Sustainable Water Management: Exploring Dam Expansion and Conservation in Lake Mendocino
“Lake Mendocino’s water management study impacts over 650,000 people across multiple California counties.”
In the face of California’s ongoing drought challenges and the pressing need for sustainable water management solutions, we are excited to share groundbreaking developments in the Lake Mendocino water supply and Coyote Valley Dam expansion project. This comprehensive study aims to address the complex water needs of Northern California, balancing agricultural demands, recreational activities, and environmental conservation along the Russian River.
As we delve into this crucial initiative, we’ll explore how innovative approaches to water storage, flood control, and infrastructure upgrades could reshape California’s water future and impact local communities. Join us as we uncover the potential of this collaborative effort to ensure a reliable water supply for generations to come.
The Urgency of Water Management in Northern California
California’s water challenges are well-documented, with recurring droughts and increasing demand putting immense pressure on existing resources. Lake Mendocino, a critical water source for over 650,000 people across Mendocino, Sonoma, and Marin counties, stands at the forefront of these challenges. The lake not only provides essential drinking water but also plays a vital role in flood control and supports local agriculture and recreation.
As climate change continues to alter precipitation patterns and exacerbate extreme weather events, the need for adaptive and resilient water management strategies has never been more urgent. The Coyote Valley Dam General Investigation Study represents a proactive approach to addressing these pressing issues.
A Collaborative Effort for Sustainable Solutions
The study brings together a diverse group of stakeholders, including:
- Mendocino County Inland Water and Power Commission
- Lytton Rancheria
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
- State and local politicians
- Tribal officials
This partnership exemplifies the collaborative spirit necessary to tackle complex water management challenges. By combining expertise from various sectors, the study aims to develop comprehensive solutions that address multiple aspects of water resource planning.
Key Objectives of the Coyote Valley Dam Expansion Study
The $3 million study, partially funded through efforts by U.S. Rep. Jared Huffman, D-San Rafael, will focus on several critical areas:
- Increased Water Storage Capacity: Evaluating options to raise the Coyote Valley Dam to its originally authorized height, potentially increasing the conservation pool and overall water storage capacity.
- Enhanced Flood Control Measures: Assessing current flood risks and exploring improved flood control strategies to protect downstream communities.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Examining necessary upgrades to the aging dam infrastructure to ensure long-term reliability and safety.
- Aquatic Species Conservation: Investigating ways to improve water quality and habitat conditions for native fish populations, including salmon and steelhead.
- Coordinated Water Transfers: Exploring opportunities to enhance water supply by coordinating transfers between the Eel and Russian rivers.
These objectives reflect a holistic approach to water management, considering not only human needs but also environmental conservation and long-term sustainability.
Potential Impacts of Dam Expansion
The proposed expansion of the Coyote Valley Dam could have far-reaching effects on the region’s water management capabilities:
- Increased Water Security: A larger reservoir capacity would provide a more reliable water supply during drought periods, benefiting both urban and agricultural users.
- Improved Flood Protection: Enhanced flood control measures could reduce the risk of downstream flooding, protecting communities and infrastructure along the Russian River.
- Enhanced Environmental Stewardship: By improving water quality and habitat conditions, the project aims to support the recovery of native fish populations and overall ecosystem health.
- Economic Benefits: A more stable water supply could bolster agricultural productivity and support recreational activities, contributing to the local economy.
As we consider these potential impacts, it’s crucial to recognize the role of advanced technology in modern water management. For instance, carbon footprinting tools can help assess the environmental impact of water management strategies, ensuring that sustainability remains at the forefront of decision-making processes.
Innovative Approaches to Water Quality Improvement
One of the study’s key focuses is on improving water quality within Lake Mendocino. Allison Conn, project manager for the San Francisco District of the Corps of Engineers, highlights two innovative approaches being considered:
- Reducing Water Turbidity: The study will explore methods to decrease water murkiness, creating a cleaner, healthier environment for aquatic life.
- Alternative Dam Outlet Location: Investigating the possibility of relocating the dam’s outlet to access clearer water, which would benefit both water users and native fish populations.
These approaches demonstrate the project’s commitment to not only increasing water quantity but also improving its quality for all users, including wildlife.
Addressing the Potter Valley Project Decommissioning
The study takes on added significance in light of PG&E’s plans to decommission the Potter Valley Project, a historic system that has long transferred water from the Eel River to the Russian River. This development has raised concerns among local politicians and residents about future water supply stability.
Mari Rodin, Ukiah City Councilmember and commission representative, emphasizes the need for evolution in the region’s water management approach: “The dam and the region’s entire water system must evolve. The climate is changing, the infrastructure is outdated, and PG&E’s exit means we need a new, coordinated approach.”
This situation underscores the importance of developing flexible, resilient water management strategies that can adapt to changing environmental and infrastructural conditions.
Balancing Multiple Water Uses
One of the most challenging aspects of the Lake Mendocino water management study is balancing the diverse needs of various stakeholders:
- Agricultural Demands: Ensuring a reliable water supply for the region’s farming communities, which play a crucial role in local and state economies.
- Urban Water Use: Meeting the drinking water needs of over 650,000 people across multiple counties.
- Environmental Conservation: Protecting and enhancing habitats for native species, particularly salmon and steelhead populations.
- Recreational Activities: Maintaining Lake Mendocino as a valuable recreational resource for local communities and tourists.
- Flood Control: Safeguarding downstream areas from potential flooding during high-precipitation events.
Striking the right balance among these competing interests requires careful planning, innovative solutions, and ongoing collaboration among all stakeholders.
Leveraging Technology for Sustainable Water Management
As we explore solutions for Lake Mendocino, it’s worth noting the role that advanced technologies can play in sustainable water management. For example, satellite-based crop monitoring systems can help optimize irrigation practices, reducing water waste in agriculture while improving crop yields.
Similarly, fleet management tools can enhance the efficiency of water delivery systems, ensuring that resources are used as effectively as possible. These technological advancements highlight the potential for innovation to address complex water management challenges.
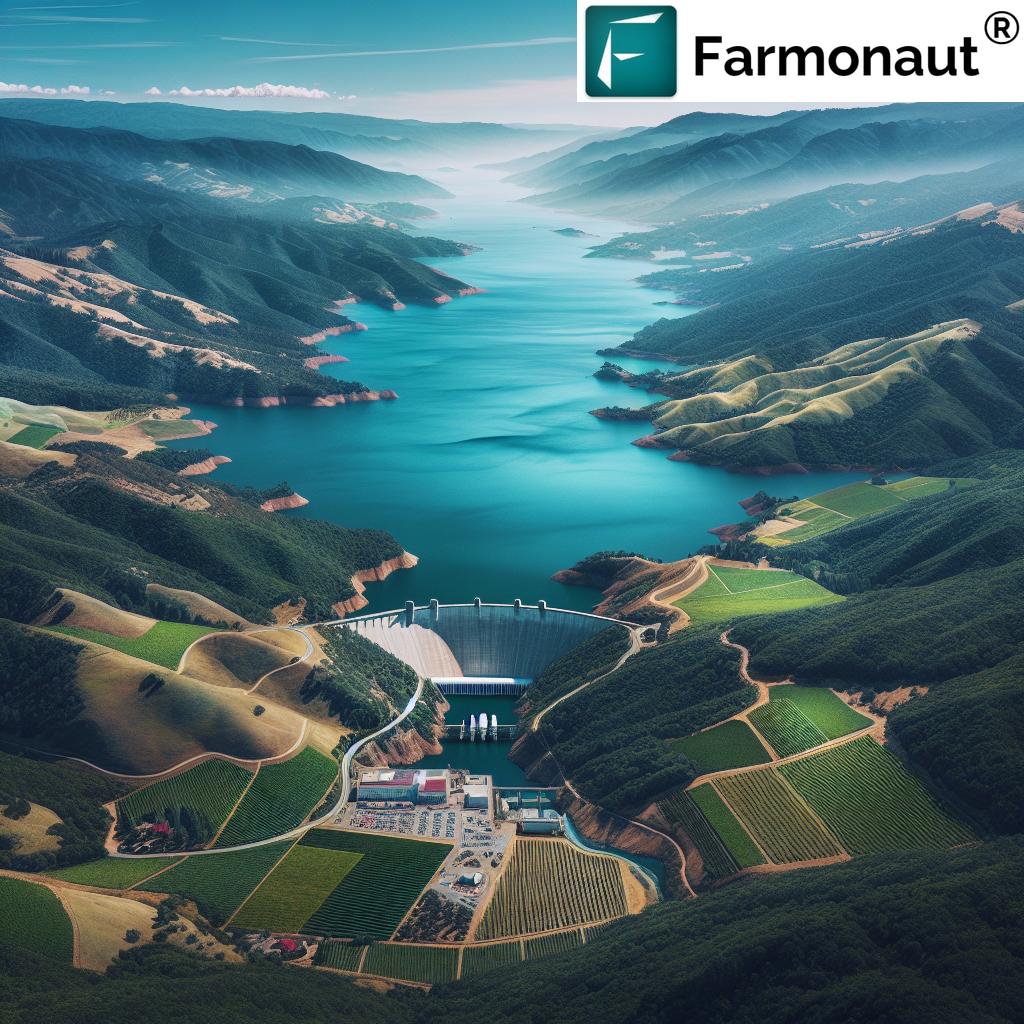

Environmental Considerations in Dam Expansion
While increasing water storage capacity is a primary goal of the study, environmental considerations play a crucial role in the planning process. The project team is committed to minimizing ecological impacts and enhancing habitat conditions for native species. Key environmental aspects being addressed include:
- Fish Passage: Ensuring that any dam modifications do not impede the movement of migratory fish species.
- Riparian Habitat: Preserving and potentially enhancing riverside ecosystems that support diverse plant and animal communities.
- Water Temperature Management: Implementing strategies to maintain appropriate water temperatures for aquatic life, particularly during warmer months.
- Sediment Transport: Addressing the natural movement of sediments in the river system to maintain ecological balance and prevent excessive buildup behind the dam.
These environmental considerations demonstrate the project’s commitment to a holistic approach to water management that balances human needs with ecosystem health.
Innovative Water Transfer Strategies
Congressman Jared Huffman highlights the potential for the dam expansion project to enhance water transfer capabilities between the Eel and Russian rivers. This innovative approach could provide several benefits:
- Increased Water Storage: The ability to store more water during wet periods without compromising flood control capabilities.
- Improved Drought Resilience: Enhanced storage capacity would help communities in the North Bay better withstand prolonged dry periods.
- Fisheries Support: Coordinated water transfers could help maintain adequate flows in the Russian River to support fish populations.
This strategy exemplifies the kind of forward-thinking, integrated water management approach needed to address California’s complex water challenges.
Economic Implications of the Lake Mendocino Project
The proposed expansion of the Coyote Valley Dam and associated water management improvements could have significant economic implications for the region:
- Agricultural Stability: A more reliable water supply would support the agricultural sector, potentially increasing crop yields and economic output.
- Recreational Tourism: Improved lake conditions could boost recreational activities, attracting more visitors and supporting local businesses.
- Flood Damage Reduction: Enhanced flood control measures could lead to reduced property damage and lower insurance costs for downstream communities.
- Job Creation: The construction and ongoing maintenance of expanded infrastructure could create new employment opportunities in the region.
While these economic benefits are promising, it’s crucial to consider them alongside environmental and social impacts to ensure a truly sustainable approach to water management.
Community Engagement and Public Participation
The success of the Lake Mendocino water management study relies heavily on community engagement and public participation. As the project moves forward, several initiatives are being implemented to involve local stakeholders:
- Public Information Sessions: Regular meetings to inform the public about project progress and gather feedback.
- Stakeholder Workshops: Collaborative sessions bringing together diverse interest groups to discuss challenges and solutions.
- Online Resources: Dedicated websites and social media channels to provide up-to-date information and collect public input.
- Educational Outreach: Programs to raise awareness about water conservation and the importance of sustainable water management.
These efforts ensure that the project remains transparent and responsive to community needs and concerns.
“The Coyote Valley Dam expansion project aims to address water needs for agriculture, recreation, and environmental conservation simultaneously.”
Technological Innovations in Water Management
As we explore solutions for Lake Mendocino, it’s important to consider how technological innovations can enhance water management practices. Modern tools and techniques can provide valuable insights and improve efficiency across various aspects of water resource planning:
- Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing: Advanced satellite technology can monitor water levels, detect changes in vegetation health, and assess soil moisture content over large areas. This data is crucial for making informed decisions about water allocation and conservation efforts.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to predict water demand, optimize distribution networks, and identify potential issues before they become critical.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors: Networked sensors can provide real-time data on water quality, flow rates, and usage patterns, enabling more responsive and efficient water management.
- Blockchain for Water Rights Management: Blockchain technology can create transparent and secure systems for managing water rights and transactions, ensuring fair allocation of resources.
Incorporating these technological advancements into the Lake Mendocino project could significantly enhance its effectiveness and long-term sustainability. For instance, advanced crop advisory systems can help farmers optimize their water use, contributing to overall conservation efforts in the region.

Comparative Analysis of Lake Mendocino Water Management Strategies
| Water Management Aspect | Current Situation | Proposed Improvements |
|---|---|---|
| Dam Height | 160 feet | Potential increase to 180 feet |
| Water Storage Capacity | 122,500 acre-feet | Estimated increase to 150,000 acre-feet |
| Flood Control Measures | Basic flood control capabilities | Enhanced flood control with improved spillway design |
| Water Quality for Aquatic Species | Moderate turbidity levels | Reduced turbidity through new outlet location and filtration systems |
| Water Transfer Coordination | Limited coordination between Eel and Russian rivers | Improved transfer system with real-time monitoring and adaptive management |
Challenges and Considerations
While the Lake Mendocino water management study offers promising solutions, it also faces several challenges that must be carefully addressed:
- Environmental Impact: Any modifications to the dam or reservoir must be carefully evaluated for their potential effects on local ecosystems and wildlife habitats.
- Funding and Cost-Benefit Analysis: Securing adequate funding for the project and ensuring that the benefits outweigh the costs will be crucial for its implementation.
- Regulatory Compliance: The project must navigate complex state and federal regulations governing water rights, environmental protection, and infrastructure development.
- Climate Change Uncertainty: Long-term planning must account for the uncertainties associated with climate change and its potential impacts on water availability and extreme weather events.
- Stakeholder Consensus: Balancing the diverse needs and interests of various stakeholders will require ongoing negotiation and compromise.
Addressing these challenges will require continued collaboration, innovative thinking, and a commitment to sustainable, long-term solutions.
The Role of Policy and Regulation
The success of the Lake Mendocino water management project will depend heavily on supportive policies and regulations at both the state and federal levels. Key policy considerations include:
- Water Rights: Ensuring that any changes to water storage and distribution are compatible with existing water rights and allocation agreements.
- Environmental Protection: Adhering to and potentially updating environmental regulations to balance conservation needs with water management goals.
- Funding Mechanisms: Developing policies that facilitate public-private partnerships and innovative funding solutions for large-scale water infrastructure projects.
- Interagency Cooperation: Fostering collaboration between local, state, and federal agencies to streamline project approval and implementation processes.
Policymakers will play a crucial role in creating a regulatory environment that supports sustainable water management while protecting the interests of all stakeholders.
Looking to the Future: A Model for Sustainable Water Management
As we conclude our exploration of the Lake Mendocino water management study, it’s clear that this project has the potential to serve as a model for sustainable water management in California and beyond. By combining innovative engineering solutions, environmental conservation efforts, and collaborative stakeholder engagement, the project demonstrates a holistic approach to addressing complex water challenges.
Key takeaways from this initiative include:
- The importance of balancing human needs with environmental conservation
- The potential of technological innovations to enhance water management practices
- The critical role of collaboration among diverse stakeholders
- The need for adaptive strategies in the face of climate change and evolving water demands
As the project moves forward, it will undoubtedly provide valuable insights and lessons for water managers, policymakers, and communities facing similar challenges around the world.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Water Future for Northern California
The Lake Mendocino water management study and Coyote Valley Dam expansion project represent a critical step towards ensuring a sustainable water future for Northern California. By addressing the complex interplay of agricultural needs, urban water demand, environmental conservation, and climate change adaptation, this initiative offers hope for a more resilient and balanced approach to water resource management.
As the project progresses, continued public engagement, technological innovation, and adaptive management will be key to its success. The lessons learned from this endeavor will undoubtedly inform water management practices not only in California but in water-stressed regions around the world.
We invite readers to stay informed about the progress of this important project and to consider how they can contribute to water conservation efforts in their own communities. Together, we can work towards a future where water resources are managed sustainably for the benefit of all.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the main goal of the Lake Mendocino water management study?
A: The main goal is to explore options for raising the Coyote Valley Dam to increase water storage capacity, improve flood control, and enhance water quality for both human use and aquatic species conservation.
Q: How many people rely on Lake Mendocino for their water supply?
A: Over 650,000 people across Mendocino, Sonoma, and Marin counties depend on Lake Mendocino for their drinking water.
Q: What are some of the environmental considerations in this project?
A: The project considers improving water quality for native fish populations, enhancing riparian habitats, and ensuring that dam modifications do not negatively impact wildlife or ecosystem health.
Q: How will the project address the decommissioning of the Potter Valley Project?
A: The study aims to develop new strategies for water management and transfers between the Eel and Russian rivers to compensate for the loss of water traditionally provided by the Potter Valley Project.
Q: What role does public participation play in this project?
A: Public participation is crucial, with the project team organizing information sessions, workshops, and online resources to gather community input and keep stakeholders informed throughout the process.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!


















I read that the authorized 1950s federal project proposed raising the dam by 36 feet. Why is a dam raise of only 20 feet now to be studied?