10 Sustainable Farming Solutions Africa Needs Now!
“Conservation agriculture can increase African crop yields by up to 50% while reducing soil erosion by 60%.”
Introduction: Why Sustainable Farming Solutions Matter in Africa
Across Africa, the challenge of feeding a rapidly growing population collides with the imperative to protect our environment, conserve resources, and ensure profitable, resilient livelihoods for farmers. Traditional farming practices have boosted food production in the past, but increasingly, we witness the environmental costs—declining soil fertility, water scarcity, biodiversity loss, and rising greenhouse gas emissions.
That’s why sustainable farming solutions are not just trends—they’re necessities. These practices encompass agroecology, conservation agriculture techniques, innovative water and energy management, and more. By focusing on ecological health, our systems aim to meet today’s agricultural needs while safeguarding future generations, balancing food production with environmental sustainability and economic viability.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the 10 Sustainable Farming Solutions Africa Needs Now, drawing on data, science, and proven approaches for the continent’s unique ecosystems and farming communities.
Unlocking Soil Organic Carbon: The Secret to Sustainable Farming with Farmonaut
Comparative Impact Table: Sustainable Farming Practices for Africa
| Farming Solution | Description | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Estimated Water Use Reduction (%) | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agroecology | Integrates traditional & modern knowledge, emphasizing biodiversity & natural processes | +20–35% | +20% | Restores soil health, boosts biodiversity, reduces chemical use |
| Conservation Agriculture | Minimal tillage, crop rotation, permanent soil cover | +30–50% | +30% | Improves water retention, reduces erosion, builds soil fertility |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Combines biological, cultural, & chemical controls | +15–25% | ~0% | Cuts pesticide use, protects ecosystems |
| Agroforestry | Integrates trees/shrubs with crops & livestock | +25–30% | +10% | Stores carbon, improves soil, increases biodiversity |
| Vertical Farming | Indoor/urban layered crop production | Up to +200%/m² | Up to +90% | Minimizes land use, reduces water & waste |
| Hydroponics & Aquaponics | Soil-less farming (water-based nutrients/with fish) | +30–50% | +80–90% | Cuts water use, enables urban farming |
| Biointensive Agriculture | Dense planting & deep soil cultivation | +50–200% (small plots) | +40% | Maximizes yield/area, enriches soil |
| Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) | Optimizes temperature, humidity, & light | +70–120% | +60–90% | Boosts efficiency, reduces chemical input |
| Efficient Water Management | Drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting | +15–35% | +60–80% | Preserves resources, improves drought resilience |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Solar/wind power for farm operations | Indirect (+10–15%) | n/a | Reduces emissions, lowers costs |
“Agroforestry practices boost farm biodiversity by 30% and improve soil fertility in African smallholder systems.”
Farmonaut Covered By Radix AI: Leveraging Remote Sensing and Machine Learning for a Greener Future
10 Essential Sustainable Farming Solutions for Africa
1. Agroecology: The Integrated Approach for Resilient Farms
At the heart of sustainable farming in Africa lies the agroecology approach. This practice merges traditional farming wisdom with modern science, forming productive systems that respect and harness natural processes.
- Biodiversity: Agroecology emphasizes diversifying crops, plants, and even livestock, reducing vulnerability to pests, diseases, and climate extremes.
- Soil Health: Increases soil fertility by cycling organic matter, utilizing compost, and reducing the reliance on chemical inputs.
- Natural Pest Control: By integrating cultural and biological techniques, we can manage threats in an ecologically balanced way.
In African contexts, organizations like the African Food Sovereignty Alliance (AFSA) have been vocal promoters, demonstrating the power of agroecology to revitalize soil, boost crop yields, and protect our ecosystems.
Source: Reuters on Agroecology in Africa
Farmonaut | Making Farming Better With Satellite Data
2. Conservation Agriculture: Soil Health and Water Retention
Conservation agriculture techniques focus on three principles: minimal soil disturbance (reduced tillage), permanent soil cover (like mulching), and smart crop rotation. Together, these practices:
- Significantly reduce soil erosion—a persistent challenge on African farmlands
- Enhance water retention, improving resilience during dry spells
- Encourage a healthy soil ecosystem by protecting soil microorganisms
- Facilitate increased yields and lower input costs over time
The effectiveness of this approach is clear in East and Southern Africa, where adoption has led to improved harvest stability, better water management, and restored soil fertility.
Learn more about Conservation Agriculture
3. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Eco-Friendly Crop Protection
Integrated Pest Management solutions (IPM) combine biological, cultural, physical, and, when necessary, chemical strategies to contain pest outbreaks. We use a mix of:
- Crop rotation to disrupt pest life cycles
- Introducing or encouraging natural predators
- Diseases-resistant crop varieties
- Judicious, minimal chemical inputs as a last resort
This strategy reduces the environmental impact of toxic pesticides and builds long-term resilience into our growing systems, promoting a balanced ecosystem and healthy food for our communities.
Source: Guide on Sustainable IPM
4. Agroforestry: Integrating Trees for Ecosystem Health
Agroforestry systems—planting trees and shrubs alongside crops and livestock—are a practice central to African sustainable farming. The benefits include:
- Increased biodiversity and support for pollinators
- Enhanced soil fertility through leaf litter and nitrogen-fixing trees
- Carbon sequestration to combat climate change
- Additional income from fruit, nuts, timber
In regions like Sahel and East Africa, agroforestry revitalizes degraded landscapes and stabilizes food production systems.
Learn more about Agroforestry Benefits
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture – Farmonaut | Agritecture | Joyce Hunter
5. Vertical Farming: Stacking Yields in Urban Spaces
Vertical farming technology allows us to grow plants in stacked layers or tall structures—maximizing limited space especially in urban environments. This method offers:
- Year-round production in controlled settings
- Up to 90% water savings compared to field agriculture
- Reduced land pressure and transport costs, especially near African cities
- Minimal pest risk and pesticide usage
For African entrepreneurs and urban communities, vertical farming opens new doors for sustainable, local food production.
More on Vertical Farming Methods
Start transforming your farm with Farmonaut’s digital app—widely accessible via web, Android, and iOS. Monitor crop health using real-time satellite data and AI-powered advisory for better yields and sustainability!
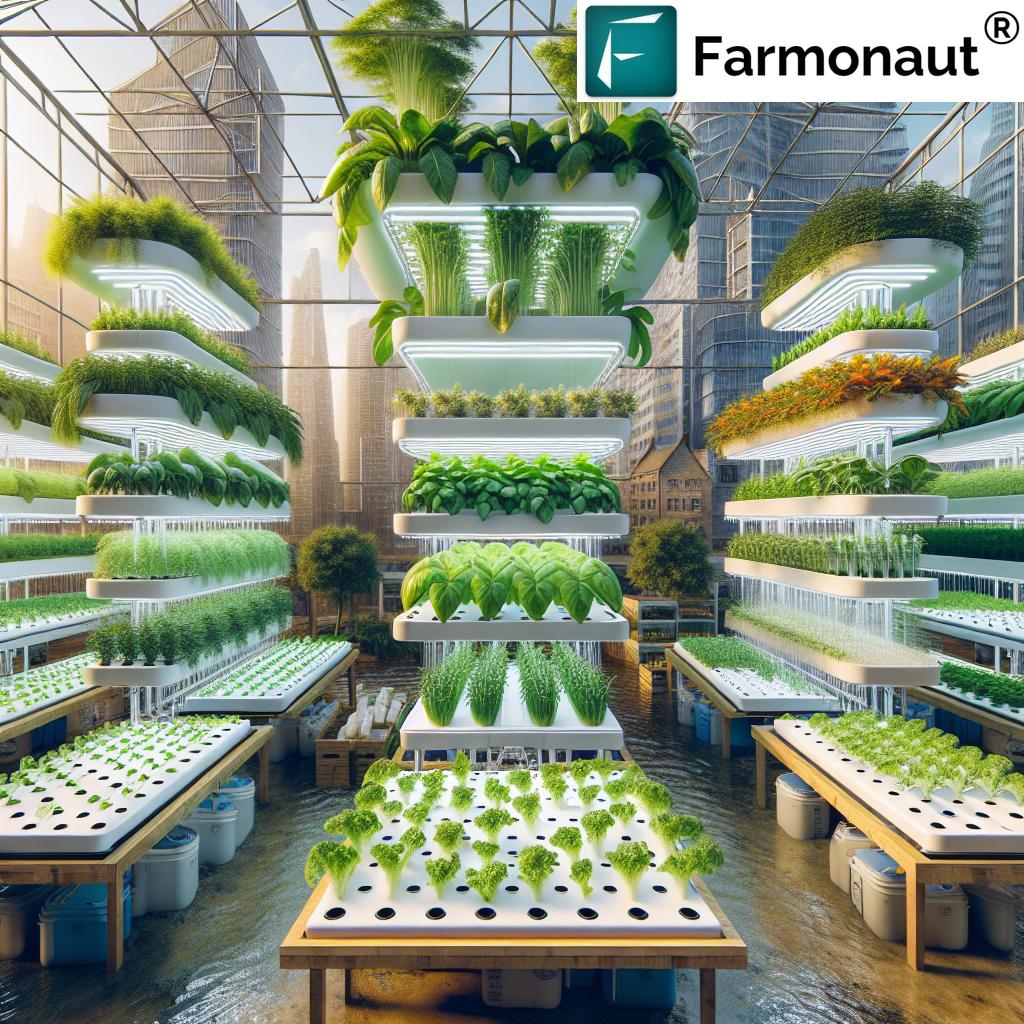
6. Hydroponics and Aquaponics: Soil-less Farming for Water Conservation
Hydroponics and aquaponics farming are rising solutions in Africa’s quest for water-wise, efficient agriculture. In these systems:
- Hydroponics: Plants are grown in nutrient-rich water rather than soil, dramatically reducing water usage—by up to 90%—and avoiding soil diseases.
- Aquaponics: Integrates fish farming, where fish waste fertilizes plants, and plants filter the water for the fish, creating a self-sustaining, circular system.
- Particularly suited to urban or resource-scarce regions, enabling year-round crop production with minimal external inputs.
African innovators are deploying these techniques in both city environments and rural communities, diversifying local diets while preserving precious water.
Read: Sustainable Hydroponics & Aquaponics
7. Biointensive Agriculture: High Output, Minimal Input
Biointensive agriculture focuses on producing high yields from small areas—a boon to Africa’s small-scale farmers. Its core principles include:
- Deep soil preparation and high-volume composting
- Dense planting to maximize space, suppress weeds, and shade soil
- Emphasis on closed nutrient cycles, requiring fewer external inputs
- Long-term improvement of soil fertility and productivity
Biointensive methods are gaining traction with African NGOs for home gardens, school feeding programs, and micro-enterprise farming.
Deep Dive: Biointensive Sustainable Agriculture
Want to manage your farm’s carbon emissions and comply with sustainability regulations? Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solution tracks your agricultural carbon output in real-time, empowering better environmental stewardship and compliance!
8. Controlled Environment Agriculture: All-Season Production
Controlled environment agriculture (CEA) lets us grow crops in optimized settings, such as greenhouses or indoor farms. We control temperature, humidity, light, and nutrients, producing food efficiently regardless of external weather. CEA is ideal for:
- Urban and peri-urban food systems losing land to development
- Regions facing unpredictable rainfall or droughts
- Consistently delivering high-value crops with minimal chemical input
CEA also reduces transport emissions and enables communities to grow food locally—enhancing nutritional security.
Info: Controlled Environment Agriculture
Ensure every step of your agri-supply chain is transparent with Farmonaut’s Blockchain-based Traceability Tool—build consumer trust and guarantee authentic African produce to the world!
9. Water Management: Maximizing Every Drop
Efficient water management in farming is not optional for African agriculture—it’s a survival strategy. Techniques for water-smart systems include:
- Drip irrigation: Delivers water directly to plant roots, significantly reducing wastage
- Rainwater harvesting: Captures and stores runoff for dry periods
- Mulching and ground cover: Retains soil moisture and reduces evaporation
- Smart sensors (IoT-integrated): Enable precision irrigation scheduling
Adopting these practices improves yields, reduces input costs, and future-proofs farms against climate-induced droughts.
Best Sustainable Farming Water Practices
Get satellite-based verification for your Crop Loan & Insurance applications with Farmonaut. Fast-track your financial support and protect your farm investment using data-backed solutions.
10. Renewable Energy Integration: Powering Sustainable Transformation
Renewable energy in agriculture is the key to reducing our sector’s carbon footprint and cutting costs for farmers. Leading renewable sources include:
- Solar energy: Powering irrigation pumps, cold storage, and processing units
- Wind power: Generating on-site electricity for rural and off-grid systems
- Bioenergy: Turning organic waste into fuel or electricity
Integrating these technologies, we boost farm resilience, stabilize operations, and contribute positively to the environment.
Renewable Energy for Farms Explained
Run a large plantation or multi-farm agribusiness? Farmonaut’s Large-Scale Farm Management platform centralizes crop monitoring and operational oversight—perfect for modern African agribusiness needs.
Optimize machinery and logistics using Farmonaut’s Fleet Management Tools, cutting costs and maximizing efficiency for every hectare.
Developers and agri-tech innovators: Integrate satellite and weather data directly into your systems via Farmonaut’s Agriculture API. Full developer documentation is available here.
Technological Innovations Driving Sustainability
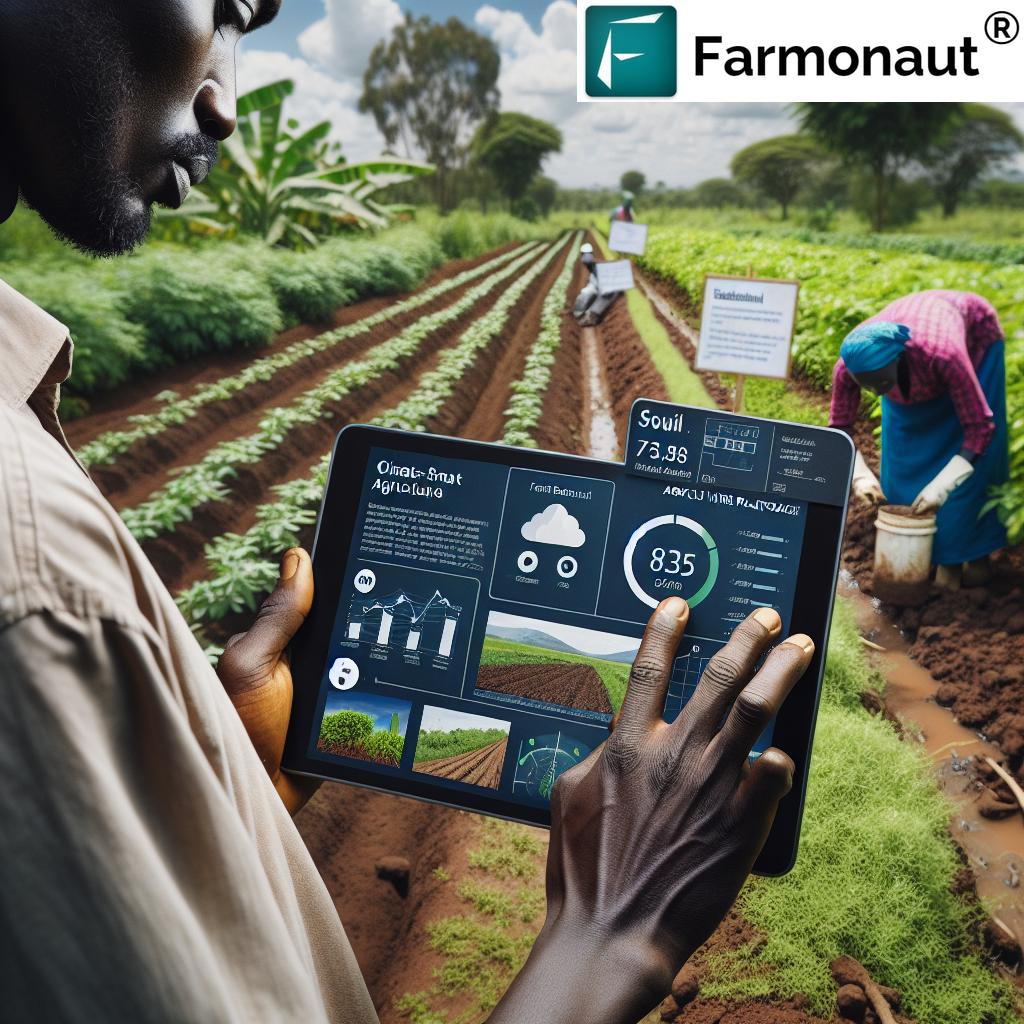
Technology is rapidly changing African agriculture. Precision farming, powered by big data and remote sensing, is now available to smallholder farmers—thanks to companies like Farmonaut.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Sensors record soil moisture, temperature, crop health in real time. The data helps us apply water, fertilizer, or pest treatments with pinpoint accuracy, conserving resources and boosting yields.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning analyze satellite and farm data to predict optimal planting times, diagnose pests/diseases, and recommend targeted actions, maximizing outcomes and reducing waste.
- Drones: Used to map fields, assess crop health, deliver inputs, and even plant seeds, drones are transforming farm management, especially in vast or hard-to-reach African landscapes.
Farmonaut’s platform combines satellite imagery, AI-based advisories, and blockchain for traceability—making precision agriculture affordable and accessible to all African farmers.
Challenges and The Road Forward
Even as the benefits of these sustainable farming practices are clear, there are real challenges to widespread adoption across Africa:
- Economic Barriers: Up-front investments in irrigation, renewables, or tech tools can be daunting, particularly for cash-strapped smallholders.
- Knowledge Gaps: Ongoing education and training are essential for farmers to understand and embrace new techniques and maximize their benefits.
- Policy Support: Policies and subsidies often still favor conventional, input-heavy agriculture.
Recommendation: Advocacy and proven impact studies can help shift incentives towards sustainability.
Key Steps Forward
- Invest in agricultural R&D: Innovations must be tailored to African soils, climates, and farmer contexts.
- Democratize access: Continue expanding affordable platforms, like Farmonaut, to reach all farmers.
- Upskill the continent: Establish continuous training programs emphasizing
sustainability, data-driven management, and ecosystem health. - Reform policies: Ensure government incentives, subsidies, and climate financing prioritize sustainable farming approaches.
Farmonaut: Empowering African Farmers with Data and Technology
Farmonaut stands at the forefront of Africa’s move towards sustainability in agriculture. Here’s how our solutions bridge the gap:
- Satellite-Based Farm Management: Real-time crop health monitoring via satellite imagery—track NDVI, soil moisture, and growth trends instantly.
- AI-Driven Advisory: The Jeevn AI system delivers personalized alerts and tactical advice tailored to your land, crops, and weather.
- Blockchain Traceability: Bring supply chain transparency and trust to your produce with secure, end-to-end tracking.
- Fleet & Resource Optimization: Manage agricultural vehicles, labor, and resources smartly—cutting losses, maximizing returns.
- Carbon Footprinting: Get actionable data on emissions and waste to meet evolving environmental standards and improve eco-ratings.
With a subscription-based model, accessible apps, and full API capabilities for tech-forward leaders, Farmonaut makes data-driven sustainable agriculture a reality for every African farmer—from urban entrepreneurs to rural cooperatives and large agribusinesses. Our goal? Boost productivity, reduce costs, and build a food system that’s future-ready—
all while healing the land.
Ready to transform your farm? Sign up for Farmonaut today, or follow our detailed Developer API Docs to build your own tech-powered solutions.
FAQ: Sustainable Farming in Africa
What is the most important sustainable farming practice for African farmers?
There’s no single “most important” practice, but conservation agriculture—including minimal tillage, crop rotation, and permanent soil cover—has shown the largest direct impacts on soil health, yields, and climate resilience in diverse African settings.
How does technology make sustainable farming possible?
Technologies like satellite imagery, IoT sensors, and AI provide timely, actionable data for precision irrigation, pest control, fertilizer use, and more. This helps even smallholder farmers maximize efficiency while minimizing environmental impact—key to sustainability.
Can sustainable practices work for small-scale, resource-limited farmers?
Absolutely. Many solutions—biointensive methods, agroecology, IPM—are specifically designed to minimize need for costly inputs and can be implemented incrementally, fitting diverse African farm settings.
How can African farmers start with precision agriculture?
Digital tools like Farmonaut’s mobile and web app provide instant access to crop health maps and advisory. Getting started usually involves registering your fields, choosing a crop, and receiving regular updates—no specialized hardware is needed.
Where can agricultural professionals access Farmonaut’s data or integrate it into their products?
Developers can use Farmonaut’s robust API Platform for satellite and weather data; full developer documentation is provided.
Conclusion: Towards a Sustainable African Agriculture
The path to African food security doesn’t just depend on growing more—it’s about doing so wisely, balancing production with the health of our soil, water, ecosystem, and communities. As we’ve seen, adopting sustainable farming practices—from agroecology and conservation agriculture to vertical farming and advanced water management—recoups environmental benefits, boosts yields, and future-proofs our livelihoods.
Let’s harness both traditional wisdom and modern technologies to empower every African
farmer with data, tools, and resilience. The solutions are at our fingertips—now’s the time to make sustainable agriculture
the foundation of Africa’s next green revolution. Join us on this journey, and together, we’ll cultivate a thriving, sustainable continent.