- Introduction to Sustainable Agriculture
- Trivia
- Comparison Table: Sustainable Agriculture Methods
- 1. Agroecology: The Ecological Approach
- 2. Organic Farming Methods
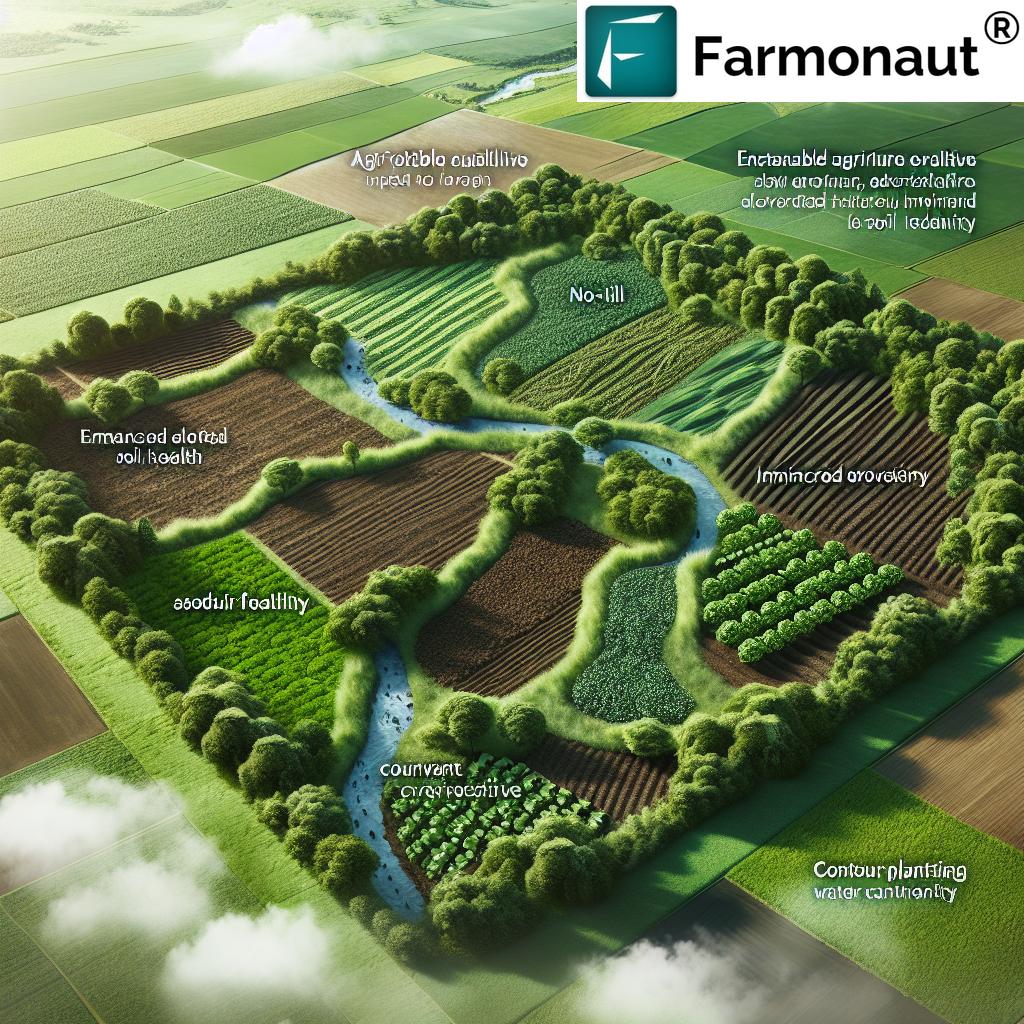
- 3. Conservation Tillage Techniques
- 4. Cover Cropping Benefits
- 5. Integrated Pest Management
- 6. Agroforestry Systems
- 7. Water Conservation in Agriculture
- 8. System of Rice Intensification (SRI)
- 9. Biosolarization
- 10. Controlled-Environment Agriculture
- Implementing Sustainable Agriculture Practices
- Farmonaut Technology for Sustainable Agriculture
- Farmonaut Subscription Plans
- FAQ
- Conclusion
10 Game-Changing Methods for Sustainable Agriculture
Discover the most impactful and innovative sustainable agriculture practices that are transforming the future of food production and environmental stewardship worldwide.
“Agroforestry can boost crop yields by up to 56% while improving biodiversity and soil health.”
Understanding Sustainable Agriculture: A Holistic Approach
As we strive to meet the rising food demands of today while safeguarding the needs of future generations, sustainable agriculture stands at the core of this mission. Sustainable agriculture emphasizes sound environmental practices, integrates ecological principles, and seeks to provide food systems that are resilient, productive, and harmonious with nature. This comprehensive approach minimizes resource wastage, reduces environmental impact, and promotes economically viable and socially responsible farming systems.
In this guide, we explore 10 game-changing methods for sustainable agriculture. Each method aims to enhance soil health, promote biodiversity, reduce dependency on synthetic inputs, conserve vital resources, and build resilient food systems for the generations to come.
Comparison Table: Sustainable Agriculture Methods
| Method Name | Main Benefit | Estimated Resource Savings | Environmental Impact | Ease of Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agroecology | Boosts biodiversity and ecological balance | 15-30% reduced synthetic inputs | High | Intermediate |
| Organic Farming | Promotes soil health and natural pest control | 45% less energy, 100% avoided chemical inputs | High | Intermediate |
| Conservation Tillage | Reduces erosion and preserves soil structure | 60-90% less soil disturbance | Medium-High | Beginner |
| Cover Cropping | Prevents erosion, improves fertility | 25-40% reduced fertilizer input | High | Beginner |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Minimizes pesticide use | 35-70% reduced pesticide input | High | Intermediate |
| Agroforestry | Enhances farm diversity and carbon storage | 10-25% reduced water and fertilizer use | High | Advanced |
| Water Conservation Management | Optimizes water use and efficiency | 30-60% less water usage | High | Beginner-Intermediate |
| System of Rice Intensification (SRI) | Increases yield, reduces water and seed input | 30-50% less water, 80-90% fewer seeds | High | Intermediate |
| Biosolarization | Controls soil pests naturally | 50-70% reduced chemical fumigants | Medium | Advanced |
| Controlled-Environment Agriculture (CEA) | Year-round, efficient production with reduced losses | Up to 90% water savings | High | Advanced |
“Organic farming uses 45% less energy than conventional methods, reducing environmental impact significantly.”
The 10 Game-Changing Sustainable Agriculture Practices
1. Agroecology: The Ecological Approach to Agriculture
Agroecology is an approach that applies ecological principles to agricultural systems. By promoting *biodiversity*, ecological balance, and sustainable methods, agroecology helps us build resilient farms that work in harmony with nature.
- Encourages polyculture, where multiple crops are grown together for increased biodiversity and natural pest control.
- Integrates trees and shrubs with crops to provide habitat for beneficial organisms, improved soil fertility, and climate regulation.
- Aims to reduce synthetic input reliance by using natural processes.
Learn more about agroecology methods
Sustainable agriculture practices like agroecology empower farmers to design agricultural systems that are economically viable, environmentally sound, and socially responsible.
2. Organic Farming Methods: Relying on Nature
Organic farming eliminates reliance on synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and chemical fertilizers. Instead, it focuses on natural solutions—
- Crop rotation to break pest cycles.
- Composting to enhance soil health and increase organic matter content.
- Use of biological pest control methods such as beneficial insects.
These organic farming methods improve soil health, reduce runoff into waterways, and support biodiversity—all while producing nutritious food for our communities.
Farmonaut aids organic farmers with satellite-based crop health monitoring and blockchain product traceability, ensuring authentic organic supply chains.
Read about organic farming benefits
3. Conservation Tillage Techniques: Preserving Our Soil
Conservation tillage minimizes or eliminates traditional plowing, preserving soil structure and reducing erosion. Popular techniques include:
- No-till farming: Seeds are directly inserted into untilled soil, reducing disturbance for better soil health.
- Mulch tillage: Involves leaving crop residues to protect soil from erosion and promote moisture retention.
- Encourages the accumulation of organic matter and supports higher microbial activity.
These conservation tillage techniques are crucial for soil health improvement in sustainable agriculture.
See more conservation tillage examples
4. Cover Cropping Benefits: Nature’s Soil Protectors
Cover crops (like clover, rye, or alfalfa) are grown to cover soil between harvest seasons. The benefits include:
- Prevents soil erosion and maintains moisture by shielding from wind and rain.
- Enhances soil fertility by fixing nitrogen, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
- Suppresses weeds and interrupts pest lifecycles.
“Cover cropping” not only prevents land degradation but also enriches soil organic matter, supporting more robust and resilient agricultural systems.
Explore cover cropping solutions
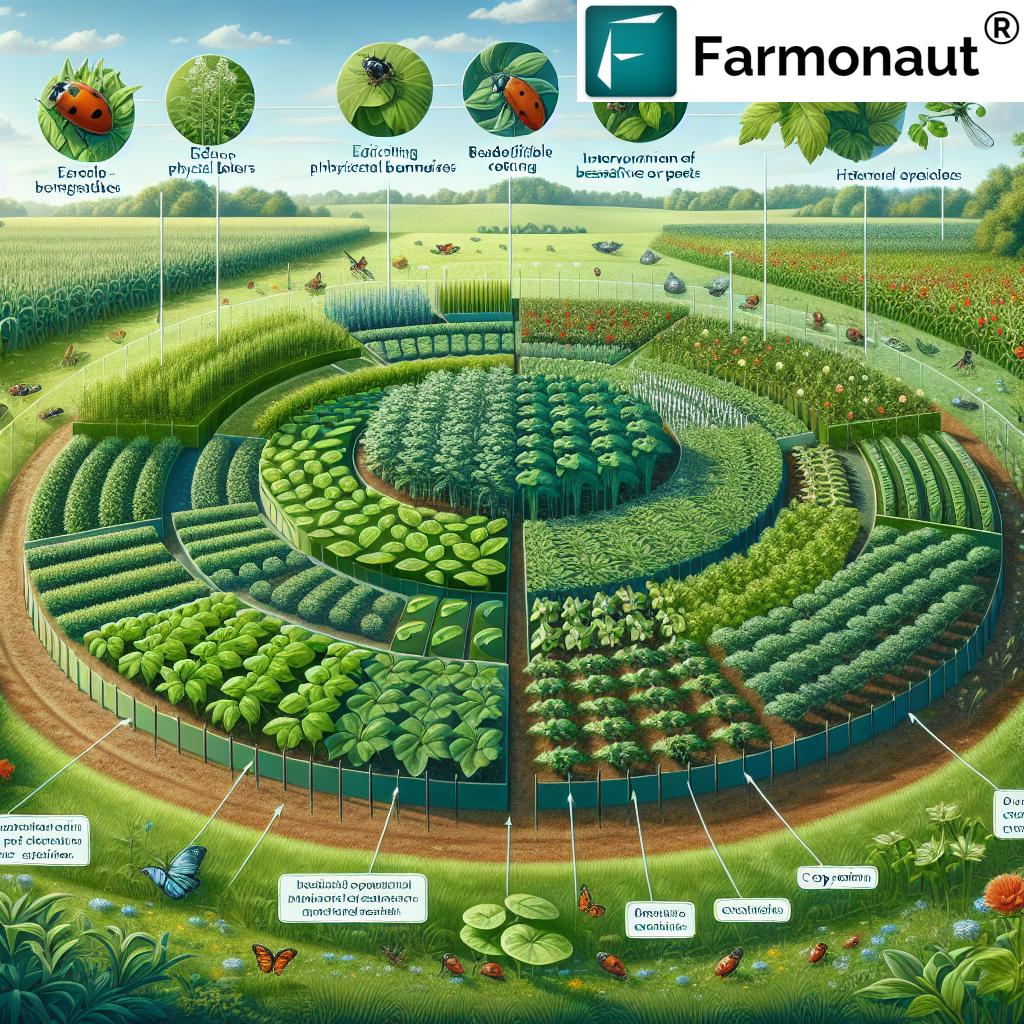
5. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Smart Pest Control
Integrated pest management (IPM) balances biological, cultural, and mechanical control techniques, using pesticides only as a last resort. This approach includes:
- Crop rotation and diversification to disrupt pest and disease cycles.
- Deploying natural predators of common pests (ladybugs, birds, beneficial nematodes).
- Selecting pest-resistant plant varieties and monitoring pest levels for timely interventions.
- Mechanical controls such as traps, barriers, or manual removal.
IPM reduces our dependency on synthetic chemical pesticides, preserves beneficial organisms, and supports sustainable agriculture practices.
Learn about integrated pest management
Farmonaut provides real-time crop health and pest monitoring via satellite imagery and fleet management solutions for on-ground pest control teams.
6. Agroforestry Systems: Integrating Trees for Resilience
Agroforestry systems combine trees, shrubs, and crops within the same land unit. The benefits include:
- Enhanced biodiversity by creating varied habitats for flora and fauna.
- Improved soil fertility through nitrogen-fixing trees and deep root systems recycling nutrients.
- Carbon sequestration—helps in addressing climate change.
- Additional income from harvests of timber, fruits, nuts, or resins.
Agroforestry is especially valuable for restoring degraded lands and supporting sustainable food and timber production.
Discover agroforestry advantages
Farmonaut offers a crop plantation & forest advisory platform—helpful for managing agroforestry projects: Get the app
7. Water Conservation in Agriculture: Efficient Water Use
Water conservation and management are essential as we face increasing water scarcity in agriculture. Top techniques include:
- Drip irrigation: Delivers water directly to plant roots, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
- Rainwater harvesting: Captures and stores rain for dry periods.
- Scheduling irrigation based on real-time soil moisture data (Farmonaut provides satellite-based insights).
Water conservation in agriculture helps ensure crop health while reducing environmental impacts and protecting future water resources.
Read more about water management methods
Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management tools enable users to track soil moisture conditions and improve water use efficiency throughout their agricultural operations.
8. System of Rice Intensification (SRI): Raising Yields Sustainably
The System of Rice Intensification (SRI) revolutionizes rice cultivation through:
- Wider spacing and planting fewer seedlings, which boosts root and tiller growth.
- Using organic fertilizers for improved soil structure and microorganism activity.
- Alternating wetting and drying instead of continuous flooding, saving water resources and improving soil aeration.
Research consistently shows that SRI results in higher yields, lower seed and water input, and reduces disease incidence.
Learn about SRI in detail
9. Biosolarization: Eco-Friendly Soil Pest and Disease Control
Biosolarization is a natural method merging the power of the sun with organic amendments to control soil pests. It involves:
- Incorporating organic material (like compost) into the soil
- Covering the soil with plastic to trap solar radiation and raise temperatures
- Pathogens, weed seeds, and pests are eliminated without chemical fumigants
Biosolarization offers a sustainable, cost-effective alternative to traditional pest and disease management and is ideal for organic and transition farms.
Explore biosolarization
10. Controlled-Environment Agriculture (CEA): The Future of Farming
Controlled-environment agriculture (CEA) leverages indoor and greenhouse settings for crop cultivation—enabling:
- Year-round production, unaffected by external weather conditions
- Massive reductions in water and fertilizer inputs through hydroponics or aeroponics
- Enhanced pest and disease control with reduced pesticide usage
- Precision monitoring for optimal plant health and resource usage
CEA is ideal for urban and peri-urban farms facing land and resource constraints.
Learn all about CEA
Farmonaut supports CEA practitioners by providing API access and developer documentation for integrating real-time farm monitoring into automated indoor growing platforms.
Implementing Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Strategies for Success
To successfully implement sustainable agriculture practices, farmers must:
- Assess local agroecological and climatic conditions—choose suitable methods for each agro-region
- Integrate multiple practices (e.g., cover cropping with conservation tillage and IPM) for system synergy
- Utilize data-driven insights (e.g., Farmonaut’s crop health and moisture monitoring tools) to refine management
- Access extension services and ongoing education for up-to-date sustainable agriculture knowledge
- Advocate for supportive policies, such as subsidies for organic inputs or water-saving technology incentives
With these strategies, farmers and stakeholders can create resilient food systems that protect the environment while meeting current and future demands.
Farmonaut Technology: Empowering Sustainable Agriculture
Farmonaut is an agricultural technology leader, committed to mainstreaming precision agriculture and advancing sustainable agriculture practices across scales. Our offerings include:
- Satellite-based crop and soil health monitoring—Receive vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture analytics, and real-time field alerts to inform water, nutrient, and pest management decisions.
- Farmonaut Jeevn AI Advisory System—Delivers personalized crop management strategies, weather updates, and resource optimization advice using satellite & on-farm data.
- Blockchain-based product traceability—Provides secure, tamper-proof records of crop journey for transparent supply chains. Supports organic and sustainable producers with traceability solutions for food safety, compliance, and market access.
- Fleet and Resource Management—Our digital fleet management system enhances equipment utilization, logistics, and crop protection operations: Explore fleet management
- Carbon footprint tracking—Monitor and reduce your farm’s emissions. Learn about Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting services.
- Scalable tools that serve individual farmers, cooperatives, agribusinesses, and government agencies.
By integrating these tools into everyday operations, users achieve better yields, resource savings, and improved environmental outcomes. Our large-scale farm management dashboard is designed for agribusinesses managing thousands of hectares—including satellite monitoring, weather integration, and resource allocation on a single platform.
Try Farmonaut for precision, sustainability, and profitability—today.
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
Choose a plan that fits your farm’s needs, acreage, and satellite monitoring requirements. Farmonaut delivers affordable satellite-powered intelligence via mobile, web, and API—accessible to farmers, communities, and big businesses alike.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Sustainable Agriculture Methods
What is sustainable agriculture?
Sustainable agriculture is a holistic approach to producing food, fiber, and other plant or animal products by integrating ecological, economic, and social principles. Its aims are to meet the current food demands without compromising the resource base for future generations.
Why is soil health improvement central to sustainable agriculture?
Healthy soil supports stronger plant growth, efficient water retention, improved nutrient cycling, and resilience to pests and climate extremes. Protecting and improving soil health is fundamental for sustainable food systems.
How does organic farming differ from conventional methods?
Organic farming avoids synthetic pesticides/herbicides and relies on natural amendments and biological pest control, leading to lower environmental footprints and healthier soil and crops. Conventional farming employs more chemical-based approaches, often with greater environmental impacts.
How can smallholder farmers start adopting sustainable agriculture practices?
Smallholders can begin by integrating cover cropping, conservation tillage, and simple water management techniques. Accessing Farmonaut’s monitoring app and using AI-based advisory tools helps make these transitions data-driven and successful.
What technology does Farmonaut offer for sustainable agriculture?
Farmonaut provides satellite imagery for real-time crop and soil monitoring, AI-powered advisory systems (Jeevn AI), blockchain traceability, resource management, and carbon footprint tracking, accessible on mobile, web, and via API.
How do these sustainable practices benefit the environment?
They reduce chemical runoff, conserve water and soil, enhance biodiversity, sequester carbon, and make food production more resilient to climate change.
Is controlled-environment agriculture suitable for all climates?
CEA allows year-round production regardless of external conditions, making it versatile for urban, arid, or extreme climates—but it often requires higher initial investments.
How can developers leverage Farmonaut’s API?
By using the Farmonaut API and developer documentation, developers and agribusinesses can integrate satellite, weather, and farm analytics into ERPs, traceability, or custom farm management platforms for scalable precision agriculture solutions.
What about crop insurance and financing?
Farmonaut’s platform enables satellite-based crop loan and insurance verification, streamlining access to finance and reducing fraud risk for farmers and lenders alike.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future with Sustainable Agriculture Practices
As we face the dual challenges of feeding a growing population and safeguarding our planet’s health, sustainable agriculture practices offer the best path forward. By integrating agroecology, organic farming methods, conservation tillage techniques, cover cropping, integrated pest management, agroforestry systems, water conservation in agriculture, system of rice intensification, biosolarization, and controlled environment agriculture, we can support resilient, productive, and eco-compatible agricultural systems.
Tools like Farmonaut empower us to implement these methods at scale—combining data-driven farm management, AI, and transparent traceability to ensure our food systems are both environmentally and economically sustainable. Together, let’s invest in soil health improvement, resource efficiency, and carbon reduction, ensuring our farming legacy nourishes both people and the planet.