New Hampshire Logger Faces Legal Consequences: Timber Harvesting Laws and Forestry Business Practices Explained

“90% of timber harvesting disputes can be prevented with proper written contracts between loggers and landowners.”
In the realm of forestry and timber harvesting, legal compliance and ethical business practices are paramount. A recent case in New Hampshire has brought these issues into sharp focus, highlighting the critical importance of adhering to timber harvesting laws and maintaining transparent forestry business practices. As we delve into this significant event, we’ll explore its implications for the logging industry, landowners, and the broader forestry sector.
The Case at a Glance: A New Hampshire Logger’s Legal Troubles
In a landmark case that has sent ripples through the forestry community, a logger from New London, New Hampshire, has faced severe legal consequences for deceptive practices in timber harvesting. Stephen O’Neill, the 51-year-old proprietor of O’Neill Timber Harvesting, recently pleaded guilty to and was convicted of deceptive forestry business practices in Hillsborough County Superior Court.
The court’s decision has resulted in significant penalties for O’Neill, including:
- A restitution order of $27,022
- Additional fines amounting to nearly $5,000
- A suspended prison sentence
This case serves as a stark reminder of the legal and financial risks associated with non-compliance in the timber industry. It underscores the need for stringent adherence to forestry regulations and ethical business conduct.
Understanding the Offense: Deceptive Forestry Business Practices
The crux of the case against O’Neill revolves around his failure to pay for timber harvested from a property in New Boston, NH. Despite having a signed contract with LandVest, the property owner, O’Neill proceeded to harvest and sell timber to a Connecticut sawmill without compensating the landowner.
This action constitutes a clear violation of New Hampshire’s Deceptive Forestry Business Practices Law, which mandates:
- A written contract between loggers and landowners before any timber harvest
- Clear stipulation of payment details in the contract
- Adherence to agreed-upon terms for timber harvesting and compensation
The case highlights the critical importance of transparent and ethical conduct in the forestry sector, emphasizing the legal protections in place for landowners and the serious consequences for those who violate these regulations.
The Role of the Forest Protection Bureau
In New Hampshire, the Forest Protection Bureau, part of the Department of Natural & Cultural Resources, plays a crucial role in enforcing forestry laws and regulations. Chief Steven Sherman of the Forest Protection Bureau emphasized the significance of the Deceptive Forestry Business Practices Law in protecting all parties involved in timber harvesting activities.
The Bureau’s involvement in this case underscores its commitment to:
- Ensuring compliance with forestry laws
- Protecting the rights of landowners
- Maintaining ethical standards in the logging industry
- Promoting sustainable forestry practices
By enforcing these regulations, the Forest Protection Bureau aims to create a fair and transparent environment for timber harvesting operations across the state.
Legal Framework Governing Timber Harvesting
The legal landscape surrounding timber harvesting is complex and multifaceted. In New Hampshire, as in many other states, several key laws and regulations govern forestry practices:
- Timber Tax Law: Regulates the taxation of harvested timber
- Forest Resources Planning Act: Outlines sustainable forest management practices
- Basal Area Law: Sets guidelines for timber harvesting intensity
- Shoreland Water Quality Protection Act: Protects water resources during logging operations
These laws work in concert to ensure that timber harvesting is conducted responsibly, with due consideration for environmental conservation and landowner rights.
The Importance of Written Contracts in Timber Harvesting
One of the key takeaways from the New Hampshire case is the critical importance of written contracts in timber harvesting operations. A well-drafted contract serves multiple purposes:
- Clearly defines the terms of the timber harvest
- Specifies pricing and payment structures
- Outlines the responsibilities of both logger and landowner
- Provides legal protection for all parties involved
By insisting on a comprehensive written agreement, both loggers and landowners can significantly reduce the risk of disputes and legal issues.
“The New Hampshire logger case resulted in fines exceeding $15,000 and a suspended prison sentence for deceptive practices.”
Implications for the Forestry Industry
The case of the New Hampshire logger has far-reaching implications for the forestry industry as a whole. It serves as a wake-up call for:
- Loggers: Emphasizing the need for strict adherence to legal and ethical standards
- Landowners: Highlighting the importance of due diligence when engaging logging services
- Regulatory bodies: Reinforcing the necessity of vigilant enforcement of forestry laws
- Industry associations: Underlining the need for ongoing education and training in legal compliance
This case may lead to increased scrutiny of logging operations and potentially stricter enforcement of existing regulations.
Best Practices for Ethical Timber Harvesting
In light of this case, it’s crucial to highlight best practices for ethical timber harvesting:
- Always use written contracts with clear terms and conditions
- Ensure transparent pricing and payment structures
- Comply with all local, state, and federal forestry regulations
- Maintain open communication between loggers and landowners throughout the harvesting process
- Implement sustainable harvesting practices to protect forest health
- Keep accurate records of all timber harvested and payments made
By adhering to these practices, loggers can minimize legal risks and build trust with landowners and regulatory bodies.
The Role of Technology in Modern Forestry Practices
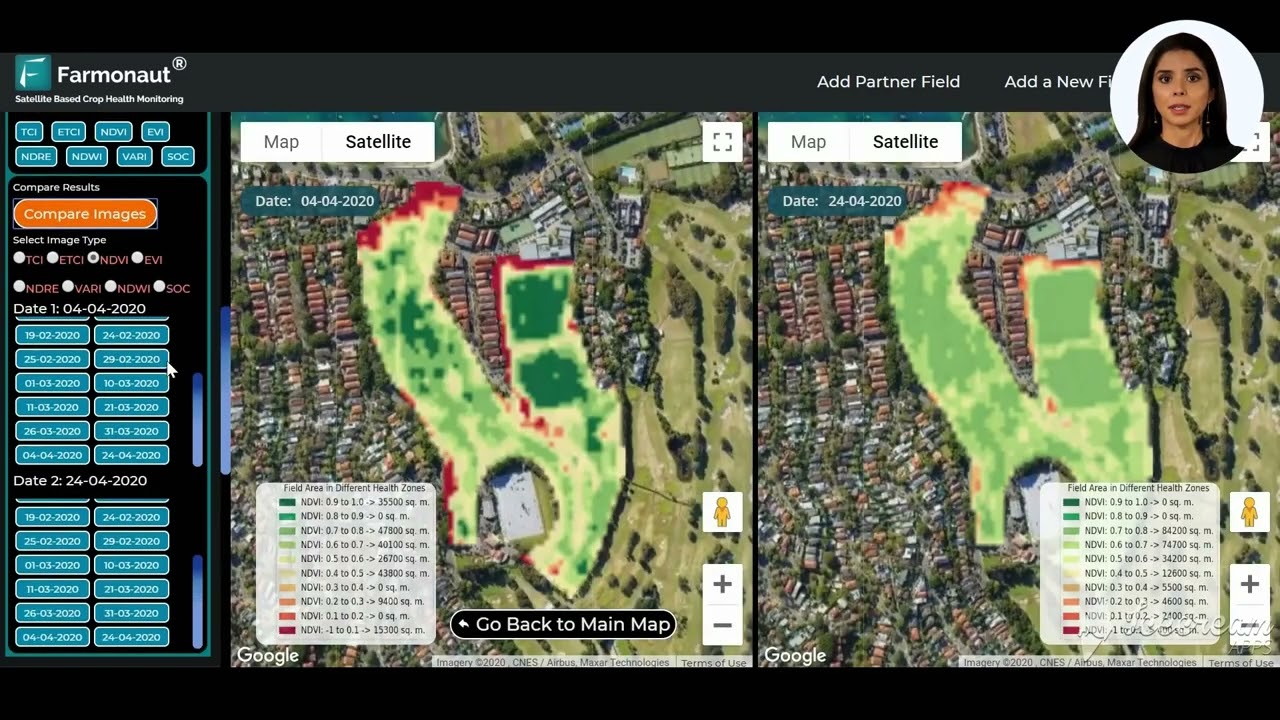
While traditional logging practices remain crucial, modern technology is playing an increasingly important role in forestry management and compliance. Innovative solutions, such as those offered by Farmonaut, are revolutionizing the way we approach forest management and resource tracking.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions, while primarily focused on agricultural applications, offer valuable insights that can be applied to forestry management. Their technology provides:
- Real-time monitoring of forest health
- AI-driven advisory systems for resource management
- Blockchain-based traceability for timber supply chains
These technological advancements can help forestry professionals make more informed decisions, improve resource allocation, and ensure compliance with regulations.
For those interested in exploring these technological solutions further, Farmonaut offers comprehensive API documentation for developers looking to integrate satellite and weather data into their forestry management systems.
Protecting Landowner Rights in Timber Harvesting
The New Hampshire case underscores the importance of protecting landowner rights in timber harvesting operations. Landowners should be aware of their rights and take proactive steps to protect their interests:
- Thoroughly research potential logging contractors
- Insist on detailed, written contracts for all timber harvesting activities
- Understand the value of their timber before agreeing to harvest
- Consider hiring a professional forester to oversee the harvesting process
- Stay informed about local and state forestry regulations
By taking these precautions, landowners can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to deceptive practices.
Environmental Considerations in Timber Harvesting
While the legal and financial aspects of timber harvesting are crucial, it’s equally important to consider the environmental impact of logging operations. Sustainable forestry practices are essential for maintaining long-term forest health and biodiversity.
Key environmental considerations include:
- Selective harvesting to maintain forest structure
- Protecting water resources and wildlife habitats
- Implementing erosion control measures
- Promoting natural regeneration or reforestation after harvest
By prioritizing these environmental factors, loggers and landowners can ensure that timber harvesting activities contribute to, rather than detract from, overall forest health.
The Economic Impact of Timber Harvesting
Timber harvesting plays a significant role in the economy of many rural communities. When conducted responsibly and ethically, it can provide substantial economic benefits:
- Job creation in logging, transportation, and wood processing industries
- Income for landowners through the sale of timber
- Tax revenue for local and state governments
- Support for related industries such as forestry equipment manufacturing
However, cases of deceptive practices, like the one in New Hampshire, can have negative economic ripple effects, potentially leading to decreased trust in the industry and stricter regulations that could impact profitability.
The Future of Forestry: Balancing Economics and Conservation
As we look to the future of forestry, it’s clear that the industry must strike a balance between economic interests and conservation efforts. This balance will likely involve:
- Increased use of technology for forest management and monitoring
- Greater emphasis on sustainable harvesting practices
- Stronger partnerships between loggers, landowners, and conservation organizations
- Continued evolution of forestry laws and regulations
By embracing these changes, the forestry industry can ensure its long-term viability while also protecting our valuable forest resources.
Legal Compliance Checklist for Timber Harvesting
To help loggers and landowners navigate the complex legal landscape of timber harvesting, we’ve compiled a comprehensive compliance checklist:
| Compliance Area | Legal Requirement | Potential Consequences of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Written Contracts | Signed agreement detailing harvest terms | Legal action, fines, contract nullification |
| Pricing Transparency | Clear stipulation of timber prices and payment terms | Accusations of fraud, legal penalties |
| Payment Structures | Adherence to agreed payment schedules | Civil lawsuits, damage to business reputation |
| Forest Protection Bureau Regulations | Compliance with state-specific harvesting rules | Fines, license suspension, criminal charges |
| Environmental Considerations | Adherence to environmental protection laws | Environmental damage fines, cease and desist orders |
| Landowner Rights | Respect for property boundaries and owner wishes | Trespassing charges, civil lawsuits |
| Logger Responsibilities | Proper licensing, insurance, and safety measures | License revocation, increased liability |
This checklist serves as a starting point for ensuring legal compliance in timber harvesting operations. However, given the complexity of forestry laws, it’s always advisable to consult with legal professionals and forestry experts for specific situations.
The Role of Industry Associations in Promoting Ethical Practices
Industry associations play a crucial role in promoting ethical practices and legal compliance within the forestry sector. These organizations often:
- Provide education and training on best practices
- Offer certification programs for loggers and forestry professionals
- Advocate for fair and effective forestry legislation
- Serve as a resource for members navigating complex regulations
By actively participating in these associations, loggers and forestry professionals can stay informed about industry standards and legal requirements.
Leveraging Technology for Compliance and Efficiency
As the forestry industry evolves, technology is becoming an increasingly valuable tool for ensuring compliance and improving operational efficiency. Platforms like Farmonaut, while primarily focused on agriculture, offer insights that can be applied to forestry management:
- Satellite-based monitoring for large-scale forest health assessment
- AI-driven advisory systems for resource management
- Blockchain technology for ensuring transparency in timber supply chains
While these technologies are not a substitute for legal expertise, they can provide valuable data to support decision-making and compliance efforts in forestry operations.
Conclusion: A Call for Ethical Timber Harvesting
The case of the New Hampshire logger serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of ethical practices and legal compliance in the timber harvesting industry. As we’ve explored, the consequences of deceptive practices can be severe, impacting not only individual loggers but also landowners and the broader forestry sector.
Moving forward, it’s crucial for all stakeholders in the forestry industry to:
- Prioritize transparent and ethical business practices
- Ensure comprehensive written contracts for all timber harvesting activities
- Stay informed about and compliant with all relevant forestry laws and regulations
- Embrace technological advancements that can improve forest management and compliance
- Consider the long-term environmental impact of logging operations
By adhering to these principles, we can create a more sustainable, ethical, and prosperous future for the timber harvesting industry.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
FAQs about Timber Harvesting Laws and Forestry Business Practices
- What are the key elements of a proper timber harvesting contract?
A proper timber harvesting contract should include clear terms on harvest boundaries, timber prices, payment schedules, harvest methods, and timeframes. It should also address liability issues and specify any environmental protection measures. - How can landowners protect themselves when entering into a timber harvesting agreement?
Landowners should research potential loggers, insist on written contracts, understand the value of their timber, consider hiring a professional forester, and stay informed about local forestry regulations. - What are the potential legal consequences for loggers who engage in deceptive practices?
Consequences can include hefty fines, restitution orders, suspended or revoked logging licenses, and in severe cases, criminal charges and imprisonment. - How does the Forest Protection Bureau enforce timber harvesting laws?
The Forest Protection Bureau enforces laws through regular inspections, investigating complaints, and collaborating with law enforcement when necessary. They also provide education and resources to promote compliance. - What role does technology play in modern forestry management?
Technology, such as satellite imaging, AI-driven advisory systems, and blockchain for supply chain tracking, is increasingly used to improve forest health monitoring, resource management, and ensure transparency in timber harvesting operations.