Texas Wildfire Crisis: How Farmonaut’s Remote Sensing Aids Sustainable Agriculture in Fire-Prone Areas
“Texas wildfires have increased by 500% in the past decade, threatening sustainable agriculture practices.”

In recent years, the Lone Star State has faced an unprecedented challenge: the Texas wildfire crisis. As ranchers and farmers grapple with increasing fire risks, the need for innovative wildfire prevention in agriculture and robust Texas wildfire preparedness strategies has never been more critical. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to leveraging cutting-edge technology to support sustainable agriculture in fire-prone areas.
In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll explore the current wildfire situation in Texas, delve into the challenges faced by the agricultural community, and discuss how remote sensing technology, like that offered by Farmonaut, is revolutionizing fire risk management for ranches and farms across the state.
The Texas Wildfire Crisis: A Growing Threat to Agriculture
The Southwestern United States, particularly Texas, has been experiencing an alarming increase in wildfire activity. This surge is attributed to a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Prolonged drought conditions
- Climate change impacts
- Increased human activity in wildland-urban interfaces
- Changes in land management practices
These factors have created a perfect storm for wildfire proliferation, putting immense pressure on local and federal resources tasked with fire suppression and containment.
The Impact on Texas Agriculture
The agricultural sector, a cornerstone of Texas’s economy, has been hit particularly hard by this crisis. Ranchers and farmers face numerous challenges, including:
- Loss of grazing land and crops
- Damage to infrastructure and equipment
- Increased costs for fire prevention and recovery
- Disruption of livestock management practices
- Long-term soil degradation due to intense fires
These impacts underscore the urgent need for innovative solutions in fire risk management for ranches and farms across the state.
Farmonaut’s Remote Sensing: A Game-Changer in Wildfire Prevention
“Remote sensing technology can detect potential wildfire hotspots with 95% accuracy, aiding in early prevention efforts.”
At Farmonaut, we’re harnessing the power of satellite technology to revolutionize wildfire prevention and management in agriculture. Our advanced remote sensing capabilities offer a range of benefits for farmers and ranchers in fire-prone areas:
- Early Detection: Our satellite-based monitoring system can identify potential fire hotspots before they escalate, allowing for rapid response and containment.
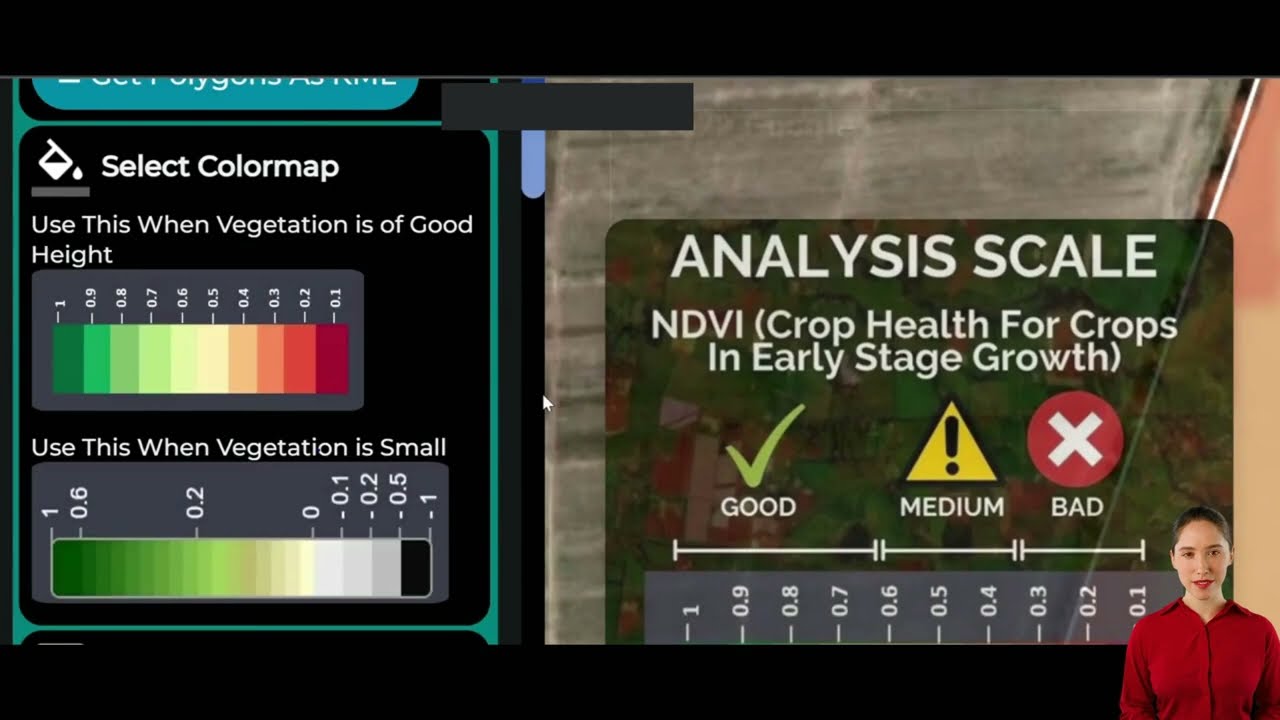
- Vegetation Health Monitoring: By tracking vegetation indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), we help farmers assess the fire risk associated with dry or unhealthy vegetation.
- Soil Moisture Analysis: Our technology provides insights into soil moisture levels, crucial for understanding fire risk and planning irrigation strategies.
- Post-Fire Assessment: After a wildfire, our remote sensing tools can quickly assess the extent of damage, aiding in recovery and rehabilitation efforts.
To explore how Farmonaut’s technology can enhance your farm’s fire preparedness, visit our web application or download our mobile apps:
Innovative Strategies for Wildfire Prevention in Agriculture
While remote sensing forms the backbone of modern wildfire prevention, a comprehensive approach includes various strategies. Let’s explore some innovative methods being employed in Texas and beyond:
1. Precision Agriculture in Fire-Prone Areas
Precision agriculture techniques, powered by remote sensing data, can significantly reduce fire risks:
- Targeted Irrigation: By precisely managing soil moisture, farmers can create natural firebreaks and reduce the spread of wildfires.
- Vegetation Management: Data-driven decisions on where to clear or thin vegetation can create effective fire barriers.
- Crop Selection: Choosing fire-resistant crops in high-risk areas can mitigate potential losses.
2. Fire-Resistant Crops and Vegetation
Incorporating fire-resistant plants into agricultural landscapes can create natural buffers against wildfire spread. Some examples include:
- Succulents like agave and aloe
- Hardwood trees such as oak and maple
- Ground covers like ice plant and sedum
These plants can be strategically placed around property boundaries and between fields to slow fire progression.
3. Advanced Wildfire Containment Strategies
Modern containment strategies leverage technology and data for more effective firefighting:
- Drone-assisted Surveillance: Drones equipped with thermal cameras can provide real-time data on fire movement.
- AI-powered Predictive Models: These models use historical data and current conditions to predict fire behavior and spread.
- GPS-guided Firefighting: Precise positioning systems help coordinate firefighting efforts more efficiently.
Climate Change and Wildfire Patterns: A Growing Concern
The relationship between climate change and wildfire patterns is becoming increasingly evident, particularly in Texas. As we navigate this challenging landscape, understanding these connections is crucial for developing effective long-term strategies.
Key Climate-Related Factors Affecting Wildfires:
- Rising Temperatures: Higher temperatures lead to drier conditions, increasing fire risk.
- Altered Precipitation Patterns: Changes in rainfall can affect vegetation growth and moisture levels.
- Extended Fire Seasons: Warmer springs and later falls expand the window for potential fire activity.
- Increased Lightning Activity: Climate change may lead to more frequent lightning strikes, a common wildfire ignition source.
At Farmonaut, we’re constantly updating our models to account for these changing patterns, ensuring our remote sensing technology remains at the forefront of fire risk assessment.

Drought Impact on Grasslands: A Catalyst for Large-Scale Fires
The impact of drought on Texas grasslands is a critical factor in the wildfire equation. Extended dry periods transform lush prairies into potential tinderboxes, significantly increasing the risk of large-scale fires. Understanding this relationship is vital for effective fire management in agricultural areas.
Drought Effects on Fire Risk:
- Vegetation Desiccation: Dry grass and vegetation become highly flammable.
- Reduced Soil Moisture: This exacerbates the dryness of surface vegetation.
- Altered Ecosystem Dynamics: Drought can change plant species composition, potentially introducing more fire-prone species.
- Increased Wind Erosion: This can spread embers and accelerate fire propagation.
Farmonaut’s remote sensing technology plays a crucial role in monitoring these conditions, providing early warnings and helping farmers adapt their land management practices to mitigate fire risks.
Agricultural Disaster Relief: Responding to Wildfire Impacts
When wildfires do occur, rapid and effective agricultural disaster relief becomes paramount. This multifaceted approach involves various stakeholders and strategies:
Key Components of Agricultural Disaster Relief:
- Immediate Emergency Response: Coordinated efforts by local, state, and federal agencies to contain fires and protect lives and property.
- Post-Fire Assessment: Utilizing remote sensing technology to quickly evaluate the extent of damage to agricultural lands.
- Financial Assistance: Government programs and insurance payouts to help farmers and ranchers recover losses.
- Soil and Land Rehabilitation: Implementing strategies to restore burnt lands and prevent erosion.
- Livestock Management: Providing resources for relocating and caring for affected livestock.
- Long-term Recovery Planning: Developing strategies to rebuild more resilient agricultural operations.
Farmonaut’s technology aids in these efforts by providing accurate, timely data for damage assessment and recovery planning.
The Role of Local and Federal Agencies in Combating Wildfires
Addressing the Texas wildfire crisis requires a coordinated effort between various agencies at local, state, and federal levels. Understanding their roles and how they interact is crucial for effective wildfire management.
Key Agencies and Their Responsibilities:
- Texas A&M Forest Service: The primary state agency responsible for wildfire prevention, detection, and suppression in Texas.
- Local Fire Departments: Often the first responders to wildfires, providing crucial initial containment efforts.
- U.S. Forest Service: Manages wildfires on federal lands and provides additional resources for large-scale fires.
- Bureau of Land Management: Responsible for fire management on public lands under its jurisdiction.
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA): Provides support and resources during major wildfire disasters.
These agencies work together to implement comprehensive wildfire containment strategies, coordinate resource allocation, and manage large-scale firefighting efforts.
Comparative Analysis of Wildfire Prevention Strategies
To better understand the various approaches to wildfire prevention and management, let’s examine a comparative analysis of different strategies:
| Prevention Strategy | Effectiveness Rating (1-5) | Estimated Cost | Environmental Impact | Implementation Difficulty | Suitability for Different Agricultural Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Sensing (e.g., Farmonaut) | 5 | Medium | Positive | Moderate | All types (Ranching, Crop Farming, etc.) |
| Fire-Resistant Crops | 4 | Medium | Positive | Moderate | Crop Farming |
| Controlled Burns | 4 | Low | Neutral | Challenging | Ranching, Forestry |
| Firebreaks | 3 | Medium | Neutral | Easy | All types |
| Advanced Irrigation Systems | 4 | High | Positive | Moderate | Crop Farming |
This comparison highlights the effectiveness of remote sensing technologies, like those offered by Farmonaut, in providing comprehensive fire risk management across various agricultural settings.
Harnessing Farmonaut’s Technology for Wildfire Prevention
Farmonaut’s advanced satellite-based farm management solutions offer powerful tools for wildfire prevention and sustainable agriculture in fire-prone areas. Here’s how our technology can be leveraged:
1. Real-Time Crop Health Monitoring
Our platform provides up-to-date information on crop health through vegetation indices like NDVI. This data is crucial for:
- Identifying areas of dry or stressed vegetation that pose higher fire risks
- Planning targeted irrigation to maintain optimal moisture levels
- Implementing strategic vegetation management to reduce fire fuel
2. AI-Powered Advisory System
Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI advisory system offers personalized recommendations for fire risk management, including:
- Customized fire prevention strategies based on local conditions
- Early warnings for potential fire hazards
- Guidance on creating effective firebreaks and defensible spaces
3. Weather Data Integration
Our platform incorporates detailed weather forecasts, crucial for fire risk assessment:
- Predicting high-risk fire weather conditions
- Planning agricultural activities to minimize fire risks during dangerous periods
- Optimizing resource allocation for fire prevention efforts
To access these powerful tools, visit our web application or explore our API capabilities at Farmonaut API.
Building a Fire-Resilient Future for Texas Agriculture
As we face the ongoing challenges of the Texas wildfire crisis, it’s clear that innovative solutions and collaborative efforts are key to protecting our agricultural lands and communities. By embracing advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s remote sensing solutions, implementing sustainable farming practices, and fostering cooperation between various stakeholders, we can build a more fire-resilient future for Texas agriculture.
Key Strategies for Long-Term Resilience:
- Continuous Monitoring and Early Detection: Utilizing remote sensing technology for ongoing assessment of fire risks.
- Adaptive Land Management: Implementing flexible strategies that respond to changing climate and fire patterns.
- Community Education and Preparedness: Empowering local communities with knowledge and resources for fire prevention and response.
- Investment in Research and Technology: Supporting the development of new tools and techniques for fire management in agriculture.
- Policy Advocacy: Working with policymakers to develop supportive regulations and funding for fire prevention initiatives.
By taking a proactive and technology-driven approach to wildfire prevention and management, we can help ensure the long-term sustainability and resilience of Texas’s vital agricultural sector.
Conclusion: Embracing Innovation for a Fire-Resilient Future
The Texas wildfire crisis presents significant challenges to the state’s agricultural sector, but it also offers opportunities for innovation and adaptation. By leveraging advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s remote sensing solutions, implementing comprehensive fire risk management strategies, and fostering collaboration between various stakeholders, we can build a more resilient and sustainable agricultural future for Texas.
As we move forward, it’s crucial to remember that wildfire prevention and management are ongoing processes that require constant vigilance, adaptability, and innovation. By staying informed, embracing new technologies, and working together, we can protect our farms, ranches, and communities from the devastating impacts of wildfires.
To learn more about how Farmonaut’s solutions can help you manage fire risks and enhance your agricultural operations, visit our web application or explore our comprehensive API documentation.
FAQs
- How can remote sensing help in wildfire prevention?
Remote sensing technologies, like those offered by Farmonaut, can detect potential fire hotspots, monitor vegetation health, and assess soil moisture levels. This information helps in early fire detection and risk assessment, enabling proactive prevention measures. - What are some fire-resistant crops suitable for Texas?
While no crop is entirely fire-resistant, some options that are more fire-tolerant include certain varieties of alfalfa, sorghum, and some native grasses. It’s best to consult with local agricultural extension offices for specific recommendations. - How does climate change affect wildfire patterns in Texas?
Climate change is leading to higher temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extended dry seasons in Texas. These factors contribute to increased fire risk by creating drier vegetation and longer fire seasons. - What resources are available for farmers affected by wildfires?
Farmers affected by wildfires can access various resources, including USDA disaster assistance programs, state-level agricultural disaster relief funds, and emergency loans. Local extension offices and the Texas A&M Forest Service can provide guidance on available resources. - How can I integrate Farmonaut’s technology into my farm’s fire prevention strategy?
You can start by signing up for Farmonaut’s web or mobile application. Our platform provides real-time data on crop health, soil moisture, and weather conditions, which can be used to assess fire risks and plan prevention strategies. For more advanced integration, consider exploring our API options.