Boost Yields and Protect Soil: Master Conservation Tillage with Farmonaut’s Precision Agriculture Solutions

“Conservation tillage can reduce soil erosion by up to 90% compared to conventional tillage methods.”
In today’s rapidly evolving agricultural landscape, we find ourselves at a critical juncture where sustainable farming practices are not just beneficial but essential. Conservation tillage farming stands at the forefront of this agricultural revolution, offering a powerful blend of environmental stewardship and economic viability. As we delve into the world of conservation tillage, we’ll explore how these innovative techniques are reshaping the future of farming, and how Farmonaut’s cutting-edge precision agriculture solutions are amplifying their impact.
Understanding Conservation Tillage: A Paradigm Shift in Farming
Conservation tillage is a suite of farming practices that minimize soil disturbance, maintain crop residues on the field surface, and protect the soil from erosion and degradation. This approach marks a significant departure from conventional tillage methods, which often involve intensive plowing and leave soil exposed to the elements.
The core principles of conservation tillage include:
- Minimizing soil disturbance
- Maintaining crop residue cover
- Enhancing soil organic matter
- Improving water retention and infiltration
- Promoting biodiversity in the soil ecosystem
By adhering to these principles, farmers can significantly reduce soil erosion, improve soil health, and create a more sustainable agricultural system. Let’s explore the various methods of conservation tillage and how they contribute to these goals.
Types of Conservation Tillage Methods
Conservation tillage encompasses several distinct approaches, each with its unique benefits and challenges. Understanding these methods is crucial for farmers looking to implement the most suitable practices for their specific conditions.
1. No-Till Farming
No-till farming is perhaps the most radical departure from conventional tillage. In this method, the soil is left undisturbed from harvest to planting, except for nutrient injection. Seeds are planted directly into the previous crop’s residue.
Benefits:
- Maximum soil protection against erosion
- Improved soil structure and organic matter content
- Reduced fuel and labor costs
- Enhanced water retention
Challenges:
- Initial investment in specialized planting equipment
- Potential increase in herbicide use for weed control
- Slower soil warming in spring in colder climates
2. Strip-Till Farming
Strip-till is a compromise between no-till and conventional tillage. It involves tilling narrow strips where seeds will be planted while leaving the rest of the field undisturbed.
Benefits:
- Combines advantages of no-till and full tillage
- Allows for precise fertilizer placement
- Facilitates earlier planting in cooler climates
Challenges:
- Requires specialized equipment
- More complex to implement than full no-till
3. Ridge-Till Farming
Ridge-till involves planting crops on raised ridges or beds. The area between ridges is left undisturbed, and crop residues remain on the surface until planting.
Benefits:
- Excellent for poorly drained soils
- Reduces erosion on sloping fields
- Facilitates better water management
Challenges:
- Requires specialized ridge-building and maintenance equipment
- May not be suitable for all crop types
4. Mulch-Till Farming
Mulch-till involves some tillage prior to planting but leaves at least 30% of crop residue on the soil surface.
Benefits:
- Balances soil protection with some of the benefits of tillage
- Can be implemented with conventional equipment
- Suitable for a wide range of soil types
Challenges:
- Requires careful management to maintain adequate residue cover
- May not provide as much erosion control as no-till or strip-till

The Role of Precision Agriculture in Conservation Tillage
While conservation tillage methods offer significant benefits, their effectiveness can be further enhanced through the application of precision agriculture technologies. This is where Farmonaut’s innovative solutions come into play, offering farmers data-driven insights to optimize their conservation tillage practices.
Farmonaut’s precision agriculture platform provides:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring
- AI-powered advisory systems
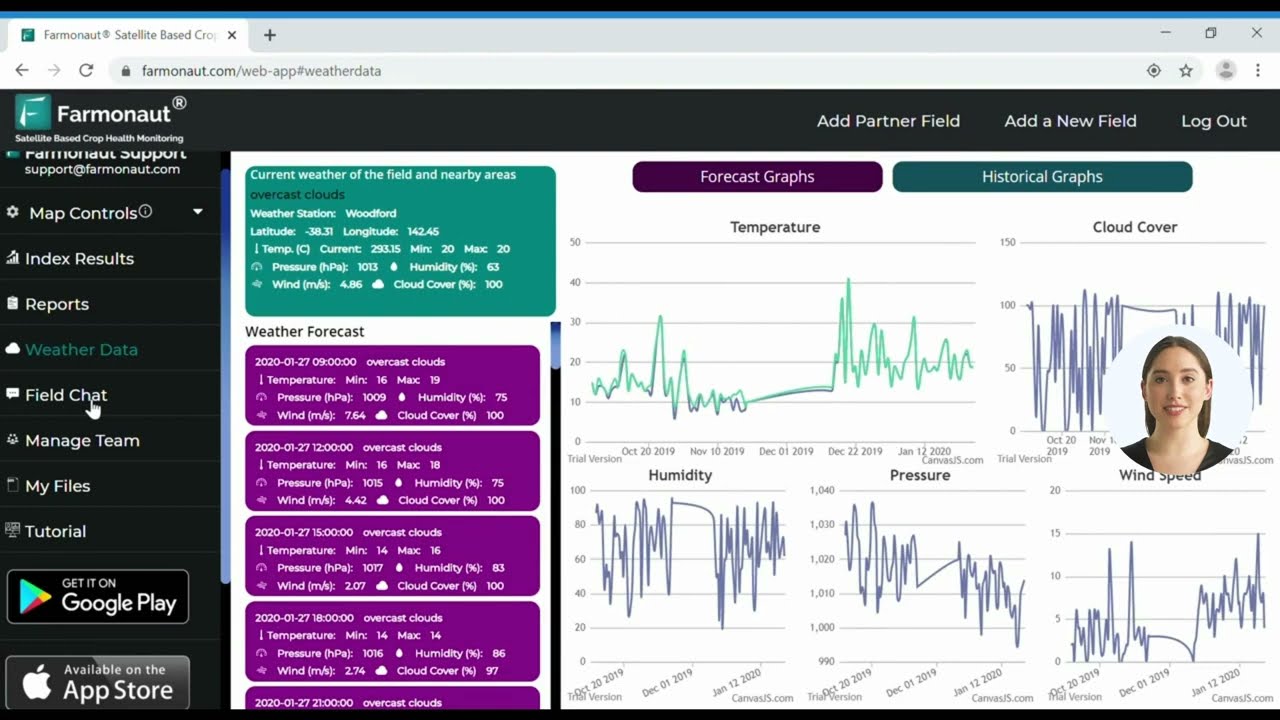
- Real-time weather forecasts
- Soil moisture analysis
- Yield prediction tools
By leveraging these technologies, farmers can make more informed decisions about crop residue management, equipment usage, and field preparation, tailoring their conservation tillage approach to their specific soil conditions and crop types.
Access Farmonaut’s precision agriculture solutions:
Benefits of Conservation Tillage
The adoption of conservation tillage practices, especially when combined with precision agriculture technologies, offers a wide array of benefits for farmers and the environment:
1. Soil Health Improvement
Conservation tillage significantly enhances soil health by:
- Increasing organic matter content
- Improving soil structure and tilth
- Enhancing microbial activity
- Reducing soil compaction
2. Erosion Prevention
By maintaining crop residue on the soil surface, conservation tillage provides excellent protection against both wind and water erosion, preserving valuable topsoil.
3. Water Conservation
Improved soil structure and increased organic matter content lead to:
- Better water infiltration
- Reduced runoff
- Increased water-holding capacity
4. Biodiversity Enhancement
Minimizing soil disturbance promotes a healthier soil ecosystem, supporting a diverse range of beneficial organisms.
5. Cost Reduction
“Farmers implementing conservation tillage techniques can save up to 50% on fuel costs and 30-50% on labor expenses.”
Conservation tillage can significantly reduce operational costs by:
- Decreasing fuel consumption
- Reducing labor requirements
- Minimizing equipment wear and tear
6. Climate Change Mitigation
By increasing soil organic matter and reducing fuel usage, conservation tillage practices contribute to carbon sequestration and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Implementing Conservation Tillage: Best Practices and Considerations
Successfully transitioning to conservation tillage requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key considerations and best practices:
1. Assess Your Field Conditions
Before implementing conservation tillage, it’s crucial to assess your field’s current conditions, including:
- Soil type and texture
- Drainage characteristics
- Existing compaction issues
- Weed pressure
Farmonaut’s satellite-based field analysis can provide valuable insights into field conditions, helping farmers make informed decisions about which conservation tillage method is most suitable.
2. Choose the Right Equipment
Depending on the chosen conservation tillage method, you may need to invest in specialized equipment such as:
- No-till planters or drills
- Strip-till implements
- Ridge-building equipment
Consult with equipment dealers and experienced conservation tillage farmers to determine the best options for your operation.
3. Manage Crop Residue Effectively
Proper crop residue management is critical for successful conservation tillage. Consider the following:
- Evenly distribute residue during harvest
- Use cover crops to supplement residue in low-yielding years
- Adjust planting equipment to handle residue effectively
Farmonaut’s crop monitoring tools can help track residue cover and identify areas that may require additional management.
4. Adapt Your Nutrient Management Strategy
Conservation tillage may require adjustments to your nutrient management approach:
- Consider banding fertilizers to improve nutrient availability
- Monitor soil fertility levels closely, especially in the transition period
- Adjust application rates and timing based on residue cover and decomposition rates
Farmonaut’s precision agriculture platform can assist in creating variable rate application (VRA) maps for more efficient nutrient management.
5. Implement Integrated Pest Management
Conservation tillage can affect pest dynamics, requiring a comprehensive integrated pest management (IPM) approach:
- Monitor fields regularly for pests and diseases
- Use crop rotation to break pest cycles
- Consider targeted pesticide applications when necessary
Farmonaut’s AI-powered crop scouting tools can help identify potential pest issues early, allowing for timely interventions.
Overcoming Challenges in Conservation Tillage
While the benefits of conservation tillage are substantial, farmers may encounter some challenges during implementation. Here’s how to address common issues:
1. Soil Temperature Management
In cooler climates, conservation tillage can result in slower soil warming in spring. To mitigate this:
- Consider strip-till to create a warmer seedbed
- Use row cleaners to clear residue from the planting zone
- Monitor soil temperature using Farmonaut’s precision agriculture tools to determine optimal planting times
2. Weed Control
Reduced tillage can lead to changes in weed pressure. Manage this by:
- Implementing diverse crop rotations
- Using cover crops to suppress weeds
- Adopting a comprehensive herbicide program
- Utilizing Farmonaut’s vegetation indices to identify problem areas early
3. Nutrient Stratification
Over time, nutrients may become concentrated in the upper soil layers. Address this by:
- Periodically soil testing at various depths
- Using deep banding for fertilizer application when necessary
- Considering occasional vertical tillage to redistribute nutrients
4. Equipment Adjustments
Transitioning to conservation tillage may require equipment modifications:
- Invest in high-quality down-pressure systems for planters
- Use residue managers to clear planting paths
- Consider guidance systems for precise strip-till operations
5. Yield Lag During Transition
Some farmers may experience a temporary yield decrease when first adopting conservation tillage. Mitigate this by:
- Gradually transitioning fields to conservation tillage
- Focusing on building soil health through cover crops and proper residue management
- Using Farmonaut’s yield prediction tools to identify and address potential issues early
The Future of Conservation Tillage with Precision Agriculture
As we look to the future, the integration of conservation tillage practices with advanced precision agriculture technologies holds immense promise for sustainable and profitable farming. Farmonaut is at the forefront of this agricultural revolution, offering innovative solutions that enhance the effectiveness of conservation tillage methods.
Key areas where precision agriculture is advancing conservation tillage include:
- Variable Rate Technology (VRT): Allowing for precise application of inputs based on field variability and crop needs.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Improving crop health monitoring and predictive analytics for pest and disease management.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors: Providing real-time data on soil moisture, temperature, and other critical parameters.
- Robotics and Automation: Enabling more precise and efficient field operations, reducing soil compaction.
By leveraging these technologies through platforms like Farmonaut, farmers can optimize their conservation tillage practices, leading to improved soil health, higher yields, and more sustainable agricultural systems.
Explore Farmonaut’s precision agriculture solutions:
- Web Application: Access comprehensive farm management tools from any device.
- Android App: Monitor your fields on-the-go with our mobile application.
- iOS App: Get real-time insights on your Apple devices.
- API Access: Integrate Farmonaut’s powerful data into your existing systems.
- API Developer Docs: Detailed documentation for seamless integration.
Comparison of Conservation Tillage Methods
| Method | Soil Disturbance Level | Erosion Prevention | Crop Residue Retention | Water Conservation | Input Cost Reduction | Yield Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Till | Very Low | High | High | High | High | Medium to High |
| Strip-Till | Low | Medium to High | Medium to High | Medium to High | Medium | High |
| Ridge-Till | Medium | Medium | Medium | High | Medium | Medium to High |
| Mulch-Till | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium | Low to Medium | Medium to High |
| Farmonaut-Enhanced | Optimized | Enhanced | Optimized | Enhanced | Enhanced | Optimized |
Conclusion: Embracing a Sustainable Future with Conservation Tillage
Conservation tillage represents a crucial step towards more sustainable and resilient agricultural systems. By minimizing soil disturbance, preserving crop residues, and leveraging precision agriculture technologies, farmers can significantly improve soil health, reduce erosion, conserve water, and enhance overall farm productivity.
As we face the challenges of climate change and the need for increased food production, the adoption of conservation tillage practices, supported by innovative solutions like those offered by Farmonaut, will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of agriculture. By embracing these methods and technologies, farmers can not only protect their land for future generations but also improve their economic viability in the short term.
We encourage farmers, agronomists, and agricultural stakeholders to explore the potential of conservation tillage and precision agriculture in their operations. With the right approach and tools, we can create a more sustainable and productive agricultural landscape that meets the needs of today while preserving our resources for tomorrow.
FAQs about Conservation Tillage and Precision Agriculture
- What is the main difference between conservation tillage and conventional tillage?
Conservation tillage minimizes soil disturbance and maintains crop residue on the surface, while conventional tillage involves intensive plowing that leaves soil exposed. - How does conservation tillage improve soil health?
It increases organic matter content, enhances soil structure, promotes microbial activity, and reduces erosion, leading to overall improved soil health. - Can conservation tillage work for all crop types?
While conservation tillage can be adapted for many crops, some may require specific modifications. It’s important to consult with agricultural experts and use tools like Farmonaut to determine the best approach for your specific crops and conditions. - How does Farmonaut’s technology enhance conservation tillage practices?
Farmonaut provides satellite-based crop monitoring, AI-powered insights, and precision agriculture tools that help optimize conservation tillage practices by providing data-driven decision support for farmers. - Is conservation tillage more expensive to implement than conventional tillage?
While there may be initial costs for specialized equipment, conservation tillage often leads to reduced operational costs over time through lower fuel consumption, less labor, and improved soil health. - How long does it take to see the benefits of conservation tillage?
Some benefits, like reduced erosion, are immediate. Others, such as improved soil structure and increased organic matter, may take several seasons to become fully apparent. - Can conservation tillage help in water management?
Yes, conservation tillage improves water infiltration, reduces runoff, and increases the soil’s water-holding capacity, leading to better water management and drought resistance. - How does conservation tillage impact weed management?
While it can change weed dynamics, conservation tillage, combined with proper crop rotation, cover crops, and targeted herbicide use, can effectively manage weeds. Farmonaut’s vegetation monitoring tools can help identify weed issues early. - Is conservation tillage suitable for all soil types?
Conservation tillage can be adapted to most soil types, but the specific method may vary. Farmonaut’s soil analysis tools can help determine the best approach for your particular soil conditions. - How does conservation tillage contribute to climate change mitigation?
By increasing soil organic matter and reducing fuel usage, conservation tillage helps sequester carbon in the soil and reduces greenhouse gas emissions from farm operations.
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
By leveraging Farmonaut’s precision agriculture solutions, farmers can take their conservation tillage practices to the next level, optimizing soil health, water management, and crop productivity. Explore our subscription plans to find the perfect fit for your farming needs and join the future of sustainable agriculture today.