Vertical Hydroponic System: 7 Shocking Urban Benefits!
“Vertical hydroponic systems can use up to 90% less water than traditional soil farming methods.”
Table of Contents
- Summary: Why Vertical Hydroponic Systems Matter
- Understanding Vertical Hydroponic Farming
- The 7 Shocking Urban Benefits of Vertical Hydroponic Farming
- Comparative Impact Table: Vertical Hydroponics vs Traditional Urban Farming
- Challenges and Critical Considerations
- Technological Innovations and Future Prospects
- Farmonaut’s Role in Sustainable Precision Agriculture
- FAQ: Vertical Hydroponic Systems Explained
- Conclusion: Powering the Future of Urban Farming
Summary: Why Vertical Hydroponic Systems Matter
Vertical hydroponic systems have captured the world’s imagination as one of the most
innovative agricultural techniques for modern cities. With a dramatic increase in food demand, limited arable land availability, water scarcity, and the urgent need for sustainable food production, these systems merge the best of vertical farming and hydroponic technology to deliver space-saving, water efficient, high-yielding, and environmentally friendly solutions. By cultivating plants without soil in carefully stacked layers and providing nutrient-rich water directly to the roots, urban and peri-urban areas can maximize productivity and lead the way in sustainable agriculture. As Farmonaut, we advocate the blend of satellite-driven precision and next-generation growing methods for resilient food systems.
Understanding Vertical Hydroponic Farming
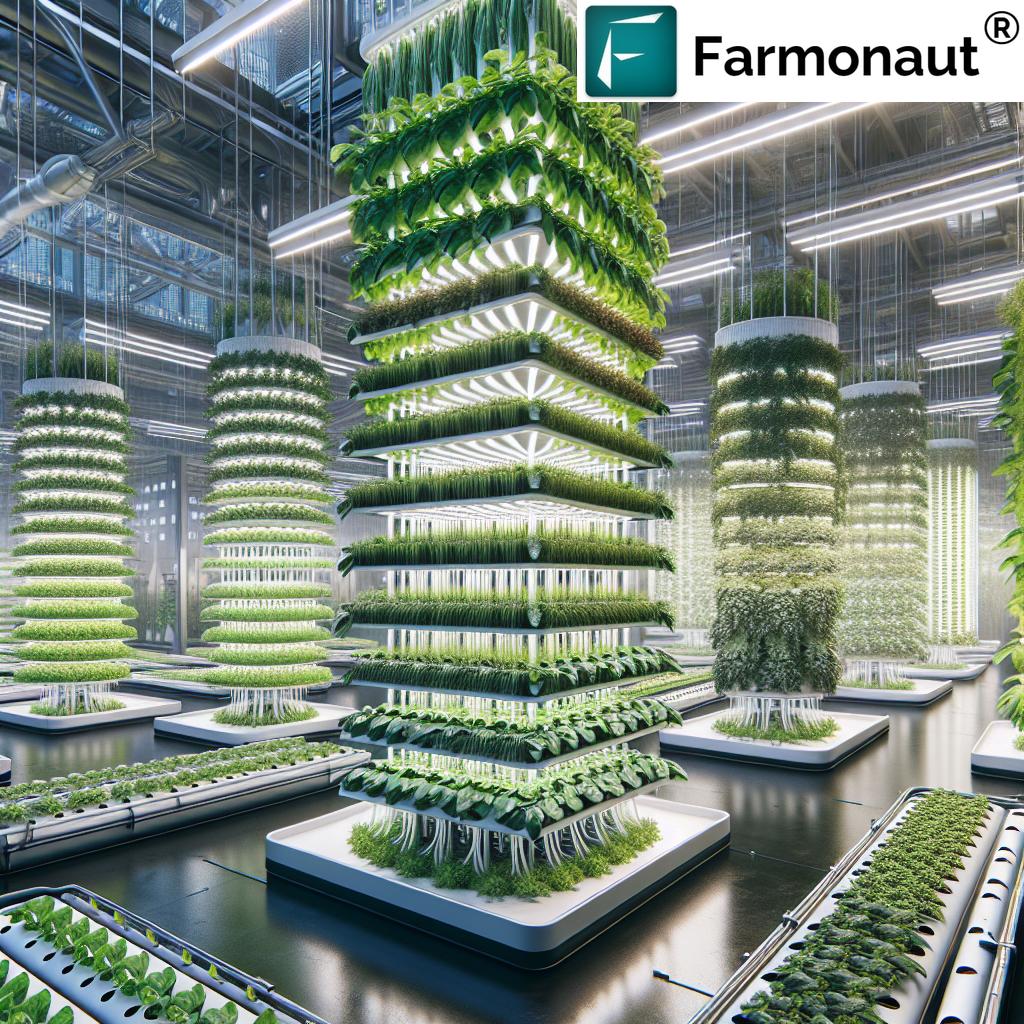
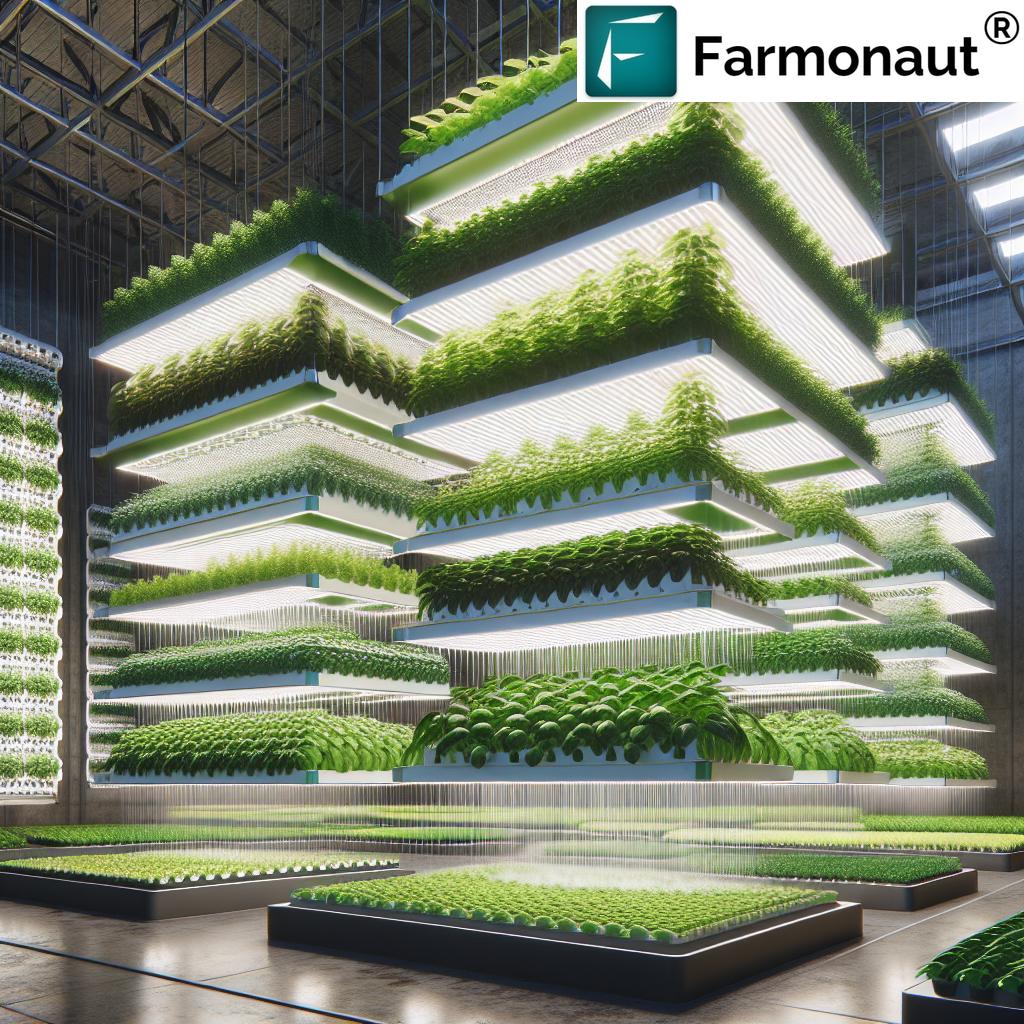
At its core, vertical hydroponic farming is a soilless cultivation method that organizes plants in layers, towers, or vertically stacked modules. Instead of relying on natural soil, these systems deliver a carefully controlled nutrient solution directly to plant roots, maximizing plant growth and resource efficiency.
- Soilless Design: Roots receive nutrients, water, and oxygen via recirculating hydroponic systems, eliminating the need for traditional fields.
- Stacked Layers: Crops are grown vertically in racks, columns, or walls, using indoor plant growing systems to capitalize on vertical space.
- Controlled Environment: These gardens leverage robust control of light, temperature, humidity, and nutrient delivery for optimum plant health and yields.
- Urban Integration: Designed for cities, rooftops, warehouses, and even repurposed shipping containers—making agriculture possible where land is scarce.
By combining vertical farming techniques with hydroponics, we redefine what’s possible in urban food production and sustainable agricultural practice. This approach is foundational for controlled environment agriculture (CEA), supporting year-round and weather-independent plant cultivation.
The 7 Shocking Urban Benefits of Vertical Hydroponic Farming
1. Space Efficiency: Maximizing Urban Acreage
Vertical hydroponic systems are designed to maximize available space, a pressing concern in dense urban environments. By stacking plants in vertical layers or hydroponic towers, growers can cultivate up to 10 times more crops per square meter compared to traditional soil-based urban farming (see trivia below and reference).
- Ideal for Cities: Rooftops, abandoned buildings, and compact lots are transformed into lush urban hydroponic gardens.
- Scalable: Grow from a few trays to warehouse-scale operations—making this method accessible for both hobbyists and commercial farms.
- Efficient Plant Arrangement: The stacked design increases sunlight or artificial lighting exposure, maximizing photosynthesis and return per square meter.
For those managing multiple farms or extensive urban food projects, tools like Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management platform become invaluable for tracking, monitoring, and optimizing both traditional and modern farm layouts.
“Urban vertical farms can yield up to 10 times more crops per square meter compared to conventional agriculture.”
2. Water Conservation: Setting the Standard for Water Efficient Agriculture
Hydroponic farming systems can save up to 90% more water than soil farming because the water is recirculated within closed-loop systems. With global concerns about water scarcity and climate change, this efficiency is transformative for urban, arid, or drought-prone regions.
- Minimal Waste: Water lost to evaporation or runoff is dramatically reduced; precise irrigation delivers water right to each plant’s roots.
- Data-Driven Conservation: When matched with Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tools, farms can monitor and reduce their environmental impact in real time.
- Enables Water-Reuse: Nutrient solutions can be filtered, topped up, and reused across many cycles, maintaining food safety standards.
This makes vertical hydroponic farming not only a solution for today but also a pillar of tomorrow’s sustainable food production.
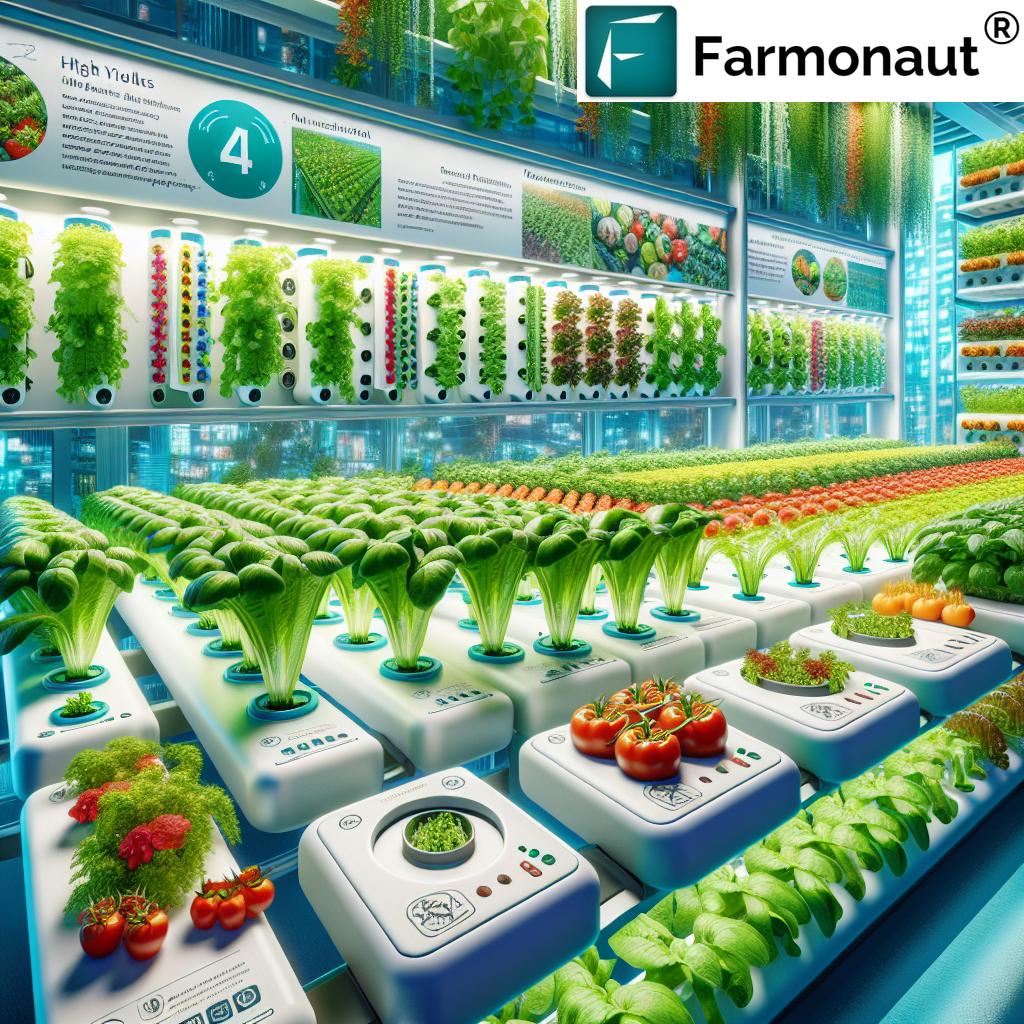
3. Faster Growth and Higher Yields: Controlled Environment for Optimal Plant Growth
In a vertical hydroponic system, growers can optimize plant nutrition and growth conditions unlike anywhere else. Hydroponic nutrients are delivered directly to the roots, and variables such as light (often artificial LED lighting), temperature, and humidity are expertly managed.
- Faster Growth Cycles: Plants typically mature more quickly, sometimes delivering multiple harvests per year instead of just one.
- Greater Yield Density: The increase in planting density and growing cycles leads to substantially higher output per year compared to soil farms.
- Digital Monitoring: Platforms employing real-time data (like Farmonaut’s satellite and AI-driven monitoring) further optimize harvest timing and nutrient formulation.
Controlled environment agriculture ensures that every square meter is as productive as possible—a vital advantage for urban agriculture.
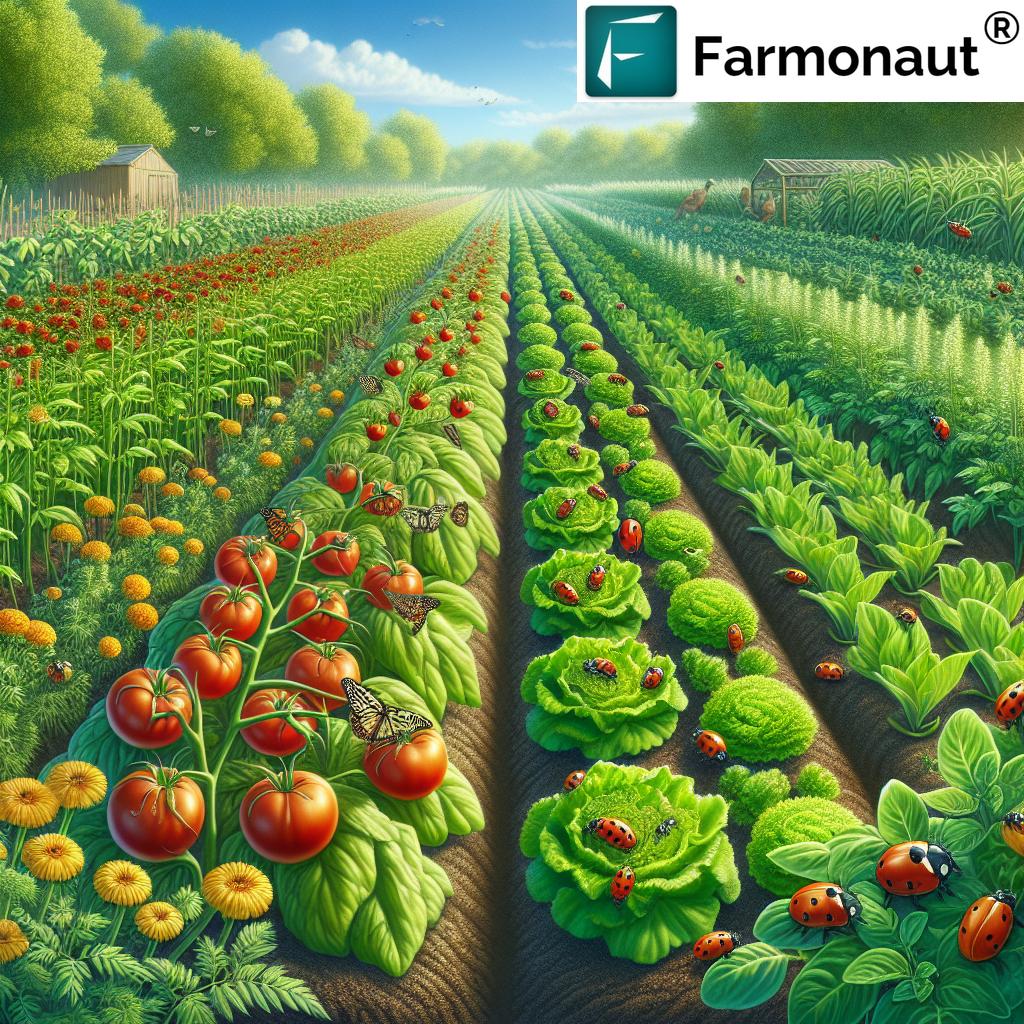
4. Reduced Pesticide and Herbicide Use: Healthier, Safer Produce
The controlled settings of vertical hydroponic farms sharply reduce exposure to pests and soil-borne diseases. As a result:
- Less Pesticides: There’s a greatly reduced need for chemical pesticides and herbicides, resulting in healthier crops.
- Cleaner Produce: Food grown in hydroponics is often fresher, cleaner, and safer for consumers, addressing growing concerns over food safety.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Lower chemical input cuts down on runoff and pollution, supporting long-term sustainability goals.
These features can be a significant selling point for urban food brands, especially when combined with Farmonaut’s blockchain-powered traceability solutions that ensure product origin and farm practices are fully transparent.
5. Year-Round Production: Freedom from Weather and Seasons
One of the foremost advantages of vertical hydroponic farming is year-round food production, independent of external weather. Urban growers can control lighting, temperature, and humidity to perfect growing conditions, regardless of season or climate events.
- Consistent Crop Availability: Supply chains are less vulnerable to weather shocks, ensuring people in cities have a stable source of fresh produce.
- Multiple Cropping Cycles: Rather than a single annual harvest, multiple crops can be grown and rotated without interruptions.
This reliability serves consumers, local restaurants, and food retailers who depend on predictable, high-quality supplies for business continuity.
6. Environmental Sustainability: Lower Carbon, Higher Impact
With global focus on sustainable food production, vertical hydroponics offer significant environmental benefits:
- Less Land Use: Growing crops vertically means a fraction of the land is needed for the same, or higher, output.
- Lower Water Footprint: Water conservation strategies directly reduce ecological pressure on limited resources.
- Shorter Supply Chains: Proximity to urban consumers minimizes the need for transport, lowering food miles and carbon emissions.
- Carbon Tracking: Utilizing platforms such as Farmonaut for carbon footprinting, growers can monitor and minimize their overall greenhouse gas emissions.
Tomorrow’s urban farmers will be called upon not just to maximize yields, but to lead in responsible, sustainable practices—and vertical hydroponic systems are a key driver for this shift.
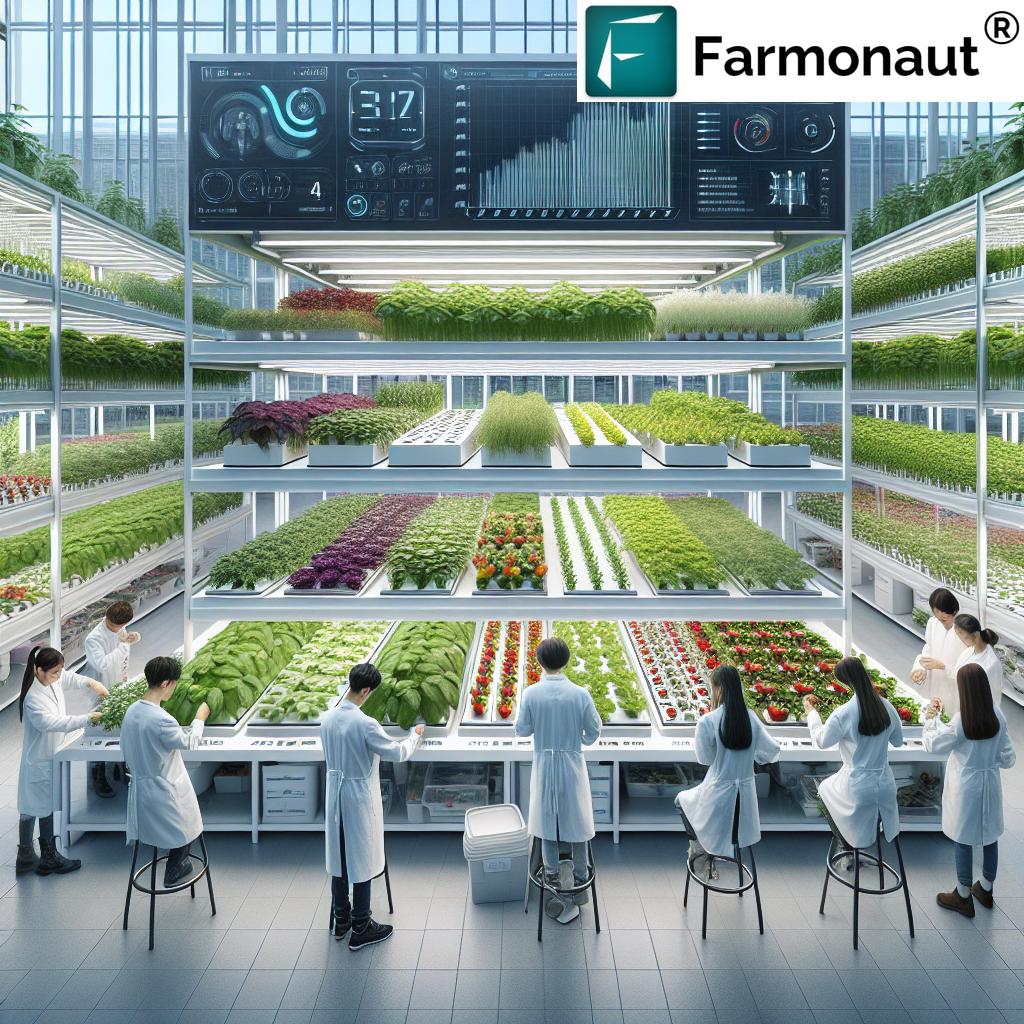
7. Technological Integration: Smart Farming Meets Vertical Innovation
The latest hydroponic technology integrates sensors, robotics, AI-driven advisory systems, and smart automation to take the guesswork out of urban crop management.
- Precision Resource Use: Digital tools monitor soil moisture, plant health, and nutrient delivery, optimizing each parameter for higher yields.
- Automation & AI: Platforms like Farmonaut use artificial intelligence for crop diagnosis, predictive analytics, and satellite-powered updates, making urban farming more efficient and data-driven.
- Seamless Connectivity: With API access (Farmonaut’s public API, developer documentation), large-scale operations and vertical farm networks can automatically fetch the latest satellite/weather data for system-wide management.
These innovations create a new frontier for urban hydroponic gardens, enabling sustainable high-tech food systems that blend tradition, science, and the power of the cloud.
Comparative Impact Table: Vertical Hydroponics vs Traditional Urban Farming
| Benefit Category | Vertical Hydroponics (Estimated Values) |
Traditional Soil-Based Farming (Estimated Values) |
Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Space Utilization (kg crops per sqm) | 8–12 | 0.8–1.5 | 700–1000% |
| Water Efficiency (liters/kg yield) | 10–35 | 100–400 | Up to 90% better |
| Crop Yield (tons/year) | 15–30 (per 100 sqm) | 1.5–2.5 (per 100 sqm) | 500–1000% |
| Resource Savings (estimated % reduction) | 70–90% | Baseline | — |
| Labor Requirement (hours/week) | 8–20 | 20–40 | 50% less |
| Pest Incidence (instances/month) | 1–3 | 6–12 | 60–90% lower |
| Carbon Footprint (CO₂ kg/year) | ~200–400 | ~500–800 | Up to 60% lower |
Challenges and Critical Considerations
While the benefits are profound, practical implementation of vertical hydroponic systems comes with significant challenges and key considerations:
- High Initial Investment: Setting up vertical hydroponic infrastructure requires substantial upfront costs. This includes modular racks, artificial lighting, environmental controllers, pumps, sensors, and more. Smaller urban farms and new growers may find this initial investment a barrier to entry.
-
Need for Technical Expertise: Operating a hydroponic system—especially at scale—demands in-depth understanding of plant physiology, nutrient balancing, system maintenance, and troubleshooting.
- Continuous learning and hands-on education are essential.
- Online platforms and mobile advisory apps can support this knowledge gap with data-driven, real-time guidance.
-
Energy Consumption: Maintaining optimal growing conditions—from artificial lighting to heating/cooling—results in higher energy use, contributing to operational costs and environmental concerns.
- Prioritizing LED and AI-optimized lighting schedules can increase energy efficiency.
- Monitoring systems can track and control overall consumption.
-
System Failures & Technical Vulnerabilities: Vertical hydroponic gardens are reliant on pumps, monitors, and electronics. Sudden failures—like a pump outage or system leak—can quickly jeopardize a crop.
- Redundancy planning, alarms, and regular system maintenance are essential.
- Smart monitoring platforms provide early-warnings for rapid intervention.
- Scalability Concerns: While small-to-mid size vertical farms are straightforward, going higher or expanding horizontally requires meticulous planning to ensure even light, water, and nutrient delivery to all layers and towers.
-
Market Acceptance and Consumer Perception: Educating consumers about the health, sustainability, and traceability benefits of soilless cultivation methods is necessary to foster broad acceptance.
- QR-scannable traceability (as offered by Farmonaut Traceability tools) can improve transparency and consumer trust.
Technological Innovations and Future Prospects
The future of vertical hydroponic farming systems lies in ongoing technological enhancement:
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning:
- Tools such as Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI advisory system enable smart nutrient scheduling, crop health diagnostics, and optimization of water and energy use — bringing data-driven precision to every harvest.
-
Robotics and Automation:
- Automated planting, harvesting, and maintenance reduce labor needs and improve consistency in large-scale operations.
-
IoT & Sensor Integration:
- Continuous, real-time monitoring of pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and environmental conditions allows for instantly addressing nutrient or system imbalances.
-
Blockchain-Based Product Traceability:
- Blockchain technology ensures complete supply chain transparency—allowing farmers and urban growers to prove the origins and conditions of their crops.
-
Environmental Footprinting & Sustainability Software:
- Carbon footprinting tools help growers quantify their emissions and resource usage, positioning their operations for green certification and urban policy compliance.
As vertical hydroponic techniques advance, we are poised to enter an era of resilient, high-tech food systems—securing food supply for growing cities worldwide.
Farmonaut’s Role in Sustainable Precision Agriculture
As a leader in agricultural technology, Farmonaut’s satellite-based platform empowers urban and peri-urban growers to get more from their vertical hydroponic systems—and all forms of modern farming.
What Does Farmonaut Offer?
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Multispectral imagery, soil moisture tracking, and NDVI analytics enable smart, timely decisions regarding irrigation and nutrient delivery for all forms of controlled environment agriculture.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Delivers real-time, field-specific advice based on weather, satellite data, and crop health, enhancing the decision-making process for commercial farms and urban gardens.
- Blockchain-Driven Traceability: Our traceability solutions offer transparent records—from seedling to harvest—building trust with consumers.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Fleet management tools streamline logistics and reduce costs for farms managing multiple locations or large urban food distribution networks.
- Carbon Monitoring: Carbon footprinting shows growers the environmental impact of their practices with real-time data.
- Flexible Subscription & API Integration: Our public satellite/weather API and developer docs allow for custom, automated, large-scale agricultural management.
These tools are vital for operators seeking efficiency, transparency, and sustainability in a rapidly changing food landscape.
FAQ: Vertical Hydroponic Systems Explained
What is vertical hydroponic farming?
Vertical hydroponic farming is an innovative agricultural approach where plants are grown in vertically stacked layers or towers using soilless cultivation methods. Nutrients, water, and oxygen are delivered directly to plant roots via a controlled hydroponic system, allowing for increased yields, water efficiency, and sustainable food production — all without traditional soil.
How does a vertical hydroponic system save water?
Vertical hydroponics uses recirculating hydroponic systems where water is continuously reused, dramatically reducing losses from evaporation and runoff. Studies show water conservation can reach up to 90% compared with conventional soil-based methods, making this method ideal for regions facing water scarcity.
Can I install a vertical hydroponic garden in a small urban apartment?
Yes! The space-efficient design of vertical hydroponic towers or wall systems means they can fit on rooftops, balconies, or even inside apartments with sufficient lighting. This makes urban hydroponic gardens accessible even in the most space-limited environments.
Does vertical hydroponic farming require pesticides?
Due to the controlled environment, hydroponic farming systems have far lower pest incidence. Most growers can drastically reduce or eliminate pesticide use, producing cleaner, healthier, and safer crops.
What crops can be grown in a vertical hydroponic system?
Leafy greens (lettuce, spinach, kale), herbs (basil, mint), strawberries, microgreens, and some vine crops (tomatoes, cucumbers) are especially well-suited for vertical hydroponic setups. With the right controlled environment agriculture techniques, an increasingly diverse range of food crops is possible.
Are there technology tools for monitoring and managing vertical hydroponic gardens?
Absolutely! Tools like Farmonaut’s precision agriculture platform provide real-time crop health alerts, satellite monitoring, and AI-based advisory, helping with nutrient optimization and early problem detection. Automated devices can monitor pH, temperature, and more.
How can I track the environmental impact of my hydroponic farm?
Using carbon footprinting software like Farmonaut, growers can assess their resource use and emissions, set sustainability targets, and share verifiable data with consumers or regulatory agencies.
Conclusion: Powering the Future of Urban Farming
Vertical hydroponic systems represent one of the most exciting frontiers in urban agriculture—delivering space efficiency, water conservation, rapid yields, and sustainable food production where it’s needed most. As cities grow and natural resources become more strained, these innovative methods allow us to cultivate plants in the least likely spaces, and often under the most challenging conditions.
While there are challenges regarding investment, technical skills, and energy usage, the benefits for urban environments, resource conservation, and consumer health are game-changing. The integration of artificial intelligence, blockchain, and advanced hydroponic technology help ensure every leaf, fruit, and root is grown with optimal conditions, transparency, and minimal environmental impact.
With robust platforms such as Farmonaut, the journey towards sustainable, smart, and resilient urban food systems becomes accessible to everyone—from the balcony gardener to the world’s biggest city.
Drive the transformation of food production—discover how modern vertical hydroponic farming backed by Farmonaut’s advanced platform can create a more abundant, sustainable future!