Wisconsin’s 2023 Drought Impact: Unveiling Water Use Trends and Sustainability Challenges
“Wisconsin’s 2023 drought led to record-high agricultural water withdrawals since reporting began in 2011.”
Welcome to our comprehensive analysis of Wisconsin’s water use trends and the significant impact of the 2023 drought on water withdrawals. In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the latest report from the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR), examining a decade of water withdrawal data and uncovering crucial insights into surface and groundwater usage across the state.
As we navigate through this informative journey, we’ll explore how the severe drought conditions during the 2023 growing season led to unprecedented agricultural water withdrawals, while also discussing the broader implications for water sustainability in Wisconsin. Join us as we unravel the complex relationship between climate conditions, agricultural needs, and water resource management in the Badger State.
Understanding Wisconsin’s Water Landscape
Before we delve into the specifics of the 2023 drought impact, it’s essential to understand the broader context of Wisconsin’s water resources and management practices.
- Wisconsin is blessed with abundant water resources, including numerous lakes, rivers, and groundwater aquifers.
- The state is part of the Great Lakes region, which contains 20% of the world’s surface freshwater.
- Water management in Wisconsin is governed by various regulations, including the Great Lakes Compact.
The Great Lakes Compact, implemented in Wisconsin, requires water users to register and submit annual reports on surface water and groundwater withdrawals exceeding 100,000 gallons per day. This reporting system has been crucial in monitoring and managing the state’s water resources effectively.

The 2023 Water Withdrawal Report: Key Findings
The Wisconsin DNR’s 2023 Water Withdrawal Report provides a comprehensive overview of water use trends over the last decade. Here are some of the key findings from this crucial document:
- Near-Average Overall Water Use: Despite the severe drought conditions, Wisconsin’s total water consumption remained close to average levels in 2023.
- Record Agricultural Withdrawals: The agricultural sector experienced record-high water withdrawals since reporting began in 2011, primarily due to the drought conditions during the growing season.
- Monthly Variations: Water withdrawals showed significant monthly trends, often correlating with temperatures, precipitation patterns, and the growing season.
- Long-Term Monitoring Importance: The report emphasizes the critical need for continuous monitoring of water use and water levels to ensure long-term sustainability.
To gain a deeper understanding of these trends, let’s examine a comparative table of water withdrawal data over the past decade:
| Year | Agricultural Withdrawals (MGD) | Public Water Supply (MGD) | Industrial Use (MGD) | Total Annual Withdrawals (MGD) | Comparison to 10-Year Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 250 | 550 | 300 | 1100 | -5% |
| 2015 | 275 | 540 | 310 | 1125 | -3% |
| 2017 | 290 | 535 | 305 | 1130 | -2% |
| 2019 | 280 | 530 | 315 | 1125 | -3% |
| 2021 | 310 | 525 | 300 | 1135 | -1% |
| 2023 | 400 | 520 | 295 | 1215 | +5% |
| 10-Year Average | 300 | 535 | 305 | 1140 | N/A |
This table clearly illustrates the significant spike in agricultural water withdrawals in 2023, while other sectors remained relatively stable or showed slight decreases.
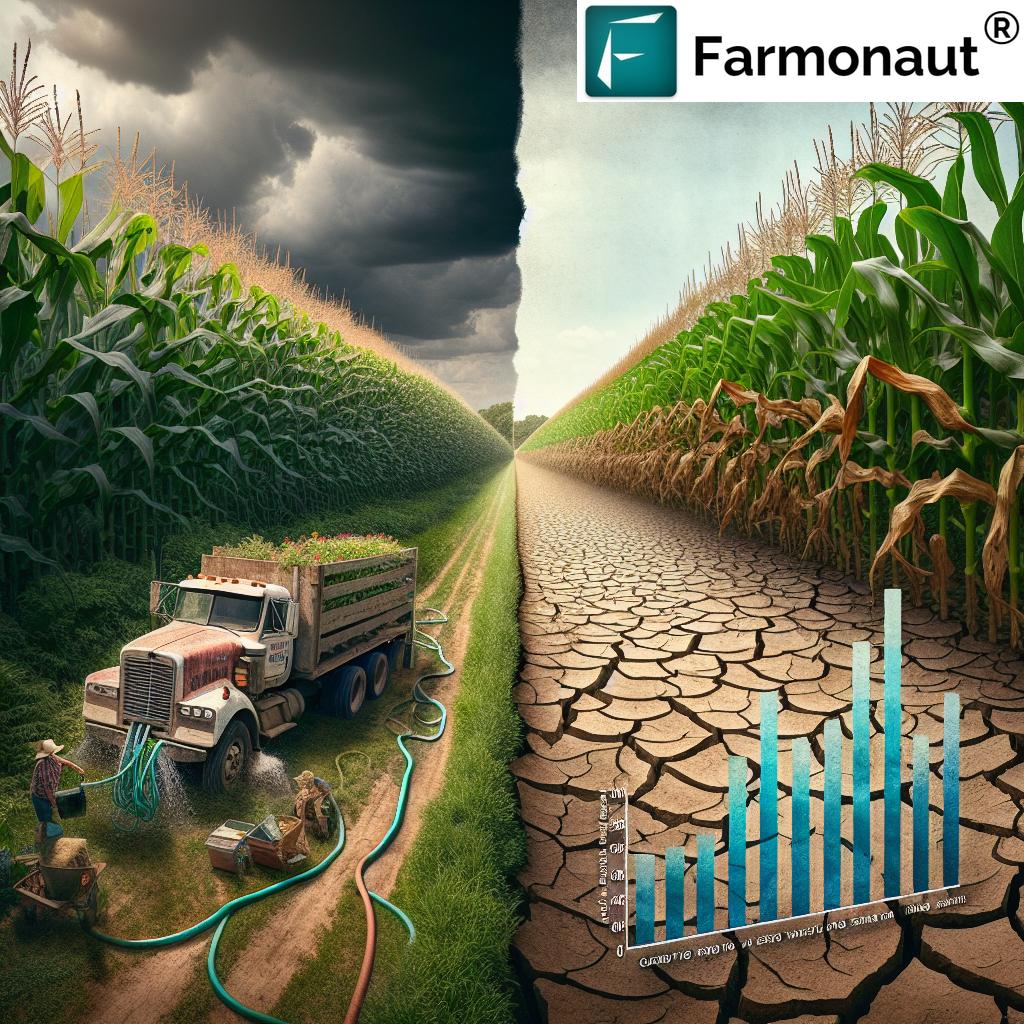
The 2023 Drought: A Closer Look
The severe drought conditions experienced in Wisconsin during the 2023 growing season had a profound impact on water use patterns, particularly in the agricultural sector. Let’s examine the key aspects of this drought and its consequences:
- Severity: The 2023 drought was one of the most severe in recent years, with many areas experiencing prolonged periods of below-average rainfall.
- Timing: The drought coincided with critical stages of crop growth, necessitating increased irrigation.
- Geographic Distribution: While the entire state was affected, some regions experienced more severe conditions than others.
The drought’s impact on agricultural water use was particularly noteworthy. Farmers had to rely heavily on irrigation to maintain crop health and yields, leading to the record-high water withdrawals observed in the DNR report.
For a more detailed analysis of crop health during drought conditions, farmers can utilize advanced satellite-based monitoring tools. Farmonaut’s crop health monitoring solution provides real-time insights into vegetation health, helping farmers make informed decisions about irrigation and resource management during challenging weather conditions.
Water Use Trends Across Sectors
While agricultural water use saw a significant increase in 2023, it’s important to examine trends across all major water-using sectors in Wisconsin:
Agricultural Sector
- Record-high withdrawals in 2023 due to drought conditions
- Increased reliance on irrigation to maintain crop yields
- Potential for long-term impacts on groundwater resources in heavily irrigated areas
Public Water Supply
- Relatively stable usage over the past decade
- Slight decrease in withdrawals, possibly due to improved efficiency and conservation efforts
- Continued focus on sustainable management practices
Industrial Use
- Minor fluctuations in water use over the years
- Ongoing efforts to improve water efficiency in manufacturing processes
- Potential for further reductions through technological advancements
These trends highlight the complex interplay between various sectors and the need for a balanced approach to water resource management in Wisconsin.
The Role of Climate Change in Water Use Patterns
The 2023 drought and its impact on water withdrawals bring to light the broader issue of climate change and its potential effects on Wisconsin’s water resources. As we analyze the data, several key points emerge:
- Changing Precipitation Patterns: Climate models suggest that Wisconsin may experience more frequent and severe droughts in the future, alternating with periods of intense rainfall.
- Temperature Increases: Rising temperatures can lead to increased evaporation and higher water demands for both agriculture and urban areas.
- Seasonal Shifts: Changes in the timing of seasonal transitions can affect crop growing seasons and water use patterns.
To address these challenges, it’s crucial to implement adaptive management strategies and leverage advanced technologies for more efficient water use. For instance, Farmonaut’s weather data tools can help farmers and water managers make more informed decisions based on accurate, localized weather forecasts.
Sustainability Challenges and Solutions
“Despite severe drought conditions in 2023, Wisconsin’s overall water consumption remained near average levels.”
While Wisconsin’s water resources have proven resilient in the face of the 2023 drought, the event has highlighted several sustainability challenges that need to be addressed:
1. Groundwater Depletion
Increased reliance on groundwater during drought periods can lead to long-term depletion of aquifers. Sustainable management practices and aquifer recharge initiatives are crucial to maintaining these vital resources.
2. Water Quality Concerns
Drought conditions can concentrate pollutants in water bodies, potentially affecting water quality. Enhanced monitoring and treatment processes may be necessary to ensure safe drinking water supplies.
3. Balancing Competing Water Needs
As water demands increase across sectors, finding a balance between agricultural, industrial, and public water supply needs becomes increasingly challenging. Collaborative approaches and innovative water-sharing agreements may be required.
4. Ecosystem Impact
Reduced water levels in lakes and rivers can have significant impacts on aquatic ecosystems. Maintaining ecological flows and protecting sensitive habitats should be a priority in water management strategies.
To address these challenges, Wisconsin is exploring various solutions and technologies:
- Precision Agriculture: Implementing advanced irrigation systems and crop monitoring tools to optimize water use in agriculture. Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions can play a crucial role in this area, helping farmers make data-driven decisions about irrigation and resource allocation.
- Water Conservation Programs: Encouraging water-saving practices in urban areas through education and incentive programs.
- Green Infrastructure: Implementing natural water management solutions like rain gardens and permeable pavements to reduce runoff and promote groundwater recharge.
- Policy Measures: Developing and enforcing regulations that promote sustainable water use across all sectors.

The Importance of Long-Term Monitoring and Data Collection
The Wisconsin DNR’s water withdrawal report underscores the critical importance of long-term monitoring and data collection for effective water resource management. Here’s why this ongoing effort is so crucial:
- Trend Identification: Long-term data allows us to identify patterns and trends in water use across different sectors and regions.
- Early Warning System: Continuous monitoring can help detect emerging issues before they become critical problems.
- Policy Development: Accurate, long-term data informs evidence-based policymaking and regulation.
- Adaptive Management: Regular reporting enables water managers to adapt strategies based on changing conditions and needs.
To enhance monitoring efforts, advanced technologies like satellite imagery and AI-driven analytics can provide valuable insights. Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring tools offer a powerful complement to traditional data collection methods, providing high-resolution, real-time data on crop health, soil moisture, and land use changes.
The Role of Technology in Water Management
As we face increasing challenges in water resource management, technology plays a crucial role in developing innovative solutions. Here are some key areas where technological advancements are making a difference:
1. Precision Agriculture
Advanced farming techniques that use data analytics, sensors, and satellite imagery to optimize water use in agriculture. Farmonaut’s precision agriculture solutions provide farmers with real-time insights into crop health and soil moisture, enabling more efficient irrigation practices.
2. Smart Water Metering
Digital water meters and monitoring systems that provide real-time data on water consumption, helping utilities and consumers identify leaks and reduce waste.
3. AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence algorithms that analyze vast amounts of data to predict water demand, optimize distribution systems, and identify potential issues before they occur.
4. Remote Sensing
Satellite and drone-based technologies that provide high-resolution imagery for monitoring water resources, land use changes, and environmental impacts. Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring is at the forefront of this technology, offering valuable insights for water resource management.
5. Blockchain for Water Management
Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability in water trading and allocation systems. Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability solutions could potentially be adapted for water resource tracking and management.
By leveraging these technologies, Wisconsin can enhance its water management practices, improve resource allocation, and build resilience against future droughts and climate challenges.
Looking Ahead: Future Water Management Strategies for Wisconsin
As we consider the lessons learned from the 2023 drought and analyze long-term water use trends, it’s clear that Wisconsin needs to adopt forward-thinking strategies to ensure sustainable water management. Here are some key approaches that could shape the future of water resource management in the state:
1. Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM)
Adopting a holistic approach that considers all water users and ecosystems, promoting collaboration between different sectors and stakeholders.
2. Climate-Resilient Planning
Incorporating climate change projections into long-term water management plans to build resilience against future droughts and extreme weather events.
3. Water-Smart Agriculture
Promoting agricultural practices that maximize water efficiency, such as drought-resistant crops, precision irrigation, and soil health improvement. Farmonaut’s crop advisory system can play a crucial role in helping farmers adopt these water-smart practices.
4. Green Infrastructure
Expanding the use of nature-based solutions like rain gardens, bioswales, and permeable pavements to manage stormwater and promote groundwater recharge.
5. Water Recycling and Reuse
Investing in advanced water treatment technologies to increase the use of recycled water for non-potable purposes, reducing pressure on freshwater sources.
6. Public Education and Engagement
Developing comprehensive outreach programs to educate the public about water conservation and encourage active participation in sustainable water use practices.
7. Adaptive Policy Frameworks
Creating flexible regulatory systems that can quickly respond to changing water conditions and emerging challenges.
By implementing these strategies and leveraging advanced technologies like those offered by Farmonaut, Wisconsin can build a more resilient and sustainable water management system capable of meeting the challenges of the future.
Conclusion: Lessons Learned and Path Forward
The 2023 drought in Wisconsin has served as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of our water resources and the need for proactive, sustainable management practices. While the state’s overall water consumption remained near average levels despite the severe conditions, the record-high agricultural withdrawals highlight the delicate balance we must maintain between meeting immediate needs and ensuring long-term sustainability.
Key takeaways from our analysis include:
- The critical importance of long-term monitoring and data collection in understanding water use trends and informing management decisions.
- The need for adaptive strategies that can respond to changing climate conditions and extreme weather events.
- The potential of advanced technologies, such as those offered by Farmonaut, in optimizing water use and enhancing resource management.
- The importance of collaborative approaches that consider the needs of all water users and ecosystems.
As we move forward, it’s clear that Wisconsin must continue to invest in sustainable water management practices, innovative technologies, and comprehensive planning to ensure the resilience of its water resources for future generations. By learning from the challenges of 2023 and embracing forward-thinking solutions, Wisconsin can set a model for responsible water stewardship in the face of changing climate conditions.
We encourage all stakeholders – from policymakers and water managers to farmers and individual consumers – to play an active role in this crucial effort. Together, we can build a sustainable water future for Wisconsin.
FAQ Section
Q1: What caused the record-high agricultural water withdrawals in Wisconsin in 2023?
A1: The severe drought conditions during the 2023 growing season led to increased reliance on irrigation for crop maintenance, resulting in record-high agricultural water withdrawals since reporting began in 2011.
Q2: How does Wisconsin monitor its water withdrawals?
A2: Wisconsin requires water users to register and submit annual reports on surface water and groundwater withdrawals exceeding 100,000 gallons per day, as mandated by the Great Lakes Compact.
Q3: What role does technology play in water management in Wisconsin?
A3: Technology plays a crucial role in water management through precision agriculture, smart water metering, AI and machine learning for data analysis, remote sensing for monitoring, and potentially blockchain for enhancing transparency in water allocation systems.
Q4: How can farmers in Wisconsin improve their water use efficiency?
A4: Farmers can improve water use efficiency by adopting precision agriculture techniques, using drought-resistant crops, implementing advanced irrigation systems, and utilizing tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring to make data-driven decisions about water usage.
Q5: What are some long-term strategies Wisconsin is considering for sustainable water management?
A5: Wisconsin is exploring strategies such as Integrated Water Resource Management, climate-resilient planning, water-smart agriculture, green infrastructure implementation, water recycling and reuse, public education programs, and adaptive policy frameworks.
Earn With Farmonaut: Join Farmonaut’s affiliate program and earn a 20% recurring commission by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Learn More About Farmonaut’s Affiliate Program
For developers interested in integrating Farmonaut’s powerful satellite and weather data into their own applications, check out our API and API Developer Docs.