Hydroponic Farming: 7 Benefits You Can’t Ignore!
“Hydroponic systems can use up to 90% less water than traditional soil farming methods.”
Summary: What Is Hydroponic Farming?
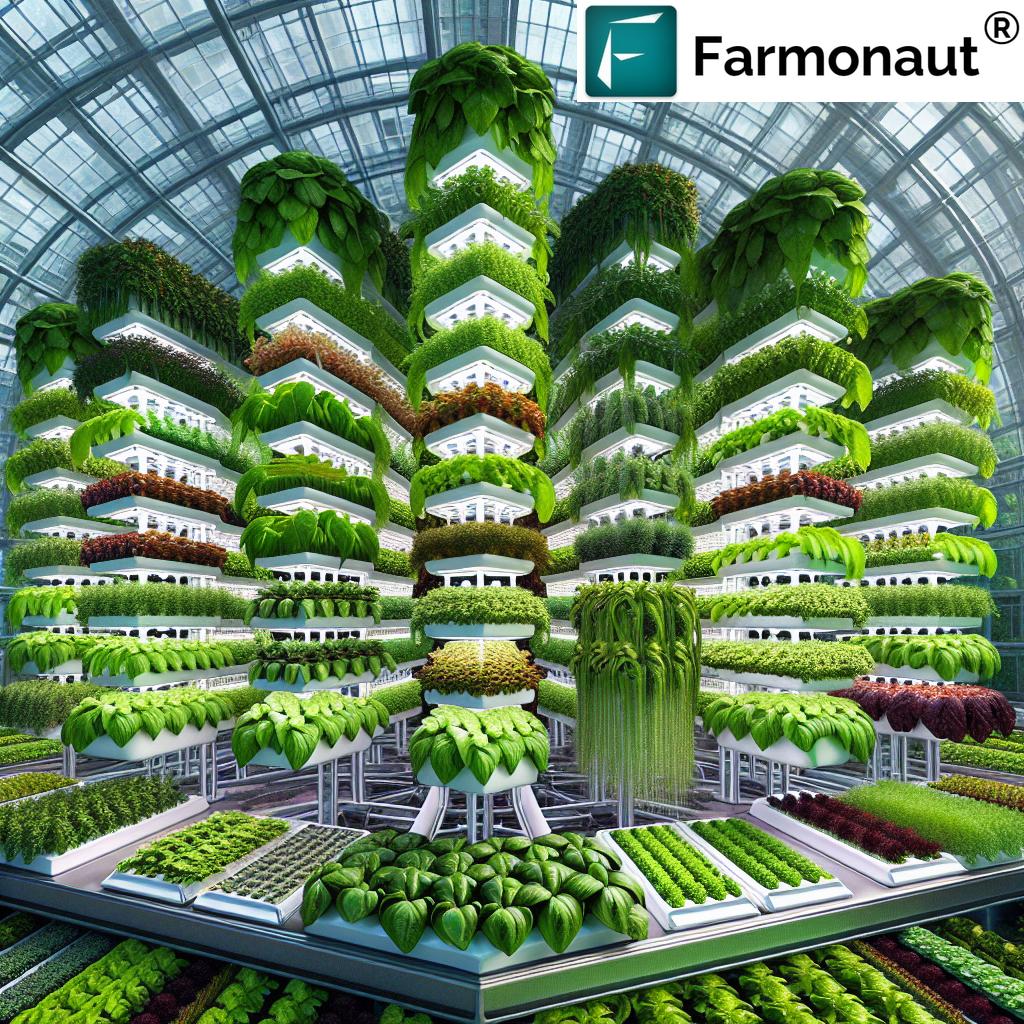
In recent years, hydroponic farming has revolutionized our approach to sustainable food production, reshaping both urban and commercial agricultural practices. This innovative technique involves growing plants without traditional soil—instead, plants receive essential nutrients through specially formulated nutrient solutions delivered directly to their roots. By maintaining complete control over environmental conditions and nutrient supply, hydroponic systems offer solutions to modern challenges like limited arable land, water scarcity, and the quest for sustainable, high-yield food production methods.
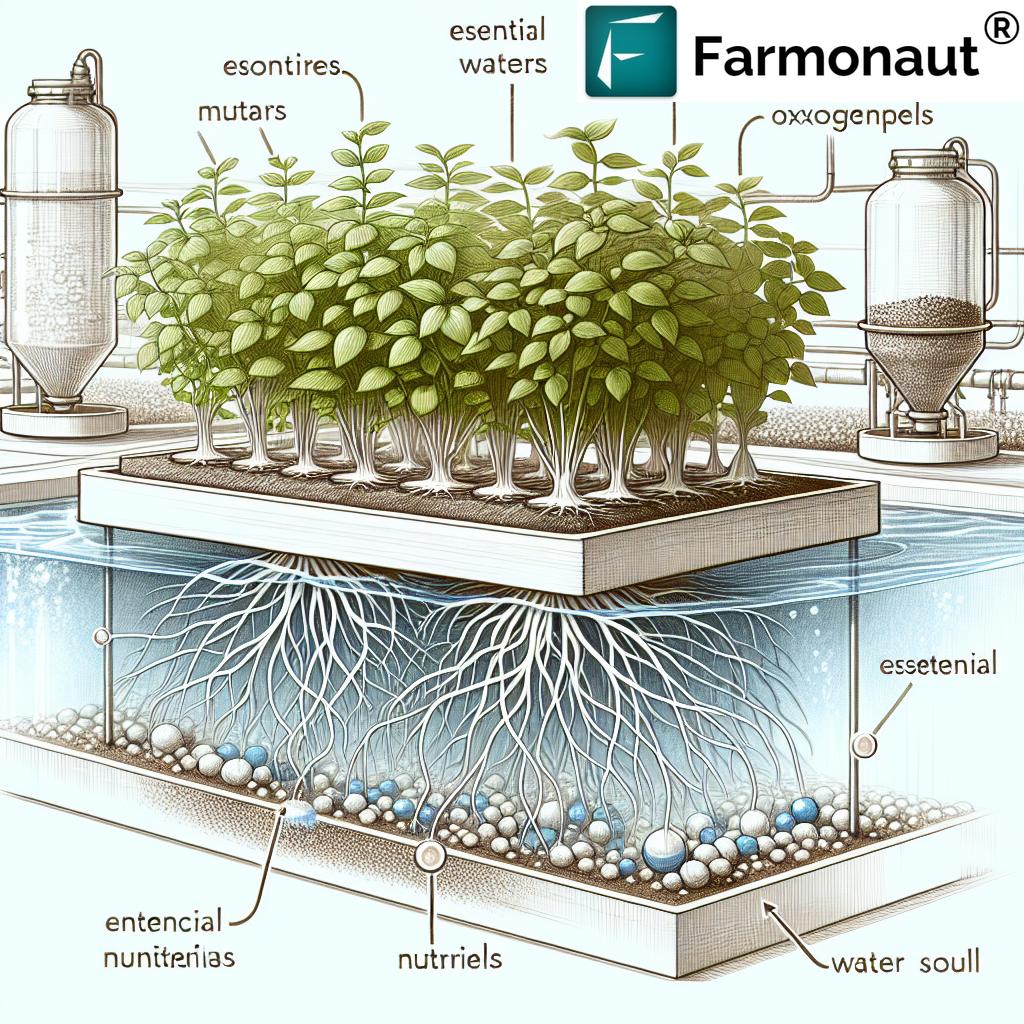
At its core, hydroponic farming is the practice of soilless cultivation using water-based nutrient solutions to provide plants with all they need to thrive. Whether implemented in urban centers or commercial greenhouses, this method enables us to grow healthy and abundant produce with remarkable efficiency—even in spaces where conventional soil-based farming is not viable.
As we explore the advantages of hydroponics, it becomes clear why this technique has captured attention globally: from water efficiency to higher yields and the potential for truly sustainable agriculture.
Historical Background of Hydroponics
The origins of soilless cultivation trace back centuries. In 1627, scholar Francis Bacon introduced the concept in “Sylva Sylvarum”, hinting that plants could be grown using water alone. By the 19th century, German botanists Julius von Sachs and Wilhelm Knop pioneered nutrient solutions for plants, demonstrating that key minerals and oxygen could be delivered directly to roots via water, completely bypassing soil.
The term hydroponics was coined in the 1930s by Dr. William Frederick Gericke of the University of California. He astounded the public by growing large tomato crops in water-based solutions, showing the technique’s vast potential for reliable, controlled food production.
These early breakthroughs form the foundation of today’s hydroponic farming systems, enabling us to leverage technology and precise resource management for a resilient agricultural future.
Hydroponic Systems: A Technical Overview
Hydroponic farming encompasses a range of innovative systems, each designed to deliver essential nutrients and oxygen directly to plant roots. Let’s explore the most prominent methods utilized in soilless cultivation:
Deep Water Culture (DWC) Hydroponics
In deep water culture hydroponics, plants are suspended above a reservoir with their roots submerged in an oxygenated, nutrient-rich solution. A continuous supply of oxygen is provided via air stones or pumps, ensuring that growth is vigorous and nutrients are optimally absorbed. DWC is favored for leafy greens and herbs due to its efficiency and simplicity.
- Roots remain submerged in water throughout
- Ideal for rapid growth cycles
- Suited to lettuce, spinach, basil, and similar crops
NFT: Nutrient Film Technique Explained
The nutrient film technique (NFT) supports plants in channels where a thin film of nutrient solution flows continuously over the roots. This setup maximizes oxygen exposure and reduces water consumption. It’s one of the most efficient hydroponic systems for crops with smaller root masses.
- Thin stream of water runs beneath a sloped gutter or tube
- Optimized for strawberries, herbs, microgreens
- Prevents waterlogging and root diseases
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
Ebb and Flow hydroponic systems use a cyclical process. Plants are periodically flooded with nutrient solutions, which are then drained back into a reservoir. This exposes roots alternately to oxygen and nutrients, supporting robust growth.
- Suitable for a wide variety of crops
- Water and energy use can be effectively regulated
- Customizable intervals for flooding and draining
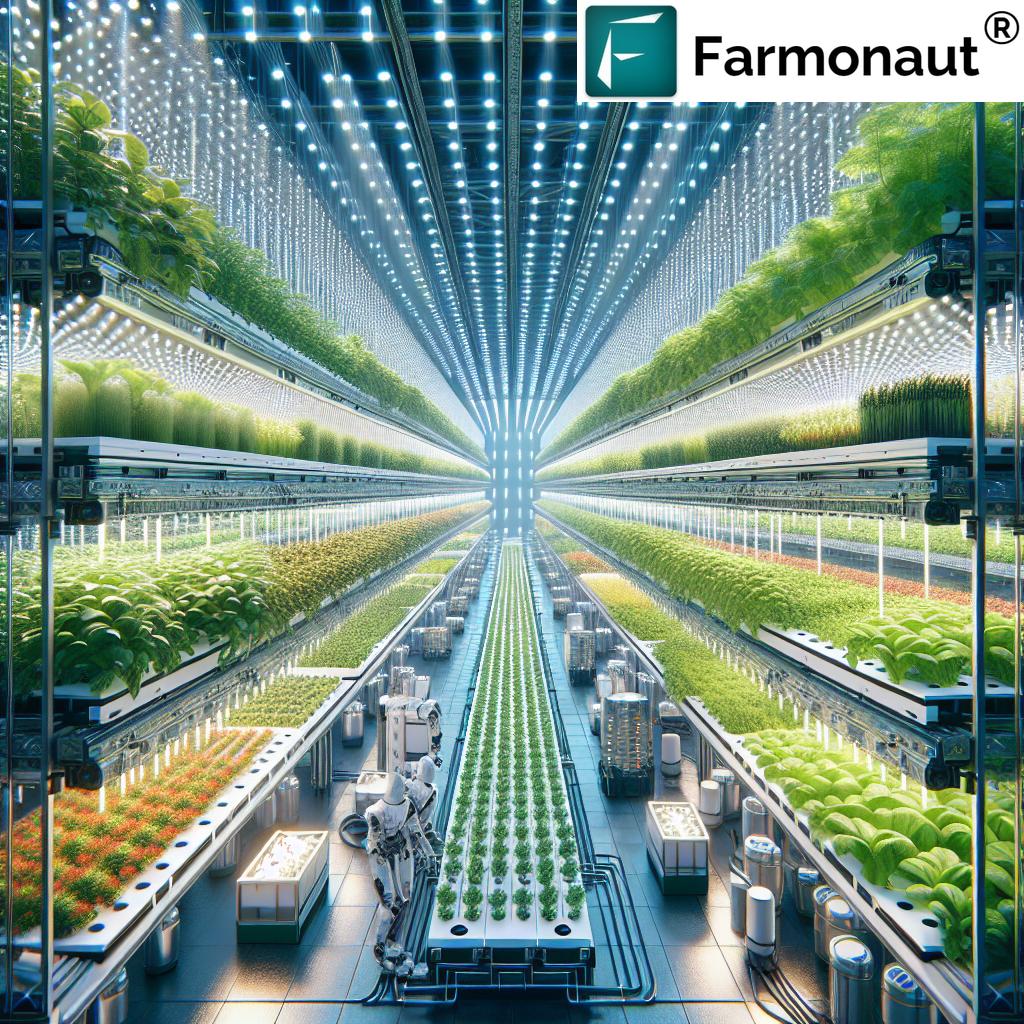
Aeroponics
Aeroponics takes soilless cultivation to the next level. Plant roots are suspended in air and misted with nutrient-rich solutions at precise intervals. The high oxygen environment accelerates growth and maximizes nutrient absorption.
- Highest oxygen exposure among hydroponic methods
- Excellent for research and maximizing productivity
- Used in advanced vertical farming facilities
Kratky Passive Hydroponics
The Kratky Method is a passive, no-electricity-required hydroponic system where plants are placed above a reservoir of nutrient solution. As the liquid level drops, roots grow downward to seek out minerals and water.
- Low technology requirement: perfect for home growers and small-scale setups
- No pumps or moving parts—minimal maintenance
- A great introduction to hydroponic farming
“Urban hydroponic farms can produce up to 240 times more crops per square meter annually than conventional farms.”
Hydroponic Farming: 7 Benefits You Can’t Ignore!
Let’s delve into the 7 standout advantages of hydroponics that are shaping the future of agricultural production and sustainability:
1. Water Savings and Efficiency
Unlike traditional farming, where a large portion of irrigated water is lost to evaporation and runoff, hydroponic systems recirculate water. This allows us to use up to 90% less water for growing the same—if not more—quantity of produce. It’s a powerful solution for regions plagued by water scarcity or limited rainfall.
- Drastically reduces overall water footprint
- Freshwater is reused, minimizing waste
- Ideal for urban hydroponic agriculture and arid environments
2. Yield Increase: Consistent, Higher Crop Production
Plants in hydroponic setups absorb nutrients directly, accelerating growth and ensuring robust health. This translates to yields that are 30–50% higher than those from soil-based farming.
- Optimized nutrients lead to continuous, predictable harvests
- Less risk of plant stress from environmental conditions
- Supports sustainable food production at scale
3. Superior Space Efficiency: Vertical Farming Techniques
Vertical farming techniques take full advantage of limited urban or indoor areas. By stacking crops in layers, we can produce vastly more food per square meter compared to traditional fields. This revolutionizes food production in cities and high-density locations.
- Grows more in less ground space
- Brings local food production to urban centers
- Conserves valuable arable land
4. Faster Growth Rate: Accelerated Plant Development
Hydroponics enables rapid plant growth due to precise control over nutrient balance, oxygen delivery, and optimal environmental conditions (light, temperature, humidity).
- Reduced time from seed to harvest (up to 2x faster for certain crops)
- More growing cycles per year—keeping supply steady
- Predictable operational planning for commercial producers
5. Reduced Pesticide and Chemical Use
With no soil, the risk of soil-borne pests and diseases plummets. As a result, our need for pesticide application is greatly decreased or even eliminated—resulting in healthier, safer produce and a lower environmental impact.
- Cleaner, residue-free crops
- Lower environmental runoff of chemicals
- Safeguards pollinators and beneficial insects
6. Urban Suitability: Meeting City Food Demands
Modern hydroponic techniques allow for scalable urban agriculture, transforming rooftops, warehouses, and unused structures into productive farms. Produce is grown closer to consumers, reducing transportation costs and emissions.
- Fresh food is locally available year-round
- Empowers food security initiatives in cities
- Reduces logistical and supply chain carbon footprint
7. Conservation of Soil and Land Resources
By removing soil from plant cultivation, we prevent land degradation and support the preservation of valuable arable land. Hydroponics is a vital technique for maintaining sustainable food production as the global population grows.
- No soil erosion or loss of fertility
- Less deforestation for new farmland
- Restores land previously considered unsuitable for farming
Hydroponic Farming Benefits Comparison Table
| Benefit | Description | Estimated Improvement vs. Traditional Farming (%) |
Example / Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Savings | Hydroponic systems recycle water, drastically reducing consumption | Up to 90% | Urban hydroponic lettuce farms in dry regions |
| Yield Increase | Direct nutrient and mineral delivery boost yields and crop quality | 30–50% | Year-round tomato and basil production in hydroponic greenhouses |
| Space Efficiency | Vertical stacking and dense planting maximize space usage | Up to 10x more/area | Vertical farms in urban warehouses |
| Faster Growth Rate | Controlled environment and nutrients accelerate plant development | 25–100% faster | Shorter harvest cycles for salad greens |
| Reduced Pesticide Use | Soil-borne pests and diseases are minimized, cutting chemical use | Up to 80% less | Clean, pesticide-free strawberries and herbs |
| Urban Suitability | Hydroponic farms can be set up in cities, close to consumers | 240x crops/sqm/yr | Rooftop vegetable farms in Mumbai, New York, or London |
| Conservation of Soil | Eliminates soil use, preserving land for natural ecosystems | 100% | Farming in non-arable or degraded regions |
Hydroponic Farming Challenges & Considerations
While the advantages of hydroponics are substantial, it’s vital for us to understand the challenges and points of consideration for successful implementation:
- Initial Setup Costs: Specialized equipment (pumps, lighting, climate control) and system infrastructure can require significant upfront investment. However, as technology advances, costs are gradually decreasing.
- Energy Consumption: Dependence on artificial lighting and climate systems increases energy consumption. Using carbon footprint tracking tools like those offered by Farmonaut helps monitor and take steps toward integrating renewable energy sources.
- Technical Knowledge: Agronomists and growers must understand plant nutrition, system maintenance, and environmental control to minimize disease risk and maximize yield.
- Disease Management: While soil-borne issues are reduced, waterborne pathogens can spread rapidly. Vigilant monitoring and sanitation are essential.
Fortunately, ongoing research and platforms—with solutions like Farmonaut’s AI-driven farm advisory and real-time data analytics—are streamlining system management and helping overcome these barriers.
Hydroponics in Modern Agriculture: Urban & Commercial Applications
The widespread adoption of hydroponic farming is changing our agricultural landscape, especially for:
- Urban Agriculture: Hydroponic systems make it possible to convert rooftops, basements, and indoor facilities into high-yielding, fresh food sources—reshaping cities for local, sustainable food production.
-
Commercial Production: Large-scale operations rely on hydroponic techniques for reliability, higher yields, and year-round supply to supermarkets and restaurants, with precision monitoring for quality control.
Explore large-scale farm management solutions for hydroponic and traditional systems with Farmonaut’s admin app.
- Research and Education: Hydroponics provides controlled environments to study plant nutrition, breeding, and pest/disease dynamics, propelling advances in plant science.
For commercial growers or educational institutions, traceability is crucial. Farmonaut’s blockchain-based product traceability ensures secure and transparent tracking of every stage from seed to supermarket, building consumer trust, and authenticating sustainable growing practices.
Hydroponics and Environmental Impact
How does hydroponic farming affect our planet? Let’s weigh up the ecological pros and cons:
- Positive: Efficient water use drastically reduces freshwater withdrawals. No soil degradation or erosion occurs. Lower pesticide usage means less chemical runoff, which benefits waterways and biodiversity.
- Negative: Energy requirements for lighting and climate control are non-trivial, especially in regions where renewable energy sources are not used. Fortunately, the trend toward solar, wind, and other clean power is making sustainable hydroponic production more achievable.
By embracing advanced carbon footprinting tools and renewable practices, hydroponic growers can maximize the environmental sustainability of their operations.
The Future of Hydroponic Farming: Technology, Innovation & Sustainability
As we look ahead, new technological advancements promise to accelerate the adoption and viability of hydroponic farming:
-
Technological Innovations:
- Automated control of temperature, humidity, and nutrient delivery systems using artificial intelligence
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring (like Farmonaut’s solutions) for remote diagnostics and optimization
- Integration of solar panels, energy-efficient LEDs, and renewable sources to reduce operational costs and environmental impact
- Accessibility for Smallholders: Development of user-friendly, lower-cost systems and mobile-based management apps open the door for smaller farms to benefit, even in challenging locations.
- Sustainability Focus: Use of biodegradable materials, water harvesting, and waste recycling systems further reduce the ecological footprint of hydroponics.
Moreover, financial access and risk reduction are key for farmers worldwide. Farmonaut offers crop loan & insurance support tools—helping farmers secure financing using verifiable satellite data, making innovative farming more inclusive and robust.
- Monitor your hydroponic or field crops in real time with AI-driven farm advisory and satellite crop health data
- Reduce your farm’s environmental impact and efficiently manage resource use via carbon footprinting solutions
- Track your produce from seed to supermarket using blockchain-based product traceability tools
- Access satellite-data-powered loans or insurance—use Farmonaut’s verification features for crop financing
- Optimize resources and logistics with fleet and resource management tools for commercial hydroponic setups
Farmonaut: Empowering Precision Agriculture & Hydroponics
Farmonaut leads the digital transformation of precision agriculture worldwide, providing cost-effective, data-driven tools for smarter farming—whether hydroponic, traditional, or hybrid. By integrating satellite imagery, artificial intelligence, and blockchain, Farmonaut empowers growers, agribusinesses, and institutions to optimize yields, monitor environmental conditions, and ensure transparent, sustainable food systems.
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring—enables farmers to track vegetation, soil moisture, and other vital metrics in real time
- AI-based personalized advisory—generates actionable insights and recommendations to maximize productivity and efficiency
- Blockchain for traceability—builds consumer trust and food security by verifying every stage of the supply chain
- Resource and fleet management tools—minimize costs and optimize logistics, especially in large or urban hydroponic setups
- Carbon footprint tracking—helping you reduce your environmental impact and comply with climate goals
Farmonaut’s mission is to democratize advanced farm management—delivering actionable data and efficiency gains to everyone, from smallholders to large commercial farms, worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is hydroponic farming?
Hydroponic farming is a soilless cultivation technique where plants are grown using nutrient-rich water solutions delivered directly to their roots, instead of soil. All essential minerals, water, and oxygen are supplied in controlled conditions, resulting in efficient growth and higher yields.
How much water does hydroponic farming save?
Hydroponic systems can use up to 90% less water than conventional soil-based farming methods, due to efficient recirculation and minimal evaporation.
Are hydroponically grown plants as nutritious as those grown in soil?
Yes—in hydroponic systems, nutrients are delivered directly to plant roots in precise amounts. This can actually result in equal or sometimes higher nutritional content compared to soil-grown plants.
What kinds of crops can be grown hydroponically?
Many commonly consumed crops can thrive in hydroponics, including leafy greens (lettuce, spinach), herbs (basil, mint), tomatoes, peppers, strawberries, cucumbers, and more. Root crops are less common but possible with specialized systems.
What are the main challenges of hydroponic farming?
Some hydroponic farming challenges include high initial system costs, energy consumption, need for technical know-how, and the management of waterborne plant diseases. However, technological advances and digital platforms are making these challenges easier to overcome.
How is Farmonaut helping hydroponic farmers?
Farmonaut provides precision-agriculture tools such as real-time crop health monitoring, AI-generated advisories, resource management, and traceability solutions—all accessible by web or mobile app. These innovations help hydroponic (and traditional) farmers maximize yield, reduce costs, and improve sustainability.
Embracing hydroponic farming unlocks unparalleled opportunities for sustainable food production, global nutrition security, and smart resource management. Whether you’re a smallholder, an urban grower, or a large enterprise, integrating advanced agricultural technologies and precision data platforms like Farmonaut paves the way for greater yields, efficiency, and environmental stewardship.