Mastering Bovine TB: Essential Guide for Farmers to Protect Cattle Health and Ensure Farm Biosecurity
“Bovine TB can cause up to 30% reduction in milk production, significantly impacting dairy farm economics.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on mastering Bovine Tuberculosis (TB) and ensuring farm biosecurity. As farmers and agricultural professionals, we understand the critical importance of protecting our cattle health and maintaining the integrity of our farms. In this blog post, we’ll delve deep into the world of bovine tuberculosis control and cattle herd management, providing you with essential information and practical strategies to safeguard your livestock and agricultural enterprise.
Bovine TB is a significant challenge facing the agriculture sector today, impacting dairy, beef cattle, and other livestock operations. As we navigate through this guide, we’ll explore the various aspects of this disease, from its transmission and symptoms to the economic implications for farmers. We’ll also discuss effective farm biosecurity measures and animal health monitoring techniques that can help protect your herd.
Understanding Bovine Tuberculosis: A Threat to Cattle Health
Bovine Tuberculosis is a chronic bacterial disease caused by Mycobacterium bovis. It primarily affects cattle but can also infect other domestic and wild animals. As a zoonotic disease, it poses a risk to human health as well, making its control crucial for both animal welfare and public health reasons.
- Transmission: Bovine TB spreads through close contact with infected animals, contaminated feed, or water sources.
- Symptoms: Early stages often show no visible signs, making regular testing essential.
- Impact: Can lead to reduced productivity, trade restrictions, and significant economic losses for farmers.
Understanding the nature of this disease is the first step in implementing effective agricultural disease prevention strategies. As farmers, we must be vigilant and proactive in our approach to managing this threat to our herds.
The Economic Impact of Bovine TB on Farms
The financial consequences of Bovine TB outbreaks can be devastating for farmers. Let’s break down the potential economic impacts:
- Loss of livestock: Infected animals often need to be culled, resulting in direct financial losses.
- Reduced productivity: Infected cattle may produce less milk or have slower growth rates.
- Trade restrictions: Farms with TB outbreaks may face limitations on selling or moving their animals.
- Increased costs: Regular testing, additional biosecurity measures, and potential quarantine expenses can add up.
These economic challenges underscore the importance of implementing robust farm biosecurity measures and leveraging modern agritech solutions for farmers to prevent and manage Bovine TB effectively.
Essential Farm Biosecurity Measures
Implementing stringent biosecurity protocols is crucial in preventing the introduction and spread of Bovine TB on your farm. Here are some essential measures to consider:
- Isolation of new animals: Quarantine new additions to your herd for at least 30 days.
- Regular testing: Conduct routine TB tests as recommended by your local veterinary services.
- Controlled movement: Limit unnecessary movement of animals between farms or grazing areas.
- Visitor protocols: Implement strict hygiene measures for visitors and vehicles entering your farm.
- Feed and water management: Ensure clean and uncontaminated sources of feed and water for your herd.
By diligently following these farm biosecurity measures, we can significantly reduce the risk of Bovine TB introduction and spread within our herds.
Leveraging Technology for Bovine TB Prevention
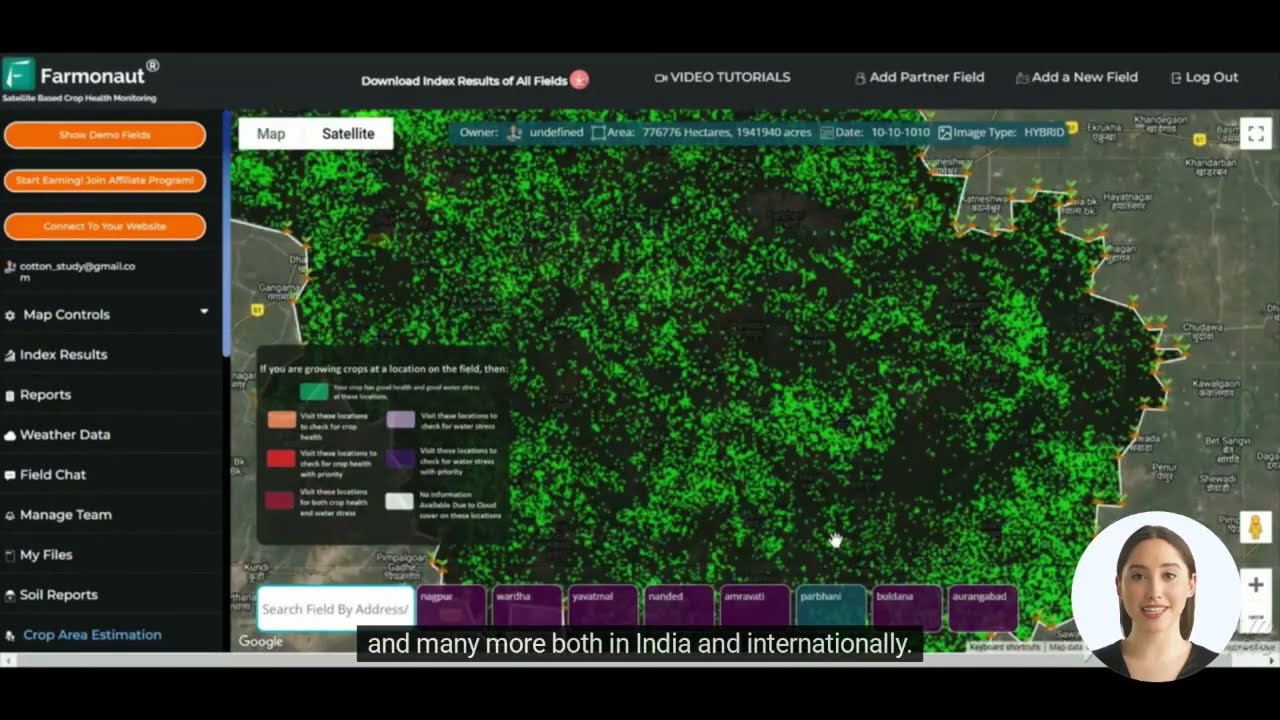
In today’s digital age, technology plays a crucial role in animal health monitoring and disease prevention. Advanced agritech solutions for farmers, such as those offered by Farmonaut, can significantly enhance our ability to manage herd health and detect potential issues early.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions provide valuable tools for monitoring crop and pasture health, which indirectly supports livestock management. By ensuring optimal grazing conditions and feed quality, we can boost the overall health and immunity of our cattle, making them more resilient to diseases like Bovine TB.
Key features of Farmonaut’s platform that can aid in Bovine TB prevention:
- Real-time crop health monitoring for better pasture management
- AI-based advisory systems for optimized farm operations
- Resource management tools to ensure efficient allocation of farm resources
While Farmonaut’s technology doesn’t directly detect Bovine TB, its comprehensive farm management capabilities contribute to creating a healthier environment for livestock, which is crucial in disease prevention.
Government Policies and Pilot Culls for Bovine TB Control
“Government-led pilot culls for Bovine TB control have targeted up to 70% of badger populations in affected areas.”
Government intervention plays a significant role in the fight against Bovine TB. Many countries have implemented comprehensive policies and programs aimed at controlling and eradicating this disease. Let’s explore some of these initiatives:
- Regular testing programs: Mandatory TB testing for cattle at specified intervals.
- Movement restrictions: Limitations on moving cattle from high-risk areas to low-risk regions.
- Compensation schemes: Financial support for farmers who have to cull infected animals.
- Wildlife management: Efforts to control TB in wildlife populations, particularly badgers in some countries.
The controversial topic of badger culling has been a part of Bovine TB control strategies in some regions. While aimed at reducing disease transmission from wildlife to cattle, these programs have sparked debates among farmers, conservationists, and policymakers.
Sustainable Farming Practices for Long-term TB Prevention
Adopting sustainable farming practices is not only beneficial for the environment but can also contribute to better animal health and disease resistance. Here are some sustainable approaches that can help in Bovine TB prevention:
- Rotational grazing: Reduces overgrazing and minimizes contact with potentially infected areas.
- Improved nutrition: Well-nourished animals have stronger immune systems.
- Stress reduction: Implementing animal welfare practices to reduce stress and boost immunity.
- Organic farming: Some organic practices may contribute to overall herd health.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees in pastures can improve animal welfare and reduce stress.
These practices align with broader agricultural trends towards sustainability and can be part of a holistic approach to Bovine TB control.

The Role of Rural Veterinary Services in Bovine TB Management
Rural veterinary services play a crucial role in the fight against Bovine TB. These professionals are on the front lines, providing essential support to farmers in disease prevention, detection, and management. Here’s how veterinary services contribute to Bovine TB control:
- Conducting regular TB testing and surveillance
- Providing expert advice on biosecurity measures
- Assisting with herd health planning
- Supporting farmers during TB outbreaks
- Liaising with government agencies on TB control programs
As farmers, maintaining a close relationship with our local veterinary services is crucial for effective cattle herd management and disease control.
Innovative Approaches to Bovine TB Detection and Prevention
The field of agricultural disease prevention is constantly evolving, with new technologies and methods being developed to combat Bovine TB. Some innovative approaches include:
- Advanced diagnostic tests: More accurate and rapid TB detection methods.
- Genetic selection: Breeding cattle with increased natural resistance to TB.
- Vaccination research: Ongoing studies into effective TB vaccines for cattle.
- Big data analytics: Using large-scale data analysis to predict and prevent TB outbreaks.
- Remote monitoring: Utilizing technology like Farmonaut’s satellite-based solutions for overall farm health monitoring.
While some of these approaches are still in development, they represent the future of Bovine TB control and offer hope for more effective management strategies.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced farm data analysis
The Impact of Bovine TB on Different Farming Sectors
Bovine TB affects various sectors of the farming industry differently. Let’s examine how this disease impacts different types of farms:
- Dairy farms: Reduced milk production and potential contamination concerns.
- Beef cattle farms: Impacts on meat quality and herd value.
- Mixed farming: Potential spread to other livestock species.
- Organic farms: Challenges in maintaining organic status while managing TB.
Understanding these sector-specific impacts helps us tailor our bovine tuberculosis control strategies to the unique needs of each farming type.
Integrating Agritech Solutions in Bovine TB Management
Modern agritech solutions for farmers can significantly enhance our ability to manage Bovine TB risks. While not directly focused on TB detection, platforms like Farmonaut offer valuable tools for overall farm management that indirectly support disease prevention efforts:
- Satellite-based crop monitoring: Ensures optimal pasture health for better cattle nutrition.
- AI-driven advisory systems: Provides insights for improved farm management practices.
- Resource management tools: Helps in efficient allocation of farm resources, reducing stress on animals.
- Weather forecasting: Aids in planning grazing patterns and reducing environmental stress on cattle.
By leveraging these technologies, we can create a more holistic approach to farm management that supports overall herd health and resilience against diseases like Bovine TB.
Check out Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs for integration options
Collaborative Efforts in Bovine TB Control
Effectively managing Bovine TB requires a collaborative approach involving various stakeholders:
- Farmers and farm workers
- Veterinarians and animal health experts
- Government agencies and policymakers
- Agricultural research institutions
- Technology providers like Farmonaut
By working together, we can develop more comprehensive and effective strategies for bovine tuberculosis control and cattle herd management.
Future Outlook: The Path to Bovine TB Eradication
While Bovine TB remains a significant challenge, the future holds promise for more effective control and potential eradication. Key areas of focus for the future include:
- Continued research into TB vaccines and treatments
- Advanced diagnostic tools for earlier detection
- Improved understanding of TB transmission in wildlife
- Integration of AI and big data in disease prediction and management
- Development of more resistant cattle breeds
As we continue to advance in these areas, the goal of Bovine TB eradication becomes increasingly attainable, securing a healthier future for our farms and cattle.
Bovine TB Prevention and Management Strategies
| Strategy | Implementation | Effectiveness | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular TB Testing | Conduct routine skin tests or blood tests | High | Medium ($50-$100 per animal) |
| Herd Isolation | Separate new animals for 30+ days | Medium | Low-Medium ($500-$2000 setup) |
| Wildlife Management | Fencing, controlled access to feed/water | Medium | High ($5000+ per farm) |
| Improved Biosecurity Measures | Visitor protocols, cleaning/disinfection | High | Medium ($1000-$3000 annually) |
| Agritech Solutions (e.g., Farmonaut) | Implement satellite monitoring, AI advisories | Medium-High | Variable (subscription-based) |
FAQ: Bovine TB and Farm Management
Q: How often should I test my herd for Bovine TB?
A: The frequency of testing depends on your location and local regulations. Generally, annual testing is recommended, but high-risk areas may require more frequent checks.
Q: Can humans contract TB from infected cattle?
A: Yes, Bovine TB can infect humans, usually through consumption of unpasteurized dairy products or close contact with infected animals. However, human cases are rare in countries with strong control programs.
Q: How can I improve my farm’s biosecurity?
A: Implement strict visitor policies, isolate new animals, maintain clean feed and water sources, and regularly clean and disinfect farm equipment and facilities.
Q: Are there any natural remedies for preventing Bovine TB?
A: While there are no natural cures for TB, maintaining good nutrition, reducing stress, and ensuring proper hygiene can help boost your herd’s overall health and resistance to disease.
Q: How can technology like Farmonaut help in managing Bovine TB risks?
A: While Farmonaut doesn’t directly detect TB, its farm management tools can help maintain optimal pasture and crop health, contributing to better overall herd health and potentially reducing disease susceptibility.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Bovine TB Management
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, mastering Bovine TB control requires a multifaceted approach. From implementing stringent farm biosecurity measures to leveraging advanced agritech solutions for farmers, every aspect plays a crucial role in protecting our herds and ensuring the sustainability of our farming operations.
Remember, the key to effective bovine tuberculosis control lies in:
- Regular testing and vigilant monitoring
- Implementing robust biosecurity protocols
- Adopting sustainable farming practices
- Collaborating with veterinary services and regulatory bodies
- Staying informed about the latest developments in TB research and control strategies
By integrating these strategies with modern technology and sustainable practices, we can significantly reduce the risk of Bovine TB outbreaks and move towards a healthier, more productive future for our farms.
As we continue to face the challenges posed by Bovine TB, let’s remain committed to innovation, collaboration, and responsible farming practices. Together, we can work towards a future where Bovine TB no longer threatens our herds, our livelihoods, and our communities.