US-India Trade Negotiations: Ethanol Tariffs and Agricultural Market Access in 2024 Bilateral Agreement
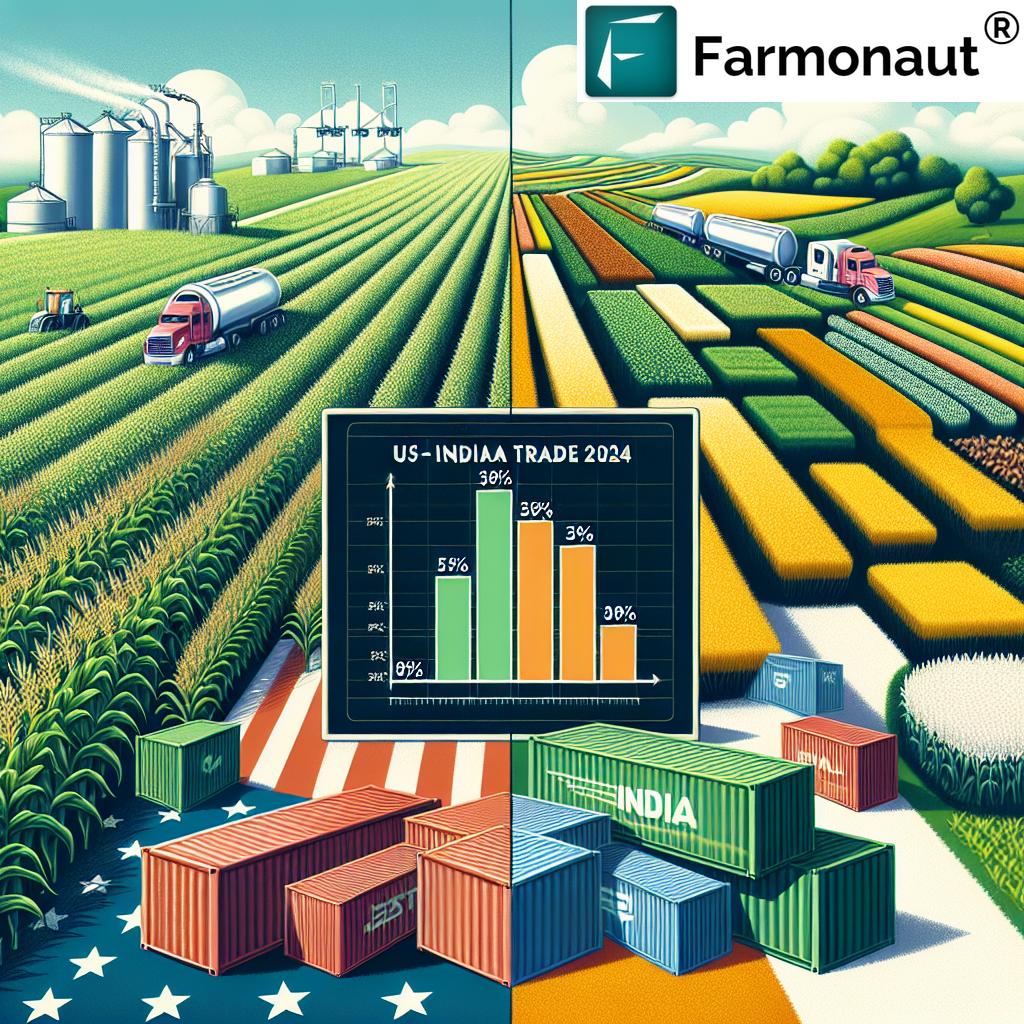
“India’s average applied MFN tariff on agricultural goods is 34 percentage points higher than the US’s at 39%.”
As we delve into the intricate world of international trade negotiations, the ongoing dialogue between the United States and India stands out as a pivotal moment in shaping global economic relations. The year 2024 marks a critical juncture as both nations aim to finalize a bilateral trade agreement that could redefine their economic partnership. At the heart of these negotiations lie several key issues, with ethanol tariffs and agricultural market access taking center stage.
In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll explore the nuances of the US-India trade dynamics, examine the disparities in tariff structures, and unpack the potential implications for bilateral economic relations in the coming years. As we navigate through this complex landscape, we’ll shed light on how these negotiations could reshape agricultural trade policies and impact global markets.
The Current State of US-India Trade Relations
Before we dive into the specifics of the 2024 bilateral agreement, it’s crucial to understand the current state of trade relations between the United States and India. Both countries have long recognized the importance of their economic partnership, yet significant disparities in trade barriers have persisted over the years.
- The United States is one of the most open economies in the world, with relatively low tariffs across various sectors.
- India, on the other hand, has maintained higher tariff rates, particularly in sectors like agriculture and automobiles.
- This lack of reciprocity has been a point of contention, contributing to a large and persistent annual trade deficit for the United States.
To illustrate these disparities, let’s consider some key statistics:
| Trade Barrier Category | United States | India | Potential Impact on Negotiations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Applied MFN Tariff on Agricultural Goods | 5% | 39% | Major point of contention; US likely to push for significant reduction |
| Ethanol Import Restrictions | 2.5% tariff | Import prohibited for fuel use | US to seek removal of import ban; potential for compromise on tariff rates |
| Dairy Market Access | Open market | Restricted access | US to demand improved access; India may resist due to domestic concerns |
| Textile Tariffs | 5-7% | Seeking reduction to 0% | Potential bargaining chip for India in exchange for agricultural concessions |
These statistics highlight the significant gap in trade policies between the two nations, setting the stage for intense negotiations in the lead-up to the 2024 bilateral agreement.
Key Sectors in Focus: Agriculture and Ethanol
As we analyze the upcoming trade negotiations, two sectors emerge as critical focal points: agriculture and ethanol. These areas not only represent significant economic interests for both countries but also embody the broader challenges of balancing domestic priorities with international trade obligations.
Agricultural Market Access
The agricultural sector has long been a contentious issue in US-India trade relations. The United States, with its highly efficient and technologically advanced agricultural industry, seeks improved access to India’s vast consumer market. However, India has traditionally maintained high tariffs and strict regulations on agricultural imports to protect its large farming population.
- The US average applied Most Favored Nation (MFN) tariff on agricultural goods is a mere 5%.
- In stark contrast, India’s average applied MFN tariff on agricultural goods stands at a towering 39%.
- This 34% gap represents a significant barrier to US agricultural exports and is likely to be a major point of discussion in the negotiations.
The disparity in agricultural tariffs not only affects US farmers and exporters but also impacts Indian consumers who may benefit from increased competition and potentially lower prices for agricultural products. As negotiations progress, finding a balance between protecting India’s agricultural sector and opening up the market to more US imports will be a delicate task.
Ethanol: A Key Point of Contention
The ethanol market has emerged as a particularly thorny issue in US-India trade relations. Despite India’s ambitious targets for blending ethanol with gasoline, the country maintains strict import restrictions on ethanol for fuel use. This policy has created a paradoxical situation where India aims to increase ethanol usage while limiting its potential supply sources.
- The US tariff on ethanol is a mere 2.5%.
- India prohibits the importation of ethanol for fuel use and requires import licenses for non-fuel purposes.
- These restrictions clash with India’s goal of achieving 20% ethanol blending in gasoline by 2025.
The ethanol issue highlights the complex interplay between trade policies, domestic energy goals, and environmental considerations. As India seeks to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels and promote cleaner energy alternatives, the potential for increased ethanol imports from the US could play a significant role in achieving these objectives.

As we delve deeper into these key sectors, it’s important to consider how technological advancements in agriculture could play a role in addressing some of the challenges faced by both countries. Platforms like Farmonaut offer innovative solutions for precision agriculture and farm management, which could potentially help bridge the gap between agricultural productivity and sustainability goals.
The Push for Reciprocity and Fair Market Access
“The US-India bilateral trade agreement, targeting completion by 2024, aims to address a 34% gap in agricultural tariffs.”
At the core of the US-India trade negotiations is the principle of reciprocity. The United States argues that the current trade relationship lacks balance, with India maintaining significantly higher trade barriers across various sectors. This imbalance, according to US officials, contributes to the persistent trade deficit and limits opportunities for American businesses in the Indian market.
Key points of contention include:
- Agricultural tariffs and market access
- Ethanol import restrictions
- Dairy product regulations
- Medical device price controls
The United States is expected to push for major concessions in these areas as part of the proposed bilateral trade agreement. In return, India is likely to seek reduced duties on labor-intensive products such as textiles, leather, and gems and jewelry, aiming to boost its export-oriented industries.
The Role of Technology in Addressing Trade Challenges
As negotiations progress, both countries are looking at innovative ways to address trade barriers and improve market access. Technology plays a crucial role in this context, offering solutions that can enhance transparency, efficiency, and compliance in international trade.
For instance, advanced agricultural technologies like those offered by Farmonaut can help farmers in both countries optimize their production, potentially easing some of the concerns around agricultural competition. Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring and AI-driven advisory systems could contribute to more efficient and sustainable farming practices, benefiting both US and Indian farmers.
To explore how Farmonaut’s solutions can benefit your agricultural operations, visit their web app or download their mobile apps:
Ethanol Market: A Case Study in Trade Disparities
The ethanol market serves as a prime example of the trade disparities between the United States and India. While the US maintains a low tariff of 2.5% on ethanol imports, India’s policies are far more restrictive. Let’s examine this issue in more detail:
- India prohibits the importation of ethanol for fuel use, despite ambitious targets for ethanol blending in gasoline.
- The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) restricts biofuel imports for non-fuel use to actual users.
- Since May 2019, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry (MOCI) requires an import license for importing biofuels.
These restrictions create a significant barrier for US ethanol producers looking to enter the Indian market. Moreover, they potentially hinder India’s own goals of increasing ethanol blending in gasoline to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
Comparing US-Brazil Ethanol Trade
To put the US-India ethanol trade situation into perspective, it’s helpful to compare it with the US-Brazil ethanol trade dynamics:
- Brazil charges an 18% tariff on US ethanol exports.
- In 2024, the US imported over $200 million in ethanol from Brazil.
- In contrast, US exports of ethanol to Brazil amounted to only $52 million.
This comparison highlights the potential for increased ethanol trade between the US and India if tariff and non-tariff barriers were to be reduced or eliminated.
Agricultural Market Access: Balancing Protection and Openness
The agricultural sector remains a critical area of focus in the US-India trade negotiations. The vast disparity in average applied MFN tariffs on agricultural goods (5% for the US vs. 39% for India) underscores the challenges in achieving a balanced trade relationship.
Key issues in agricultural market access include:
- High tariffs on US agricultural exports to India
- Non-tariff barriers such as sanitary and phytosanitary measures
- India’s concerns about protecting its large farming population
- US push for increased access to India’s dairy market
As negotiations progress, both countries will need to find creative solutions that address these concerns while promoting mutually beneficial trade. This may involve phased tariff reductions, targeted market access improvements, and cooperation on agricultural technology and best practices.
The Role of Agricultural Technology in Trade Negotiations
Advanced agricultural technologies could play a significant role in addressing some of the concerns surrounding agricultural trade. By improving productivity, sustainability, and traceability, these technologies can help both countries achieve their agricultural goals while potentially easing trade tensions.
Farmonaut’s solutions, for instance, offer valuable tools for precision agriculture that could benefit farmers in both the US and India:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring for optimized resource use
- AI-driven advisory systems for improved decision-making
- Blockchain-based traceability for enhanced supply chain transparency
To learn more about how Farmonaut’s technologies can transform agricultural practices, visit their web app or explore their API for custom integrations.
Implications for Global Markets and Trade Policies
The outcome of the US-India trade negotiations will have far-reaching implications beyond the bilateral relationship. As two of the world’s largest economies, any shifts in their trade policies can significantly impact global markets and set precedents for future trade agreements.
Potential implications include:
- Reshaping of global agricultural trade flows
- Influence on World Trade Organization (WTO) negotiations
- Impact on developing countries’ trade policies
- Acceleration of technological adoption in agriculture and trade
As these negotiations unfold, it’s crucial for businesses and policymakers worldwide to stay informed and adapt to the changing landscape of international trade.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
As the US and India work towards finalizing their bilateral trade agreement by 2024, both countries face significant challenges and opportunities. The negotiations will require careful balancing of domestic interests with the benefits of increased trade and cooperation.
Key challenges include:
- Bridging the gap in tariff structures, especially in agriculture
- Addressing non-tariff barriers and regulatory issues
- Aligning domestic policies with international trade obligations
- Managing political pressures from various stakeholders
However, the potential opportunities are equally significant:
- Expanded market access for businesses in both countries
- Increased investment flows and technology transfer
- Enhanced cooperation in strategic sectors like renewable energy
- Strengthened geopolitical partnership between the US and India
As negotiations progress, innovative solutions and technologies will play a crucial role in addressing these challenges and capitalizing on opportunities. Companies like Farmonaut, with their advanced agricultural technologies, can contribute to more efficient and sustainable farming practices, potentially easing some of the tensions around agricultural trade.
Conclusion: Towards a Balanced and Mutually Beneficial Agreement
As we look ahead to the potential finalization of the US-India bilateral trade agreement in 2024, it’s clear that both countries have much to gain from a balanced and mutually beneficial partnership. The negotiations surrounding ethanol tariffs and agricultural market access represent just a fraction of the complex issues at play, but they highlight the importance of finding common ground and innovative solutions.
Key takeaways from our analysis include:
- The need for greater reciprocity in trade policies between the US and India
- The potential for technological solutions to address agricultural trade challenges
- The importance of balancing domestic interests with international trade obligations
- The far-reaching implications of US-India trade negotiations on global markets
As these negotiations unfold, it will be crucial for businesses, policymakers, and stakeholders in both countries to stay informed and engaged. The outcome of these talks could reshape not only US-India economic relations but also influence global trade dynamics for years to come.
For those interested in staying at the forefront of agricultural innovation and its impact on international trade, exploring solutions like Farmonaut can provide valuable insights. To learn more about how advanced agricultural technologies can transform farming practices and contribute to more efficient global trade, visit Farmonaut’s web app or explore their API Developer Docs.
FAQ Section
- Q: What are the main issues in the US-India trade negotiations?
A: The main issues include agricultural market access, ethanol tariffs, dairy product regulations, and medical device price controls. The US is seeking improved access to India’s markets, while India aims for reduced tariffs on its exports like textiles and jewelry. - Q: Why is the ethanol market a contentious issue?
A: India prohibits ethanol imports for fuel use despite having ambitious ethanol blending targets. This clashes with the US desire to export ethanol to India, creating a significant trade barrier. - Q: How do agricultural tariffs differ between the US and India?
A: The US average applied MFN tariff on agricultural goods is 5%, while India’s is 39%, creating a significant disparity in market access. - Q: What role can technology play in addressing trade challenges?
A: Advanced agricultural technologies, like those offered by Farmonaut, can improve productivity and sustainability, potentially easing some trade tensions by enhancing efficiency and traceability in farming practices. - Q: When is the bilateral trade agreement expected to be finalized?
A: The US and India aim to finalize the bilateral trade agreement by 2024.
Earn With Farmonaut
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
For more information on the affiliate program, visit Farmonaut’s Affiliate Program.
Farmonaut Subscriptions
By leveraging advanced technologies and fostering open dialogue, the US and India have the opportunity to forge a trade agreement that not only benefits both nations but also sets a positive precedent for global trade relations in the 21st century.