Hairy Caterpillars
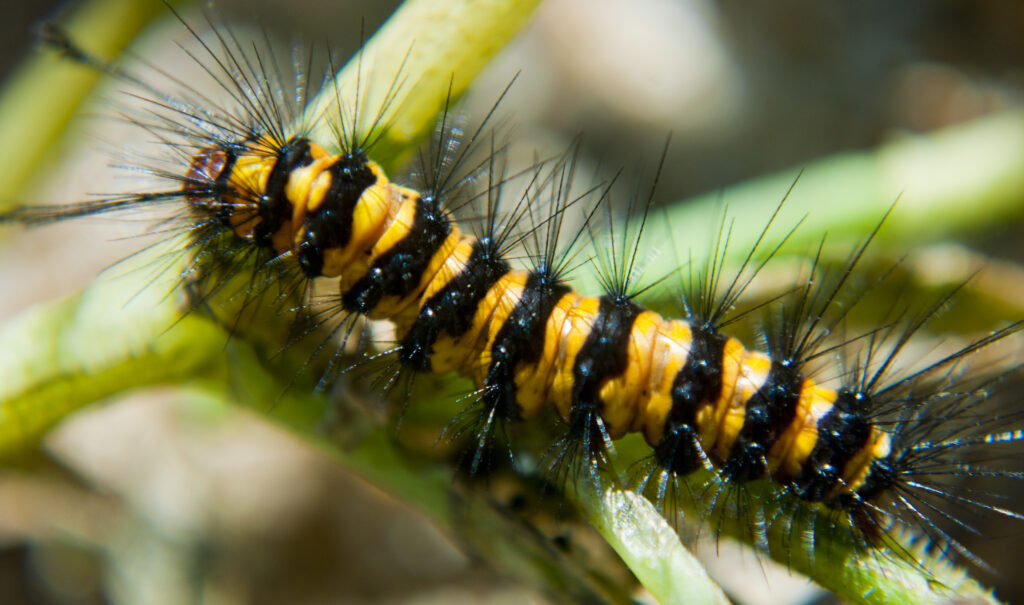

Hairy caterpillars
EUPROCTIS FRATERNA
Factors –
a- Defoliation of the mango trees caused by reddish brown, hairy larvae with single tufts on each end.
b- Young pupil larvae are covered with whitish hair.
c- The moth is bright yellow with darker lines and black dots on forewings.
Hosting body – MANGO
Identifiable traits
In the early stage of hairy caterpillars have long white hairs coming from the flanks of their body. Their main feed is leaves of mango trees in groups and several other tree species.
The developed/mature larvae feature a red head covered with white hair and a reddish brown body. Larvae pupate in a cocoon of hairs on branches and leaves and also have a single tuft in the head. The moths are bright yellow and has forewings with transversal lines which are dark and black dots near the edge of wings.
Inducing factors
They are similar to two species of caterpillars with similar features which damages leaves and defoliation. The females lay yellow, circular, flat eggs in clusters on the lower surface of leaves. Their laid eggs are suspicious because they are covered with yellow brown hair and scales over them. These larvae hatch generally between 4-10 days. They feed for about 13 to 29 days on tree leaves until they convert to a cocoon. In between 9-25 days in a silk cocoon the adult moth hatches. During winter season the larvae may perform dormancy.
Organic remedies
Burning torches can be used to terminate/decimate them as they feed in tight groups. Sprays of neem (Azadirachta indica L.) and dhatura (datura stramonium L.) extracts controls caterpillar populations and reduces it. The bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis is a microbial pesticide which kills the caterpillar by crippling the gut.
Chemical remedies
If available, always consider an integrated approach with preventive measures together with biological treatments. Insecticide sprays containing cyphermethrin, deltamethrin, fluvalinat are effective against hairy caterpillars.
Extra remedies
Regular monitoring of the orchard for eggs, larvae, moths and cocoons. Find, collect and destroy the caterpillars, cocoons and egg clusters in minor cases. Adult moths can be controlled using light traps.
We will keep posting about any such informative information on to our blogs, to help as many people as possible. Farmonaut is built upon a vision to bridge the technological gap between farmers and strives to bring state-of-the-art technologies in the hands of each and every farmer. For any queries/suggestions, please contact us at support@farmonaut.com.
We have some more interesting articles coming up soon. Stay tuned!
Wait!!
Before that…
Follow us at:
Facebook: https://facebook.com/farmonaut
Instagram: https://instagram.com/farmonaut
Twitter: https://twitter.com/farmonaut
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/farmonaut/
Pinterest: https://in.pinterest.com/farmonaut/
Tumblr: https://farmonaut.tumblr.com/
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCYWOOPPKATLgh4L6YRlYFOQ
AppLink: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.farmonaut.android
Website: https://farmonaut.com
Satellite Imagery: https://farmonaut.com/satellite-imagery
Satellite Imagery Samples: https://farmonaut.com/satellite-imagery-samples