Organic Pomegranate Revolution: How Samsat’s Sustainable Farming Practices Are Transforming Agriculture and Boosting Exports
“Organic pomegranate farming in Samsat, Turkey has increased export opportunities by 40% in the last 5 years.”
In the heart of Turkey’s Adıyaman province lies Samsat, a district that has become synonymous with organic pomegranate production. We are witnessing a remarkable transformation in agriculture as Samsat’s sustainable farming practices revolutionize the cultivation of this ancient fruit. This blog explores how traditional methods blend seamlessly with modern techniques to produce high-quality, organic pomegranates that are not only transforming local economies but also making waves in international markets.
The Rise of Organic Pomegranate Cultivation in Samsat
Samsat’s journey towards organic pomegranate production is a testament to the power of sustainable agriculture. The district has embraced organic farming methods, eschewing chemical fertilizers and pesticides in favor of natural alternatives. This shift has not only improved the quality of the pomegranates but has also had a profound impact on the local environment and economy.
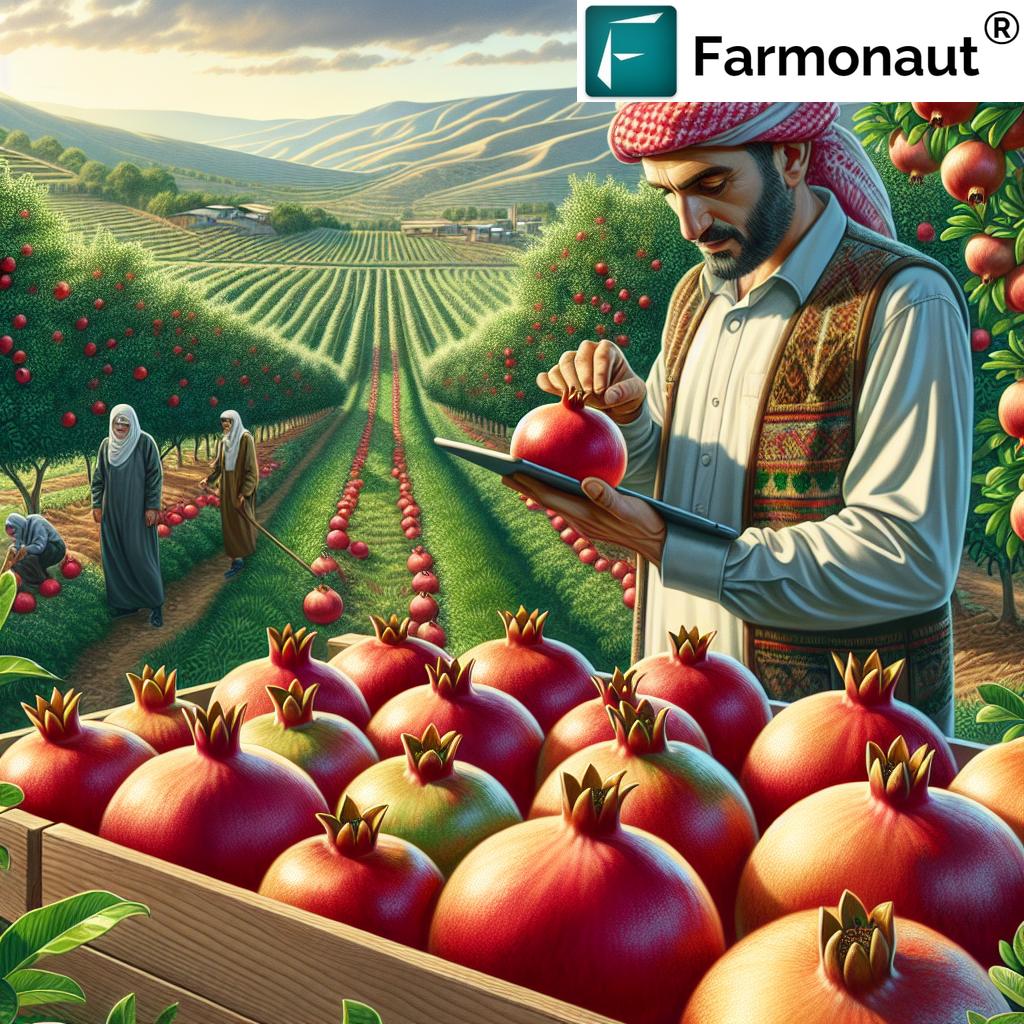

The district now produces approximately 43,000 tons of pomegranates annually, with an impressive 15,000 tons coming specifically from Samsat. This surge in production is not just about quantity; it’s about quality and sustainability. The careful harvesting process ensures that each fruit maintains its superior taste and nutritional value, making Samsat’s pomegranates highly sought after in both domestic and international markets.
The Benefits of Organic Farming in Pomegranate Production
Organic farming practices in Samsat have brought about numerous benefits, both environmental and economic. Let’s delve into some of the key advantages:
- Improved Soil Health: By avoiding chemical fertilizers and pesticides, organic farming methods help maintain and improve soil fertility naturally.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: Organic farms support a wider variety of plant and animal life, contributing to a healthier ecosystem.
- Water Conservation: Organic farming techniques often require less water, making them more sustainable in the long run.
- Higher Quality Produce: Organically grown pomegranates are often richer in flavor and nutrients.
- Economic Benefits: The premium prices commanded by organic produce translate to better incomes for farmers.
To better understand the impact of organic farming, let’s compare traditional and organic pomegranate farming practices in Samsat:
| Farming Aspect | Traditional Method | Organic Method | Environmental Impact | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Management | Chemical fertilizers | Organic compost, crop rotation | Improved soil health | Lower input costs |
| Pest Control | Synthetic pesticides | Natural predators, companion planting | Increased biodiversity | Reduced pesticide expenses |
| Fertilization | Artificial fertilizers | Animal manure, green manure | Reduced water pollution | Sustainable soil fertility |
| Water Usage | Conventional irrigation | Drip irrigation, mulching | Water conservation | Lower water costs |
| Biodiversity | Monoculture | Polyculture, cover crops | Enhanced ecosystem | Natural pest control |
| Yield (estimated) | Higher initial yield | Stable long-term yield | Sustainable production | Consistent income |
| Export Value (estimated) | Standard market prices | Premium prices | N/A | Higher profit margins |
| Carbon Footprint (estimated) | Higher | Lower | Reduced emissions | Potential carbon credits |
As we can see, the shift to organic farming methods in Samsat has brought about significant improvements across various aspects of pomegranate cultivation.
The Role of Agricultural Technology in Organic Pomegranate Farming
While organic farming emphasizes natural processes, it doesn’t mean turning away from technology. In fact, modern agricultural technology plays a crucial role in making organic farming more efficient and productive. Farmers in Samsat are increasingly turning to innovative solutions to enhance their organic pomegranate production.
One such solution is provided by Farmonaut, a pioneering agricultural technology company that offers advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions. Through its android, iOS, and web applications, Farmonaut makes precision agriculture accessible and affordable to farmers worldwide.
Farmonaut’s platform provides valuable services such as:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- AI-based advisory systems
- Blockchain-based traceability
- Resource management tools
These technologies are particularly beneficial for organic pomegranate farmers in Samsat, helping them to:
- Monitor crop health without the need for chemical interventions
- Optimize water usage through precise irrigation management
- Detect pest and disease outbreaks early, allowing for timely organic interventions
- Ensure traceability of their organic produce, building trust with consumers
By leveraging these technological advancements, Samsat’s organic pomegranate farmers are able to maintain high yields and quality while adhering to organic farming principles.
The Pomegranate Syrup Market: A Value-Added Opportunity
“Samsat’s organic pomegranate syrup production has grown 300% since adopting sustainable farming practices, boosting local economies significantly.”
One of the most exciting developments in Samsat’s organic pomegranate industry is the production of organic pomegranate syrup. This value-added product has opened up new economic opportunities for farmers and processors alike.
To produce one liter of high-quality organic pomegranate syrup, approximately 15 kilograms of pomegranates are required. This syrup commands a market value between 400 to 450 liras, representing a significant value addition to the raw fruit.
The production of organic pomegranate syrup offers several advantages:
- Higher profit margins for farmers
- Extended shelf life compared to fresh pomegranates
- Easier transportation and export opportunities
- Versatility in culinary and health applications
The growing demand for organic pomegranate syrup in international markets, particularly in European countries, has further boosted the local economy of Samsat. This success story demonstrates how organic farming practices, combined with value-added processing, can transform agricultural economies.
Environmental Sustainability and Soil Health in Organic Pomegranate Cultivation
At the heart of Samsat’s organic pomegranate revolution lies a deep commitment to environmental sustainability. Organic farming practices not only produce healthier fruits but also contribute significantly to maintaining and improving soil health.

Key aspects of soil health in organic pomegranate farming include:
- Organic Matter Content: Regular addition of organic matter improves soil structure and fertility.
- Microbial Activity: Organic practices encourage beneficial soil microorganisms, enhancing nutrient cycling.
- Water Retention: Improved soil structure leads to better water retention, reducing irrigation needs.
- Erosion Control: Cover crops and minimal tillage practices help prevent soil erosion.
Farmonaut’s technology plays a crucial role in monitoring and maintaining soil health. Their satellite-based crop health monitoring system allows farmers to track vegetation health indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), which can indicate soil health and crop stress levels.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced agricultural insights
Exporting Organic Fruits: Samsat’s Growing International Presence
The success of Samsat’s organic pomegranate industry is not limited to domestic markets. The region has seen a significant increase in exports, particularly to European countries where demand for organic fruits is on the rise.
Factors contributing to the export success of Samsat’s organic pomegranates include:
- High quality and nutritional value of organically grown fruits
- Strict adherence to international organic certification standards
- Efficient supply chain management
- Growing global awareness of the health benefits of pomegranates
The export of organic pomegranates and pomegranate products has not only boosted the local economy but has also put Samsat on the global agricultural map. This international recognition further encourages local farmers to maintain and improve their organic farming practices.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the organic pomegranate industry in Samsat has seen remarkable success, it’s not without its challenges. Some of the key issues faced by farmers include:
- Initial lower yields during the transition to organic farming
- Higher labor costs associated with organic farming practices
- Need for continuous education and training in organic farming methods
- Market fluctuations and competition from other pomegranate-producing regions
Despite these challenges, the future looks bright for Samsat’s organic pomegranate industry. With continued support from local government, adoption of advanced agricultural technologies, and growing global demand for organic products, Samsat is well-positioned to remain a leader in organic pomegranate production.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Farming
As we look to the future of organic pomegranate farming in Samsat, technology will continue to play a crucial role. Farmonaut’s innovative solutions are at the forefront of this technological revolution in agriculture.
Farmonaut’s platform offers:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Allows farmers to track crop health remotely, enabling early detection of issues.
- AI Advisory System: Provides personalized recommendations for crop management based on real-time data.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Ensures transparency in the supply chain, from farm to consumer.
- Resource Management Tools: Helps optimize the use of water, fertilizers, and other resources.
These technological advancements are making sustainable farming more accessible and efficient for Samsat’s pomegranate farmers.
Conclusion: A Model for Sustainable Agriculture
The organic pomegranate revolution in Samsat serves as a shining example of how sustainable farming practices can transform agriculture and boost exports. By embracing organic methods and leveraging modern agricultural technology, Samsat has not only improved the quality of its pomegranates but has also created a more sustainable and profitable agricultural sector.
As we look to the future, the success of Samsat’s organic pomegranate industry offers valuable lessons for other agricultural regions worldwide. It demonstrates that with the right blend of traditional wisdom, modern technology, and a commitment to sustainability, it’s possible to create an agricultural system that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment alike.
FAQs
- Q: What makes Samsat’s pomegranates unique?
A: Samsat’s pomegranates are grown using entirely organic practices, which enhance their quality and nutritional value while maintaining ecological balance. - Q: How has organic farming impacted the local economy of Samsat?
A: Organic farming has boosted farmers’ incomes through premium pricing and opened up new export opportunities, significantly contributing to the local economy. - Q: What role does technology play in Samsat’s organic pomegranate farming?
A: Advanced technologies like satellite-based crop monitoring and AI advisory systems help farmers optimize their organic practices and improve yields. - Q: How does organic pomegranate farming contribute to environmental sustainability?
A: Organic farming practices improve soil health, enhance biodiversity, and reduce water pollution, contributing to overall environmental sustainability. - Q: What are the main challenges faced by organic pomegranate farmers in Samsat?
A: Challenges include initial lower yields during transition, higher labor costs, and the need for continuous education in organic farming methods.