7 Vertical Farming Solutions That Will Blow Your Mind!
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Vertical Farming – The Revolution in Food Production
- Historical Context & Evolution
- 7 Vertical Farming Solutions Overview
- Comparative Feature Table: Vertical Farming Technologies
- Technological Innovations Driving Vertical Agriculture
- Advantages of Vertical Farming
- Overcoming Vertical Farming Challenges
- Expanding Applications: Urban, Forestry, and Beyond
- Farmonaut: Empowering Precision Agriculture
- Future Outlook: The Potential and Promise
- FAQ: All About Vertical Farming
“Vertical farms can use up to 95% less water than traditional farming methods, revolutionizing urban agriculture efficiency.”
Introduction: Vertical Farming – The Revolution in Food Production
As we face growing challenges in traditional agriculture, from depleted arable land and water scarcity to urbanization and climate uncertainties, the world is seeking urgent and innovative solutions. Vertical farming has emerged as an innovative agricultural practice that involves cultivating crops in vertically stacked layers or integrated structures, often placed directly within our cities. Using controlled environment agriculture (CEA) methods such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics, vertical farming is fundamentally reshaping the future of sustainable food production.
In this deep-dive, we will explore seven vertical farming solutions—from high-tech urban towers to modular hydroponic labs—that are driving innovation, efficiency, and new urban agriculture solutions. We will also examine how platforms like Farmonaut are strengthening this revolution by offering vital, real-time crop insights, traceability, and environmental monitoring, making modern precision agriculture accessible to everyone.
Historical Context & Evolution: The Journey to Modern Vertical Farming
The concept of vertical farming stretches back through historical context, with its origins in early 20th-century architectural proposals. Visionaries like Le Corbusier imagined “Immeubles-Villas” (1922), envisioning spaces where nature and habitat merged inside urban areas. Decades later, the innovatively named SITE’s “Highrise of Homes” (1972) incorporated urban farming into high-rise homes—laying the groundwork for what would become modern vertical farms. While these ideas remained conceptual for much of the century, recent decades have seen a rapid building of momentum.
Today, a convergence of technological advancements—including hydroponic, aeroponic, and automated robotics systems—has enabled scalable, efficient urban agriculture solutions. The result? Modern vertical farming is now a practical, powerful tool for sustainable food production—directly addressing challenges like limited arable land, water scarcity, energy costs, and urban population growth.
“Some vertical farms achieve crop yields 390 times greater per square foot compared to conventional field farming.”
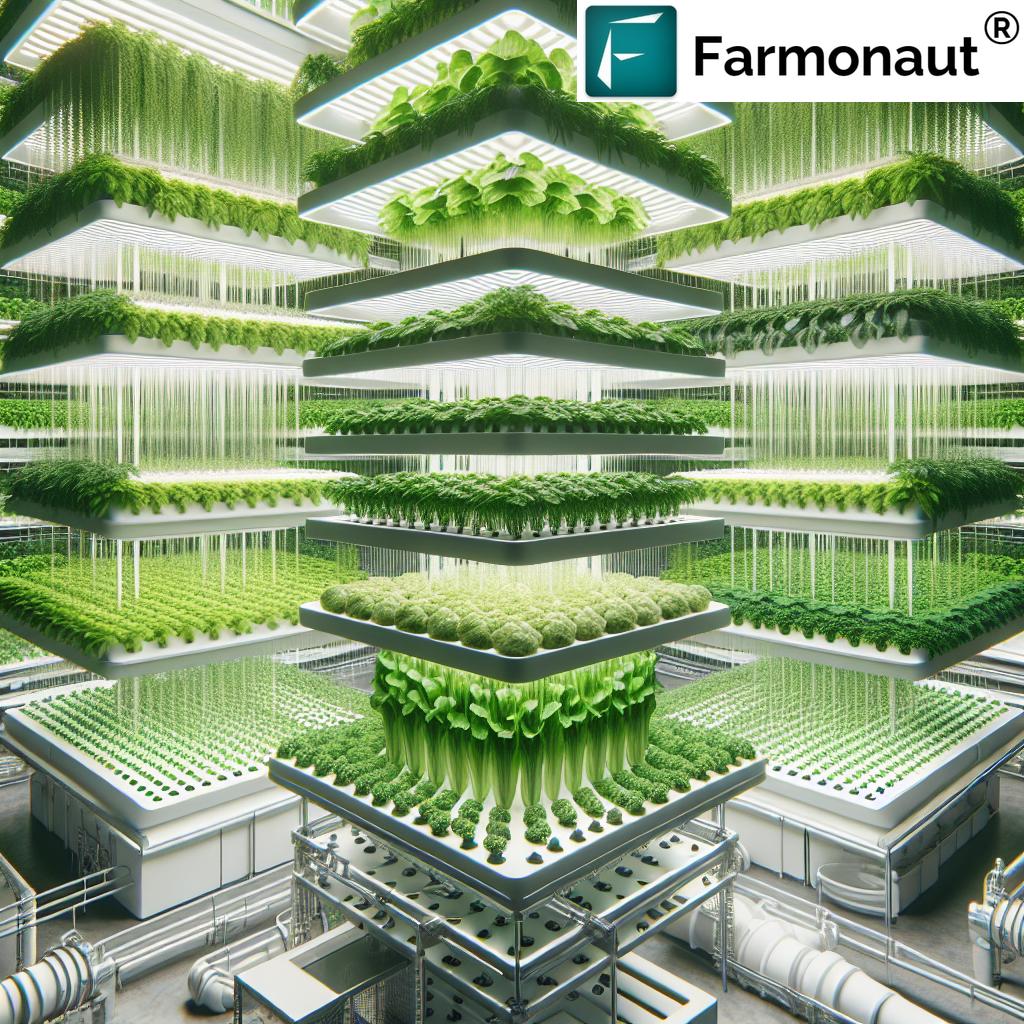
7 Vertical Farming Solutions That Are Transforming Agriculture
Let’s explore the top seven vertical farming solutions—each offering a unique answer to the challenges in traditional agriculture. These innovative methods employ a variety of technologies, structures, and systems to optimize plant growth, space, and resource efficiency, from hydroponic towers to modulation-based CEA farms.
-
Hydroponic Vertical Wall Farms
Best for urban spaces, balconies, and indoor agriculture.- Plants are grown in vertically stacked “walls” without soil, using circulating nutrient-rich water.
- Extremely efficient for optimizing limited land within cities.
- Common hydroponic farming systems include NFT (Nutrient Film Technique) and drip systems.
-
Aeroponic Tower Systems
Perfect for leafy greens, herbs, and swift growth cycles.- Plants are suspended in air, and roots receive ultra-fine mist of nutrients.
- Aeroponics dramatically reduces water usage and increases oxygen delivery to roots.
-
Modular Container Vertical Farms
Adaptable for urban lots, restaurant supply, and disaster relief.- Self-contained steel or polycarbonate modules are stackable and mobile.
- Facilitate year-round crop cultivation in fully controlled conditions.
-
Multi-Layer Hydroponic Shelving Farms
Scalable for commercial indoor farming operations.- Multiple horizontal hydroponic shelves facilitate dense plant production vertically.
- Commonly used in warehouses and urban farm buildings.
-
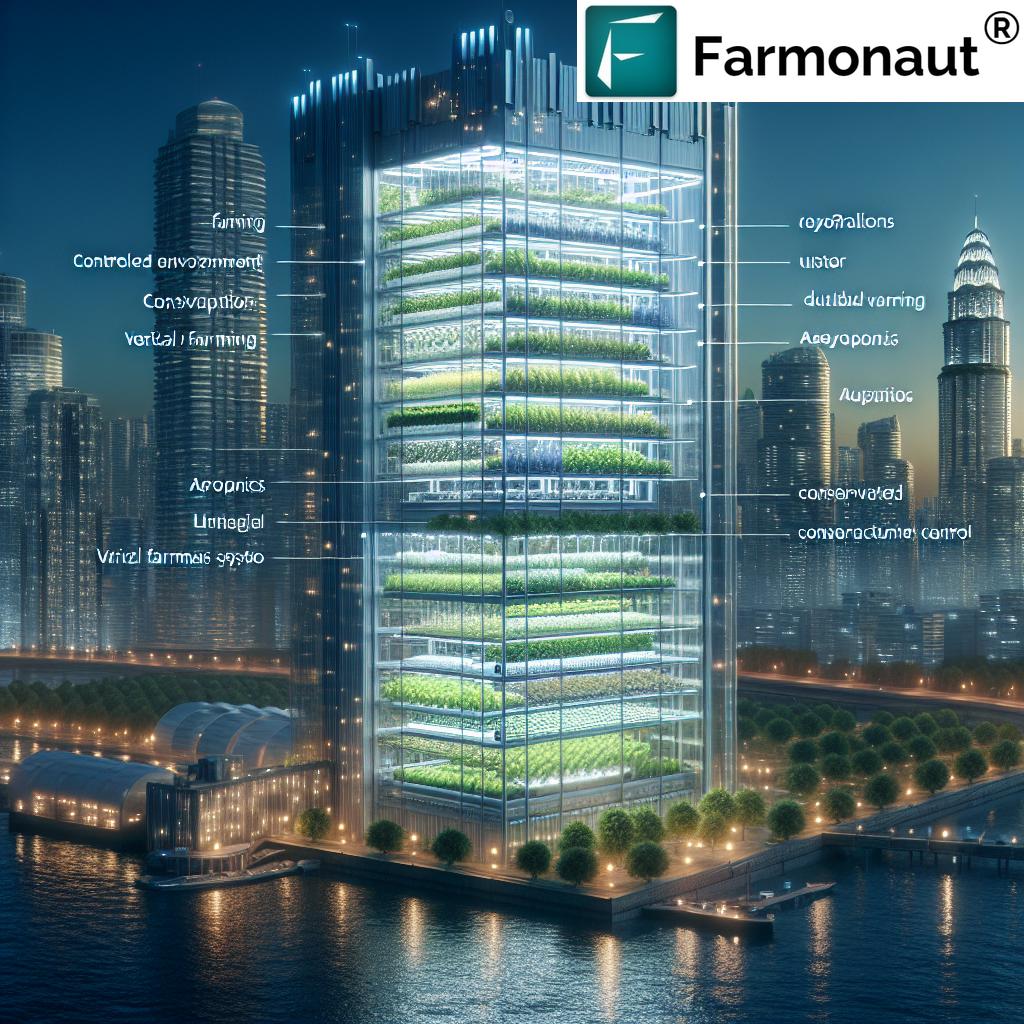
Skyscraper Greenhouse Structures
High-rise farms designed for city integration.- Large-scale glass or polymer buildings, reaching several stories high, with integrated CEA systems.
- Utilize both natural and artificial lighting for major commercial output.
-
Hybrid Aquaponics Systems
Merges fish farming with hydroponic plant production.- Fish waste provides nutrients; plants filter water to maintain aquatic health.
- Extremely water efficient and a dual food source system.
-
Robotic Automated Vertical Farms
Leverages full automation for planting, care, and harvesting.- Employ robotics, sensors, and AI-driven control for labor savings and precise environmental regulation.
- Excellent for high-value and sensitive crops requiring continuous monitoring.
Comparative Feature Table: Vertical Farming Technologies
| Solution Name | Technology Used | Scale (Est. Production/year) | Light Source Type | Water Usage (L/year) | Energy Efficiency (kWh/kg) | Unique Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroponic Vertical Wall Farms | Hydroponics (NFT/Drip) | 2–5 tons | LED, Achievable Sunlight | 7,000–13,000 | 2.0 | Wall-mounted, retrofits in small urban areas |
| Aeroponic Tower Systems | Aeroponics, Mist Nutrient Delivery | 3–12 tons | Full Spectrum LED | 4,500–8,000 | 1.7 | Extremely low water usage, high oxygenation |
| Modular Container Vertical Farms | Hydroponic/Aeroponic Hybrid | 10–20 tons | LED & Some UV | 12,000–16,000 | 2.4 | Mobile, scalable for disaster or site-specific food supply |
| Multi-Layer Hydroponic Shelving Farms | Hydroponics (Flood, NFT) | 16–32 tons | Full Spectrum LED | 20,000–40,000 | 2.2 | Warehouse-scale output, can integrate robotics |
| Skyscraper Greenhouse Structures | CEA with Large-scale Glass Greenhouse | 100–200 tons | Natural Sun, Supplemental LED | 85,000–160,000 | 1.4 | Urban integration, sustainable building design |
| Hybrid Aquaponics Systems | Aquaponics (Fish + Hydroponic Plants) | 4–15 tons (plus fish yield) | LED + Some Natural | 3,500–7,500 | 1.8 | Dual food production, natural nutrient cycling |
| Robotic Automated Vertical Farms | AI, Robotics, Sensor Networks | 25–50 tons | Fully Adaptive LED | 30,000–55,000 | 1.5 | Labor automation, big data analytics for optimization |
Technological Innovations Powering Vertical Farm Efficiency
The rise of vertical farming is intrinsically tied to technological advancements. Our ability to optimize growing conditions inside controlled environments has unlocked new levels of resource efficiency and year-round crop cultivation, making these methods ideal for urban environments and beyond. Here’s a breakdown of the most exciting technologies leveraged in modern vertical farms:
Hydroponics: Soilless, High-Performance Cultivation
- Hydroponic farming systems deliver water-soluble nutrients directly to plant roots.
- Growers can precisely control the nutrient balance, pH, and water usage.
- Common systems include Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), deep-water culture, and drip irrigation platforms.
- Reducing water usage in agriculture by up to 90%, hydroponics enables dense produce output in limited spaces.
Aeroponics: Maximum Oxygen, Minimum Water
- Roots are suspended in air, periodically sprayed with a fine nutrient mist.
- Increases uptake of oxygen, leading to enhanced plant growth and reduced disease.
- Can use as little as 5% of the water required by traditional agriculture methods.
Aquaponics: Circular Resource Systems
- Integrates aquaculture (fish) with hydroponic plant cultivation.
- Fish waste is converted by microbes into plant nutrients; plants purify water for the fish.
- Promotes a closed-loop system of natural resource optimization and year-round food production.
Artificial Lighting: LED and Adaptive Light Scenarios
- Full-spectrum and programmable LEDs provide customizable intensity and wavelengths matching plant needs at every growth stage.
- Artificial climate control through lighting allows vertical farms to flourish regardless of outdoor weather.
Automated Robotic & AI Systems
- Robotics streamline planting, harvesting, crop monitoring, and maintenance.
- AI-powered sensors and data analytics enable precision control of environment for maximum productivity and resource savings.
- Advanced machine learning can predict pest pressures, future growth rates, and energy optimization needs.
Climate Control Systems
- Automated systems actively regulate temperature, humidity, and CO₂ levels for optimal crop growth.
- Reduce crop losses by creating a consistent ecosystem, independent of external weather conditions.
Are you an AgriTech developer?
Access Farmonaut’s satellite and weather data through our API Developer Documentation to power your own solutions and applications!
Advantages of Vertical Farming: Why It’s a Game Changer
Adopting vertical farming yields multiple benefits over conventional agriculture, especially in the context of sustainable food production in urban environments:
- Resource Efficiency & Water Savings
- Reducing water usage in agriculture by up to 90–95%
- Recirculating systems minimize loss to evaporation or runoff
- Space Optimization
- Capable of producing up to 390 times more crops per square meter compared to open field agriculture
- Utilizes limited urban land and spaces otherwise unfit for traditional cultivation
- Year-Round Crop Cultivation
- Strong control of climate conditions enables harvests every season
- Shortens supply chains and delivers consistently fresh food
- Reduced Pesticide and Herbicide Usage
- Closed-loop, controlled environments lower the risk of pests and contamination
- Produces cleaner, healthier crops with less environmental impact
- Lower Carbon Footprint
- Urban agriculture solutions minimize transport emissions and food miles
- Enables localization of food production within cities
- Scalability and Modularity
- From single walls to skyscraper farms, scale is highly adaptable
Overcoming Vertical Farming Challenges: What Lies Ahead?
Despite its promise, vertical farming does not come without challenges:
- High Initial Investment—Infrastructure, lighting, and automation mean startups can face substantial setup costs.
- Energy Consumption—Continuous, large-scale use of artificial lighting and climate systems can drive up electricity needs. However, advances in energy efficiency, on-site renewables, and AI-driven controls are helping offset this.
- Technical Expertise—Operating these advanced systems requires specialized knowledge in hydroponics, automation, and crop science.
- Crop Selection—Some staple crops (e.g., cereals) remain more challenging to produce cost-effectively in vertical setups.
As a result, ongoing research and technological innovation are focusing on reducing costs, broadening the types of crops viable for vertical production, improving energy efficiency, and making solutions more accessible worldwide.
Expanding Applications: Urban Agriculture, Forestry, and Beyond
The versatility of vertical farms is extending their impact well beyond just urban lettuce or microgreen production. Let’s look at some powerful applications in agricultural and forestry systems:
- Urban Agriculture Solutions
- Empower cities to achieve food security and sustainability with fresh, local produce.
- Reduce environmental impact by minimizing long-distance transport and packaging waste.
- Forestry and Tree Propagation
- Controlled growth chambers accelerate the production of healthy tree seedlings for reforestation, habitat restoration, and landscaping.
- Improves survival rates for newly planted trees by providing optimal growth conditions pre-transplant.
- Learn more about tree propagation and large-scale crop plantation & forest advisory service via Farmonaut’s dedicated plantation management platform.
- Integration with Smart Resource Management Platforms
- Fleet management for vertical farm deliveries, and satellite monitoring for health status, are critical for efficiency. Farmonaut’s Fleet Management tool helps optimize urban food logistics, control costs, and ensure transparency across the supply chain.
Farmonaut: Scaling Precision & Sustainability in Modern Vertical Agriculture
While advanced vertical farming solutions lead the charge in technological innovation, data-driven platforms like Farmonaut provide the essential tools to ensure these farms operate with maximum resource efficiency, transparency, and sustainability. Let’s review how Farmonaut is revolutionizing farm and environmental management:
-
Satellite-based Crop Health Monitoring:
- Monitor the health of both traditional and urban agricultural crops in real-time using multispectral satellite imagery (NDVI, soil moisture, etc.).
- Empower individual farmers and urban growers alike to make data-driven decisions that optimize yields and minimize resource usage.
-
Jeevn AI Advisory System:
- Receive tailored recommendations on irrigation, fertilization, and pest management based on real-time field and weather data.
- Automated insights result in reduced waste and improved production efficiency.
-
Blockchain-based Product Traceability:
- Blockchain traceability secures food supply chains, especially crucial in fresh produce and urban vertical farm systems, increasing consumer trust and reducing fraud.
-
Fleet & Resource Management Tools:
- Track and optimize logistics for farm to table urban supply, reducing costs and ensuring efficient food delivery.
-
Carbon Footprinting:
- Track, analyze, reduce, and report the environmental impact of your vertical farm operations.
- See how Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solutions are fueling sustainable practices
-
Large-scale Farm Management:
- Centralize control of operations, planning, and land/resource allocation—even across multiple urban farm locations—with the Farmonaut Agro Admin App.
-
Insurance & Loan Verification:
- Automate crop insurance and loan processes, reducing fraud with satellite-based verification. Learn about satellite-driven crop loan and insurance verification.
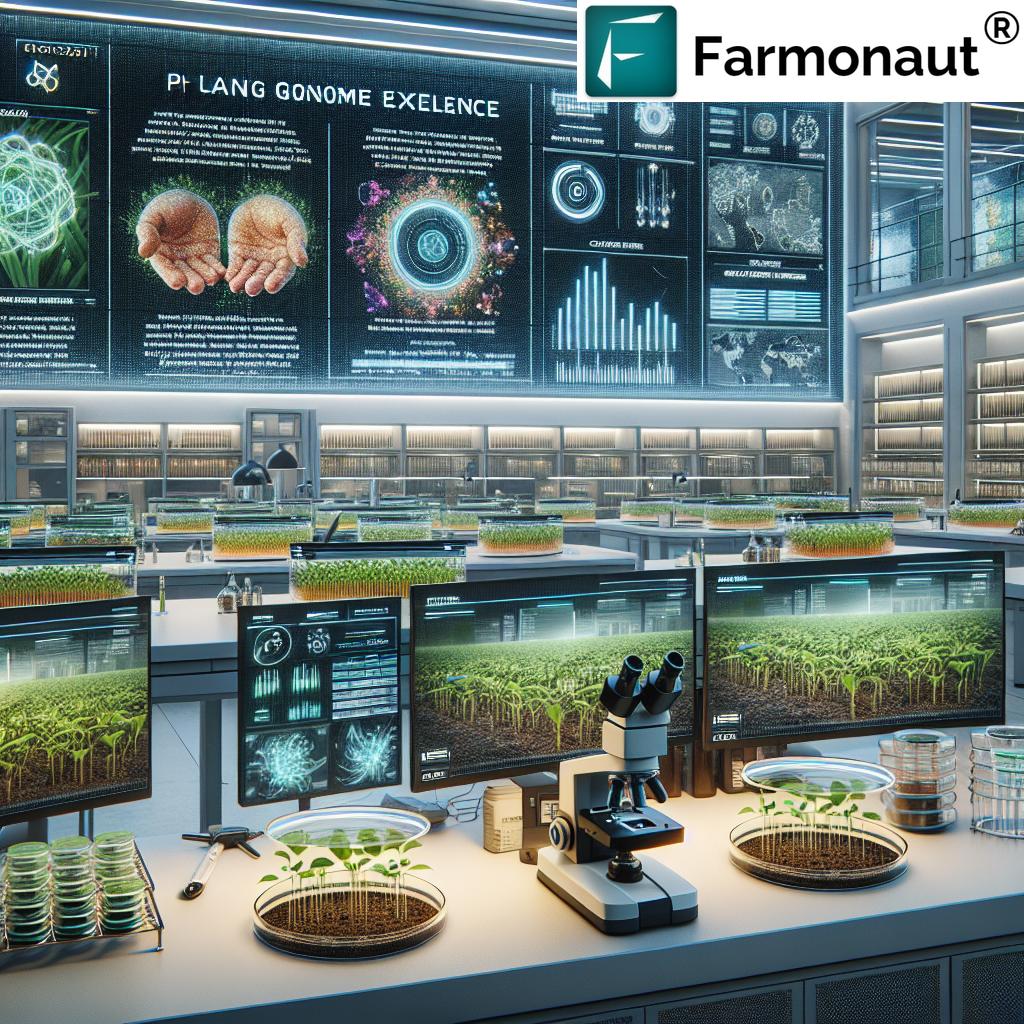
Future Outlook: Unlocking the Full Potential of Vertical Farming
As urban populations rise and climate unpredictabilities intensify, our need for sustainable food production and resource optimization will only grow. Looking ahead, the future of vertical farming will be marked by even deeper:
- Integration with other urban sustainability systems (e.g., renewable energy, smart water recycling, IoT networks).
- Expansion into staple crops using more advanced methods, genome editing, and crop science.
- Growing role of artificial intelligence, automation, and satellite remote sensing for monitoring, predicting, and adjusting real-time operating parameters.
- Broader adoption of traceability and carbon footprint tracking as consumers and regulators demand sustainable, transparent food systems.
- Opportunities for urban economies to create jobs, increase food security, and shorten supply chains—one “vertical farm” at a time!
With the convergence of bold innovation, scalable technology, and intelligent platforms like Farmonaut, we are poised to transform how humanity produces and consumes food—responsibly, sustainably, and efficiently.
FAQ: All About Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is an innovative agricultural practice involving the cultivation of crops in vertically stacked layers or structures, often integrated into urban areas. This method uses controlled environment agriculture (CEA) techniques—like hydroponics, aeroponics, or aquaponics—to optimize plant growth, resource efficiency, and sustainability.
How is water used more efficiently in vertical farming?
Hydroponic and aeroponic farming systems recirculate nutrient-rich water, significantly reducing water waste compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. Some vertical farms use up to 95% less water—making them key in regions of water scarcity.
Is vertical farming sustainable?
Yes. Vertical farming reduces the need for arable land, pesticides, herbicides, and transport, promoting sustainable food production. Platforms like Farmonaut enhance sustainability with precision monitoring, carbon footprint tracking, and data-driven management tools.
What are the main challenges of vertical farming?
The biggest challenges include high initial setup costs (infrastructure, lighting), ongoing energy requirements, and technical expertise for managing systems. However, continuous innovations, improved energy efficiency, and accessible precision agriculture platforms are solving many of these issues.
Can vertical farms be profitable for startups or small farms?
While startup costs are higher, vertical farms’ space optimization, rapid growth cycles, and potential year-round crop cultivation can offer competitive returns. Using management tools like Farmonaut further boosts efficiency and resource savings, improving profitability.
Does Farmonaut build or operate vertical farms?
Farmonaut is not a manufacturer, online marketplace, or regulatory body. Instead, it empowers vertical and traditional farmers alike with cutting-edge digital monitoring, AI-based advisory, supply chain traceability, and sustainability solutions—making precision agriculture affordable and globally accessible.
How can I use Farmonaut for my urban or vertical farm?
Simply download the Farmonaut app (Android, iOS, or web), choose your subscription, and start tracking health, moisture, yield, and environmental impact—no extra on-site sensors required!
Conclusion: Vertical Farming – Cultivating the Future of Agriculture
Vertical farming stands out as one of the most innovative methods in modern agricultural practice, adeptly addressing the pressing challenges of urbanization, arable land scarcity, and sustainable food production. Harnessing the potential of controlled environment agriculture and advanced vertical farm technologies, this revolution is enabling us to optimize growth, minimize resource usage, and reimagine farming for the 21st century.
As platforms like Farmonaut continue to democratize AI, satellite insights, and traceable farm management for everyone—from smallholders to urban vertical farms—our collective power to build a sustainable food future has never been greater.
Now is the time to embrace the advantages of vertical farming. Join us in redefining agriculture—for cities, communities, and the planet.