Mirro factory site represents more than just a change in land use; it symbolizes Manitowoc’s transition from its industrial heritage to a future focused on sustainable, community-oriented development. The proposed 59-unit workforce housing project is at the heart of this vision, offering several key benefits:
- Addressing local housing shortages
- Providing affordable options for the city’s workforce
- Attracting new residents to the area
- Stimulating local economic growth
The developer’s intention to apply for affordable housing tax credits further underscores the project’s commitment to accessibility and inclusivity. If approved, these credits could accelerate the construction timeline, potentially seeing groundbreaking as early as this summer or fall.
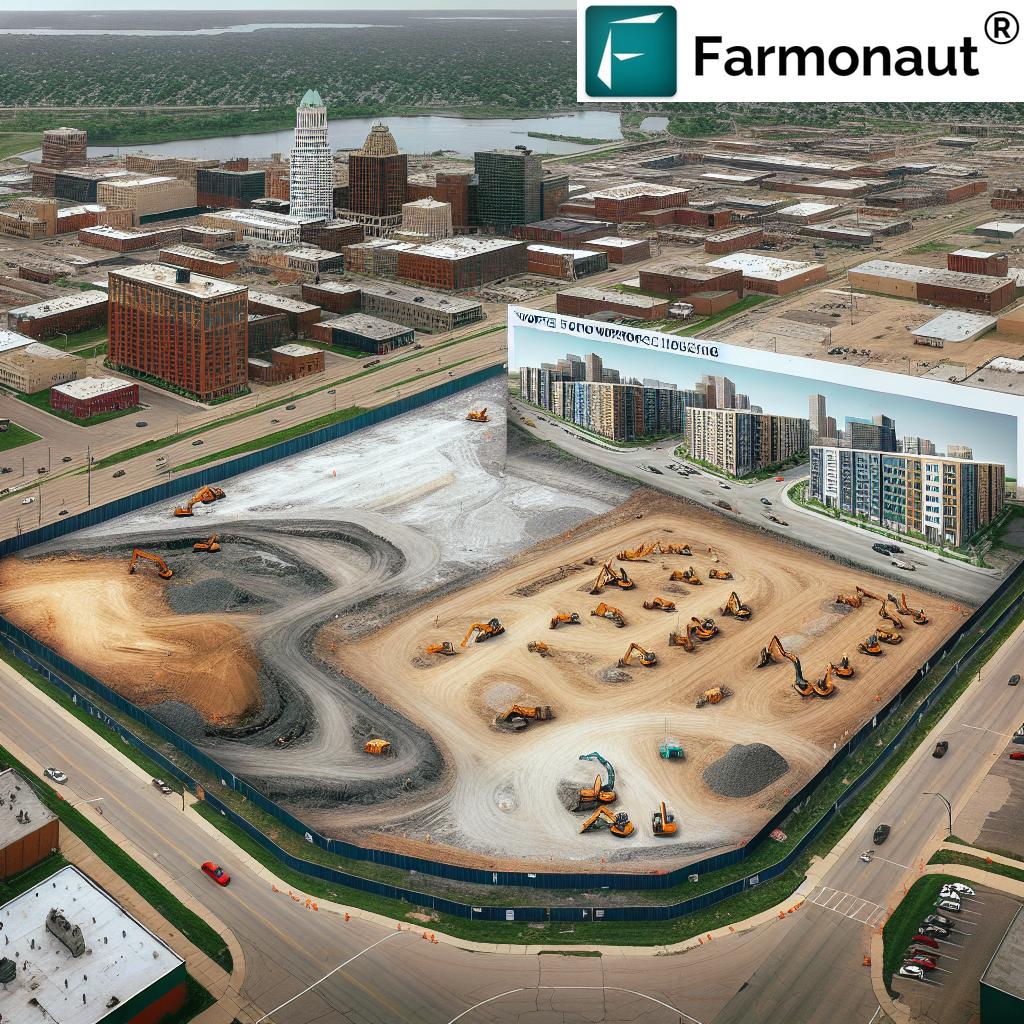

Environmental Remediation: A Cornerstone of Urban Renewal
At the core of Manitowoc’s urban revival project is a commitment to environmental stewardship. The process of transforming a contaminated industrial site into a safe, habitable area involves several complex steps:
- Site Assessment: Thorough evaluation of soil and groundwater contamination levels
- Contaminated Soil Removal: Excavation and proper disposal of polluted earth
- Structural Demolition: Removal of existing concrete slabs and utility tunnels
- Soil Replacement: Introduction of clean topsoil and fill to create a safe foundation
- Environmental Monitoring: Ongoing testing to ensure the site meets all safety standards
This comprehensive approach to environmental remediation not only prepares the site for future development but also contributes to the overall health and well-being of the surrounding community. By addressing these environmental concerns, Manitowoc is setting a precedent for responsible urban development that prioritizes both human and ecological health.
Economic Implications of the Redevelopment Project
The economic impact of Manitowoc’s urban renewal project extends far beyond the immediate construction phase. By transforming a vacant, contaminated site into a thriving residential area, the city is poised to reap numerous economic benefits:
- Job Creation: Both during construction and in ongoing property management
- Increased Property Values: Revitalization often leads to appreciation in surrounding areas
- Tax Base Expansion: New residential units contribute to local tax revenues
- Attracting Businesses: Improved housing options can draw new employers to the area
- Workforce Retention: Affordable housing helps retain skilled workers in the community
Moreover, the project’s focus on workforce housing addresses a critical need in many urban areas—affordable options for middle-income residents. By providing housing that’s accessible to teachers, nurses, first responders, and other essential workers, Manitowoc is investing in the backbone of its community.
The Role of Technology in Urban Planning and Development
As we consider the complexities of urban renewal projects like Manitowoc’s, it’s worth noting the increasing role of technology in facilitating such transformations. Advanced tools and platforms are revolutionizing how cities approach planning, environmental assessment, and community engagement.
One such innovative solution is offered by Farmonaut, a company at the forefront of agricultural technology. While primarily focused on farm management, Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring and AI-driven analytics have applications that extend to urban planning and environmental assessment.
For instance, Farmonaut’s technology could potentially assist in:
- Assessing soil quality and contamination levels through satellite imagery
- Monitoring vegetation health in urban green spaces
- Tracking the progress of land remediation efforts
- Providing data for environmental impact assessments
While not directly involved in Manitowoc’s project, the existence of such technologies underscores the potential for data-driven decision-making in urban renewal efforts. Cities like Manitowoc could benefit from integrating these advanced tools into their planning processes, ensuring more efficient and effective redevelopment strategies.
To learn more about innovative satellite-based solutions, you can explore Farmonaut’s offerings:
Community Engagement and Participatory Planning
A crucial aspect of successful urban renewal projects is community engagement. Manitowoc’s approach to redeveloping the Mirro factory site demonstrates a commitment to inclusive planning processes. By involving residents, local businesses, and community organizations in the decision-making process, the city ensures that the project aligns with the needs and aspirations of its citizens.
Key elements of community engagement in this project include:
- Public hearings and town hall meetings to gather input
- Transparent communication about project timelines and impacts
- Collaboration with local workforce development agencies
- Partnerships with environmental groups to ensure sustainable practices
This participatory approach not only builds public support for the project but also helps identify potential challenges and opportunities that might have been overlooked. It’s a model of civic engagement that other cities can learn from as they embark on their own urban renewal initiatives.

Challenges and Considerations in Urban Redevelopment
While Manitowoc’s urban revival project offers numerous benefits, it’s important to acknowledge the challenges inherent in such ambitious undertakings. Some of the key considerations include:
- Environmental Risks: Ensuring all contamination is properly addressed
- Funding Stability: Securing ongoing financial support beyond the initial grant
- Construction Timelines: Managing potential delays and disruptions
- Community Impact: Addressing concerns about gentrification and displacement
- Infrastructure Needs: Upgrading surrounding utilities and transportation networks
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing cooperation between city officials, developers, environmental experts, and community stakeholders. It’s a complex process that demands flexibility, transparency, and a long-term commitment to the project’s vision.
The Broader Impact on Urban Planning Trends
Manitowoc’s approach to redeveloping the Mirro factory site is part of a larger trend in urban planning that emphasizes:
- Brownfield redevelopment
- Mixed-use developments
- Sustainable urban design
- Affordable housing initiatives
- Smart city technologies
This project serves as a case study for other municipalities facing similar challenges with post-industrial sites. By successfully integrating environmental remediation, affordable housing, and economic development, Manitowoc is creating a blueprint that can be adapted and replicated in cities across the country.
For those interested in exploring how technology can support urban planning and development, Farmonaut offers innovative solutions through its API and API Developer Docs. While primarily focused on agricultural applications, these tools demonstrate the potential for satellite and AI technologies in various planning and monitoring scenarios.
Looking to the Future: Manitowoc’s Vision for Sustainable Growth
As Manitowoc moves forward with this transformative project, it’s clear that the city’s vision extends beyond simply redeveloping a single site. This initiative is part of a broader strategy for sustainable urban growth that includes:
- Revitalizing downtown areas
- Enhancing public spaces and green infrastructure
- Promoting energy-efficient building practices
- Improving public transportation options
- Fostering a diverse and inclusive community
By addressing these interconnected aspects of urban development, Manitowoc is positioning itself as a forward-thinking city ready to meet the challenges of the 21st century. The Mirro factory site redevelopment is just the beginning of what promises to be a comprehensive urban renaissance.
Comparative Analysis: Before and After
To fully appreciate the scope of Manitowoc’s urban revival project, let’s take a closer look at the transformation of the former Mirro factory site:
| Aspect | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Land Use | Contaminated Factory | Workforce Housing |
| Number of Housing Units | 0 | 59 |
| Environmental Status | Contaminated | Remediated |
| Economic Impact | Vacant | Attracting New Residents |
| Infrastructure | Outdated | Modernized |
| Community Benefit | Hazard | Affordable Housing |
This transformation illustrates the profound impact of Manitowoc’s urban renewal efforts, turning a liability into an asset for the community.
Lessons for Other Cities
Manitowoc’s approach to urban revival offers valuable lessons for other cities facing similar challenges:
- Leverage Federal Support: Seek out and utilize available grants and funding opportunities.
- Prioritize Environmental Remediation: Address contamination issues as a foundation for redevelopment.
- Focus on Community Needs: Align projects with local housing and economic requirements.
- Embrace Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborate with developers to bring projects to fruition.
- Integrate Sustainable Practices: Incorporate green building and energy-efficient designs.
- Engage the Community: Involve residents and local stakeholders in the planning process.
- Think Long-Term: Consider the broader impact on urban growth and sustainability.
By following these principles, cities can transform neglected industrial sites into vibrant, sustainable neighborhoods that serve the needs of their communities.
Conclusion: A Model for Urban Transformation
Manitowoc’s bold initiative to transform the contaminated Mirro factory site into a thriving workforce housing development exemplifies the potential of thoughtful urban renewal. By addressing environmental concerns, housing needs, and economic development in a single project, the city is setting a new standard for sustainable urban planning.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that projects like this will play a crucial role in revitalizing cities across the nation. They offer a path forward for communities grappling with the legacy of industrial decline, demonstrating how vision, collaboration, and strategic investment can turn challenges into opportunities.
Manitowoc’s urban revival project is more than just a local success story—it’s a blueprint for sustainable, community-focused development that other cities can learn from and adapt to their own unique circumstances. As we continue to monitor the progress of this transformative initiative, we’re excited to see how it will shape Manitowoc’s future and inspire similar efforts across the country.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the main goal of Manitowoc’s urban revival project?
A: The main goal is to transform a contaminated factory site into a 59-unit workforce housing development, addressing both environmental remediation and local housing needs.
Q: How is the project being funded?
A: The project is primarily funded by a nearly $2 million grant from the federal infrastructure law, with additional potential support from affordable housing tax credits.
Q: What environmental challenges does the project address?
A: The project involves removing contaminated soil, demolishing existing structures, and preparing the site for safe residential use through comprehensive environmental remediation.
Q: When is construction expected to begin?
A: If tax credits are approved, construction could begin as early as the summer or fall of this year.
Q: How will this project benefit the local community?
A: The project will provide affordable housing options, attract new residents, stimulate economic growth, and improve the overall environmental health of the area.
Exploring Innovative Solutions in Urban Development
As cities like Manitowoc lead the way in urban revival, it’s worth considering how innovative technologies can support and enhance these efforts. While not directly involved in Manitowoc’s project, companies like Farmonaut are pioneering solutions that have potential applications in urban planning and environmental monitoring.
While Farmonaut’s primary focus is on agricultural technology, their satellite-based monitoring and AI-driven analytics demonstrate the potential for data-driven approaches in urban development. As cities continue to evolve and tackle complex environmental and social challenges, integrating such innovative technologies could provide valuable insights and support more efficient, sustainable urban planning processes.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Urban Renewal
Manitowoc’s urban revival project sets a powerful precedent for cities across the nation. As we look to the future, several key trends are likely to shape urban renewal efforts:
- Increased focus on sustainable and resilient urban design
- Greater integration of smart city technologies
- Emphasis on mixed-use developments that combine housing, commercial, and public spaces
- Continued prioritization of affordable and workforce housing
- Innovative approaches to financing urban renewal projects
By embracing these trends and learning from successful projects like Manitowoc’s, cities can create more vibrant, equitable, and sustainable urban environments for future generations.
In conclusion, Manitowoc’s transformative project serves as a beacon of hope and a model for urban revival. By addressing environmental concerns, meeting housing needs, and stimulating economic growth, the city is charting a course towards a more sustainable and prosperous future. As other municipalities face similar challenges, they can look to Manitowoc’s example for inspiration and guidance in their own urban renewal efforts.