Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Revolution of Precision Farming
- Trivia: Crop Yield Enhancement Through Technology
- What is Precision Farming?
- Benefits of Precision Farming
- Precision Farming: 7 Advanced Technologies Boosting Crop Yields
- Technology Impact Comparison Table
- Farmonaut: Affordable Precision Agriculture for All
- The Future of Precision Agriculture: Trends to Watch
- Challenges and Considerations in Precision Farming
- Getting Started: Accessing Precision Agriculture with Farmonaut
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Precision Farming: 7 Advanced Technologies Boosting Crop Yields
In today’s fast-evolving agriculture landscape, precision farming—also known as precision agriculture—stands out as a transformative practice that employs advanced technologies to optimize resources, increase yields, and boost sustainability. As we, the global farming community, strive to reduce waste and minimize environmental impact, embracing data-driven tools like AI, remote sensing, and IoT becomes crucial.
Let’s embark on a detailed exploration of precision farming—unraveling its core technologies, the associated benefits, and how platforms like Farmonaut democratize access to these innovations.
What is Precision Farming?
Precision farming refers to a modern agricultural practice that utilizes a suite of advanced technologies—including GPS, GIS, remote sensing in agriculture, IoT devices, and AI-driven analytics—to monitor and manage field variability in crops. Through the precise mapping and analysis of fields, farmers can tailor input use (like fertilizers and pesticides) exactly where and when it’s needed.
This data-driven farming approach not only boosts crop yields and operational efficiency but also helps us reduce costs and environmental impacts, paving the way for truly sustainable farming practices.
TIP: You can use the Farmonaut API and API Developer Docs to integrate satellite crop monitoring systems and remote sensing into your own farm management tools.
Core Benefits of Precision Farming
- Enhanced Efficiency: The precise application of inputs (water, fertilizers, pesticides) reduces waste, optimizes resource usage and increases profitability.
- Increased Yields: By monitoring crop health and managing field variability, farmers can address issues early, ensuring higher yields and better crop quality.
- Environmental Sustainability: Minimizing input use leads to lower runoff and soil degradation, actively promoting sustainable agriculture.
- Data-Driven Decisions: The integration of satellite data, IoT sensors, and AI-driven analytics empowers us to make informed decisions for farm management and risk mitigation.
Precision Farming: 7 Advanced Technologies Boosting Crop Yields
With advanced farm management at our fingertips, leveraging the right technologies becomes essential for improving crop yields with technology and promoting sustainability. Here’s a deep dive into the seven key precision agriculture technologies transforming modern faming:
-
1. Global Positioning System (GPS)
The Global Positioning System (GPS) delivers accurate location data for mapping, soil sampling, and input application. By using GPS in our machinery, we avoid overlaps and missed spots, reducing waste and input costs.
- Main Functions: Field mapping, yield monitoring, tractor guidance, and machine management.
- Benefits: Resources are allocated efficiently, chemical inputs are applied with precision, and environmental impact is minimized.
- Use Case: GPS-guided tractors enable site-specific application of fertilizers and pesticides, drastically reducing waste.
Resource:
Read more about GPS in Precision Farming -
2. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Geographic Information Systems are advanced spatial analysis and visualization tools that help us understand field variability by mapping soil types, moisture levels, and crop health. GIS enables the creation of tailored maps that identify specific zones needing unique inputs.
- Main Functions: Mapping and analysis of field variability, spatial monitoring of crop conditions, and supporting data-driven decisions.
- Benefits: Enhanced ability to optimize inputs, implement targeted interventions, and track field performance over time.
Resource:
Detailed analysis on GIS for Precision Agriculture -
3. Remote Sensing (Satellite Imagery and Drones)
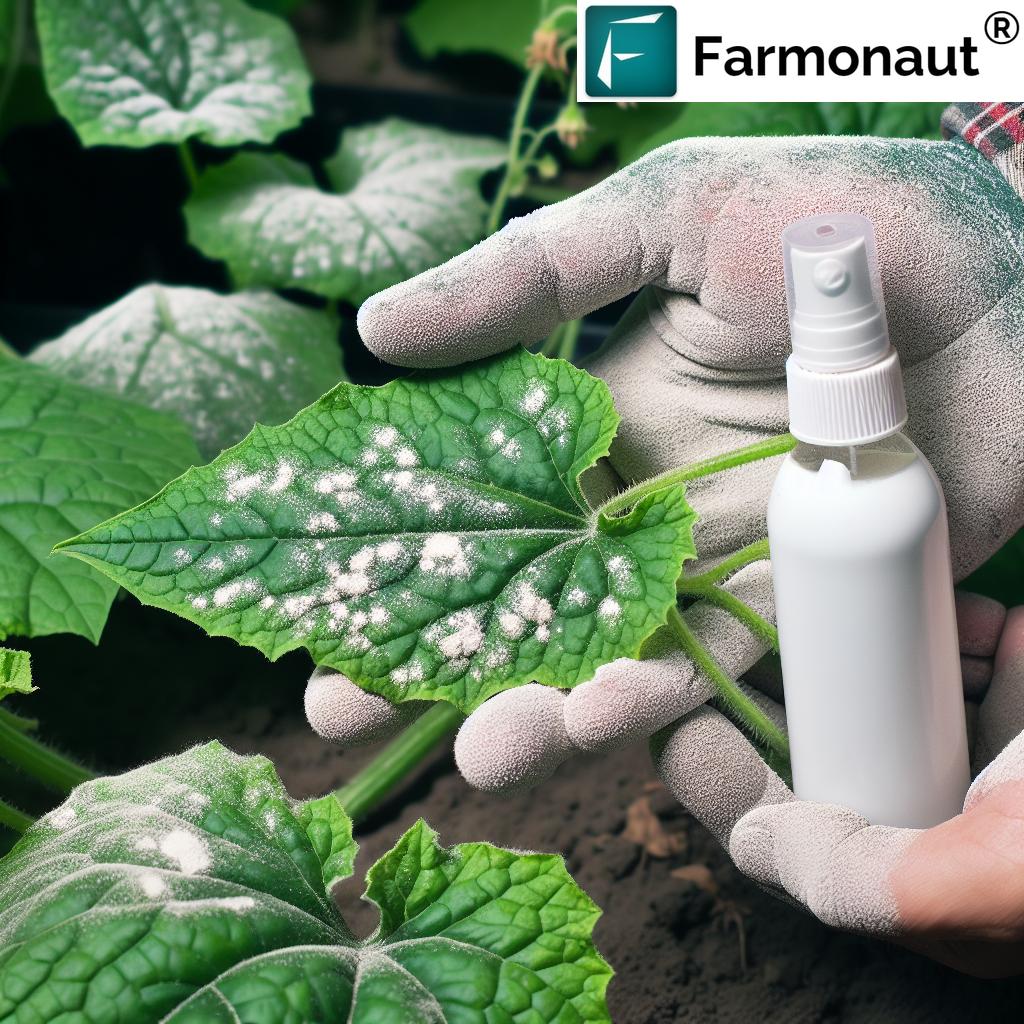
Remote sensing in agriculture leverages satellite imagery and aerial drones for timely crop health monitoring, soil moisture assessment, and pest detection. These technologies bring real-time insights directly to our screens, allowing us to intervene early and prevent yield losses.
- Main Functions: Crop monitoring, soil moisture measurement, pest and disease detection, growth stage tracking.
- Benefits: Early identification of issues, reduced crop loss, and optimized resource use.
Resource:
Explore Remote Sensing in Agriculture -
4. Variable Rate Technology (VRT)
Variable rate technology (VRT) empowers us to apply inputs like water, fertilizer, and pesticides at varying rates across our fields. By analyzing remote sensing data, we can deliver the right amount of inputs to each zone, improving input efficiency and crop yield.
- Main Functions: Site-specific input application, nutrient prescription mapping, fertilizer / pesticide optimization.
- Benefits: Reduced input costs, higher yields, and lower
environmental impact .
Resource:
In-depth insight into VRT Solutions -
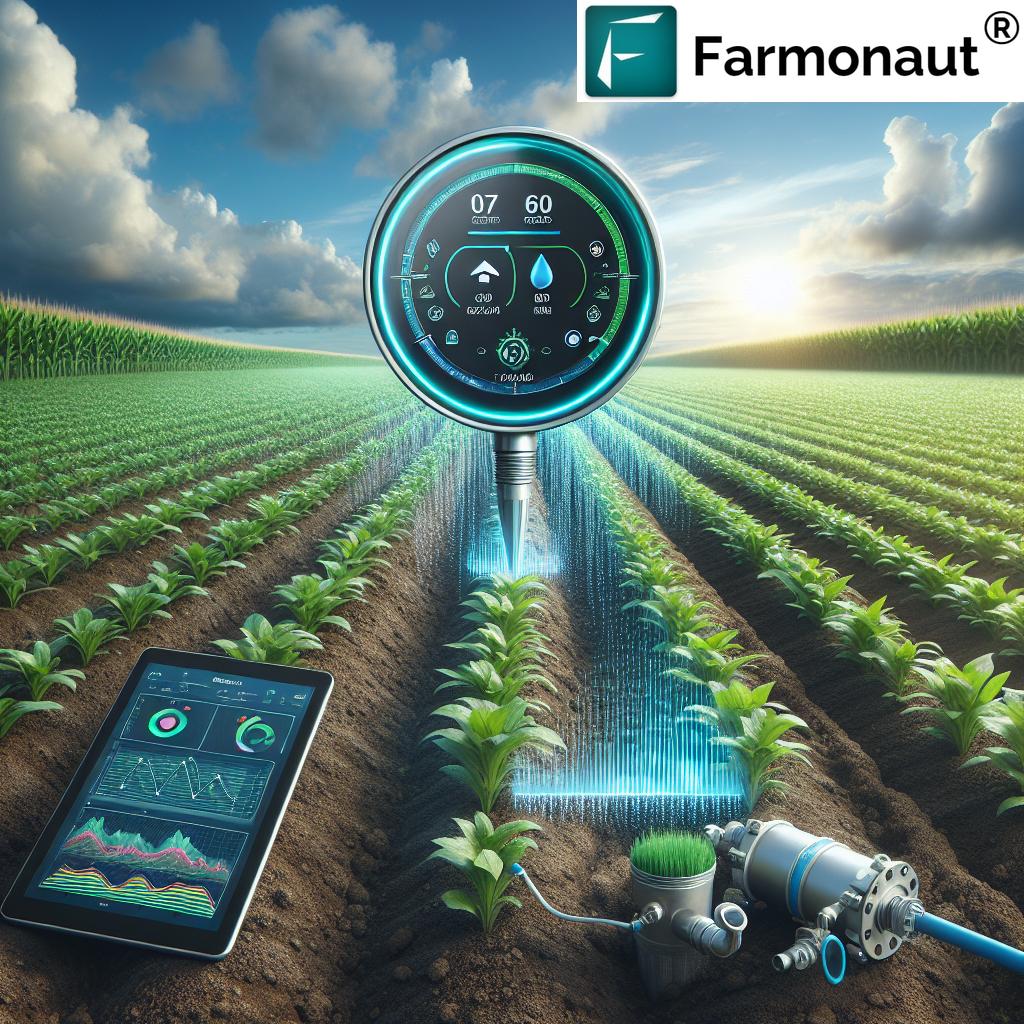
5. Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT revolutionizes farming by connecting various devices—soil moisture sensors, weather stations, automated irrigation regulators—to central crop monitoring systems. This continuous data flow spots issues as soon as they arise and enables automation, improving efficiency and yield.
- Main Functions: Continuous monitoring of field conditions, automated irrigation and input control, real-time alerts.
- Benefits: Improved input usage, lower labor costs, and enhanced response time.
Resource:
How IoT Advances Precision Agriculture -
6. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI in precision agriculture analyzes vast swaths of farm data to predict pest infestations, crop diseases, irrigation needs, and even harvest timing. Machine learning algorithms detect patterns invisible to the human eye, driving better decisions and making crop management both proactive and reactive.
- Main Functions: Yield forecasting, pest/disease detection, irrigation scheduling, data analytics for resource optimization.
- Benefits: Optimal input use, higher crop yields, and more efficient farm management.
Resource:
Learn about AI in Agriculture -
7. Farm Management Software & Data Analytics Platforms
Centralized farm management software platforms and data analytics suites integrate and analyze information from all our devices and sensors. These tools help us track crop health, manage operations, and streamline decision-making.
- Main Functions: Data aggregation, visualization, action planning, resource tracking, profitability analysis.
- Benefits: Transparency, accountability, enhanced planning, and support for sustainable farming practices.
Resource: Explore Farm Management Tools
Technology Impact Comparison Table: Precision Farming Technologies
| Technology Name | Main Function | Estimated Yield Increase (%) | Sustainability Benefits | Current Adoption Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Positioning System (GPS) | Instrument Guidance, Precise Field Mapping, Input Application | 10–15% | Reduced fertilizer/pesticide waste, lower emissions | High |
| Geographic Information Systems (GIS) | Spatial Data Analysis and Visualization | 6–12% | Enables targeted interventions, reduces over-application of inputs | Medium |
| Remote Sensing (Satellite/Drones) | Crop Health, Soil Moisture & Pest Monitoring | 15–30% | Early issue detection reduces losses, supports timely responses | Medium |
| Variable Rate Technology (VRT) | Input Application at Variable Rates | 8–18% | Reduces chemical & water use, improves efficiency | Medium |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Continuous Field Monitoring | 10–20% | Minimizes overuse of water/inputs, allows rapid intervention | Low |
| AI & Machine Learning | Prediction, Detection, and Recommendation | 12–28% | Detection of anomalies, reduces losses and misuse | Medium |
| Farm Management Software & Analytics | Integrated Planning & Decision Support | 5–14% | Enables holistic resource management & traceability | Medium to High |
Farmonaut: Affordable Precision Agriculture for All
Farmonaut is at the forefront of making precision farming accessible and affordable to farmers globally. We believe every farmer deserves real-time insights and advanced tools—irrespective of their farm’s size or location.
Our platform leverages satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-powered advisory, and blockchain traceability to deliver actionable data and expert advice via smartphone, web, or API—all without requiring expensive on-field hardware.
Key Precision Farming Features on Farmonaut
-
Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Utilizing multi-spectral satellite imagery for real-time vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture monitoring, and pest detection. This enables precise and timely interventions.
Learn more about Large-Scale Farm Management with Farmonaut - Jeevn AI Advisory System: Our AI-driven advisor analyzes satellite data and provides personalized crop management recommendations, weather forecasts, and pest management advisory—helping farmers get the most out of every yield.
-
Blockchain Traceability: With Farmonaut’s traceability solution, every step of the crop journey—from farm to consumer—can be tracked and verified on a secure blockchain ledger.
Explore Blockchain-Based Agriculture Traceability -
Resource & Fleet Management: Track fleet and optimize farm machinery usage, reducing operational costs.
Optimize Fleet with Farmonaut Solutions -
Carbon Footprinting: Monitor and minimize your environmental impact by quantifying farming emissions.
Discover Sustainability Monitoring -
Satellite-Based Crop Loan & Insurance Management: Receive satellite verification for faster, more reliable crop loan approvals and insurance claims.
Learn about Crop Loan & Insurance Verification
Note: With Farmonaut, farmers, agribusinesses, and supporting organizations can reduce input costs, improve yield outcomes, enhance traceability, and actively promote sustainable agriculture by leveraging satellite data and AI.
The Future of Precision Agriculture: Trends to Watch
The ongoing integration of AI, big data, machine learning, and autonomous equipment continues to redefine precision farming. Here are the most promising trends we see emerging:
- Autonomous Machinery: Self-driving tractors and harvesters boost efficiency, labor savings, and input precision.
- AI & Machine Learning Expansion: Automated pest detection, predictive weather analytics, and real-time disease forecasting will further minimize losses.
- IoT & Big Data Integration: Larger connected ecosystems with more sensors mean greater data for insight-driven decisions.
- Sustainable Practices: Micro-irrigation, renewable energy integration, and persistent site-specific management will continue to reduce farming’s environmental footprint.
Looking ahead, the adoption of precision farming technologies will not be a luxury, but a necessity—for both sustainable and profitable agriculture globally.
Challenges and Considerations in Precision Farming
As with all transformative technologies, precision agriculture presents practical challenges that we need to address to ensure successful and widespread adoption.
- High Initial Costs: Implementing advanced systems and devices requires considerable investment, although solutions like Farmonaut’s satellite-based approach greatly lower these barriers for smaller farms.
- Technical Expertise: Utilizing precision agriculture technologies often demands training and continuous learning. However, simplified interfaces and AI-driven advice are closing the knowledge gap.
- Data Management & Security: The massive volume of farm data requires robust systems for storage, analysis, and data privacy—areas we at Farmonaut address with secure platforms and blockchain.
- Connectivity Issues: Many rural areas still lack reliable internet—an essential for remote data transmission. Offline functionality and API integrations help alleviate some friction.
Getting Started: Accessing Precision Agriculture with Farmonaut
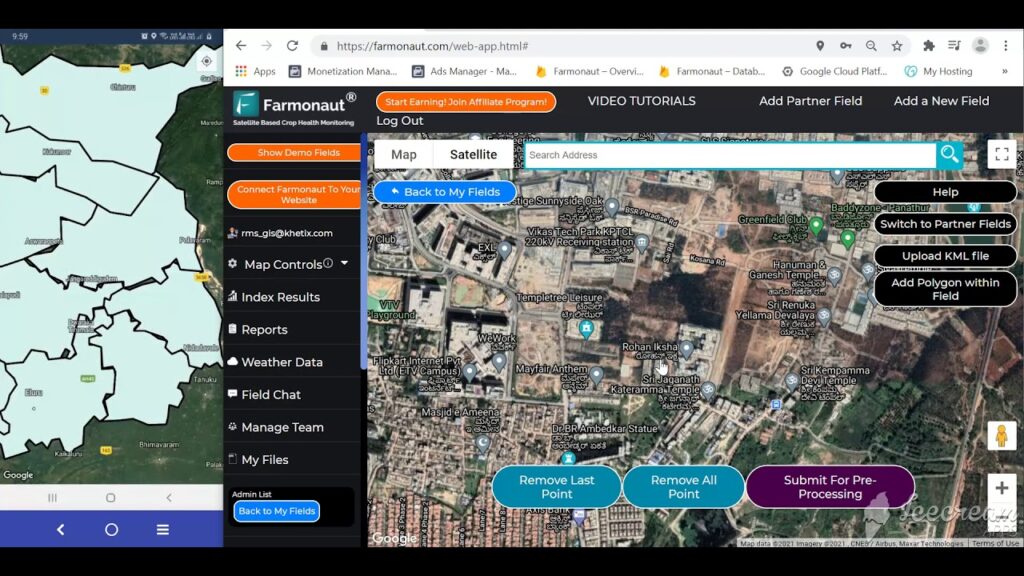
Ready to experience the advantages of modern data-driven farming? With Farmonaut, you don’t need substantial investment in new machinery—just a mobile phone or web browser is enough. Here’s how to begin:
- Register on the Farmonaut Platform via web, Android, or iOS app for instant access to your crop monitoring dashboard.
- Add your fields: Draw or upload boundaries for accurate satellite-based monitoring.
- Monitor Your Crops: Track vegetation health, soil moisture, pest risks, and more—get alerts and precise recommendations.
- Automate Resources: Use the Jeevn AI Advisor for personalized strategies that optimize irrigation, fertilizer use, and pest control.
- Scale Up As Needed: From single fields up to large plantations, Farmonaut adapts to your operation’s scale.
Want to automate farm data integration? Access Farmonaut’s API and Developer Docs for advanced applications.
Choose a Farmonaut Subscription Plan:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is precision farming, and how does it differ from traditional farming?
Precision farming is a data-driven, technology-enabled approach to managing field variability in agriculture. By employing satellite imagery, AI, IoT sensors, and advanced analytics, we apply inputs only where and when needed, maximizing resource use and minimizing waste. In contrast, traditional farming often uses blanket applications, leading to inefficiencies and higher environmental impacts.
How does remote sensing in agriculture benefit farmers?
Remote sensing, including satellite imagery and drones, offers near-real-time assessment of crop health, soil moisture, and potential threats. It supports early detection of pest or disease outbreaks, allowing for rapid and targeted interventions that reduce crop losses and optimize resources.
What is variable rate technology (VRT)?
Variable rate technology enables the application of inputs at different rates across a field based on real-time data analysis. This brings optimization by ensuring each field area receives exactly what it needs—improving efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and boosting yields.
How does AI in precision agriculture enhance farm operations?
AI in precision agriculture processes huge volumes of farm data and offers insights for pest detection, crop disease forecasting, input scheduling, and yield prediction. This leads to smarter, quicker, and more impactful decisions.
How does Farmonaut support sustainability and resource management?
Farmonaut provides detailed carbon footprint tracking, satellite-based monitoring, and AI-driven advice to foster both sustainability and efficiency. Our platform supports traceability, reduces input waste, and helps manage resources—enhancing both farm profitability and the health of our environment.
Is Farmonaut suitable for small and medium-scale farms?
Absolutely. Farmonaut’s low-cost, satellite-based methodology and scalable subscription model make it ideal for both smallholders and large agribusinesses. It’s all about democratizing access to precision farming!
Conclusion: Transforming Agriculture with Technology & Data
Precision farming is reshaping agriculture as we know it. By integrating GPS, GIS, remote sensing, VRT, IoT, AI, and data analytics into our daily farm management routines, we are boosting efficiency, safeguarding the environment, and driving sustainable crop yields.
Farmonaut stands as a leader, making advanced crop monitoring accessible and actionable for farmers worldwide—opening the doors to a more informed, profitable, and sustainable farm future.
Join us on the journey toward precision agriculture—empower your field with the tools and data that ensure you stay ahead in tomorrow’s farming.