Revolutionizing Virtual Reality: Ohio Researchers Develop Groundbreaking e-Taste Technology for Digital Sensory Experiences
“The e-Taste interface can accurately replicate 5 distinct flavor profiles: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami.”
In the ever-evolving landscape of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), we are witnessing a revolutionary breakthrough that promises to transform our digital sensory experiences. Researchers at The Ohio State University have developed a groundbreaking technology called the ‘e-Taste’ interface, which aims to introduce taste as a new sensory connection in the virtual realm. This innovative system employs chemical sensors and wireless dispensers to enable remote taste perception, bridging the gap between the digital and physical worlds in ways we never thought possible.
As we delve into this exciting development, we’ll explore how this virtual reality taste technology is set to revolutionize not only our VR experiences but also open up new avenues for research in brain sensory processing and enhance accessibility in virtual spaces. Let’s taste the future of digital interactions!
The e-Taste Interface: A Leap in Sensory Technology
The e-Taste interface represents a significant advancement in the field of virtual reality and augmented reality. This novel technology combines sophisticated chemical sensors with wireless dispensing systems to create a unique platform for remote taste perception. But what exactly makes this system so revolutionary?
- Chemical Sensors: Calibrated to detect glucose and glutamate molecules, representing the five basic tastes.
- Wireless Dispensers: Enable the delivery of taste sensations remotely.
- Digital Taste Simulation: Accurately replicates sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami flavors.
- Intensity Control: Allows for varied taste intensities, enhancing the realism of the experience.
The development of this system was inspired by previous biosensor work, showcasing how interdisciplinary research can lead to groundbreaking innovations in seemingly unrelated fields.
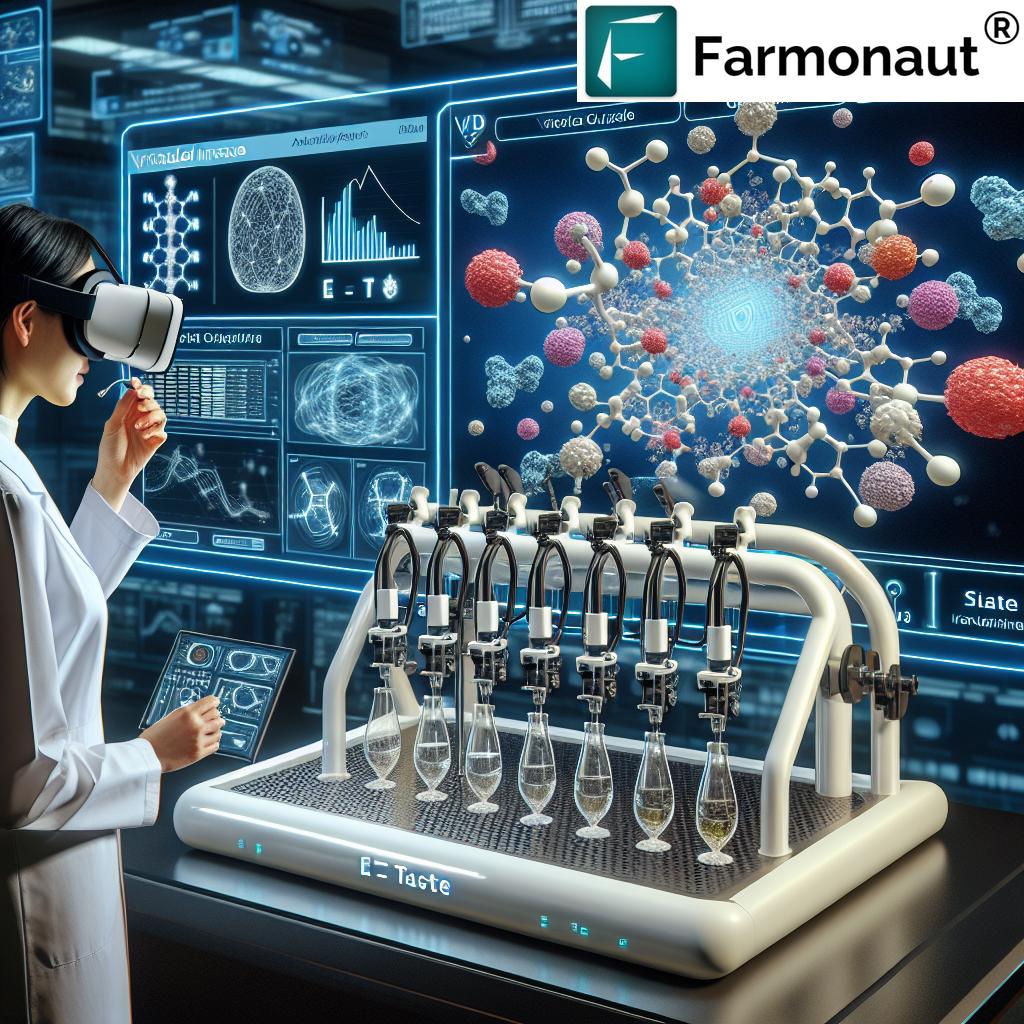
How the e-Taste System Works
The e-Taste system utilizes an innovative actuator with two main components:
- Mouth Interface: This part interacts directly with the user’s mouth, delivering the taste sensations.
- Electromagnetic Pump: A small pump connected to a liquid channel of chemicals.
When an electric charge passes through the electromagnetic pump, it causes vibrations that push the chemical solution through a special gel layer and into the user’s mouth. The intensity and strength of the taste can be easily adjusted by controlling the duration of the solution’s interaction with the gel layer.
Jinghua Li, co-author of the study and assistant professor of materials science and engineering at Ohio State, explains, “Based on the digital instruction, you can also choose to release one or several different tastes simultaneously so that they can form different sensations.”
The Science Behind Taste Perception
To fully appreciate the significance of the e-Taste technology, it’s crucial to understand the complexity of taste perception. Taste is a subjective sense that can vary from moment to moment and person to person. It’s the product of two of the body’s chemical sensing systems working in tandem:
- Gustation: The sense of taste detected by taste buds on the tongue.
- Olfaction: The sense of smell, which greatly influences our perception of flavor.
“Taste and smell are greatly related to human emotion and memory,” Li notes. “So our sensor has to learn to capture, control and store all that information.”
This intricate relationship between taste, smell, emotion, and memory presents both challenges and opportunities for the e-Taste system. By successfully replicating these sensations, the technology has the potential to create deeply immersive and emotionally resonant experiences in virtual environments.
Field Testing and Human Trials
The e-Taste interface has undergone rigorous field testing to ensure its effectiveness and safety. Researchers at The Ohio State University conducted a series of experiments to validate the device’s capabilities:
- Taste Intensity Discrimination: In human trials, participants could distinguish between different sour intensities with an accuracy rate of about 70%.
- Long-Range Capabilities: Tests demonstrated that remote tasting could be initiated in Ohio from as far away as California, showcasing the system’s potential for long-distance sensory experiences.
- Food Identification: Subjects attempted to identify five food options they perceived, including lemonade, cake, fried egg, fish soup, and coffee.
These successful trials not only validate the e-Taste technology but also highlight its potential for creating diverse and engaging virtual food experiences.
Implications for Virtual Reality and Beyond
“Researchers successfully tested the e-Taste device’s ability to create varied taste intensities and transmit flavors wirelessly over long distances.”
The development of the e-Taste interface opens up a world of possibilities for enhancing virtual reality experiences and expanding our understanding of sensory processing. Here are some key implications of this groundbreaking technology:
- Immersive VR Experiences: By adding taste to the sensory palette of virtual reality, we can create more realistic and engaging digital environments.
- Brain Sensory Processing Research: The e-Taste system provides scientists with a unique tool to study how the brain processes sensory signals from the mouth, potentially leading to new insights in neuroscience.
- Improved Accessibility: This technology could enhance accessibility in virtual spaces for individuals with disabilities, such as those with traumatic brain injuries or Long Covid-related gustatory loss.
- Remote Tasting Possibilities: The ability to transmit taste sensations over long distances opens up new avenues for remote culinary experiences and food industry applications.
As we continue to explore the potential of the e-Taste interface, it’s clear that this technology represents a significant step towards creating truly multisensory digital experiences.
Key Features of e-Taste Technology in Virtual Reality
| Feature | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Taste Replication | Accurately simulates sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami flavors | Enhanced realism in VR food experiences |
| Wireless Dispensing System | Delivers taste sensations remotely without physical contact | Enables long-distance taste sharing and virtual food tasting |
| Electromagnetic Pump Mechanism | Pushes chemical solutions through a gel layer for taste delivery | Precise control over taste intensity and duration |
| Gel Layer for Taste Delivery | Special layer that interacts with chemical solutions to create taste sensations | Ensures safe and controlled taste delivery to users |
| Long-Range Taste Transmission | Capable of initiating taste experiences across large distances | Opens possibilities for global culinary experiences and remote food industry applications |
| Intensity Control | Allows for adjustment of taste strength and duration | Customizable taste experiences for various VR applications and user preferences |
Future Developments and Challenges
While the e-Taste interface represents a significant breakthrough, there are still areas for improvement and challenges to overcome. The research team at Ohio State University is focusing on several key areas for future development:
- Miniaturization: Further reducing the size of the system to make it more practical for everyday use in VR and AR applications.
- Chemical Compatibility: Improving the system’s ability to work with a wider range of chemical compounds found in food, expanding the variety of taste sensations it can produce.
- Integration with Existing VR/AR Systems: Ensuring seamless compatibility with current virtual and augmented reality platforms.
- Safety and Regulation: Addressing potential concerns about the safety of delivering chemical solutions for taste simulation and navigating regulatory requirements.
As we work to overcome these challenges, the potential applications of the e-Taste technology continue to expand, promising to revolutionize not only gaming and entertainment but also fields such as culinary arts, healthcare, and education.
Potential Applications Across Industries
The e-Taste interface has the potential to transform various industries beyond just virtual reality gaming. Let’s explore some exciting possibilities:
Culinary Industry
- Virtual Food Tasting: Restaurants could offer remote taste testing of their menus.
- Cooking Classes: Online culinary courses could provide students with the ability to taste dishes virtually.
- Food Product Development: Companies could conduct taste tests and gather feedback without physical product distribution.
Healthcare
- Taste Disorder Diagnosis: The e-Taste system could be used to assess and diagnose taste-related disorders remotely.
- Rehabilitation: Patients recovering from injuries or conditions affecting their sense of taste could use the system for therapy.
- Nutritional Education: Virtual taste experiences could be used to educate patients about healthy eating habits.
Education
- Virtual Field Trips: Students could experience tastes from different cultures and regions without leaving the classroom.
- Chemistry Classes: The system could be used to demonstrate chemical reactions through taste perception.
- Food Science Education: Students could explore flavor profiles and food pairings in a virtual environment.
Marketing and Advertising
- Product Sampling: Companies could offer virtual taste samples of new products to consumers.
- Immersive Advertisements: Ads could incorporate taste experiences to create more engaging content.
- Market Research: Taste preferences could be gathered more efficiently through virtual testing.
The Role of e-Taste in Enhancing Virtual Reality Experiences
The introduction of taste sensations to virtual reality environments marks a significant leap forward in creating truly immersive digital experiences. By engaging multiple senses simultaneously, VR developers can create more realistic and emotionally resonant virtual worlds. Here’s how e-Taste technology is set to enhance VR experiences:
- Multisensory Gaming: Imagine tasting the virtual foods your character consumes in a game, adding a new layer of realism to role-playing and simulation games.
- Virtual Tourism: Experience the flavors of different cuisines as you virtually explore new destinations, enhancing the cultural immersion of virtual travel.
- Social VR: Share meals with friends and family in virtual spaces, complete with the ability to taste the food, creating more meaningful social interactions in digital environments.
- Training Simulations: Enhance the realism of training programs for chefs, sommeliers, and other professionals in the food and beverage industry.
The integration of e-Taste technology with existing visual and auditory VR systems creates a more holistic sensory experience, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in virtual reality.
Ethical Considerations and User Safety
As with any new technology that interacts directly with our senses, the e-Taste interface raises important ethical considerations and safety concerns that must be addressed:
- Chemical Safety: Ensuring that the substances used to create taste sensations are safe for human consumption and do not cause allergic reactions or other adverse effects.
- Data Privacy: Protecting users’ taste preference data, which could be considered sensitive personal information.
- Addiction Potential: Addressing concerns about the potential for users to become addicted to virtual taste experiences, especially in gaming environments.
- Informed Consent: Ensuring that users fully understand the technology and its potential effects before engaging with e-Taste systems.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Considering how to make the technology accessible to individuals with various disabilities or sensory impairments.
Researchers and developers must work closely with ethicists, regulatory bodies, and healthcare professionals to establish guidelines and best practices for the safe and responsible use of e-Taste technology.
The Future of Sensory Experiences in Virtual Reality
As we look to the future, the e-Taste interface represents just the beginning of a new era in virtual reality technology. The integration of taste sensations opens the door to a more comprehensive sensory experience in digital environments. Here are some exciting possibilities for the future:
- Full Flavor Simulation: Combining e-Taste technology with olfactory (smell) simulation to create complete flavor experiences in VR.
- Personalized Taste Profiles: AI-driven systems that learn and adapt to individual taste preferences for customized virtual experiences.
- Haptic Feedback Integration: Combining taste sensations with touch feedback to simulate texture and temperature of virtual foods.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: Direct neural stimulation to create taste sensations without the need for chemical delivery systems.
These advancements could revolutionize not only entertainment and gaming but also have significant implications for fields such as healthcare, education, and scientific research.
Conclusion: A Taste of the Future
The development of the e-Taste interface by researchers at The Ohio State University marks a significant milestone in the evolution of virtual reality technology. By introducing taste as a new sensory dimension in digital experiences, we are opening up a world of possibilities for more immersive, engaging, and realistic virtual environments.
From enhancing gaming experiences to revolutionizing remote communication, culinary education, and healthcare applications, the potential impact of this technology is vast and exciting. As we continue to refine and expand the capabilities of e-Taste systems, we can look forward to a future where our digital interactions are richer, more meaningful, and truly multisensory.
While challenges remain in terms of miniaturization, chemical compatibility, and addressing ethical concerns, the groundwork has been laid for a new era of sensory experiences in virtual reality. As this technology evolves, it will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of how we interact with digital worlds and each other in virtual spaces.
The e-Taste interface is more than just a technological innovation; it’s a gateway to a new dimension of digital experiences that engage our senses in ways we’ve only dreamed of before. As we stand on the brink of this exciting new frontier, one thing is clear: the future of virtual reality is set to be deliciously immersive.
FAQ Section
Q: How does the e-Taste interface work?
A: The e-Taste interface uses chemical sensors to detect taste molecules and a wireless dispensing system to deliver taste sensations to the user’s mouth. An electromagnetic pump pushes a chemical solution through a special gel layer, creating varied taste intensities.
Q: What types of tastes can the e-Taste system replicate?
A: The system can accurately replicate the five basic tastes: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami.
Q: Is the e-Taste technology safe for human use?
A: Safety is a top priority in the development of e-Taste technology. Researchers are working to ensure that all chemical solutions used are safe for human consumption and that the system meets all necessary regulatory requirements.
Q: Can e-Taste technology be used for long-distance taste transmission?
A: Yes, researchers have successfully demonstrated long-range taste transmission, initiating taste experiences in Ohio from as far away as California.
Q: What are some potential applications of e-Taste technology beyond gaming?
A: E-Taste technology has potential applications in fields such as culinary education, healthcare (for taste disorder diagnosis and rehabilitation), virtual tourism, and remote food product testing.
Q: How accurate is the e-Taste system in replicating real food tastes?
A: In human trials, participants could distinguish between different taste intensities with an accuracy rate of about 70%. The technology is continuously being improved to enhance its accuracy and range of flavors.
Q: Will e-Taste technology be available for home use in the near future?
A: While the technology is still in the research and development phase, efforts are being made to miniaturize the system and improve its compatibility with existing VR/AR platforms, potentially leading to future home applications.
Q: How does e-Taste technology impact the field of sensory research?
A: E-Taste provides scientists with a unique tool to study how the brain processes taste signals, potentially leading to new insights in neuroscience and sensory perception research.
Q: Can e-Taste technology help people with taste disorders?
A: Yes, the technology shows promise in helping individuals with taste disorders or those experiencing taste loss due to conditions like Long Covid. It could be used for both diagnosis and rehabilitation purposes.
Q: What challenges need to be overcome before e-Taste becomes widely available?
A: Key challenges include further miniaturization of the system, improving chemical compatibility to replicate a wider range of tastes, ensuring seamless integration with existing VR/AR platforms, and addressing safety and regulatory requirements.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
For those interested in exploring innovative agricultural technologies, consider checking out Farmonaut’s advanced satellite-based farm management solutions:
For developers interested in integrating agricultural data into their applications, explore Farmonaut’s API: