Midwest Soybean Watch: Critical Growth Stages, Drought Impacts, and Precision Ag Solutions for Iowa Farmers
“Iowa farmers implementing precision agriculture technology have seen up to 20% increase in soybean yields.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Midwest soybean farming, where we delve into the critical challenges and innovative solutions shaping the agricultural landscape. As we navigate through the crucial growth stages of soybeans, explore the impacts of drought, and uncover the latest precision agriculture technologies, we aim to equip farmers in Iowa, Minnesota, and beyond with the knowledge needed to thrive in today’s dynamic farming environment.

The State of Midwest Soybean Farming
In the heart of America’s breadbasket, soybean farming faces a convergence of challenges and opportunities. From the rolling prairies of Iowa to the fertile fields of Minnesota, farmers are adapting to changing weather patterns, implementing cutting-edge technologies, and striving for sustainable practices. Let’s dive into the current state of Midwest soybean farming and explore how it’s shaping the future of agriculture in the United States.
Climate Challenges in the Midwest
- Drought conditions impacting crop yields
- Unpredictable rainfall patterns affecting planting and harvesting schedules
- Increased pest pressure due to changing climate
The Midwest, particularly states like Iowa and Illinois, has been grappling with increasingly erratic weather patterns. Drought conditions have become more frequent, posing significant challenges to soybean farmers. These climate shifts not only affect crop yields but also influence crucial decisions about planting dates, irrigation strategies, and pest management.
Technological Advancements in Agriculture
- Precision agriculture tools revolutionizing farm management
- Satellite-based crop monitoring systems providing real-time insights
- AI and machine learning algorithms optimizing resource allocation
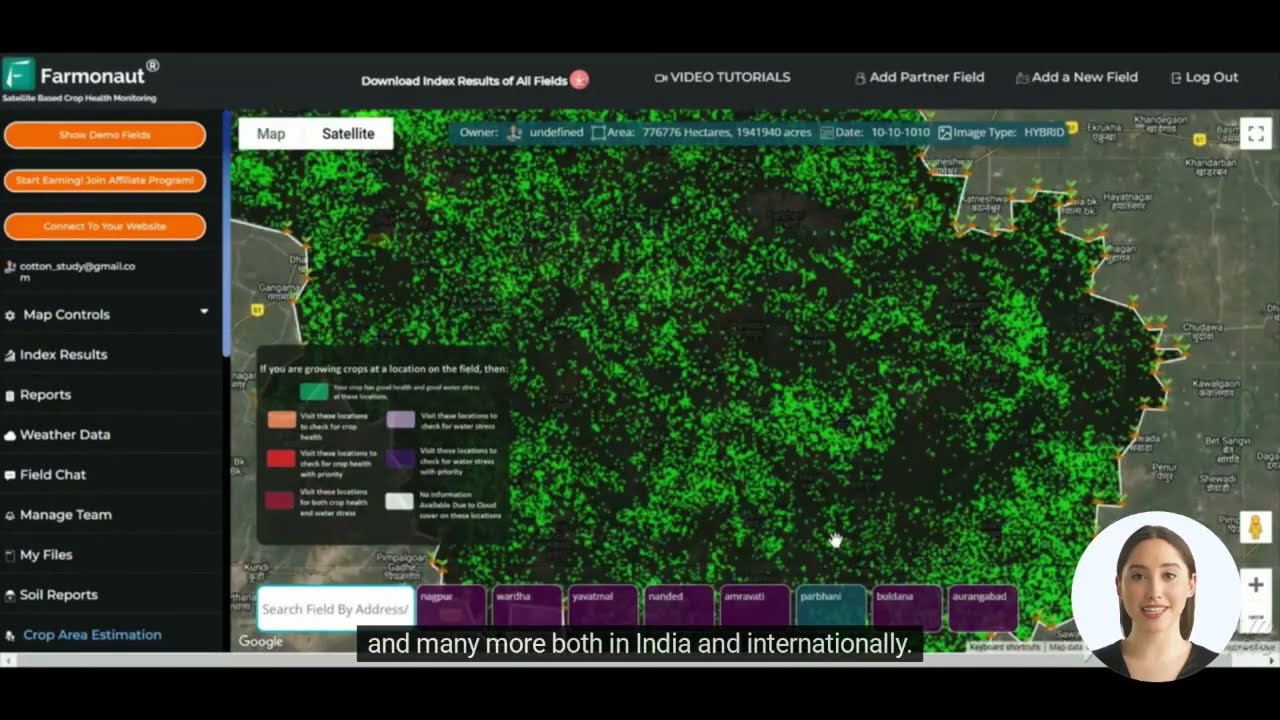
In response to these challenges, Midwest farmers are turning to advanced technologies to enhance their operations. Precision agriculture has emerged as a game-changer, allowing farmers to make data-driven decisions and optimize resource use. Satellite-based crop monitoring systems, like those offered by Farmonaut, are providing invaluable insights into crop health, soil moisture levels, and potential pest issues.
Critical Growth Stages of Soybeans
Understanding the growth stages of soybeans is crucial for effective crop management. Let’s explore the key phases and what they mean for Midwest farmers:
| Growth Stage | Estimated Days After Planting | Critical Factors | Management Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emergence (VE) | 5-10 days | Soil temperature, moisture | Monitor for seedling diseases, adjust planting depth |
| Vegetative (V1-V5) | 15-30 days | Nutrient uptake, weed competition | Implement early-season weed control, monitor for pests |
| Flowering (R1-R2) | 45-60 days | Drought sensitivity, pollination | Ensure adequate irrigation, consider foliar fertilizers |
| Pod Development (R3-R4) | 65-80 days | Pod set, stress vulnerability | Monitor for pod-feeding insects, maintain soil moisture |
| Seed Fill (R5-R6) | 80-110 days | Nutrient demand, disease risk | Apply fungicides if needed, maintain optimal soil moisture |
| Maturity (R7-R8) | 110-120 days | Drying conditions, harvest timing | Plan for timely harvest, monitor moisture levels |
Each stage presents unique challenges and opportunities for crop management. By leveraging precision agriculture technologies, farmers can make informed decisions at each critical point in the soybean lifecycle.
Drought Impacts on Midwest Soybean Farming
“Recent rainfall patterns in the Midwest have affected over 50 million acres of soybean farmland.”
Drought conditions have become an increasingly pressing concern for soybean farmers across the Midwest. The impacts of drought extend far beyond reduced yields, affecting every aspect of farm operations. Let’s examine the multifaceted effects of drought on soybean farming and explore strategies for mitigation:
Yield Reduction
- Stunted plant growth and reduced pod development
- Decreased seed size and quality
- Premature plant death in severe cases
Drought stress during critical growth stages can significantly reduce soybean yields. Farmers in states like Iowa and Missouri have reported yield losses of up to 40% in severely affected areas. To combat this, many are turning to drought-resistant crop varieties and implementing advanced irrigation techniques.
Soil Health Degradation
- Increased soil erosion due to dry conditions
- Reduced microbial activity in soil
- Nutrient imbalances affecting future crop cycles
The long-term effects of drought on soil health can be devastating. Midwest farmers are increasingly adopting conservation tillage practices and cover cropping to improve soil moisture retention and overall soil health.
Economic Impacts
- Increased production costs due to additional irrigation needs
- Potential loss of crop insurance coverage
- Market volatility affecting soybean prices
The economic ripple effects of drought can be felt throughout the agricultural sector. Farmers in states like Kansas and Nebraska are diversifying their crops and exploring alternative revenue streams to mitigate financial risks.

Precision Agriculture Solutions for Iowa Farmers
In the face of these challenges, precision agriculture has emerged as a beacon of hope for Midwest soybean farmers. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies, farmers can optimize their operations, reduce resource waste, and improve crop yields. Let’s explore some of the key precision ag solutions making a difference in Iowa and beyond:
Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
Satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies are revolutionizing crop management. Platforms like Farmonaut provide farmers with real-time insights into crop health, allowing for timely interventions and optimized resource allocation.
- NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) mapping for assessing crop health
- Soil moisture monitoring to guide irrigation decisions
- Early detection of pest infestations and disease outbreaks
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced satellite data integration
Variable Rate Technology (VRT)
VRT allows farmers to apply inputs like fertilizers and pesticides at varying rates across their fields, optimizing resource use and minimizing environmental impact.
- Precision fertilizer application based on soil nutrient maps
- Variable rate seeding to optimize plant populations
- Targeted pesticide application reducing overall chemical use
AI-Powered Decision Support Systems
Artificial Intelligence is transforming farm management by providing data-driven insights and recommendations. Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI advisory system is at the forefront of this revolution, offering personalized crop management strategies.
- Predictive analytics for yield forecasting
- AI-driven pest and disease identification
- Optimal planting and harvesting date recommendations
Access Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs for custom integrations
Sustainable Farming Practices in the Midwest
As we navigate the challenges of modern agriculture, sustainability has become a cornerstone of successful farming operations. Midwest soybean farmers are increasingly adopting practices that not only improve their yields but also preserve the land for future generations. Let’s explore some of the sustainable farming practices gaining traction in the region:
Conservation Tillage
- Reduces soil erosion and improves water retention
- Increases organic matter in soil over time
- Lowers fuel consumption and labor costs
Many farmers in Iowa and Illinois are transitioning to no-till or reduced tillage systems, which help maintain soil structure and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Cover Cropping
- Improves soil health and biodiversity
- Reduces nutrient runoff and erosion
- Provides natural weed suppression
The use of cover crops like rye and clover between soybean rotations is becoming increasingly common, particularly in states like Minnesota and Missouri.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Reduces reliance on chemical pesticides
- Promotes beneficial insect populations
- Lowers environmental impact and production costs
IPM strategies are helping Midwest farmers combat pests more effectively while minimizing the use of harmful chemicals.
The Role of Technology in Modern Soybean Farming
As we’ve seen, technology plays a crucial role in addressing the challenges faced by Midwest soybean farmers. From satellite-based monitoring to AI-driven advisory systems, these innovations are reshaping the agricultural landscape. Let’s delve deeper into how farmers can leverage these technologies to optimize their operations:
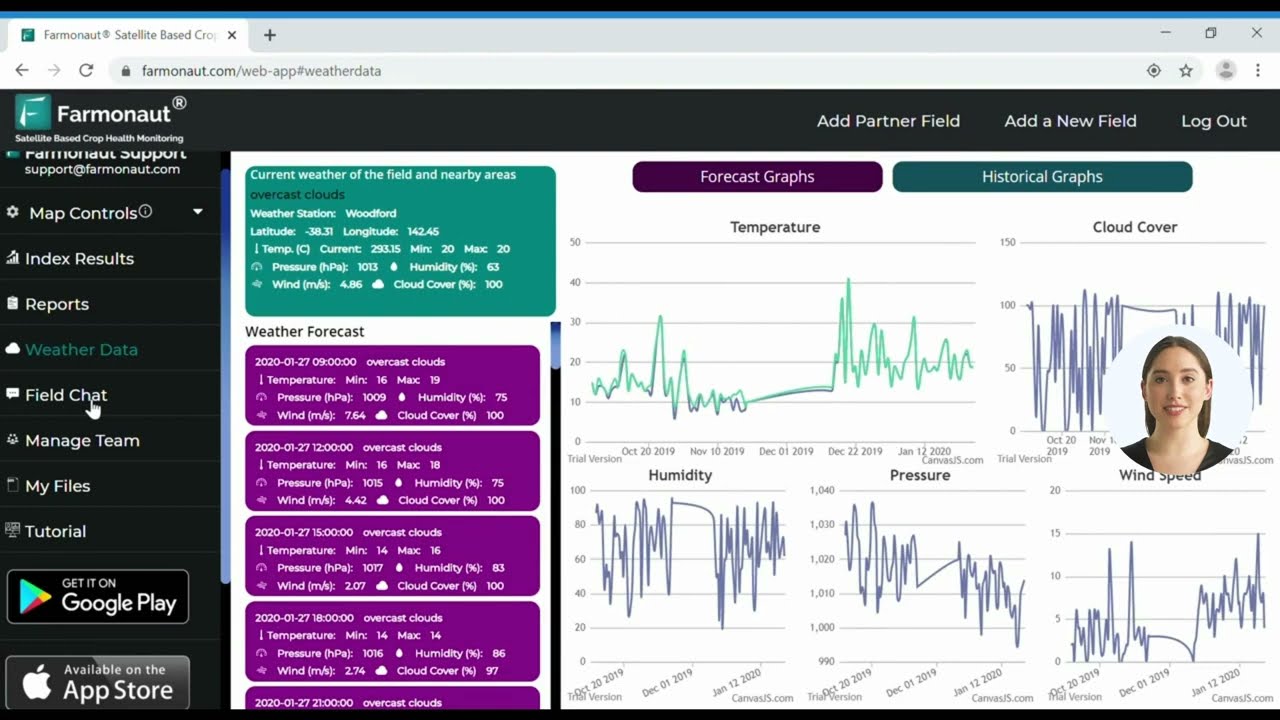
Real-Time Weather Monitoring and Forecasting
Accurate weather data is crucial for making informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and harvesting. Farmonaut’s platform provides farmers with hyper-local weather forecasts and historical data, enabling better planning and risk management.
- Customized weather alerts for critical events
- Integration of weather data with crop models for yield predictions
- Historical weather analysis for long-term planning
Drone Technology in Agriculture
While satellite imagery provides broad coverage, drones offer high-resolution, on-demand data collection for more detailed analysis of crop health and field conditions.
- Precise crop scouting and damage assessment
- Generation of 3D field maps for drainage planning
- Targeted application of inputs in hard-to-reach areas
IoT Sensors and Smart Farming Equipment
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and smart farming equipment are enabling farmers to monitor and control various aspects of their operations remotely.
- Soil moisture sensors for optimized irrigation
- Smart sprayers for precise pesticide application
- Automated tractors and harvesters for increased efficiency
Market Trends and Export Opportunities for Midwest Soybeans
Understanding market trends and export opportunities is crucial for Midwest soybean farmers looking to maximize their profits and expand their operations. Let’s explore the current landscape:
Global Demand for Soybeans
- Increasing demand from emerging markets, particularly in Asia
- Growing use of soybeans in biofuel production
- Rising popularity of plant-based proteins driving soybean consumption
Farmers in states like Iowa and Illinois are well-positioned to capitalize on these global trends, with their high-quality soybean production and established export infrastructure.
Trade Policies and International Relations
- Impact of trade agreements on soybean exports
- Navigating tariffs and trade disputes
- Emerging markets opening up for U.S. soybean exports
Staying informed about international trade policies is crucial for Midwest farmers looking to expand their export opportunities.
Value-Added Soybean Products
- Growing market for specialty soybean varieties
- Opportunities in soybean oil and meal production
- Emerging markets for soy-based industrial products
Diversifying into value-added soybean products can help Midwest farmers increase their profit margins and reduce market volatility risks.
The Future of Midwest Soybean Farming
As we look to the future, several trends and innovations are poised to shape the landscape of Midwest soybean farming:
Gene Editing and Advanced Breeding Techniques
- Development of drought-resistant soybean varieties
- Enhanced pest and disease resistance through genetic improvements
- Breeding for specific nutritional profiles to meet market demands
Blockchain Technology in Agriculture
Blockchain is set to revolutionize supply chain management and traceability in agriculture. Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability solutions are at the forefront of this innovation, offering transparency and security throughout the soybean supply chain.
- Enhanced food safety and quality assurance
- Improved efficiency in supply chain management
- Greater transparency for consumers and stakeholders
Carbon Markets and Sustainable Agriculture
- Growing opportunities for farmers to participate in carbon credit markets
- Increased focus on regenerative agriculture practices
- Development of sustainability certifications for soybean production
Midwest farmers are well-positioned to benefit from these emerging trends, particularly with the adoption of sustainable farming practices and precision agriculture technologies.
Conclusion
The landscape of Midwest soybean farming is rapidly evolving, driven by technological innovations, changing climate patterns, and shifting market dynamics. By embracing precision agriculture solutions, implementing sustainable farming practices, and staying informed about market trends, farmers in Iowa, Minnesota, and throughout the Midwest can navigate these challenges and capitalize on new opportunities.
As we’ve explored in this comprehensive guide, tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring and AI-driven advisory systems are becoming indispensable for modern soybean farmers. These technologies, combined with sustainable farming practices and a deep understanding of crop growth stages, empower farmers to make data-driven decisions that optimize yields, reduce environmental impact, and improve profitability.
The future of Midwest soybean farming is bright, with exciting developments in gene editing, blockchain technology, and carbon markets on the horizon. By staying adaptable and embracing innovation, Midwest farmers can continue to play a crucial role in feeding the world while building resilient and sustainable agricultural systems.
FAQ Section
- What are the most critical growth stages for soybeans?
The most critical growth stages for soybeans are flowering (R1-R2) and pod development (R3-R4), as these stages are highly sensitive to environmental stresses and greatly impact final yield. - How can precision agriculture help in drought management?
Precision agriculture tools like satellite-based crop monitoring can help in early detection of drought stress, allowing farmers to implement targeted irrigation strategies and optimize water use efficiency. - What are the benefits of using cover crops in soybean farming?
Cover crops improve soil health, reduce erosion, suppress weeds, and can help fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting the subsequent soybean crop. - How does satellite imagery assist in soybean crop management?
Satellite imagery provides valuable insights into crop health, soil moisture levels, and potential pest or disease outbreaks, enabling farmers to make timely and informed management decisions. - What are the emerging markets for U.S. soybean exports?
Emerging markets for U.S. soybean exports include Southeast Asian countries, parts of Africa, and expanding opportunities in established markets like China and the European Union.