California Wildfires Economic Impact: 7 Major Ag Losses
California’s wildfires have become one of the most devastating threats to the state’s agriculture, farming, and forestry, casting a long shadow over the entire economy. In this comprehensive blog, we explore the multifaceted economic impact of wildfires in California, specifically focusing on seven major agricultural losses—from crop and livestock destruction to infrastructure damage and environmental services. As wildfires grow more intense and frequent, understanding these challenges is vital for policymakers, producers, and communities. Read on for data-driven insights, recovery strategies, and the role of advanced technology in building resilience for the future.
“California wildfires caused over $3.5 billion in agricultural losses between 2018 and 2021 alone.”
Introduction: Rising Wildfire Risks in California
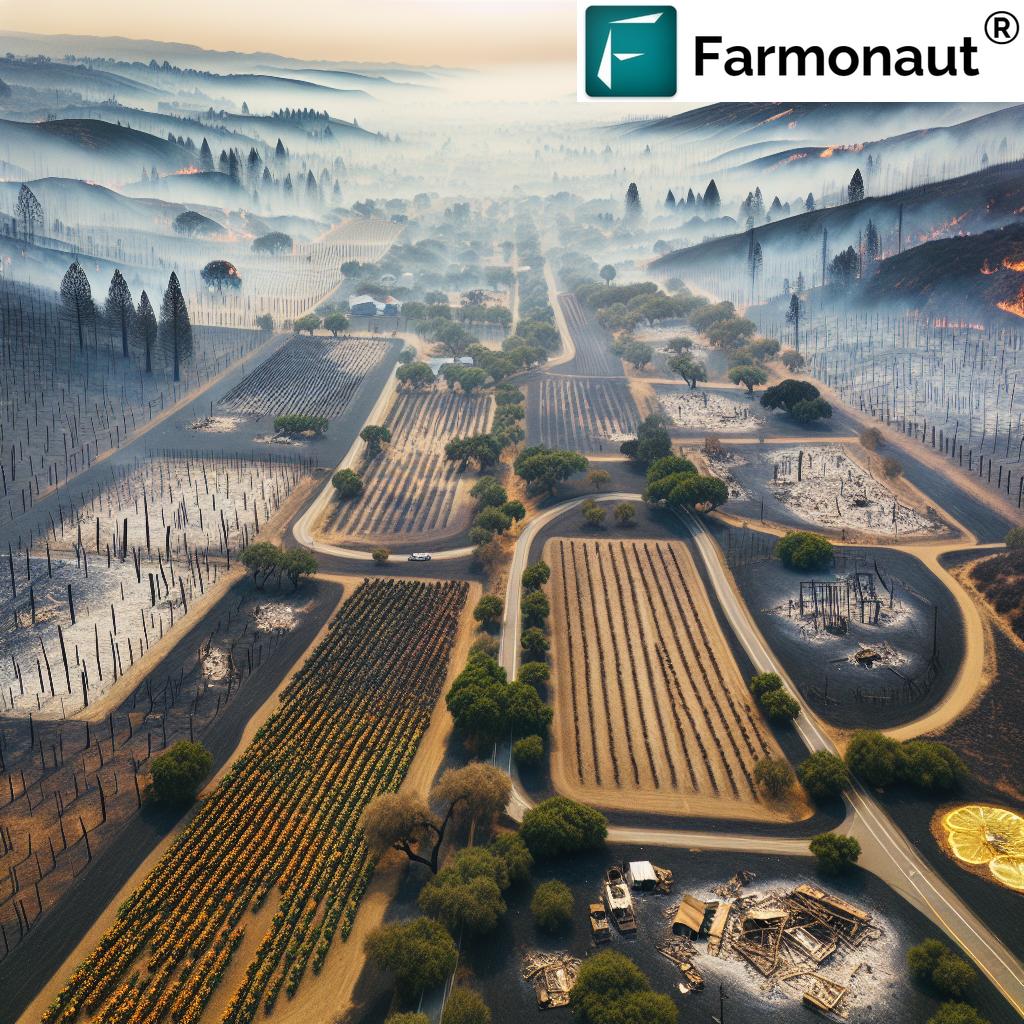
California, the United States’ agricultural powerhouse, consistently leads in national and global crop production. However, our state now faces a new, unrelenting adversary: wildfires. Fueled by extended droughts, rising temperatures, and a growing wildland-urban interface, wildfires have reached unprecedented frequency and ferocity. In only a few years, millions of acres of precious farmland, forests, and grazing lands have been consumed by flames, placing the entire agricultural sector at risk.
The california wildfires impact on agriculture has not been contained to charred fields and burned forests. The repercussions ripple throughout California’s economy—shaking supply chains, reducing exports, destabilizing rural livelihoods, and impairing ecosystem services. As we face another wildfire season, it’s crucial to take stock of damage, response, funding, recovery efforts, and innovative resilience strategies. Let’s break down the financial and environmental toll of these disasters across seven major agricultural categories.
“More than 1.2 million acres of California farmland were affected by wildfires in the past five years.”
Summary Table of Major Agricultural Losses by Sector
| Sector | Estimated Economic Loss (USD millions) |
% Share of Total Loss |
Notable Impact | Recovery Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vineyards (Napa, Sonoma counties, grapevines, winemaking) | $3,700 | 27% | Smoke taint to grapes, destruction of wineries, reduced wine quality and quantity | 2–4 years |
| Orchards (lemons, citrus, nuts) | $800 | 6% | Burned trees, yield loss, export disruptions | 5–10 years (tree replacement) |
| Dairy | $490 | 4% | Evacuations, heat/smoke stress on animals, destruction of facilities | 1–2 years |
| Vegetables/Row Crops | $210 | 2% | Crop yield losses due to fire, supply shortfalls | 1 year |
| Forestry & Timber Industry | $5,400 | 39% | Forest destruction, loss of timber value, job losses | 10+ years |
| Livestock (cattle, sheep, pasture) | $725 | 5% | Animal deaths, feed shortage, pasture destruction | 2–3 years |
| Agricultural Infrastructure (barns, fences, machinery, irrigation) | $2,100 | 15% | Destruction of property, irrigation, loss of tools/equipment | 1–3 years |
Note: Estimates based on data from wildfire years 2018–2022; values are approximations for demonstration purposes only. Sectors and losses highlight the widespread economic impact of wildfires in California.
Economic Impact of Wildfires in California: Agriculture & Farming
As the backbone of our state’s prosperity, California’s agriculture sector encompasses over 400 commodities and generates more than $50 billion annually. However, the threat of recurring wildfires jeopardizes both the productivity and resilience of our farming communities. Let’s examine how these ferocious fires disrupt the production, supply chains, trade, and economic stability of California agriculture:
- Direct Crop Damage and Destruction: Wildfires burning through fields and orchards cause immediate and total crop loss. Not only does this mean millions in lost revenue for the season, but the land may remain unproductive for years if soils are scorched or tree crops destroyed.
- Livestock Losses and Feed Shortages: Cattle, sheep, goats, and other animals suffer injury, death, or displacement. Feed supplies are also lost as pastures and storage facilities burn, causing cascading costs for farm operations.
- Disrupted Infrastructure and Supply Chains: The destruction of barns, processing plants, irrigation lines, and rural roads cuts farmers off from markets, extends recovery timelines, and causes supply shortfalls across the U.S. and export destinations.
- Reduced Exports and Trade Challenges: International trade partners—including Canada, Japan, and South Korea—depend on California crops like almonds, lemons, and grapes. Interruptions due to wildfire losses reverberate through global markets and pricing.
- Increasing Insurance and Operating Costs: Farmers face higher premiums or may find insurance unavailable in fire-prone areas, making recovery more financially challenging. Learn about advanced crop insurance solutions via Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop loan and insurance.
Wildfire Damage to Crops: Impacts on Key California Sectors
The wildfire damage to crops can be sudden and extensive. High-value sectors like wine grapes, citrus orchards, and specialty row crops have borne the brunt of recent mega-fires. Notably, smoke taint is a growing concern, where crops not directly burned are rendered unsellable by pervasive smoke.
1. California Wine Industry Wildfire Losses
-
The 2018 Camp Fire and subsequent fire events torched much of Northern California’s wine country, leading to:
- Destruction of more than 18,800 buildings and significant loss in Napa and Sonoma wineries
- Estimated $3.7 billion in wine sector losses (nextideamatters.com)
- Widespread smoke taint—grapevines absorb smoke, imparting undesirable flavors to wine, resulting in unmarketable vintages
- Market data confirm that these california wildfires impact on agriculture downstream—disrupting exports, reducing supply for domestic consumers, and raising prices.
2. Lemon Orchards and Citrus Export Disruptions
- California is the largest U.S. producer of lemons, supplying over half of the nation’s crop.
- Fires in key lemon-growing regions scorched farmlands, destroyed orchards, and led to a 10–20% annual loss in production for affected years.
- This disruption impacted both domestic consumers and high-value markets in Canada, Japan, and South Korea, causing price volatility and straining farmer finances.
3. Row Crops, Tree Nuts, and Specialties
- Export-oriented crops like almonds, pistachios, and leafy greens saw reduced yield and slow market recovery—delivering both direct financial losses and global supply chain headaches.
- Many vegetable fields near fire zones experienced crop contamination or spoilage, often causing the wildfires and supply chain disruption that ripples across the national food system.
Loss and Displacement of Livestock
Wildfires not only ravage crops but profoundly affect livestock and animal production across California:
- Direct Loss of Cattle, Sheep, and Poultry: Many ranchers in the path of fires are forced to evacuate or lose their herds to flames and smoke inhalation, compounding emotional and financial stress for producers.
- Pasture Destruction: Fire incinerates grazing land, forcing farmers to purchase expensive feedstuffs or reduce herd sizes. The loss of pasture may require seasons to recover.
- Diminished Production and Market Supply: Loss of livestock means less meat, milk, and other products, raising prices and destabilizing the entire supply chain.
- Stranded and Stressed Animals: Even herds that survive must be relocated, leading to health problems, lower weight gain, and reduced breeding success.
For immediate support, disaster assistance for farmers is available, such as programs by the USDA, which help with emergency feed, water hauling, and low-interest recovery loans.
Infrastructure and Supply Chains Disrupted by Fire
The destruction of property, barns, fences, and water systems undermines the operational backbone of farming and forestry enterprises. In the 2018 Camp Fire alone, over 18,800 buildings were flattened, including rural homes, processing facilities, greenhouses, and warehouses.
- Road Closures, Transportation Hurdles: Blocked or destroyed rural roads and highways isolate farming regions, delaying harvests and preventing products from reaching local and export markets.
- Machinery and Irrigation System Losses: Tractors, harvesters, and drip irrigation lines are highly vulnerable to fire, increasing replacement costs and prolonging downtime.
- Supply Chain Disruption: With critical infrastructure erased, agricultural goods cannot move efficiently, pushing up costs for both producers and consumers.
Smart fleet tracking and management solutions, such as those provided in Farmonaut’s fleet management tools, offer a way for agribusinesses to optimize logistics and reduce operational losses during such emergencies.
Forest Destruction and Timber Industry Collapse
Wildfires are catastrophic for both California’s public and privately-owned forests. The timber industry and associated sectors face some of the longest-lasting damage:
- Massive Forested Area Loss: The 2018 fire season and several subsequent events have decimated hundreds of thousands of acres of forested timber, much of it irreplaceable in a human lifetime.
- Lost Timber and Logging Revenue: Downed and ruined trees cut deeply into the timber industry’s revenues and employment, with full economic recovery projected to take a decade or longer.
- Costly Firefighting and Recovery Operations: Defensive firefighting, cleanup, and restoration place additional financial burdens on the state and local forestry management agencies.
For forestry stakeholders, rapid recovery, monitoring, and resiliency planning is essential. Explore how smart technology and AI-driven large-scale farm and forest management platforms can assist in post-fire analysis and reforestation strategies.
Environmental Impact of California Wildfires
Beyond direct monetary losses, wildfires profoundly damage our ecosystem services and shift the balance of natural resources management in California.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Wildfires are among the largest one-time sources of greenhouse gases in California, undermining the carbon sequestration efforts of our forests and agriculture. For farms and agribusinesses seeking to monitor and minimize their emissions, Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tool offers a real-time, affordable solution.
- Biodiversity Loss and Habitat Destruction: Many endangered species’ habitats are in fire-prone regions. The loss of vegetation and soil erosion further destabilizes entire ecosystems.
- Water Quality and Availability: Fire changes watershed hydrology, increasing sedimentation and runoff into rivers, canals, and reservoirs, and straining water supplies critical to both farming and natural systems.
- Long-Term Soil Health Decline: Nutrient cycles are disrupted and topsoil may be lost permanently, reducing future agricultural productivity.
A sustainable future requires continuous environmental monitoring and restoration. Advanced advisory and traceability platforms now make it possible to track carbon cycles, ecosystem recovery, and product origin—read more about product traceability for transparency.
State Response, Resilience Efforts, and Recovery Programs
Recognizing the growing economic, social, and environmental burden of wildfires, California has significantly increased its funding and institutional capacity to support wildfire resilience and recovery.
Wildfire Resilience Funding in California
-
From 2021, annual investments in wildfire and forest resilience have surged from $200 million to nearly $2.5 billion. These funds support:
- Forest stewardship and thinning to minimize fire risk
- Community education, evacuation planning, and fire-adapted infrastructure
- Restoration of burned watersheds, soils, and wildlife habitats
- Technology adoption for early-warning and post-fire analysis
To learn about state forest projects visit: California Forest Stewardship.
Federal Assistance Programs for California Producers
-
The USDA disaster assistance programs now operate on both a rapid-response and ongoing basis, offering:
- Direct compensation for lost production and infrastructure damage
- Low-interest loans for rebuilding and recovery
- Emergency feed, water hauling, and drought assistance
These funding streams and programs play a vital support role for producers as they rebuild and adapt to a changing climate.
For more resources, including data service integrations for risk mitigation, review our Farmonaut Satellite API and API Developer Documentation.
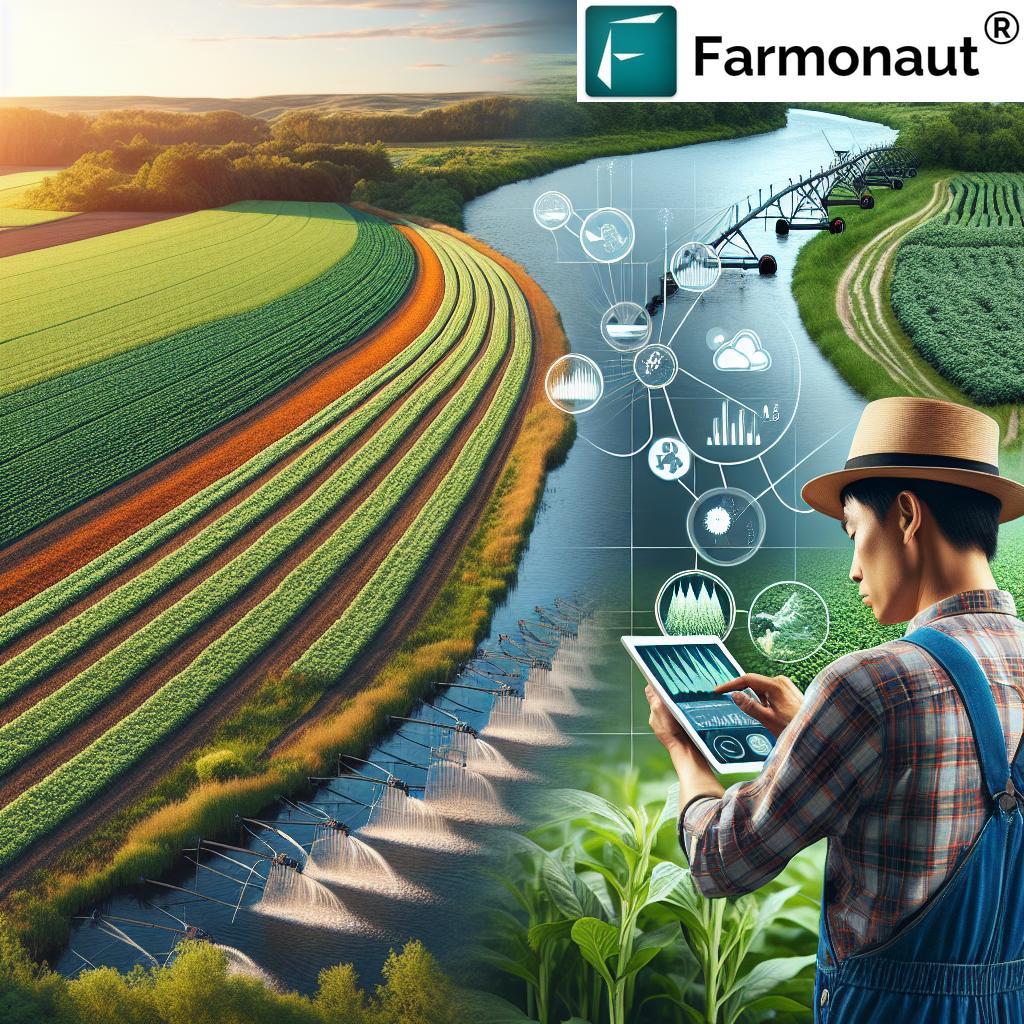
Technological Innovations: Building Wildfire Resilience in Agriculture
To build a fire-resilient future and expedite recovery after disaster, advanced satellite monitoring, AI-based advisory, and precision agriculture tools are game-changers for California farming and forestry.
- Real-Time Crop & Forest Monitoring: Satellite-based platforms make it possible to detect fire risk areas, monitor post-fire regrowth, and optimize water usage remotely.
- Predictive Analytics & Early Warning: Artificial intelligence leverages weather forecasts, fuel load data, and field records to generate timely alerts and customized guidance for growers.
- Blockchain Traceability & Recovery Recordkeeping: Transparent, immutable ledger systems help track inventory loss, facilitate insurance claims, and prove origin in disrupted supply chains.
Read about carbon monitoring for sustainability and how modern digital agriculture platforms enable informed response to disaster and climate risk.
How Farmonaut Empowers California’s Agricultural Resilience
As wildfires intensify, Farmonaut stands at the forefront of affordable agricultural technology, providing California farmers and forestry stakeholders with powerful, data-driven tools to fortify their operations—today and for the future.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Via real-time multispectral imagery, we empower farmers to track vegetation health, soil moisture, and fire impacts—enhancing both disaster risk reduction and recovery planning.
- Jeevn AI Personalized Farm Advisory: Our AI delivers up-to-the-minute weather alerts, crop management strategies, and tailored recommendations for both routine operations and emergency response.
- Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: Especially important after fire-related supply chain disruption, our blockchain systems guarantee transparent, secure, and fraud-resistant tracking—from farm to consumer to export markets.
- Fleet and Resource Management: By integrating logistics and equipment monitoring, we help agribusinesses optimize emergency response and reduce post-fire downtime.
- Carbon Footprinting: Our technology tracks emissions and carbon cycles, empowering growers to quantify and reduce their environmental impact—essential for compliance and sustainability.
Our flexible, scalable large-scale farm management platform serves everyone from individual farmers to enterprise agribusinesses and state agencies. Farmonaut’s subscription-based service brings precision agriculture, resource optimization, and disaster-prep within reach of all.
Whether accessed via web, Android, iOS, or developer API integration, Farmonaut enhances resilience for California agriculture and forestry sectors—making technology accessible, affordable, and actionable.
Conclusion: Charting a Sustainable Path Forward
The threat of wildfires to California’s agriculture, forestry, and economy is undeniable—and growing. The destruction of crops, forests, livestock, and infrastructure leaves behind financial, social, and environmental scars that may take years, even decades, to heal. But through a combination of state and federal support, robust resilience funding, innovative technology solutions, and transparent monitoring, we can collectively chart a more secure future for California’s vital industries.
- Proactive risk reduction—through firewise practices, improved stewardship, and community planning—remains the first line of defense.
- Rapid, precision monitoring and robust data infrastructure empower timely recovery, smart insurance, and traceable supply chains.
- Commitment to sustainability—through carbon tracking, ecosystem restoration, and smart water management—ensures long-term viability of California agriculture and forestry.
It is up to all of us to support smart funding, empower innovation, and build a truly resilient, thriving California agricultural landscape.
FAQs: California Wildfires & Agricultural Impact
-
Q: What are the main economic impacts of wildfires on California agriculture?
A: Wildfires cause massive losses in crops, livestock, infrastructure, and forestry, disrupt exports and supply chains, and raise costs for recovery and insurance. -
Q: How do wildfires affect the wine industry in Napa and Sonoma counties?
A: Fires destroy wineries, burn grapevines, and cause smoke taint, which makes grapes unsuitable for winemaking. This results in billions of dollars in losses. -
Q: Which federal and state assistance programs support affected farmers?
A: Programs by the USDA, along with increased state wildfire resilience funding, offer financial relief, emergency loans, and recovery guidance to producers. -
Q: What tools help farmers monitor farms during wildfire seasons?
A: Satellite-based monitoring (like Farmonaut), AI advisories, and resource management tools optimize water, fertilizer, and help in risk prediction and rapid response. -
Q: How do wildfires impact the environment?
A: They increase greenhouse gas emissions, disrupt carbon sequestration processes, threaten biodiversity, degrade water resources, and decrease soil health. -
Q: Can new technology reduce wildfire risks for California agriculture?
A: Yes, platforms like Farmonaut deliver real-time field insight, risk alerts, blockchain traceability, and sustainability metrics to help build fire resilience and improve recovery.