Organic and Chemical Thrips Control: Protecting Fruits and Vegetables from Western Flower Thrips Damage

In the world of agriculture, we often face challenges that can significantly impact crop yields and quality. One such persistent problem is the infestation of thrips, particularly the Western Flower Thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis). These tiny yet destructive insects pose a significant threat to a wide range of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the nature of thrips, their impact on various crops, and effective control methods, both organic and chemical.
Understanding Thrips: A Common Agricultural Pest
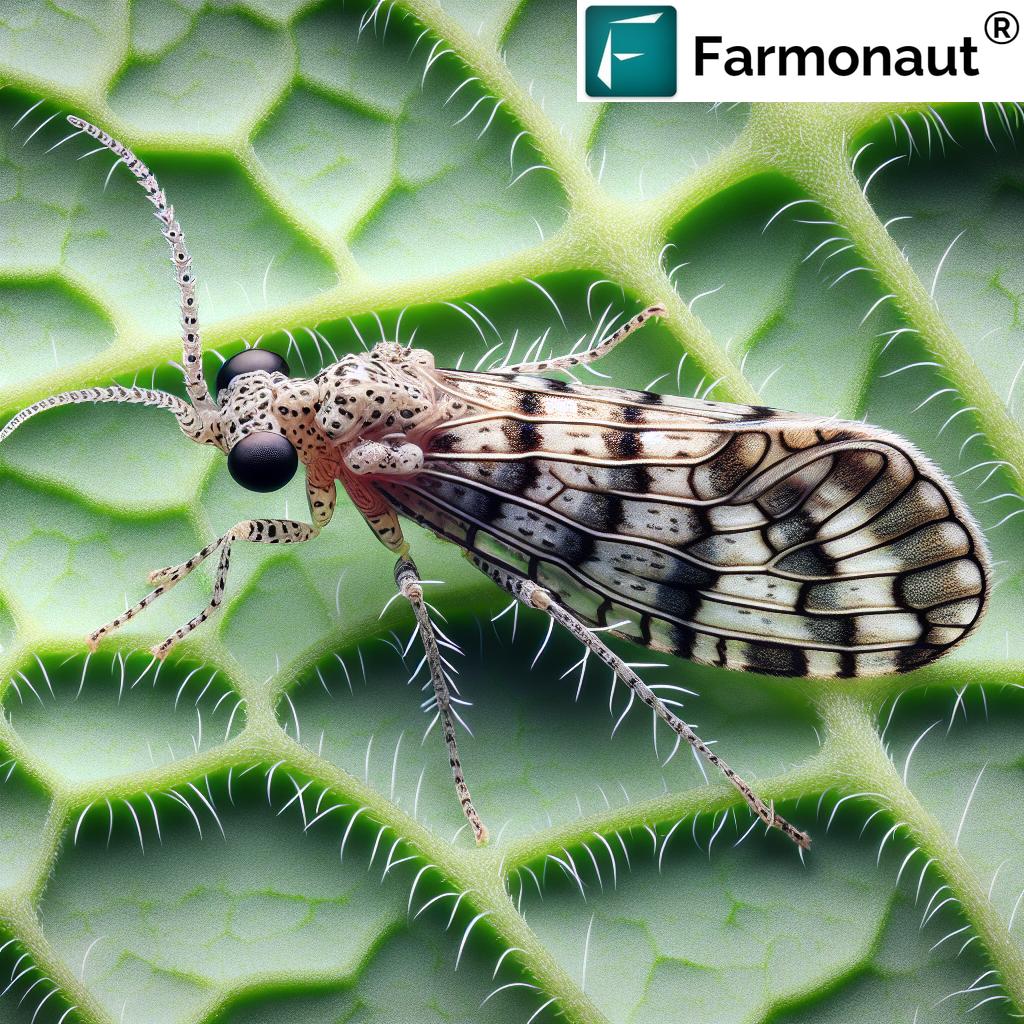
Thrips are small, slender insects that belong to the order Thysanoptera. While there are thousands of thrips species worldwide, the Western Flower Thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis) is one of the most problematic in agriculture. These pests are known for their ability to rapidly reproduce and spread, making them a significant concern for farmers and gardeners alike.
Characteristics of Western Flower Thrips
- Size: Typically 1-2 mm long
- Color: Varies from pale yellow to dark brown
- Wings: Fringed wings, capable of flight
- Reproduction: Rapid lifecycle, with multiple generations per year
- Feeding Habit: Piercing-sucking mouthparts that damage plant cells
The Impact of Thrips on Crops
Thrips can cause significant damage to a wide variety of plants, including many economically important crops. Their feeding activity not only directly harms plants but can also transmit viruses, leading to further complications.
Crops Commonly Affected by Thrips
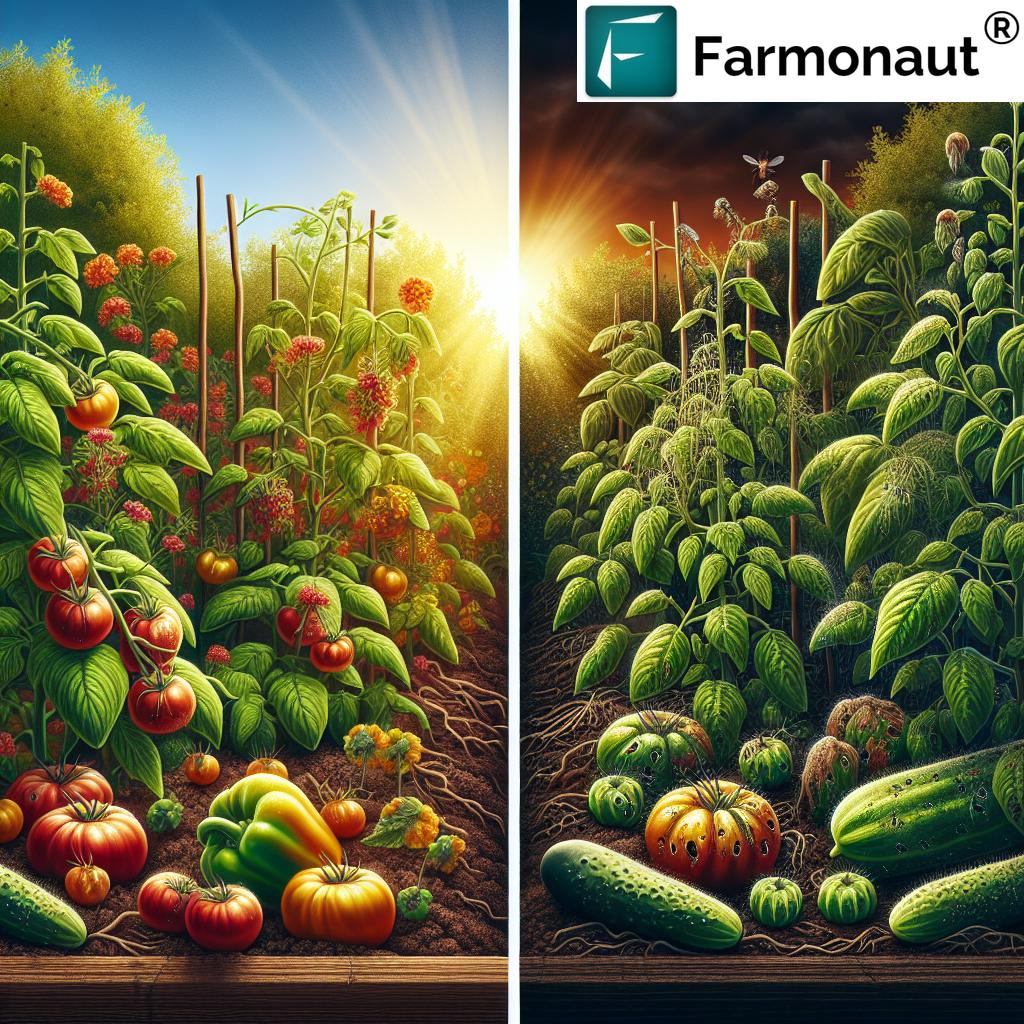
- Fruits: Grapes, strawberries, plums, nectarines, peaches, watermelons
- Vegetables: Tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, eggplants, melons, peas
- Other Crops: Cotton, peanuts, chrysanthemums, basil
Types of Damage Caused by Thrips
- Direct Feeding Damage: Thrips use their mouthparts to pierce plant cells and extract their contents. This feeding activity can lead to:
- Silvery or bronzed patches on leaves
- Distorted growth of leaves and flowers
- Scarring on fruits
- Virus Transmission: Thrips are known vectors for several plant viruses, including:
- Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus (TSWV)
- Impatiens Necrotic Spot Virus (INSV)
- Yield Reduction: Severe infestations can significantly reduce crop yields and quality.
Early Detection: The Key to Effective Thrips Control
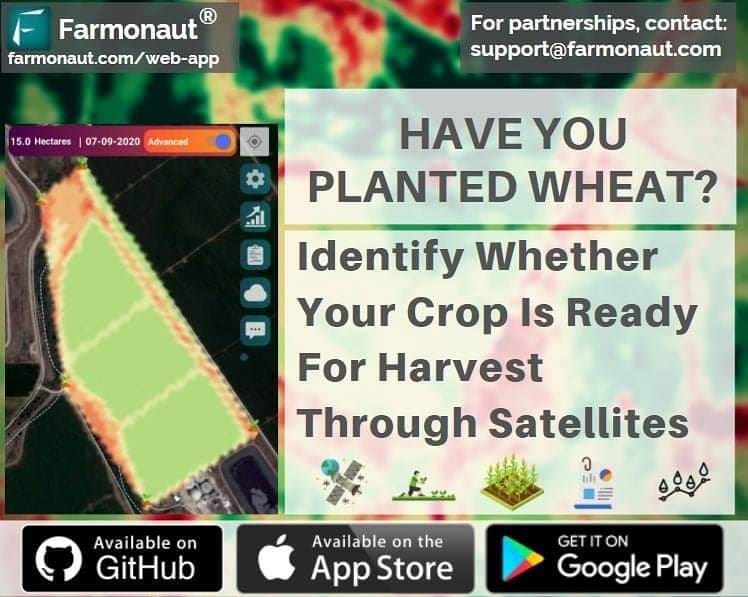
Identifying thrips infestations early is crucial for implementing timely and effective control measures. Traditional methods of detection often rely on visual inspection, which can be time-consuming and may miss early-stage infestations. At Farmonaut, we’re leveraging advanced satellite technology to revolutionize pest detection, including thrips.
| Detection Method | Accuracy | Speed | Coverage Area | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Moderate (depends on inspector’s expertise) | Slow (labor-intensive) | Limited (small areas at a time) | Low (high labor costs for large areas) |
| Farmonaut’s Satellite-Based System | High (detects subtle changes in plant health) | Fast (real-time monitoring) | Extensive (entire fields at once) | High (cost-effective for large areas) |
Our satellite-based early detection system at Farmonaut can identify thrips infestations earlier than traditional methods, allowing for timely interventions and reduced crop damage across large areas. By analyzing multispectral satellite imagery, we can detect subtle changes in plant health that may indicate thrips activity before visible symptoms appear.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Thrips Control
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach to thrips control. This strategy combines various methods to manage pest populations effectively while minimizing environmental impact and preserving beneficial insects.
Components of an Effective IPM Strategy for Thrips
- Monitoring: Regular inspection of plants and use of sticky traps to detect thrips presence.
- Cultural Controls: Implementing practices that make the environment less favorable for thrips.
- Biological Controls: Utilizing natural predators and parasites of thrips.
- Chemical Controls: Using insecticides when necessary, with a preference for less toxic options.
Organic Thrips Control Methods
For those seeking to manage thrips populations without synthetic chemicals, there are several effective organic control methods available:
1. Beneficial Insects
- Predatory Mites: Species like Amblyseius cucumeris and Neoseiulus californicus feed on thrips larvae.
- Minute Pirate Bugs: These tiny predators actively hunt and consume thrips.
- Lacewings: Both adults and larvae feed on thrips and other small insects.
2. Neem Oil
Neem oil is a natural insecticide derived from the neem tree. It disrupts the feeding and reproductive cycles of thrips and other pests.
3. Insecticidal Soaps
These soaps work by breaking down the protective outer layer of thrips, causing dehydration.
4. Diatomaceous Earth
This fine powder made from fossilized algae can be dusted on plants to deter thrips. It works by physically damaging the insects’ exoskeletons.
5. Companion Planting
Certain plants can repel thrips or attract their natural predators:
- Marigolds
- Chrysanthemums
- Alyssum (attracts minute pirate bugs)
Chemical Control Options for Thrips
While organic methods are preferable, severe infestations may require the use of chemical insecticides. It’s crucial to use these products responsibly and in accordance with local regulations.
Common Insecticides Used for Thrips Control
- Spinosad: A natural substance produced by soil bacteria, effective against thrips and other insects.
- Imidacloprid: A systemic insecticide that’s taken up by the plant and affects thrips when they feed.
- Abamectin: Derived from soil bacteria, it’s effective against thrips and mites.
- Pyrethrins: Natural insecticides derived from chrysanthemum flowers.
Note: Always follow label instructions and consider the potential impact on beneficial insects when using chemical controls.
Crop-Specific Thrips Management Strategies
Different crops may require tailored approaches to thrips management. Here, we’ll explore strategies for some commonly affected crops:
Tomatoes
Tomato plants are particularly susceptible to thrips damage and the viruses they transmit. Our strategies include:
- Regular monitoring using blue or yellow sticky traps
- Removing weeds that can harbor thrips
- Using reflective mulches to repel thrips
- Applying neem oil or insecticidal soaps at first sign of infestation
- Considering the use of systemic insecticides for severe cases
Peppers
Peppers, like tomatoes, are vulnerable to thrips and the viruses they carry. Our approach includes:
- Implementing a robust monitoring program
- Using thrips-resistant pepper varieties when available
- Applying beneficial nematodes to the soil to control pupating thrips
- Using fine mesh screens in greenhouses to prevent thrips entry
Grapes
Thrips can cause significant damage to grape vines and fruit. Our management strategies include:
- Monitoring with sticky traps and visual inspection of leaves and clusters
- Pruning and thinning to improve air circulation and reduce hiding spots for thrips
- Applying kaolin clay as a barrier treatment
- Using targeted insecticides during critical growth stages if necessary
Strawberries
Thrips can affect both strawberry foliage and fruits. Our control methods include:
- Using predatory mites as biological control agents
- Applying insecticidal soaps or neem oil to plants
- Removing old leaves and debris that can harbor thrips
- Considering the use of plastic mulch to deter thrips
Leveraging Technology for Advanced Thrips Management
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of integrating cutting-edge technology into pest management strategies. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system offers several advantages for thrips control:
- Early Detection: Our system can identify subtle changes in plant health that may indicate thrips infestation before visible symptoms appear.
- Large-Scale Monitoring: Satellite imagery allows for monitoring of vast agricultural areas efficiently.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: We provide detailed analytics to help farmers make informed decisions about when and where to implement control measures.
- Integration with Weather Data: Our system correlates pest activity with weather patterns, allowing for predictive management strategies.
To learn more about how our technology can revolutionize your pest management approach, visit our Farmonaut app or explore our API documentation.
Sustainable Practices for Long-Term Thrips Management
While immediate control measures are often necessary, implementing sustainable practices can help reduce thrips populations over time and create a more resilient agricultural ecosystem.
1. Crop Rotation
Rotating crops can disrupt the life cycle of thrips and reduce their populations. This practice is particularly effective for thrips species that specialize in certain plant types.
2. Intercropping
Planting different crops together can create a more diverse ecosystem that’s less favorable for thrips. It can also attract beneficial insects that prey on thrips.
3. Soil Health Management
Healthy soils promote strong plant growth, making plants more resistant to pest damage. Practices like composting and cover cropping can improve soil health.
4. Water Management
Proper irrigation practices can help plants withstand thrips infestations better. Avoid over-watering, which can create conditions favorable for thrips.
5. Plant Selection
When possible, choose plant varieties that are naturally resistant or tolerant to thrips. This can significantly reduce the need for interventions.
The Role of Weather in Thrips Management
Understanding the relationship between weather patterns and thrips activity is crucial for effective management. At Farmonaut, we integrate weather data into our pest management recommendations:
- Temperature: Thrips populations tend to increase rapidly in warm weather. Our system alerts farmers to potential population explosions based on temperature trends.
- Humidity: High humidity can favor thrips development. We monitor humidity levels and provide recommendations for adjusting management strategies accordingly.
- Rainfall: Heavy rains can naturally reduce thrips populations. Our system takes rainfall into account when suggesting control measures.
- Wind: Thrips can be carried by wind currents. We track wind patterns to predict potential infestations in new areas.
To access our detailed weather-based pest management insights, check out our Farmonaut Satellite Weather API.
Economic Impact of Thrips and the Value of Effective Management
The economic impact of thrips infestations can be substantial. By implementing effective management strategies, farmers can significantly reduce crop losses and improve overall profitability.
Potential Costs of Thrips Infestations
- Reduced crop yields
- Lower quality produce, resulting in reduced market value
- Increased labor costs for monitoring and treatment
- Expenses related to control measures (e.g., insecticides, beneficial insects)
- Potential loss of organic certification if chemical controls are used
Benefits of Effective Thrips Management
- Improved crop yields and quality
- Reduced need for costly interventions
- Preservation of beneficial insects and overall ecosystem health
- Potential for premium pricing for high-quality, pest-free produce
- Long-term sustainability of farming operations
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping farmers maximize their returns by providing cutting-edge tools for pest management. Our satellite-based monitoring system can significantly reduce the costs associated with thrips control while improving overall crop health and yield.
Future Trends in Thrips Management
As agricultural technology continues to evolve, we anticipate several exciting developments in thrips management:
1. Precision Agriculture
Advanced sensors and data analytics will allow for highly targeted pest control measures, reducing the need for broad-spectrum treatments.
2. Genetic Engineering
Development of crop varieties with enhanced resistance to thrips and the viruses they transmit.
3. Biological Control Advancements
Discovery and development of new biological control agents specifically tailored to different thrips species and agricultural environments.
4. Artificial Intelligence in Pest Detection
AI-powered image recognition systems that can instantly identify and quantify thrips infestations, allowing for rapid response.
5. Pheromone-Based Control Methods
Development of synthetic pheromones to disrupt thrips mating patterns and reduce populations.
At Farmonaut, we’re constantly exploring these emerging technologies to provide our users with the most advanced and effective pest management tools available.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Thrips Management
Effectively managing thrips populations requires a comprehensive, integrated approach that combines traditional methods with cutting-edge technology. By leveraging a combination of cultural practices, biological controls, and targeted interventions guided by advanced monitoring systems, farmers can significantly reduce the impact of thrips on their crops.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to empowering farmers with the tools and knowledge they need to implement successful thrips management strategies. Our satellite-based monitoring system, combined with expert analysis and recommendations, provides a powerful solution for early detection and effective control of thrips infestations.
By adopting a holistic approach to thrips management, farmers can not only protect their crops but also contribute to more sustainable and resilient agricultural practices. As we continue to face challenges in global food production, innovative pest management strategies will play a crucial role in ensuring food security and agricultural sustainability.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can help you implement effective thrips management strategies on your farm, visit our website or download our app:
FAQs about Thrips Management
- Q: How can I tell if my plants are infested with thrips?
A: Look for silvery or bronzed patches on leaves, distorted growth, and tiny, slender insects. You can also use sticky traps to monitor for thrips presence. - Q: Are there any natural predators of thrips?
A: Yes, several natural predators feed on thrips, including predatory mites, minute pirate bugs, and lacewings. - Q: How often should I monitor my crops for thrips?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial. We recommend checking your crops at least weekly, and more frequently during peak thrips seasons or in high-risk areas. - Q: Can thrips develop resistance to insecticides?
A: Yes, thrips can develop resistance to insecticides over time. It’s important to rotate between different classes of insecticides and integrate non-chemical control methods. - Q: How does Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring help with thrips management?
A: Our satellite monitoring system can detect subtle changes in plant health that may indicate thrips infestation before visible symptoms appear, allowing for earlier and more targeted interventions. - Q: Are organic methods effective against severe thrips infestations?
A: Organic methods can be effective, especially when used preventively or for mild infestations. For severe cases, a combination of organic and conventional methods may be necessary. - Q: How can I prevent thrips from infesting my crops in the first place?
A: Implement good sanitation practices, use reflective mulches, remove weeds, and consider using physical barriers like fine mesh screens in greenhouses. - Q: Can thrips survive winter?
A: Some thrips species can overwinter in plant debris or soil. Proper sanitation and crop rotation can help reduce overwintering populations. - Q: How do weather conditions affect thrips populations?
A: Thrips populations tend to increase in warm, dry conditions. Our weather integration feature can help predict potential population explosions based on weather patterns. - Q: Is it possible to completely eliminate thrips from my farm?
A: Complete elimination is rarely achievable or necessary. The goal is to manage thrips populations below economically damaging levels through integrated pest management strategies.
For more information on thrips management and to explore how Farmonaut can help protect your crops, visit our website or contact our team of agricultural experts.