Agricultural Revolution: 4 Shocking Advances Revealed
“AI-driven digital farming has increased crop yields by up to 30% in the last decade.”
Introduction: Understanding the Agricultural Revolution
Our journey as humans is inseparable from the history of agriculture. The term agricultural revolution describes several transformative periods when revolutionary farming innovations and agriculture advancements dramatically increased food production and redefined our societies, economies, and environments. From the earliest domestication of plants and animals to the current surge in AI-driven technologies and digital farming, each epoch has shaped not just the way we farm, but also how we live, trade, and protect our planet’s resources.
In this comprehensive review, we unravel the four seismic agricultural advances that shocked the world and continue to impact everything from food security to sustainable agricultural practices and beyond. As stewards of modern agriculture, we dive deep into:
- The ancient Neolithic Revolution
- The transformative British Agricultural Revolution
- The productivity surge of the Green Revolution
- The ongoing Digital and AI Revolution
We’ll also explore how agroforestry and other sustainable innovations are rewriting the rules of agricultural management, and how pioneering platforms like Farmonaut are making precision agriculture accessible and affordable for farms of all scales. This knowledge empowers us to make informed choices that ensure bountiful harvests and a healthier planet for generations to come.
The First Agricultural Revolution: The Neolithic Revolution
Let’s take a step back over 10,000 years—to a world where our ancestors roamed as hunter-gatherers. The Neolithic Revolution marked a turning point that transformed the very fabric of human existence. With the domestication of plants and animals, humans shifted from a nomadic lifestyle to building permanent settlements. We began cultivating staple crops like wheat, barley, rice, and maize, and rearing sheep, goats, and cattle.
Key Innovations in Early Agriculture
- Domestication: Carefully selecting and planting wild plants and taming animals for food, labor, and materials.
- Permanent Settlements: Communities developed around fertile lands, creating the blueprint for social organization and trade.
- Tools Advancement: The first ploughs, sickles, grinding stones, and irrigation schemes increased productivity and laid foundations for later technologies.
- Population Growth: Stable food sources spurred explosive growth in human numbers and the development of more complex societies.
These changes didn’t just transform food production—they birthed new economies, expanded trade routes, and set the stage for urban centers. As we tamed the land, we also began exerting significant influence on our environments, a narrative that continues to this day.
The first agricultural revolution underpins all later agriculture advancements. Its outcomes—both beneficial and challenging—are ever relevant as we explore modern sustainability, the role of digital farming technologies, and the integration of agroforestry benefits into our livelihoods.
The Second Agricultural Revolution: The British Agricultural Revolution
Fast-forward several millennia to 17th–19th century Britain, where a second wave of farming innovations catalyzed another leap in agricultural productivity. The British Agricultural Revolution turned traditional systems on their head with transformative breakthroughs in crop rotation systems, selective breeding, consolidated land management, and the mechanization of daily farm tasks.
Driving Forces Behind Increased Productivity
- Crop Rotation Systems: The Norfolk system introduced a 4-course rotation of wheat, turnips, barley, and clover—preserving soil fertility, reducing pests, and minimizing fallow lands.
- Enclosure Movement: Consolidation of once-shared fields into individually owned landholdings enabled more efficient management and innovation.
- Selective Breeding: Robert Bakewell and others selectively bred livestock—improving the size, strength, and output of sheep, cattle, and goats.
- Mechanization: Jethro Tull’s seed drill mechanized planting, improving seed distribution, reducing labor, and boosting yields.
This era was pivotal in breaking the cycle of food scarcity. The resulting surpluses catalyzed urbanization—population growth in cities, a new labor force for the Industrial Revolution, and the development of more complex economies.
Lasting Impact of British Agricultural Innovations
- Farming became more efficient and profitable, laying the groundwork for modern technologies and digital farming.
- Intensified agricultural productivity and crop diversity supported massive population growth and shifted global economic balances.
- However, enclosure and mechanization also had social implications—some traditional communities were displaced, and environments felt new pressures.
By analyzing the legacy of the British agricultural revolution, we gain crucial insight into today’s efforts to balance productivity, environmental stewardship, and sustainable agricultural practices.
The Third Agricultural Revolution: The Green Revolution
The 20th century saw the global challenge of hunger and malnutrition addressed with unprecedented urgency. The Green Revolution unleashed agriculture advancements that included high-yielding crops, chemical fertilizers, synthetic pesticides, and terminological modification of irrigation systems. While this wave primarily impacted Asia and Latin America, its influences reshaped worldwide farming and food systems.
Hallmarks of the Green Revolution
- High-Yielding Varieties (HYVs): Wheat and rice strains bred for robust yields in various climates.
- Fertilizers & Pesticides: Introduction of chemical nutrients and pest-control agents dramatically increased harvest potential but sparked critical environmental debates.
- Irrigation Expansion: Massive investments in systems to ensure water access and crop reliability.
- Mechanization & Management Techniques: Adoption of new tools for planting, tending, and harvesting at larger scales.
The outcomes were extraordinary. Countries like India witnessed a remarkable transformation in food sufficiency. Food production soared, labor shifted as rural populations urbanized, and forestry was impacted through land conversion.
But every advancement carries complex trade-offs. The Green Revolution’s reliance on external inputs accelerated concerns over soil depletion, loss of biodiversity, increased pollution, and long-term sustainability. Today, we look to smarter management, technology, and ecological design to address these legacies.
“Agroforestry practices can boost farm biodiversity by over 50% compared to conventional monoculture systems.”
Key Takeaways from the Green Revolution
- Production increases: Global grain output rose by up to 60% in several regions.
- Ecological costs: Soil fertility, water resources, and forest areas have been stressed, highlighting the need for integrated sustainable agricultural practices and improved resource management.
- Equitable access: Disparities emerged between large and small-scale farmers—driving a new search for technology that is both affordable and impactful, such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based digital farming.
The Fourth Agricultural Revolution: The Digital and AI Revolution
Today, we are living through perhaps the most rapidly evolving agricultural revolution in history. The Fourth Agricultural Revolution—often called digital farming or AI-driven agriculture—integrates precision agriculture, artificial intelligence, and advanced data-driven management systems across fields and farms of all sizes.
Digital Farming Technologies Transforming Agriculture
- Precision Agriculture: GPS-guided tractors, soil nutrition maps, drones, satellites, and sensors enable pinpoint application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- AI and Machine Learning: Algorithms analyze big data sets for yield predictions, early disease detection, optimal planting schedules, and custom crop recommendations—see the Farmonaut Satellite & Weather API for integrated analytics, or dive into developer documentation.
- Robotics & Automation: Autonomous planting, harvesting, and weeding machines reduce the need for manual labor and boost efficiency in large and small operations alike.
- Blockchain Traceability: Entire food journeys—from field to fork—are tracked securely, building consumer trust and tackling fraud. Explore Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability for transparent supply chains.
- Resource and Fleet Management: Smart management systems optimize equipment usage and reduce environmental footprints. Farmonaut’s Fleet Management tool offers seamless monitoring for agribusinesses.
Types of AI-Driven Solutions and Their Impact in Agriculture
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Personalized, real-time recommendations using satellite & field data, like those provided by Farmonaut, support optimal crop management and boost farm productivity.
- Carbon Footprinting: Monitoring and managing farm emissions using tools like Farmonaut’s carbon footprint solution strengthens sustainability in agricultural management and compliance.
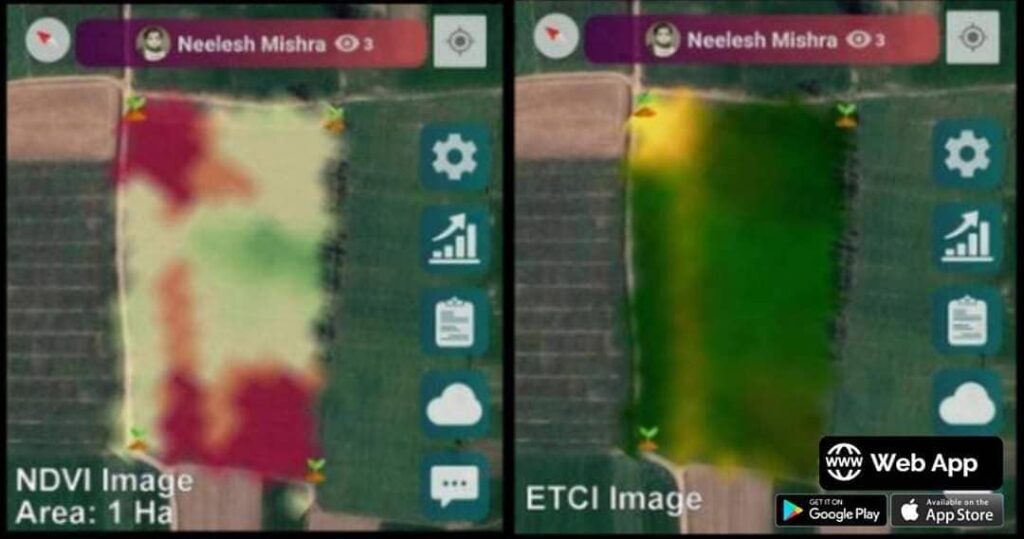
- Satellite Crop Health Monitoring: Affordable, hardware-free insights into crop health, soil moisture, and nutrient status through advanced platforms.
- Digital Apps and API Accessibility: Solutions for Android, iOS, web, and true API integration make precision technologies universally reachable.
The impact of AI in agriculture is already visible—with digital & AI-powered solutions supporting yield gains up to 30% and driving the future of sustainable agricultural practices. Crucially, these technologies democratize agriculture advancements by putting powerful farm management tools in the hands of both small and large producers worldwide.
Agroforestry: Integrating Trees into Agricultural Systems
An often overlooked breakthrough in the history of agriculture is the strategic integration of trees alongside traditional crops and livestock—known as agroforestry. Unlike monoculture, agroforestry invites ecological diversity directly onto the farm, blending the best of agriculture and forestry.
Key Agroforestry Benefits
- Environmental: Soil conservation, reduced erosion, and improved moisture retention.
Trees also act as carbon sinks, helping to combat climate change. - Biodiversity: Agroforestry practices can boost farm biodiversity by over 50% versus monoculture. Mixed systems create habitats and foster wildlife, ensuring healthy, balanced environments.
- Economic: Income diversification through the sale of timber, fruits, nuts, and resins—providing resilience against market shocks.
- Social: Enhances food security and supports local communities by diversifying food sources and rural economies.
Whether shelterbelts in the British countryside or large-scale forest-crop plantation management in tropical regions, agroforestry adapts to every climate and context. These sustainable practices bridge the gap between modern productivity and ecological longevity.
Comparative Impact Table: The Advances Side-by-Side
| Agricultural Advance | Year/Period Introduced (Estimated) | Key Technologies/Practices | Impact on Productivity (Estimated % Increase) | Sustainability Benefits | Notable Examples or Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neolithic Revolution | ~10,000 BCE | Domestication of plants and animals, basic hand tools, early irrigation | 200% – 400% (vs hunter-gatherer output) | Enabled permanent settlements, set stage for more sustainable land management | Domesticated wheat, barley, rice, maize; first herds of cattle, sheep, goats |
| British Agricultural Revolution | 17th-19th centuries | Crop rotation systems, selective livestock breeding, mechanization, land enclosure | 100% – 150% | Better soil conservation, reduced fallow, increased efficiency | Norfolk 4-course system, Jethro Tull’s seed drill, improved livestock breeds |
| Green Revolution | 1940s-1970s | High-yielding crop varieties, synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, widespread irrigation | 50% – 60% | Reduced hunger, but led to soil depletion, biodiversity loss, pollution | HYV wheat/maize/rice, large-scale mechanization |
| Digital, AI, and Agroforestry Advancements | 2000s–present | Precision agriculture, satellite imagery, AI/machine learning, blockchain, robotics, agroforestry management | Up to 30% for AI-driven farms; up to 50% biodiversity boost for agroforestry | Major water, input, and emission savings; carbon sequestration; improved biodiversity | Farmonaut digital platform, Jeevn AI, advanced crop traceability, integrated agroforestry systems |
Farmonaut: Leading the Digital Shift in Agricultural Management
As we embrace the Digital and AI Revolution, making precision agriculture cost-effective, accessible, and actionable for farmers globally becomes paramount. Farmonaut, a pioneering agricultural technology company, is at the forefront of this transformation. Let’s explore how Farmonaut brings together satellite imagery, AI-based advisory, blockchain traceability, and advanced management systems to power next-gen farming.
Farmonaut’s Advanced Technologies
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Real-time NDVI, soil moisture, and crop stress analysis. Farmers receive actionable insights for irrigation, fertilizer, and pest management.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Personalized, dynamic advice that draws from remote sensing, weather, and field data—helping maximize yields, efficiency, and sustainability.
- Blockchain-Enabled Traceability: Full visibility across the supply chain, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud. Find out more about product authenticity with Farmonaut’s traceability solutions.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Large agribusinesses efficiently monitor field operations, optimize logistics, and minimize resource wastage. Explore the potential at Farmonaut Fleet Management.
- Carbon Footprinting: Track and act on real-time farm emissions—ensuring compliance, environmental credits, and a greener footprint. Learn about Farmonaut’s carbon monitoring.
- Flexible Business Model: Individual farmers, cooperatives, governments, agribusinesses, and even developers (via API: Farmonaut Satellite & Weather API) are serviced using affordable subscription plans.
Farmonaut isn’t an input marketplace, nor a regulatory body; it’s the digital backbone of modern farm management—making agriculture advancements a reality at farmonaut.com.
Curious about how this platform can make a difference in your fields? The Large-Scale Farm Management solution is perfect for agribusinesses seeking detailed, scalable control across multiple land parcels.
Sustainable Practices: The Backbone of Future-Focused Agriculture
Every phase of the agricultural revolution has shown us that lasting productivity depends on maintaining the health of soil, water, forestry, and related environments. In the digital era, sustainable agricultural practices are more advanced and data-driven than ever, integrating:
- Rotation and Diversification: Adaptive crop rotation systems, mixed cropping, and agroforestry reduce disease, conserve resources, and support biodiversity.
- Resource Optimization: Using real-time analytics to minimize fertilizer, pesticide, and water use—protecting soil and securing long-term yields.
- Data-Driven Carbon Management: Tracking emissions, analyzing trends, and taking action with dedicated tools. See Farmonaut carbon footprinting.
- Traceability and Transparency: Empowering smart consumers and supporting regulatory frameworks with trusted data; discover traceability platforms.
Embracing these agriculture advancements not only preserves our farmlands and forests but also supports climate resilience and market competitiveness in an ever-more connected world.
Impact on Forestry: From Deforestation to Agroecological Harmony
The legacy of each agricultural revolution isn’t limited to fields—it echoes deeply in the world’s forests. As agricultural land expanded, especially during the Green Revolution, deforestation increased, disrupting precious ecosystems and imperiling crucial biodiversity.
However, this narrative is changing rapidly thanks to the agroforestry benefits and smarter land management practices of the Digital Revolution. By integrating trees into farming systems, we are restoring balance—improving soil stability, recharging water tables, and providing habitat corridors for wildlife.
Farmonaut’s Role in Forest-Agriculture Synergy
- Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory: Farmonaut’s platform provides critical data and guidance for large-scale forest and crop integration, promoting environmental harmony and reducing destructive land conversion.
- Smart Monitoring: Satellite imagery helps track deforestation, plan reforestation, and optimize tree placement to maximize ecosystem benefits.
As society calls for both food security and natural conservation, sustainable agricultural practices and eco-sensitive management systems are the blueprint for a thriving future.
Conclusion: Lessons from the Agricultural Revolutions
The agricultural revolution is a story of adaptation, innovation, and responsibility. From ancient domestication to digital farming technologies and the promise of AI, every major advance has brought both staggering opportunity and vital challenges.
- We learned that the management of land and natural resources must be both ambitious and sustainable.
- We saw how technology—from the first sickle to modern AI—transforms food production, empowers communities, and shapes societies.
- We recognized the power of integration: agroforestry, diversified cropping, and transparency-driven supply chains all reinforce resilience.
- We embraced the responsibility to restore and protect biodiversity, not just for our own food security today, but for the prosperity of future generations.
By harnessing the best of agriculture advancements—from precision agriculture to holistic agroforestry—and championing advanced, affordable solutions like Farmonaut, we can ensure that the next chapter in the history of agriculture is one of abundance, balance, and hope.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about the Agricultural Revolution and Modern Agriculture
What is the agricultural revolution?
The agricultural revolution refers to major periods in which key agriculture advancements—such as plant and animal domestication, mechanization, chemistry, and digital technologies—transformed global farming, increased food production, and reshaped societies and economies.
How did crop rotation systems improve sustainable agricultural practices?
By alternating different crops (like wheat, barley, clover, and turnips) yearly on a field, crop rotation systems preserved soil fertility, limited pests, and minimized the need for fallow periods, supporting long-term sustainable productivity.
What are the main digital farming technologies available today?
Core digital farming technologies include satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisory systems, precision soil and weather analytics, drone/sensor networks, robotic machinery, and blockchain for supply chain traceability.
How does AI impact agriculture and farming?
AI in agriculture empowers farmers to optimize planting, resource management, yield prediction, and disease control. It enables real-time decision-making, reduces waste, and increases sustainability through platforms like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI.
What are the benefits of agroforestry in agriculture?
Agroforestry integrates trees into farm systems, leading to improved soil and water quality, boosted biodiversity, increased resilience to climate shocks, additional income sources, and a reduction in agricultural carbon footprint.
Why is sustainable agriculture important today?
Sustainable agricultural systems ensure food security and economic viability while protecting natural resources and biodiversity—vital for community resilience in the face of climate change and population growth.
How can Farmonaut help me manage my farm efficiently?
Farmonaut provides farmers and agribusinesses with real-time satellite crop health monitoring, AI-based crop advisory, supply chain traceability, fleet/resource management, and sustainability tracking—making precision agriculture both affordable and powerful.
Where can I access Farmonaut’s digital agriculture solutions?
Farmonaut’s solutions are available via web and mobile apps (Android, iOS), and through API for integration into other platforms. Individual farmers, large agribusinesses, governments, and developers can all benefit from its modular offerings.
Farmonaut Subscriptions: Unlock Next-Gen Precision Agriculture
Transform your agriculture management with Farmonaut’s flexible, affordable subscription plans—tailored to suit everyone from individual farmers to large-scale agribusinesses and organizations. Enjoy real-time satellite insights, AI-driven advisories, traceability, resource management, and sustainability analytics—all accessible from anywhere with our user-friendly apps and robust API.
Ready to bring your farm into the future? Find the subscription tier that fits your needs below!