Revolutionizing Rural America: How Smart Water Infrastructure Drives Sustainable Agriculture and Economic Prosperity

“Smart irrigation systems can reduce water usage in agriculture by up to 50%, promoting sustainable farming practices in rural America.”
In recent years, the landscape of rural America has been undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the convergence of smart water infrastructure and sustainable agriculture technology. As we navigate the challenges of the 21st century, from climate change to economic uncertainty, the importance of these innovations cannot be overstated. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into how investments in clean water and wastewater systems are uplifting communities, enhancing public health, and stimulating growth across the United States.
At the heart of this revolution lies the critical role of water – a resource that’s both precious and pivotal for the prosperity of rural regions. We’ll uncover how cutting-edge solutions, including those offered by pioneering companies like Farmonaut, are reshaping farming practices, promoting water conservation, and boosting agricultural productivity. From the rolling fields of the Midwest to the arid landscapes of the Southwest, smart water management is becoming the cornerstone of sustainable rural development.
The State of Rural Water Infrastructure in America
Before we dive into the transformative potential of smart water infrastructure, it’s crucial to understand the current state of rural water systems across the United States. Many rural communities face significant challenges when it comes to accessing clean, safe water for both domestic use and agricultural purposes.
- Aging Infrastructure: Much of rural America’s water infrastructure was built decades ago and is now reaching the end of its operational life.
- Limited Resources: Rural water districts often struggle with limited budgets and technical expertise to maintain and upgrade their systems.
- Water Quality Concerns: Contamination from agricultural runoff, industrial pollutants, and naturally occurring elements pose threats to rural water supplies.
- Accessibility Issues: Some remote areas lack access to centralized water systems, relying instead on private wells that may be vulnerable to contamination or depletion.
These challenges have far-reaching implications for rural communities, affecting everything from public health to economic development. However, the tide is turning as innovative solutions and targeted investments begin to address these longstanding issues.
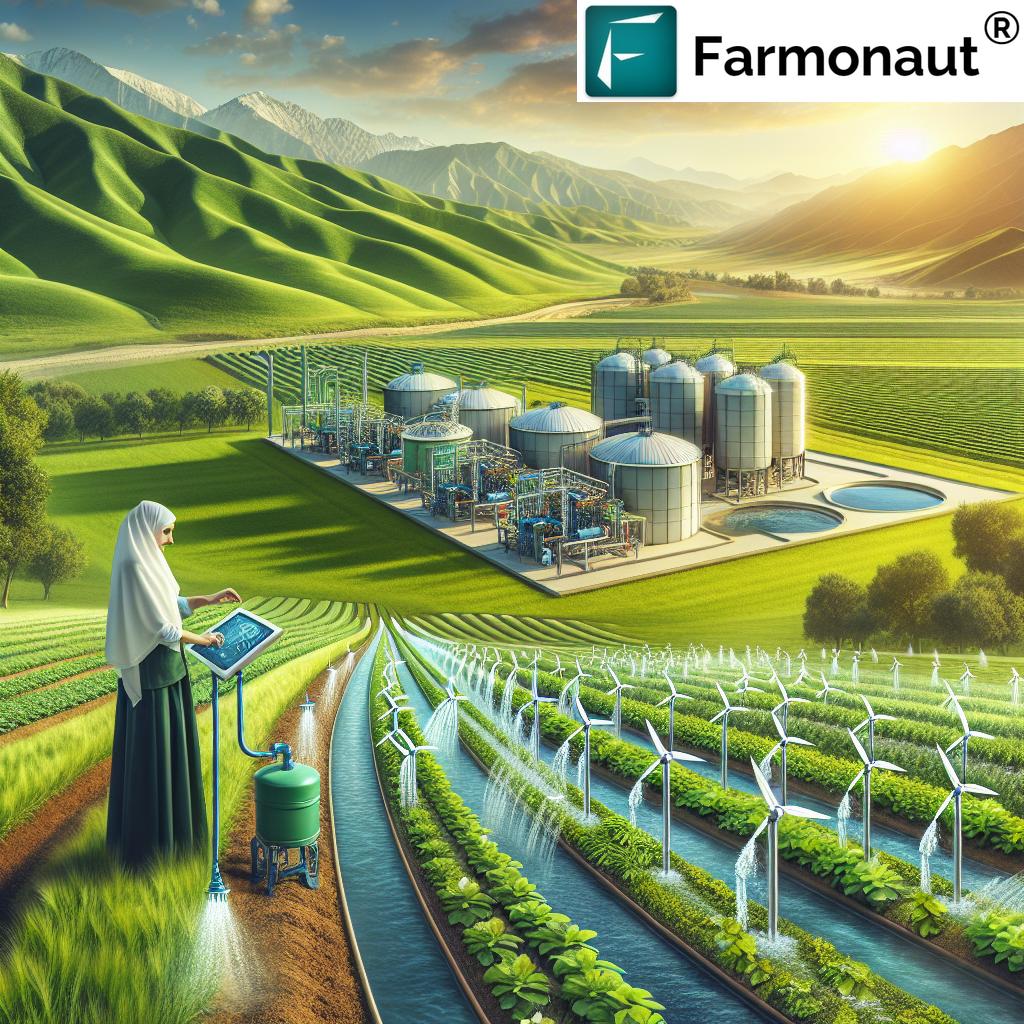
The Promise of Smart Water Infrastructure
Smart water infrastructure represents a paradigm shift in how we manage, distribute, and conserve water resources. By integrating advanced technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, these systems offer unprecedented levels of efficiency, reliability, and sustainability.
Key Components of Smart Water Infrastructure:
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- Leak Detection and Prevention Systems
- Smart Pumps and Pressure Management
- Water Quality Monitoring Sensors
- Predictive Maintenance Tools
The implementation of these technologies is transforming rural water management, allowing for real-time monitoring, rapid response to issues, and data-driven decision-making. This not only improves the reliability of water services but also contributes significantly to conservation efforts.
Sustainable Agriculture Technology: A Game-Changer for Rural America
Alongside improvements in water infrastructure, sustainable agriculture technology is playing a pivotal role in revolutionizing farming practices across rural America. These innovations are enabling farmers to produce more with less, while simultaneously reducing their environmental impact.
Key Sustainable Agriculture Technologies:
- Precision Agriculture Systems
- Smart Irrigation Solutions
- Crop Monitoring and Predictive Analytics
- Soil Health Management Tools
- Agricultural Waste Management Systems
One company at the forefront of this agricultural revolution is Farmonaut. Their innovative platform leverages satellite technology and artificial intelligence to provide farmers with crucial insights into crop health, soil moisture levels, and optimal resource management strategies.
Farmonaut’s solutions exemplify the potential of agritech to transform rural farming practices. By providing real-time data and AI-driven recommendations, they empower farmers to make informed decisions that optimize water usage, reduce waste, and increase yields.
The Economic Impact of Smart Water Infrastructure
Investments in smart water infrastructure and sustainable agriculture technology are not just environmental imperatives; they’re economic catalysts for rural communities. The benefits extend far beyond the farm gate, stimulating growth across various sectors of the rural economy.
“Investments in rural water infrastructure can boost local economies by creating up to 16 jobs for every $1 million spent.”
Economic Benefits Include:
- Job Creation in Construction and Maintenance
- Increased Agricultural Productivity and Profitability
- Attraction of New Businesses to Rural Areas
- Reduced Healthcare Costs Due to Improved Water Quality
- Enhanced Property Values
Moreover, the implementation of smart water systems can lead to significant cost savings for rural water districts, freeing up resources for other community needs. This economic ripple effect is crucial for the long-term sustainability and prosperity of rural America.
Case Studies: Transformative Projects Across Rural America
Across the United States, innovative water infrastructure and sustainable agriculture projects are already making a tangible difference in rural communities. Let’s explore some notable examples:
1. Minnesota’s Fond du Lac Reservation: Integrated Water Management
The Fond du Lac Band of Lake Superior Chippewa in Minnesota has implemented a comprehensive water management system that integrates traditional knowledge with modern technology. This project includes:
- Advanced wastewater treatment facilities
- Wetland restoration for natural water filtration
- Smart metering to monitor water usage and detect leaks
The result has been improved water quality, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced community resilience.
2. Tennessee’s Cumberland Plateau: Precision Agriculture Initiative
In partnership with local universities and agritech companies, farmers in Tennessee’s Cumberland Plateau region have adopted precision agriculture techniques to optimize water use and reduce runoff. Key components include:
- Drone-based crop monitoring
- Variable-rate irrigation systems
- Soil moisture sensors and weather stations
These technologies have led to significant water savings and increased crop yields, boosting the local agricultural economy.
The Role of Government and Policy in Rural Water Infrastructure
The transformation of rural water infrastructure is not solely a technological endeavor; it requires supportive policies and strategic investments from all levels of government. In recent years, we’ve seen increased recognition of the importance of rural water systems at the federal, state, and local levels.
Key Policy Initiatives and Programs:
- USDA Rural Development Water and Environmental Programs
- EPA’s Water Infrastructure Finance and Innovation Act (WIFIA)
- State-level grant and loan programs for rural water projects
- Public-private partnerships to leverage expertise and resources
These initiatives are crucial for providing the financial support and technical assistance needed to implement smart water infrastructure in rural communities. However, there’s still work to be done to ensure equitable access to these resources across all rural areas.
Climate-Smart Farming Practices and Water Efficiency
As climate change continues to impact weather patterns and water availability, the adoption of climate-smart farming practices becomes increasingly critical. These practices not only help farmers adapt to changing conditions but also contribute to water conservation efforts.
Climate-Smart Farming Techniques:
- Cover Cropping and No-Till Agriculture
- Agroforestry and Silvopasture Systems
- Drought-Resistant Crop Varieties
- Rainwater Harvesting and Storage
- Precision Irrigation Scheduling
Farmonaut’s platform plays a crucial role in supporting these practices by providing farmers with real-time data on soil moisture, crop health, and weather patterns. This enables more precise decision-making around irrigation and resource management.
The Intersection of Rural Broadband and Smart Water Management
The success of smart water infrastructure and precision agriculture technologies is intrinsically linked to the availability of reliable broadband internet in rural areas. As we look to the future of rural development, the expansion of broadband access is a critical component.
Benefits of Rural Broadband for Water Management:
- Real-time data transmission from smart water meters and sensors
- Remote monitoring and control of water infrastructure
- Access to cloud-based analytics and decision support tools
- Improved communication between water utilities and customers
- Enhanced ability to implement precision agriculture techniques
Efforts to expand rural broadband access, such as the USDA’s ReConnect Program, are helping to bridge the digital divide and pave the way for more widespread adoption of smart water technologies.
Innovative Approaches to Agricultural Waste Management
As we strive for more sustainable agricultural practices, effective waste management becomes increasingly important. Innovative approaches to handling agricultural waste not only reduce environmental impact but can also create new value streams for farmers.
Emerging Agricultural Waste Management Solutions:
- Anaerobic Digestion for Biogas Production
- Composting and Soil Amendment Creation
- Waste-to-Energy Technologies
- Precision Nutrient Management to Reduce Runoff
- Circular Economy Models for Agricultural Byproducts
These solutions not only address waste management challenges but also contribute to water conservation efforts by reducing pollution and improving soil health.
The Future of Rural Water Infrastructure: Trends and Innovations
As we look to the future, several emerging trends and innovations are poised to further revolutionize rural water infrastructure and sustainable agriculture:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Advanced algorithms will enable more accurate predictions of water demand, crop yields, and potential system failures.
- Blockchain Technology: Improving traceability and transparency in water management and agricultural supply chains.
- Nanotechnology: Enhancing water treatment processes and developing more efficient irrigation systems.
- Biotechnology: Creating drought-resistant crops and developing biological solutions for water treatment.
- Satellite and Drone Technology: Providing even more detailed and frequent monitoring of water resources and crop health.
Companies like Farmonaut are at the forefront of these innovations, continuously developing new tools and technologies to support sustainable agriculture and water management.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for cutting-edge agritech solutions
Impact of Smart Water Infrastructure on Rural America
| Aspect | Before Smart Infrastructure | After Smart Infrastructure | Farmonaut’s Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Productivity | Variable yields, inefficient resource use | 20-30% increase in crop yields | Real-time crop health monitoring and AI-driven advisories |
| Water Conservation | High water waste, up to 50% in some areas | 30-50% reduction in water usage | Smart irrigation systems and soil moisture monitoring |
| Economic Growth | Limited job opportunities, stagnant local economies | Creation of 16 jobs per $1 million invested | Stimulating agritech sector growth and improving farm profitability |
| Public Health | Water quality issues, higher health risks | Significant reduction in waterborne illnesses | Indirect impact through improved agricultural practices |
| Environmental Sustainability | High environmental impact from agriculture | Reduced carbon footprint and improved ecosystem health | Carbon footprinting tools and sustainable farming advisories |
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential benefits of smart water infrastructure and sustainable agriculture technology are immense, there are still challenges to overcome:
- Initial Costs: The upfront investment required for these technologies can be substantial, particularly for small rural communities and farmers.
- Technical Expertise: There’s a need for skilled professionals to implement and maintain these advanced systems.
- Data Privacy and Security: As more systems become connected, ensuring the security of sensitive data becomes crucial.
- Equitable Access: Ensuring that all rural communities, regardless of size or resources, can benefit from these advancements.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Updating policies and regulations to support and govern the use of new technologies in water management and agriculture.
Addressing these challenges will require collaborative efforts from government agencies, private sector companies, and rural communities themselves.
The Role of Community Engagement and Education
For smart water infrastructure and sustainable agriculture technology to truly transform rural America, community engagement and education are essential. Successful implementation requires buy-in and active participation from local residents, farmers, and policymakers.
Key Strategies for Community Engagement:
- Public workshops and demonstrations of new technologies
- Partnerships with local schools and colleges for education and training programs
- Farmer-to-farmer mentorship programs to share best practices
- Regular community meetings to discuss water management strategies and goals
- Citizen science initiatives to involve residents in water quality monitoring
By fostering a sense of ownership and understanding among community members, these initiatives can help ensure the long-term success and sustainability of smart water infrastructure projects.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future for Rural America
As we’ve explored throughout this article, the convergence of smart water infrastructure and sustainable agriculture technology holds immense promise for rural America. From boosting economic prosperity to enhancing environmental sustainability, these innovations are paving the way for a brighter, more resilient future for rural communities.
Companies like Farmonaut are playing a crucial role in this transformation, providing farmers and rural water managers with the tools and insights needed to make more informed decisions and optimize resource use. As we continue to invest in these technologies and build the necessary infrastructure, we’re not just improving water management – we’re investing in the very fabric of rural America.
The journey towards fully integrated smart water systems and sustainable agriculture practices is ongoing, but the progress we’ve seen is encouraging. By continuing to innovate, collaborate, and invest in our rural communities, we can ensure that they not only survive but thrive in the face of 21st-century challenges.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that water will remain at the heart of rural prosperity. By embracing smart technologies and sustainable practices, we can ensure that this precious resource continues to nourish our communities, our economy, and our environment for generations to come.
Learn more about Farmonaut’s API capabilities in our Developer Docs
FAQs
- What is smart water infrastructure?
Smart water infrastructure refers to the use of advanced technologies like IoT sensors, AI, and data analytics to manage water resources more efficiently. It includes systems for leak detection, water quality monitoring, and smart metering. - How does sustainable agriculture technology benefit rural communities?
Sustainable agriculture technology helps farmers optimize resource use, increase crop yields, and reduce environmental impact. This leads to improved profitability, food security, and environmental sustainability in rural areas. - What role does Farmonaut play in rural water management?
Farmonaut provides satellite-based farm management solutions that help farmers monitor crop health, soil moisture, and weather patterns. This enables more efficient water use and better agricultural decision-making. - How can rural communities fund smart water infrastructure projects?
Funding options include federal programs like USDA Rural Development grants, state-level initiatives, public-private partnerships, and low-interest loans from organizations like the EPA’s Water Infrastructure Finance and Innovation Act (WIFIA) program. - What are some challenges in implementing smart water systems in rural areas?
Challenges include high initial costs, the need for technical expertise, ensuring data privacy and security, and providing equitable access to these technologies across diverse rural communities.