Vietnam’s Son La Province: A Model for Sustainable Agriculture and Ecological Farming Transformation
“Son La province’s shift from monoculture to diverse fruit tree plantations has increased biodiversity by up to 40% in some areas.”
In the lush, mountainous terrain of northern Vietnam, a quiet revolution is taking place. The Son La province, known for its picturesque landscapes and rich agricultural heritage, is emerging as a beacon of hope for sustainable agriculture practices and ecological farming methods. As we delve into this transformative journey, we’ll explore how this region is not just adapting to change but actively shaping the future of food system transformation in Vietnam and beyond.
The Dawn of Ecological Agriculture in Son La
Son La’s journey towards sustainable agriculture is a testament to the power of innovation and community-driven change. As we witness the global challenge of feeding an ever-growing population without compromising our planet’s health, Son La stands out as a living laboratory for solutions that could revolutionize farming practices worldwide.
The province’s transformation aligns perfectly with Vietnam’s National Action Plan for the Transformation of the Food System, launched in 2023. This ambitious initiative aims to overhaul the country’s agriculture and food sectors, prioritizing sustainability while addressing critical environmental challenges such as soil degradation and the pitfalls of monoculture farming.

Circular Economy: The Heart of Son La’s Agricultural Revolution
At the core of Son La’s agricultural metamorphosis is the implementation of circular economy principles. This innovative approach is transforming how farmers think about waste, resources, and productivity. Let’s explore how this is playing out on the ground:
- Livestock Feeding and Fertilization: Farmers are now integrating crop residues and animal waste into a closed-loop system, reducing the need for external inputs and minimizing environmental impact.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: The introduction of diverse plant species in coffee plantations is creating resilient ecosystems that support both agriculture and local wildlife.
- Soil Conservation: Agroforestry techniques are being employed to combat soil erosion, particularly in the steep terrain where coffee is traditionally grown.
These practices are part of the “Ecological Agricultural Transformation and Safe Food System” (Asset) program, a five-year initiative launched in 2020. This collaborative effort, coordinated by the Centre for International Cooperation in Agricultural Research for Development (Cirad), brings together 15 local and international partners, including research institutions and governmental organizations.
Nam Hamlet: A Microcosm of Sustainable Change
To truly understand the impact of these sustainable agriculture practices, let’s zoom in on Nam hamlet, a rural community in Son La that’s embracing ecological farming methods with open arms. Here, 30 villagers are pioneering circular agricultural practices, revitalizing not just their farms but the entire local ecosystem.
Pascal Lienhard, an agricultural engineer from Cirad, highlights the potential of these practices to breathe new life into livestock farming. This sector had previously taken a back seat to monoculture farming, but now it’s becoming an integral part of a more holistic and sustainable agricultural system.
Agroforestry: Restoring Ecological Balance
In Nam hamlet, six local farmers are taking sustainable coffee cultivation to the next level. They’re implementing agroforestry techniques designed to restore forest ecosystems while maintaining productive coffee plantations. This approach is proving that agriculture and conservation can go hand in hand, creating a win-win situation for farmers and the environment.
The benefits of agroforestry in coffee cultivation are manifold:
- Improved soil health through natural mulching and nitrogen fixation
- Enhanced biodiversity, supporting pollinators and natural pest control
- Increased resilience to climate change impacts
- Diversified income streams for farmers through additional tree crops
“Sustainable coffee cultivation in Son La has reduced water usage by 30% while improving soil health and crop yields.”
Challenges and Triumphs in Son La’s Agricultural Transformation
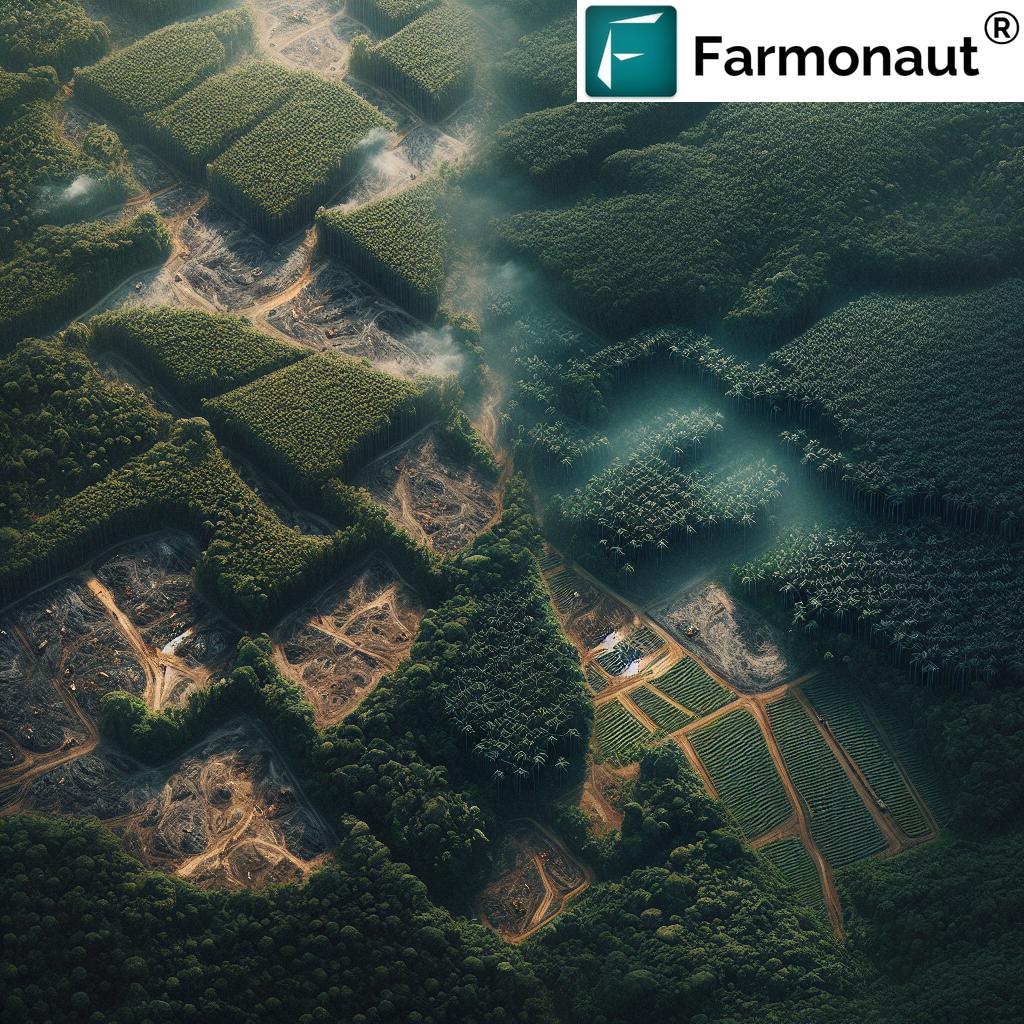
The path to sustainable agriculture in Son La hasn’t been without its challenges. Economic pressures, labor shortages, and the increasing impacts of climate change have pushed many farmers towards intensive monoculture practices. Coffee farming, which accounts for about 70% of villagers’ income in some areas, has been a double-edged sword – providing economic stability but at the cost of environmental degradation.
However, the province’s response to these challenges has been nothing short of remarkable. Between 2015 and 2020, Son La undertook substantial reforms:
- Reduced the area of soil-degrading monoculture crops like maize from 169,000 hectares to 70,000 hectares
- Expanded fruit tree cultivation from 29,000 hectares to 84,000 hectares
This strategic shift not only enhances ecological sustainability but also improves economic viability for farmers in the long run.
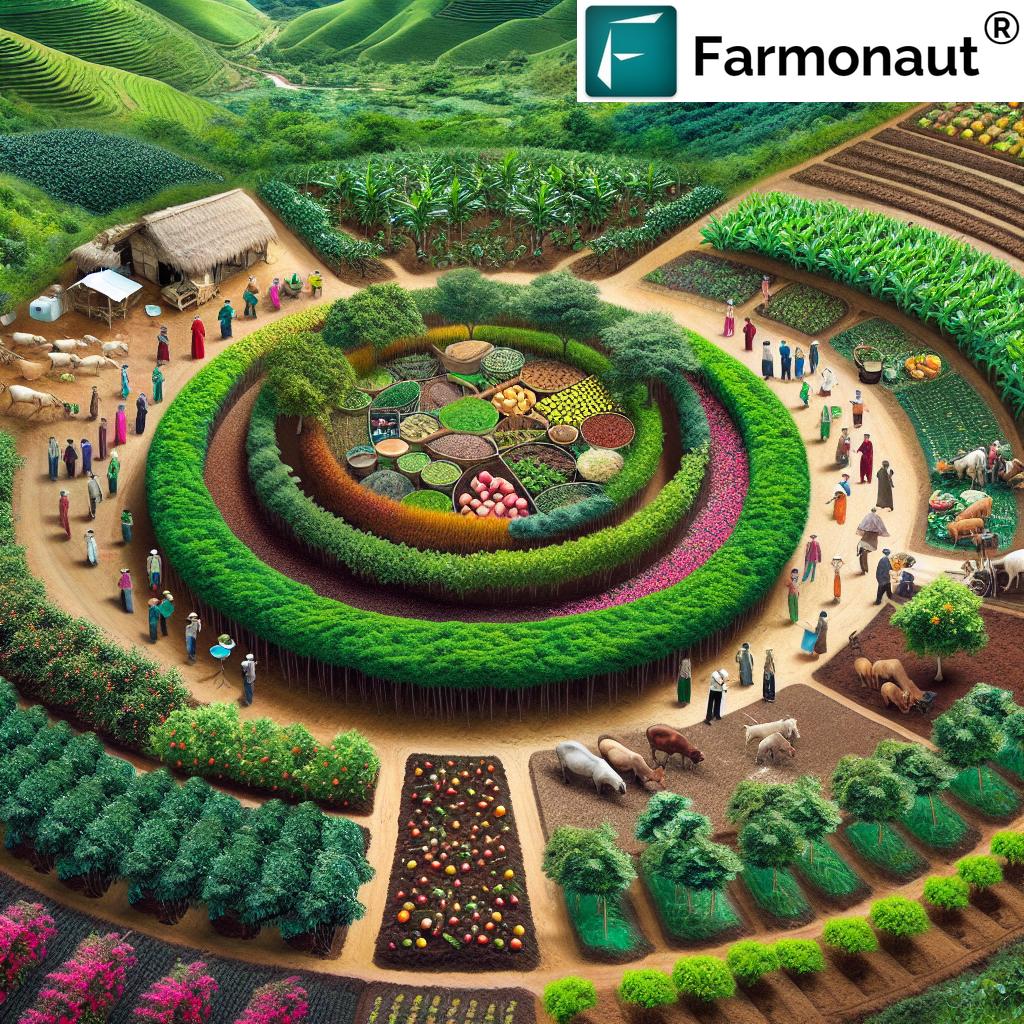

The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
As we explore Son La’s agricultural transformation, it’s important to recognize the role of technology in facilitating these changes. Advanced tools and platforms are enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource use, and monitor their progress towards sustainability goals.
For instance, satellite-based farm management solutions, like those offered by Farmonaut, are becoming increasingly valuable in regions like Son La. These technologies provide real-time crop health monitoring, AI-based advisory systems, and resource management tools that can significantly enhance the effectiveness of sustainable farming practices.
Climate-Resilient Farming: Adapting to Change
As climate change continues to pose significant challenges to agriculture worldwide, Son La’s farmers are at the forefront of developing and implementing climate-resilient farming strategies. These approaches not only help farmers adapt to changing conditions but also contribute to mitigation efforts through practices like reforestation and carbon sequestration.
Key climate-resilient farming practices in Son La include:
- Drought-resistant crop varieties
- Water-efficient irrigation systems
- Soil conservation techniques to prevent erosion
- Integrated pest management to reduce chemical use
By adopting these practices, farmers in Son La are not only protecting their livelihoods but also contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
Agro-tourism: A New Frontier for Sustainable Agriculture
The Moc Chau district of Son La is pioneering another aspect of sustainable agriculture: agro-tourism. This innovative approach is creating new economic opportunities for farmers while promoting ecological farming methods to a wider audience.
Agro-tourism in Son La offers visitors the chance to:
- Experience traditional farming techniques firsthand
- Learn about sustainable agriculture practices
- Taste locally-produced, organic foods
- Contribute directly to the local economy
This connection between consumers and eco-friendly producers not only supports sustainable agriculture but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the food system and the environment.
The Future of Sustainable Farming in Son La and Beyond
As we look to the future, Son La’s journey offers valuable lessons for regions around the world grappling with similar agricultural challenges. The province’s success in balancing productivity with sustainability demonstrates that it’s possible to feed a growing population while preserving our planet’s precious resources.
Key takeaways from Son La’s agricultural transformation include:
- The importance of community engagement in driving sustainable change
- The potential of circular economy principles in agriculture
- The role of technology in supporting sustainable farming practices
- The value of diversification in building resilient agricultural systems
As we continue to face global challenges like food security and climate change, the example set by Son La offers hope and practical solutions for a more sustainable agricultural future.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices in Son La Province
| Traditional Methods | Sustainable Practices | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Monoculture farming | Crop diversification and agroforestry | 40% increase in biodiversity, improved soil health |
| Chemical-intensive soil management | Organic fertilizers and cover crops | 50% reduction in chemical use, enhanced soil fertility |
| Inefficient irrigation | Water-efficient systems and rainwater harvesting | 30% reduction in water usage, increased drought resilience |
| Synthetic pesticides | Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | 60% decrease in pesticide use, improved ecosystem balance |
| Single income source (e.g., coffee) | Diversified income through fruit trees and agro-tourism | 25% increase in farmer income, reduced economic vulnerability |
Leveraging Technology for Sustainable Agriculture
In the digital age, technology plays a crucial role in advancing sustainable agriculture practices. Farmers in Son La and around the world are increasingly turning to innovative solutions to optimize their operations and enhance sustainability. Here are some ways technology is making a difference:
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions provide real-time insights into crop health, helping farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
- AI-Powered Advisory Systems: Advanced algorithms analyze farm data to provide personalized recommendations, optimizing resource use and improving crop yields.
- Precision Agriculture: GPS-guided machinery and drones enable precise application of inputs, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Blockchain for Traceability: Blockchain technology ensures transparency in the supply chain, connecting consumers with the origins of their food and promoting sustainable practices.
These technological advancements are not just improving efficiency; they’re also making sustainable farming more accessible and economically viable for farmers of all scales.
The Global Impact of Son La’s Agricultural Revolution
The sustainable agriculture practices and ecological farming methods implemented in Son La have implications far beyond the borders of Vietnam. As the world grapples with the challenge of feeding a growing population in the face of climate change and resource scarcity, Son La’s model offers valuable insights and replicable strategies.
Key lessons from Son La that can be applied globally include:
- The importance of government support and policy alignment in driving sustainable agriculture
- The power of international collaboration in sharing knowledge and resources
- The potential of integrating traditional farming wisdom with modern sustainable practices
- The role of education and community engagement in fostering long-term change
As we look to the future, the success of Son La’s agricultural transformation serves as an inspiration and a roadmap for regions around the world seeking to build more sustainable and resilient food systems.
Empowering Farmers with Digital Tools
In the quest for sustainable agriculture, access to information and tools is crucial. Digital platforms and mobile applications are playing an increasingly important role in empowering farmers to adopt and optimize sustainable practices. Here are some resources that can help farmers on their sustainability journey:
Mobile Apps for On-the-Go Monitoring:


For developers and researchers interested in integrating agricultural data into their own systems, API access is available. Detailed documentation can be found in the API Developer Docs.
Sustainable Agriculture Subscription Services
For farmers and agricultural professionals looking to access advanced sustainable farming tools and insights, subscription services offer a cost-effective solution. These services provide regular updates, personalized recommendations, and access to cutting-edge technologies that can significantly enhance sustainable farming practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the main sustainable agriculture practices implemented in Son La Province?
A: The main practices include crop diversification, agroforestry, organic soil management, water-efficient irrigation systems, and integrated pest management.
Q: How has the shift to sustainable agriculture impacted farmers’ incomes in Son La?
A: While specific figures vary, many farmers have seen increased and more stable incomes due to diversified crops and premium prices for sustainably produced goods.
Q: What role does technology play in Son La’s sustainable agriculture model?
A: Technology, including satellite-based crop monitoring and AI advisory systems, helps farmers optimize resource use, monitor crop health, and make data-driven decisions.
Q: How is Son La addressing the challenges of climate change in agriculture?
A: The province is implementing climate-resilient farming strategies, including drought-resistant crops, water conservation techniques, and soil management practices that enhance resilience to extreme weather events.
Q: Can the Son La model of sustainable agriculture be replicated in other regions?
A: While specific practices may need to be adapted to local conditions, the overall principles of Son La’s sustainable agriculture model can be applied in many regions facing similar challenges.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future Rooted in Son La
As we’ve explored throughout this journey, Vietnam’s Son La province stands as a shining example of how sustainable agriculture practices and ecological farming methods can transform a region’s food system. From the implementation of circular economy principles to the adoption of agroforestry techniques, Son La’s farmers are pioneering approaches that not only enhance productivity but also protect and regenerate the environment.
The success of Son La’s agricultural revolution offers hope and practical solutions for global food security and environmental stewardship. By balancing traditional wisdom with modern technology, engaging communities, and fostering international collaboration, Son La has created a model that can inspire and guide sustainable agricultural development worldwide.
As we face the challenges of feeding a growing global population in an era of climate change, the lessons from Son La remind us that sustainable, resilient, and productive agriculture is not just possible – it’s essential. The future of farming is being written in the fields and forests of Son La, and it’s a future that promises a healthier planet and a more secure food system for generations to come.