Sweet Corn Insect Control: 7 Shocking Pest Killers!
Discover the most effective corn pest management and sweet corn insect control strategies to protect your yield, quality, and farm profitability. This comprehensive guide explores the primary pests threatening sweet corn, profiling their identification, damage symptoms, and the best IPM strategies for sweet corn, including cultural, biological, and chemical controls, natural predators, monitoring, and advanced technological solutions!
Meta Description: Sweet corn faces serious insect threats, but effective corn pest management and pest ID with IPM strategies can safeguard yield and quality. Discover shocking pest killers and controls now!
Table of Contents
- Why Insect Control Is Essential in Sweet Corn
- Primary Insect Pests of Sweet Corn: Identification and Damage
- Comparative Pest Control Methods Table
- Integrated Pest Management in Corn: Strategies & Controls
- Farmonaut for Precision Corn Pest Management
- Natural Predators and Biological Controls for Corn Pests
- Monitoring and Scouting: Keys to Effective Sweet Corn Insect Control
- Sweet Corn Insecticide Applications: Best Practices & Tips
- Advanced Techniques & Technology for IPM Strategies in Sweet Corn
- Summary & Conclusion
- FAQ: Sweet Corn Pest Control & IPM
Why Insect Control Is Essential in Sweet Corn
Sweet corn is a beloved staple in diets around the globe, cherished for its flavor, nutrition, and versatility. But every growing season, our crops face relentless insect threats that can cause significant yield loss and reduce crop quality. Whether we manage small family plots or large-scale commercial fields, maintaining healthy plants means understanding the primary pests targeting sweet corn and deploying integrated controls at the right time.
- Pest infestations can reduce yield by up to 80% if left unchecked.
- Insect damage impacts kernel development, plant vigor, and even opens entry for pathogens.
- Adopting corn pest management, IPM strategies for sweet corn, and advanced monitoring tools is essential for economic viability.
Let’s explore the 7 most impactful pest killers, their identification, and how we can use a holistic approach—including innovative technology—to master sweet corn insect control!
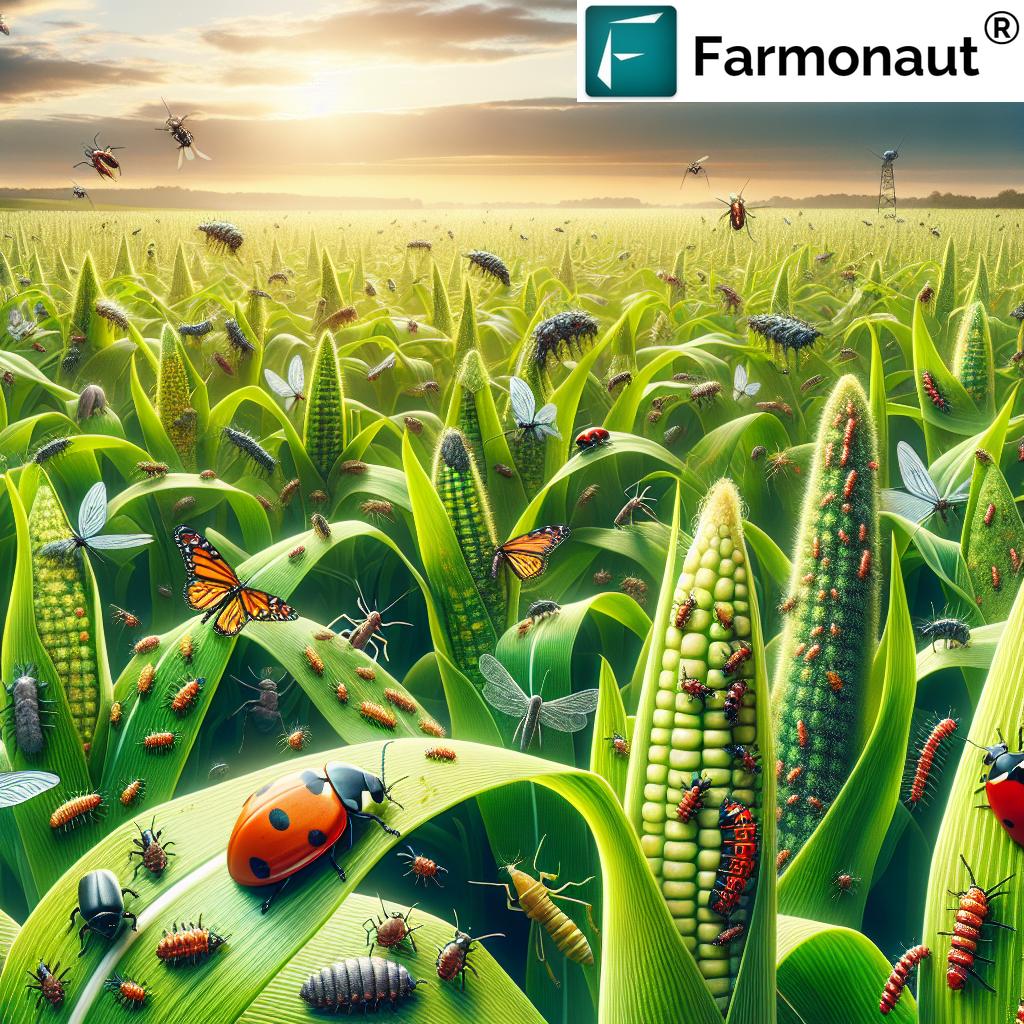
Primary Insect Pests of Sweet Corn: Identification and Damage
Correct identification of our corn pests is the foundation of effective management. Recognizing adult insects, their larvae, and damage symptoms is the first step in our defense. Let’s examine the seven most damaging insect pests of sweet corn and how targeted sweet corn insect control can drastically reduce yield losses.
- Corn Earworm (Helicoverpa zea)
- European Corn Borer (Ostrinia nubilalis)
- Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda)
- Aphids (e.g., Corn Leaf Aphid Rhopalosiphum maidis)
- Japanese Beetles (Popillia japonica)
- Stink Bugs (e.g., Green Stink Bug Chinavia halaris)
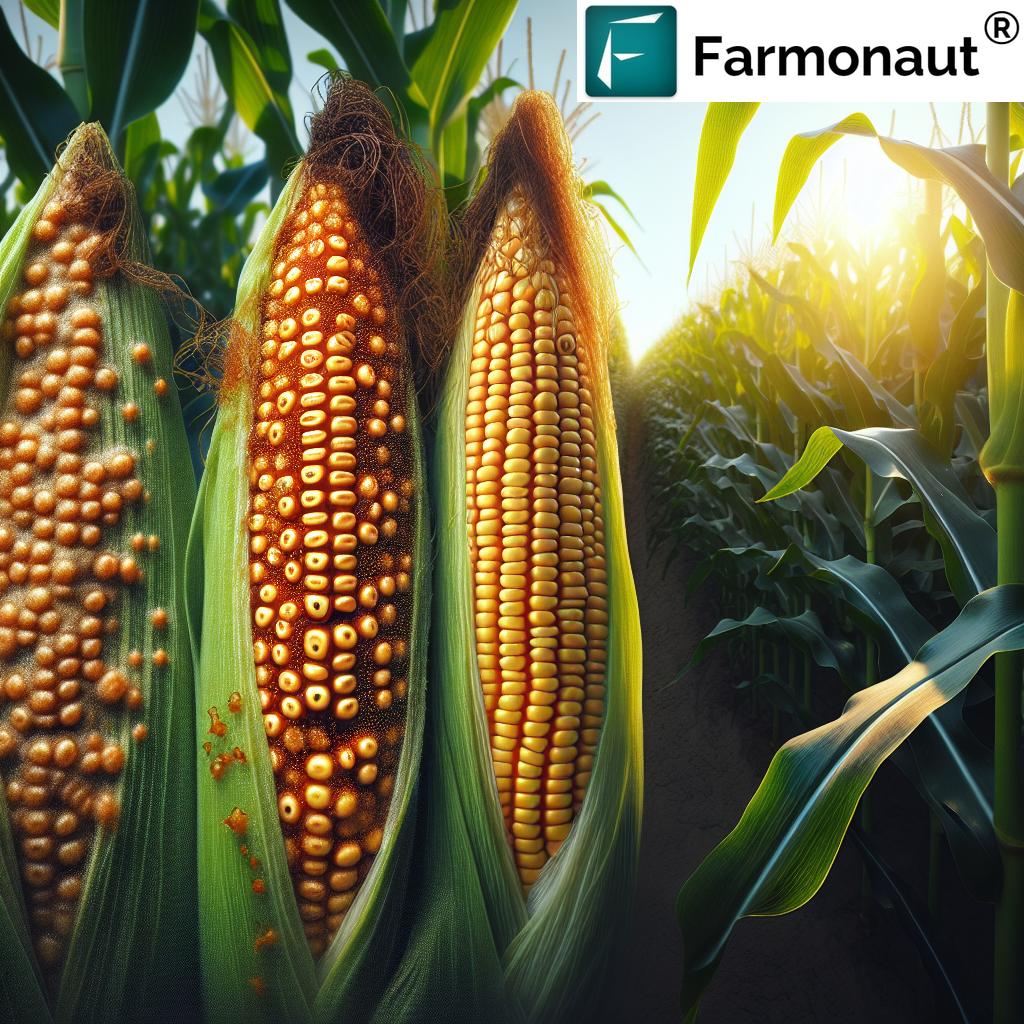
1. Corn Earworm (Helicoverpa zea): Identification, Damage & Control
- Identification: Adult moths are light brown with a wingspan of approximately 1.5 inches. Larvae vary in color from green to brown, bearing alternating light and dark stripes along their bodies.
- Damage: Larvae feed on corn silks and kernels, causing significant ear damage and sometimes affecting leaves and stems. Infestation leads to reduced yield and quality loss.
- Control: Once larvae enter the ear, chemical control becomes difficult. The key is timely insecticide applications during the silking stage to target young larvae on exposed ear tips. Effective sampling and monitoring using pheromone traps help us detect adult activity. (More on management)
2. European Corn Borer (Ostrinia nubilalis): Identification, Damage & Control
- Identification: Adults are yellowish-brown moths with wavy wing markings. The pale larvae, marked with dark spots, can grow up to an inch.
- Damage: Larvae tunnel into stalks and ears, causing structural weakness, plant breakage, and reduced corn yield.
- Control: Deploy pheromone traps to detect adult moth activity. Timely insecticide applications should be aimed at young larvae before they enter the plant tissues. Scouting for egg masses is critical. (More here)
3. Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda): Identification, Damage & Control
- Identification: Adult moths are grayish-brown, with larvae from green to brown, featuring a distinctive inverted “Y” mark on the head.
- Damage: Larvae feed on corn leaves, causing ragged holes, and sometimes attack ears by feeding on kernels.
- Control: Regular scouting for small larvae is essential. Insecticides should be applied when larvae are young, before damage becomes significant. Fall armyworm control in corn relies on rapid detection and intervention.
4. Aphids (e.g., Corn Leaf Aphid Rhopalosiphum maidis): Identification, Damage & Control
- Identification: Small, soft-bodied insects, usually green or black, located on leaves and tassels.
- Damage: Suck plant sap, reducing vigor, and excrete honeydew—leading to sooty mold. Heavy infestations can suppress growth.
- Control: Natural predators (lady beetles, lacewings) are highly effective. Severe populations may require insecticidal soaps or oils. (Source)
5. Japanese Beetles (Popillia japonica): Identification, Damage & Control
- Identification: Metallic green adults with coppery-brown wings.
- Damage: Feed on corn silks, interfering with pollination. Leads to poor kernel set.
- Control: Handpicking works for small fields; larger infestations may require targeted insecticides. (Source)
6. Stink Bugs (e.g., Green Stink Bug Chinavia halaris): Identification, Damage & Control
- Identification: Shield-shaped insects, green or brown, releasing a distinctive odor when disturbed.
- Damage: Pierce corn kernels with their mouthparts, causing shriveling and opening ears to secondary infections.
- Control: Monitoring and prompt insecticide application can reduce populations. (Read more)
Comparative Pest Control Methods Table
| Pest Name | Identification Features | Estimated Yield Loss Without Control (%) | Control Method | Estimated Effectiveness (%) | Application Timing / Method | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn Earworm (Helicoverpa zea) |
Light brown moth; larvae green to brown with stripes | 30-50% | Chemical (timed insecticide), IPM | 70-90% | Begin at first silk, repeat during silking | Medium |
| Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) |
Gray-brown moth, larvae with inverted “Y” on head | 25-70% | IPM, Biological (Bt), Chemical | 65-95% | Early larval stage; field scouting required | Variable (Low w/ Bt, Med-high w/ chemical) |
| European Corn Borer (Ostrinia nubilalis) |
Yellow-brown wavy moth, pale larvae w/ black spots | 20-35% | IPM, Chemical, Resistant varieties | 65-90% | Before larvae enter stalks/ears | Medium |
| Aphids | Small, soft-bodied; green/black on undersides | 10-20% | Biological, Natural Predators, Soaps | 60-95% | On detection; repeat if necessary | Low |
| Japanese Beetles | Metallic green/copper adults | 15-40% | Chemical, Handpicking | 70-85% | At pollination | Medium |
| Stink Bugs | Shield-shaped, green/brown, odoriferous | 5-15% | Chemical, Monitoring | 65-80% | Prior to/during kernel fill | Medium |
Integrated Pest Management in Corn: Winning Strategies for Sweet Corn Insect Control
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) in corn is the systematic, science-backed approach for sweet corn insect control. It emphasizes pest identification, monitoring, threshold-based intervention, and the use of cultural, biological, and chemical controls in harmony. Here’s how we can implement effective IPM strategies for sweet corn:
1. Cultural Controls
- Crop Rotation: Rotating corn with non-host crops interrupts pest life cycles, reducing resident pest populations significantly.
Read more on corn production management - Planting Timing: Early spring planting helps crops escape peak insect activity. This is particularly useful for pests whose populations increase through the season. (Source)
- Field Sanitation: Remove crop residues and plow after harvest to eliminate overwintering pest populations.
2. Biological Controls
- Natural Predators & Parasitoids: Encourage beneficial insects—like lady beetles, lacewings, and parasitic wasps—to naturally suppress aphids, eggs, and larvae. Providing flowering plants adjacent to cornfields supports natural predator populations.
- Biopesticides (Bt): Using products containing Bacillus thuringiensis targets caterpillar pests with reduced environmental and non-target impact.
3. Chemical Controls & Resistance Management
- Best Insecticides for Sweet Corn: Choose insecticides based on accurate monitoring and established economic thresholds. Overuse risks resistance; always rotate insecticides with different modes of action. (Details)
- Seed Treatments: Protect young corn plants from early-season insects through insecticide seed coatings.
4. Resistant Varieties
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Sweet Corn: GM sweet corn varieties expressing Bt proteins are powerful against lepidopteran pests (like earworm and armyworm), reducing the need for chemical interventions. Supplementary insecticide applications may still be needed under high pest pressure.
Want to integrate satellite-based crop health and pest detection data into your systems?
Try Farmonaut’s API for real-time monitoring and decision-making, or explore detailed documentation here: API Developer Docs
Drive transparency in your agribusiness supply chains with Farmonaut’s blockchain-based Product Traceability. Enhance trust with farm-to-plate data!
5. Monitoring & Scouting (See Details Below)
- Employ pheromone traps for early detection of adult moth activity.
- Regular field scouting means timely interventions and minimizes overuse of chemicals.
- Field notes, satellite crop imagery, and digital records (see below) help us track pest movement and severity.
Download the Farmonaut App today to access satellite-based crop health, pest detection, and AI farm advisory personalized for your field!
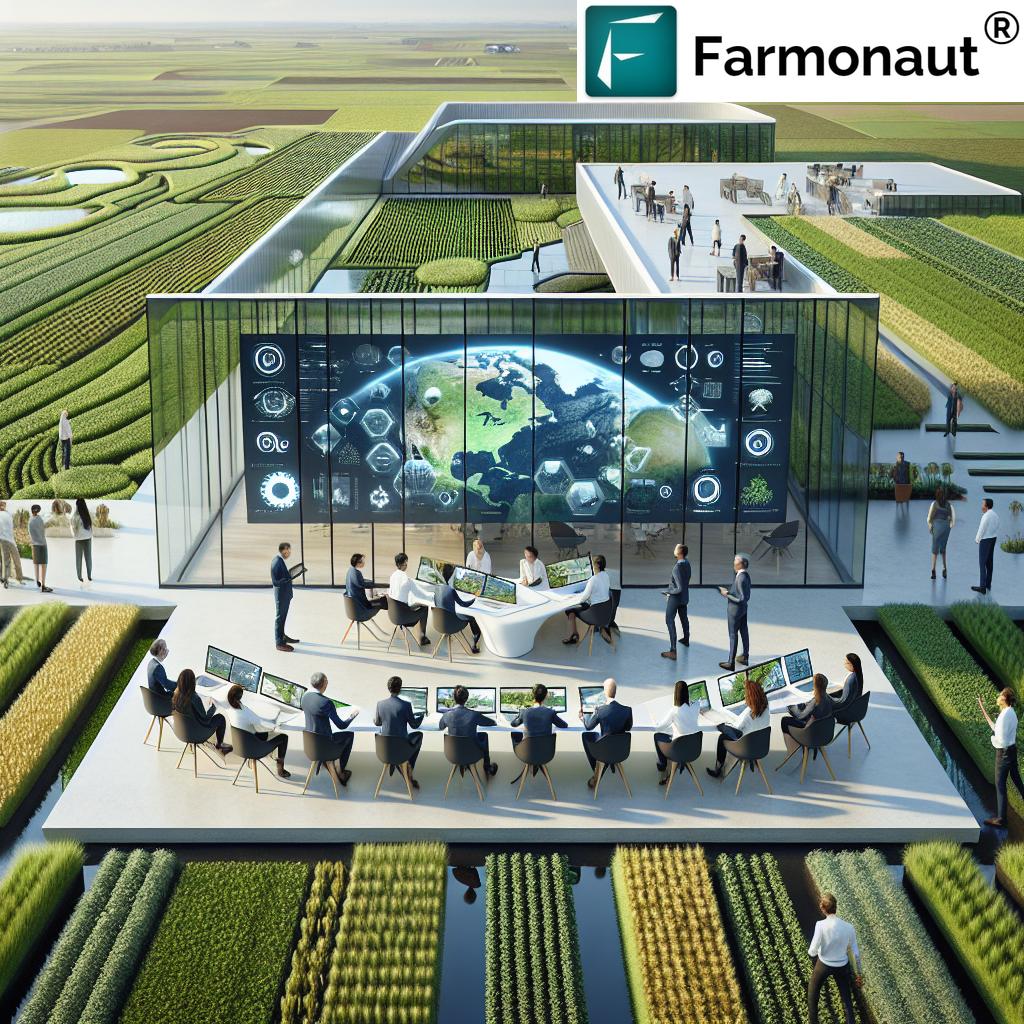
Farmonaut for Precision Corn Pest Management
Farmonaut empowers us to revolutionize sweet corn insect control with precision monitoring, AI insights, and digital alerts, optimizing both yield and resource use. Here’s how:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Real-time NDVI maps, moisture indices, and temperature data flag early signs of pest stress—enabling targeted scouting and intervention.
- Jeevn AI Advisory: Receives personalized pest management tips, weather forecasts, and actionable suggestions for corn pest management.
- Mobile, web, and API access: Decide promptly from anywhere with Farmonaut’s cross-platform app—monitor, compare, and protect multiple fields at once.
- Compliance and Reporting: Satellite-based blockchain traceability ensures transparency across the supply chain. Great for food companies and exporters—learn more about traceability solutions.
- Sustainability: Track and manage your carbon footprint for compliant, climate-smart corn operations!
Farmonaut enables cost-effective, scalable, and eco-friendly pest management for small, medium, and large sweet corn crops.
Looking to manage dozens or thousands of hectares? Check out large-scale farm management with Farmonaut agro admin tools for full-field monitoring and reporting.
Natural Controls and Predators for Corn Pests
Natural predators for corn pests play an indispensable role in integrated pest management in corn. Our goal is to build a robust ecosystem in and around the sweet corn fields to naturally reduce insect populations, enhance crop resilience, and minimize chemical usage. Here’s how we can harness nature for sweet corn insect control:
- Lady Beetles (Ladybugs): Voracious consumers of aphids and soft-bodied insects. Release or attract them with border flowers.
- Lacewings: Larvae feed actively on aphids, moth eggs, and young caterpillars.
- Parasitic Wasps: Many wasps lay eggs inside pest larvae, suppressing earworm, armyworm, and corn borer populations.
Encouraging these natural controls—by planting companion flowers and avoiding broad-spectrum chemicals—can be integral in our corn ear damage prevention and overall field IPM strategies for sweet corn.
Monitoring Pests in Corn Crops: Scouting and Early Detection
Consistent scouting and monitoring form the backbone of effective sweet corn insect control. Identifying pest outbreaks early enables us to intervene before infestations become unmanageable. Here’s what we recommend:
- Pheromone traps: Detect adult moth activity and flights, informing our insecticide timing (especially for earworm, armyworm).
- Field Scouting: Walk rows every 3-5 days during critical growth (silking, tasseling, young ear stages). Look for eggs, larvae, or chewed leaves and silks.
- Sample Early and Often: Begin sampling at first visible silk—this can be the most vulnerable time for ear damage.
The Farmonaut App sends pest alerts using satellite and AI, making it easier and faster to get the right data in your hands!
Sweet Corn Insecticide Applications: Best Practices & Tips
Proper timing and coverage are critical for successful insecticide applications in sweet corn. Overuse can lead to resistance and unnecessary expense; underuse means yield loss.
- Apply early, target the young: Corn earworm and fall armyworm are easiest to control when larvae are small and feeding outside the ear or on leaves.
- Rotate chemical classes: To delay resistance, alternate insecticides with different modes of action.
- Thorough coverage: Especially for ear protection, ensure silks and ear tips are treated—the entry point for larvae.
- Monitor after application: Continue scouting to verify efficacy and adjust future strategy if necessary.
Always read labels, follow local guidelines, and respect withholding periods for food safety.
Advanced Techniques & Technology for IPM Strategies in Sweet Corn
Technology has brought massive advances in corn pest management:
- Satellite Imagery (via Farmonaut): Spot spatial stress patterns, detect irregular canopy reflectance linked to pest outbreaks—directing scouting teams effectively.
- AI & Machine Learning: Predict pest hotspots and optimal times for intervention, reducing both risk and chemical costs.
- Mobile Apps: Get real-time pest alerts, field weather updates, and resource management all in the palm of your hand!
- Resource Optimization: Integrate Farmonaut Fleet Management to deploy your machines efficiently for spraying and transport.
Combined with traditional IPM, these advanced tools help us achieve the highest possible yield with minimal environmental impact.
For smart, location-specific guidance on crop, plantation, and forest management, access the Farmonaut Crop, Plantation & Forest Advisory.
Summary & Conclusion: Shocking Pest Killers for Sweet Corn Yield and Quality
Sweet corn faces numerous threats from insect pests including corn earworm, fall armyworm, European corn borer, aphids, Japanese beetles, and stink bugs. Effective control begins with accurate identification and regular scouting. By implementing integrated pest management in corn—combining cultural, biological, and chemical controls, natural predators, and advanced technologies such as satellite monitoring with Farmonaut—we can significantly reduce damage and protect our yield.
- Start with accurate pest ID and monitoring using pheromone traps, scouting, and digital field records.
- Incorporate natural predators and biopesticides to minimize resistance and pollinator harm.
- Apply insecticides selectively and at correct timings for maximum effectiveness and reduced environmental impact.
- Leverage Farmonaut’s precision monitoring and AI-driven insights to focus interventions where and when most needed—optimizing cost, yield, and sustainability.
Insect control is not just about prevention; it’s about optimizing every plant’s potential and ensuring food safety, economic viability, and environmental stewardship.
Note: Farmonaut provides advanced monitoring, advisory, and digital tools to empower farmers and agribusinesses. It does not sell agricultural inputs, machinery, or function as a regulatory authority.
Start protecting your sweet corn crop with smart, sustainable, and data-driven insect control—download Farmonaut now!
FAQ: Sweet Corn Pest Control & IPM
-
What is the most damaging pest in sweet corn?
The corn earworm (Helicoverpa zea) is often the most damaging, causing significant losses in yield and quality, especially if left uncontrolled during silking and ear fill.
-
When should we apply insecticides for maximum effectiveness in sweet corn?
Insecticides should be applied at the onset of silking when young larvae are exposed—timely targeting is essential for corn earworm and armyworm control.
-
How can we naturally reduce aphid populations in corn?
Preserve and attract natural predators like lady beetles and lacewings, and avoid broad-spectrum insecticides that disrupt beneficial insect populations. Interplanting companion flowers helps, too.
-
Can satellite apps really help with corn pest management?
Yes! Platforms like Farmonaut use real-time satellite scans, AI analytics, and mobile alerts to flag hotspots and direct field scouting, optimizing insecticide use and improving yield outcomes.
-
Are there non-GMO ways to control corn borers?
Yes—besides Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) corn, we can use targeted biological and cultural controls, timely insecticides, pheromone disruption, and crop rotation to control borer populations without GMOs.
-
How do we know if chemical control is really necessary?
Always monitor regularly using scouting and pheromone traps. Apply insecticides only when pest numbers exceed economic thresholds for your crop stage and region.
-
Does Farmonaut provide satellite verification for crop loans or insurance?
Yes. Farmonaut offers satellite verification for crop loan and insurance to help reduce fraud and expedite the financial process for growers.
Still have questions? Reach out to our advisory team through the Farmonaut App or view more solutions on our official website.