Preventive Pest Control: 7 Shocking Crop-Saving Hacks
- Understanding Preventive Pest Control
- Why Prevention Trumps Cure in Pest Management
- Preventive Pest Control: 7 Shocking Crop-Saving Hacks
- 1. Cultural Practices and Crop Rotation for Pest Control
- 2. Biological Pest Control Methods
- 3. Physical and Mechanical Pest Control Methods
- 4. Sanitation and Hygiene in Agriculture
- 5. Soil Management for Healthy Crops
- 6. Monitoring and Early Detection of Pests
- 7. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Comparison Table of Preventive Pest Control Methods and Their Sustainable Impact
- Farmonaut: Empowering Preventive Pest Control with Innovation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Preventive Pest Control
- Conclusion
Within agriculture and forestry, preventive pest control has emerged as a transformative strategy for promoting uninterrupted crop growth, healthy soil, and reducing the reliance on chemical interventions. As we collectively face environmental challenges and strive for higher agricultural productivity, integrating sustainable agriculture practices becomes a necessity. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve deep into the world of preventive pest control, uncover seven game-changing hacks, and share how advanced technologies—such as those offered by Farmonaut—can reinforce these strategies throughout the agricultural ecosystem.
From cultural rotation and biological controls to advanced field and soil monitoring, these methods empower us as farmers, foresters, and agricultural professionals to proactively manage pests, protect biodiversity, and support environmental sustainability in farming. Whether you manage a small farm, industrial agribusiness, or vast forests, understanding and implementing preventive pest control methods is vital for long-term success.
Understanding Preventive Pest Control
Preventive pest control is a proactive approach within farming, agriculture, and forestry, aimed at minimizing pest damage before it occurs. Instead of reacting to pest outbreaks after crops and soil health have already been compromised, we focus on anticipating problems, modifying practices, and fortifying our agroecosystems against pest infestations. This method underpins a profound shift towards sustainability, environmental stewardship, and reducing pesticide use.
By implementing preventive pest control strategies, we create robust environments for crops and forests to flourish. Our actions are guided by scientific predictions, ecosystem monitoring, crop rotation, biological pest control methods, and cutting-edge tools for data-driven decision-making. This comprehensive approach not only protects yields and livelihoods, but also enhances biodiversity and maintains the delicate balance within our farms and forests.
- Objective: Anticipate and prevent pest infestations before damage occurs
- Scope: Applies to all types of agriculture, farming, and forestry systems
- Benefits: Lowers chemical interventions, promotes healthy ecosystems, and supports sustainable agriculture practices
Why Prevention Trumps Cure in Pest Management
Traditional pest control often relies on chemical interventions applied only after pests have significantly damaged crops. This can lead to:
- Escalating pest resistance and resurgence due to overreliance on pesticides
- Harmful residues in soil and water, threatening non-target organisms and biodiversity
- Disrupted ecosystem balance, reducing populations of beneficial predators and pollinators
- Increased input costs and reduced farm profitability due to repeated treatments
In contrast, preventive pest control is centered around sustainable, cost-effective management.
By focusing on prevention, monitoring, and ecosystem-based strategies, we significantly reduce the likelihood of major infestations, protecting both our economic interests and the health of the planet.
Preventive Pest Control: 7 Shocking Crop-Saving Hacks
1. Cultural Practices and Crop Rotation for Pest Control
Cultural control is a cornerstone in our preventive pest control methodology. By modifying crop management and the environment, we make it harder for pests to invade, establish, and proliferate. Crop rotation—the process of alternating different types of crops each season or year—is a time-proven method that disrupts pest life cycles and reduces chances for pest buildup.
- Crop Rotation for Pest Control: We prevent specialized pests from thriving by regularly varying crops. For example, rotating cereals with legumes limits the carryover of hosts for specific soil-borne insects and pathogens.
-
Intercropping: By planting complementary crops together, such as cereals with legumes or repellent flowers, we deter pests—a brilliant example being the “push-pull” strategy where repellent “push” plants expel insects away and trap “pull” plants lure them to a controlled area.
Learn more about Push-Pull Pest Management -
Trap Cropping: By utilizing attractive “trap” plants at field edges, we draw pests away from our main production area, focusing control where needed.
Read about Trap Cropping Techniques
Benefits: These cultural practices not only reduce pest populations, but also support soil fertility, increase crop yield, and align with sustainable agriculture practices.
Did you know? Crop rotation for pest control enhances both productivity and resilience against outbreaks.
2. Biological Pest Control Methods
Biological control leverages nature’s own arsenal against pests. By employing voluntary natural predators, parasitoids, and pathogens, we harness ecological processes to manage infestations without introducing harmful chemicals.
- Natural Predators: Lady beetles, lacewings, and birds feed on aphids, mites, and other crop pests. Conserving and introducing these beneficial organisms allows us to keep harmful insect populations in check naturally.
- Parasitoids: Certain wasps lay their eggs in or on pest insects, eventually killing the host. These biological agents act as precise, targeted “internal assassins” against specific threats.
-
Biological Pathogens: Microorganisms like Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) infect and destroy caterpillar pests without harming beneficial species or humans.
Explore Biological Pest Control
Benefits: Biological pest control methods can reduce pesticide dependency, promote biodiversity, and sustain healthy farm and forest ecosystems.
- Tip: Encourage flowering plants around field edges to provide nectar for beneficial predators and parasitoids.
3. Physical and Mechanical Pest Control Methods
Sometimes, the simplest measures are the most effective. Employing physical barriers, manual removal, and non-chemical soil treatments creates a line of defense against invading pests.
- Row Covers: Lightweight, permeable fabrics protect young plants from flying insects while allowing light, air, and water through. Especially valuable for organic vegetable production.
-
Diatomaceous Earth: Sprinkling this natural powder on soil and plant surfaces damages the exoskeletons of soft-bodied insects, leading to dehydration and death. It’s safe for crops, wildlife, and pollinators.
Discover Physical Pest Control Methods - Manual Removal: Regular hand-picking of pest insects, egg clusters, and infested plant parts reduces initial populations and slows outbreaks. Using simple tools like nets, hand traps, and vacuum devices can assist the process.
Benefits: Physical methods are chemical-free, safe for the environment, and suitable for all scales of farming and forestry operations.
4. Sanitation and Hygiene in Agriculture
Keeping our farms and forests clean is a simple, yet powerful, preventive pest control strategy. Proper sanitation disrupts pest habitats and removes sources of infestation.
- Equipment and Tools: Regular cleaning of machinery, vehicles, and fleet reduces inadvertent pest dispersal from one field or forest plot to another.
- Disposal of Debris: Removing and safely destroying infected crop residues, fallen fruit, and dead branches prevents pests—and pathogens—from overwintering.
- Weed Management: Many weeds harbor pest insects and disease agents. By keeping field boundaries tidy and removing volunteer plants, we minimize alternative hosts.
Benefits: Effective sanitation is low-cost, environmentally friendly, and reduces the likelihood of major outbreaks.
Best Management Practices for Pest Control
5. Soil Management for Healthy Crops
Healthy, well-managed soil is the foundation for robust plant growth and natural pest resilience. Integrated soil management strategies minimize stress on crops, making them less susceptible to infestations and boosting overall productivity.
- Use of Organic Amendments: Apply compost and well-rotted manure to replenish nutrients, improve water retention, and nurture beneficial soil organisms. Enhanced soil microbiome suppresses pathogens and supports plant immunity.
- Soil Aeration: Occasional tillage, cover cropping, and root diversification improve soil structure and root zone ventilation, which are critical for healthy root systems and pest resistance.
-
pH Management: Maintaining soil pH at optimal levels for your target crops curbs unsuitable conditions for specific pests and disease organisms.
Soil Management and Pest Control
Benefits: Soil management enhances plant vigor, reduces chemical dependency, and preserves the long-term sustainability of our fields.
6. Monitoring and Early Detection of Pests
Early identification of pests through diligent monitoring is one of the most effective preventive pest control hacks. Utilizing technology, routine inspections, and data-driven decision-making helps us react quickly and appropriately.
- Regular Field Inspections: Walk fields or forests frequently, searching for pest signs such as chewed leaves, frass, or discoloration.
- Pest Identification and Thresholds: Accurately identify species and set action thresholds, ensuring we only intervene when necessary to maintain ecological balance.
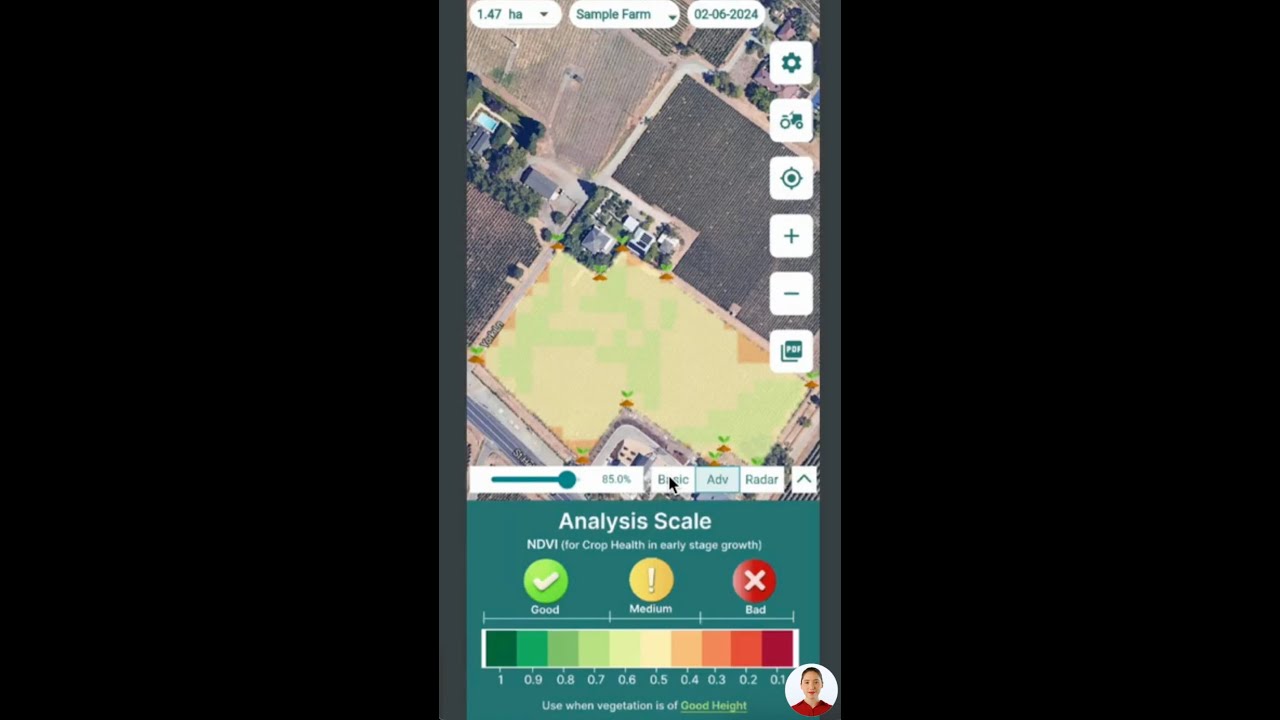
- Remote Sensing and Satellite Monitoring: Leverage tools like Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management and Plantation & Forest Advisory platforms. These use satellite data, AI, and machine learning to monitor crop health, detect anomalies, and alert us to early-stage pest issues.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Use modern apps and APIs (Farmonaut Satellite API, Developer Docs) to access real-time crop and pest insights. Integration enables timely interventions and minimizes losses.
Benefits: Monitoring increases awareness, reduces overuse of pesticides, improves yield, and protects beneficial organisms.
Guidelines for Monitoring and Thresholds
7. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management is the holistic framework that combines all the preventive pest control hacks mentioned above into a logical, adaptable program. Through continual monitoring, risk assessment, and escalation from least to most invasive interventions, we minimize crop loss while sustaining environmental health.
-
IPM Framework:
- Cultural: Start with rotation, resistant varieties, and field hygiene
- Physical and Mechanical: Employ barriers, traps, and manual removal
- Biological: Release or conserve natural predators and beneficial pathogens
- Chemical: Use pesticides only as a last resort, with precise timing and minimal impact
- Benefits: Maximizes economic viability, enhances yield and product quality, and upholds our commitment to environmental sustainability in farming.
- Example: IPM programs integrate cultural rotation, regular crop health monitoring (via platforms like Farmonaut), targeted biological releases, and precise, sparing chemical interventions.
Comparison Table of Preventive Pest Control Methods and Their Sustainable Impact
| Method | Description | Estimated Reduction in Pest Incidence (%) | Impact on Soil Health | Environmental Friendliness (1-5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop Rotation | Alternating crops across seasons to disrupt pest cycles | Up to 80% | Enhances soil fertility and structure | 5 |
| Biological Control | Employing natural predators, parasitoids, and pathogens | 60% | Supports soil microbial diversity | 5 |
| Physical & Mechanical | Using barriers, diatomaceous earth, and manual removal | 40-50% | Neutral (does not disturb structure) | 5 |
| Sanitation | Cleaning equipment, removing debris, weed control | 35-50% | Indirectly beneficial | 5 |
| Soil Management | Amendments, aeration, pH optimization | 30-40% | Strongly positive | 5 |
| Monitoring & Early Detection | Field scouting, tech-based and visual inspections, threshold management | Up to 70% | Prevents over-application of inputs | 5 |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Combines all hacks, applies minimal chemicals last | 70-85% | Maximizes long-term soil and crop health | 5 |
Farmonaut: Empowering Preventive Pest Control with Innovation
We understand that successful preventive pest control increasingly relies on technology, data, and actionable insights. Farmonaut stands at the forefront of this digital transformation, providing us with state-of-the-art tools to amplify the effectiveness of our pest management strategies.
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Farmonaut’s platform delivers real-time, multispectral satellite images, enabling us to monitor crop health, soil moisture, and vegetation trends. This empowers timely interventions and routine monitoring and early detection of pests.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Receive intelligent, context-specific advice from AI-driven tools, which interpret satellite data and recommend optimal actions for pest prevention and crop care.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: For those seeking transparency and authenticity in the agricultural supply chain, Farmonaut’s Traceability Solution secures every step—from planting to harvest—strengthening consumer and regulatory trust.
- Fleet Management: With Farmonaut’s Fleet & Resource Management, agribusinesses can minimize cross-field pest contamination via optimized vehicle and equipment scheduling.
- Carbon Footprinting: Measure and reduce your agricultural carbon emissions through Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting feature—supporting environmentally responsible farming.
- Crop Loan and Insurance Facilitation: By providing satellite-verified crop loan and insurance solutions, Farmonaut helps secure economic stability and encourages investments in best pest management practices.
Why Choose Farmonaut for Sustainable, Precision Agriculture?
- Affordability: No expensive hardware—just powerful, satellite-powered data and analytics at low cost.
- Accessibility & Scalability: Available via web and mobile apps, Farmonaut meets the needs of individual farmers, cooperatives, large agribusinesses, and government agencies.
- Increased Productivity: With precision data, farming decisions are optimized for yield, soil health, and pest-resistant systems.
- Environmental Sustainability: Integrates resource management, reduces pesticide use, and promotes biodiversity for resilient, long-term agroecosystems.
- Transparency and Trust: Blockchain-enabled traceability ensures supply chain authenticity for food and agriproducts.
Try Farmonaut via:
Or access Farmonaut’s API for seamless agriculture & weather integration into your own solutions:
Farmonaut Satellite API |
API Developer Docs
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Preventive Pest Control
What is the main difference between preventive pest control and traditional pest management?
Preventive pest control focuses on anticipating, monitoring, and acting before pests become a serious problem, using cultural, biological, and physical interventions. Traditional pest management is often reactive, responding only after pest populations cause damage, typically with chemical solutions.
Can preventive pest control be used in all types of farming?
Yes. These methods are effective in various settings—including irrigated croplands, dryland farms, horticulture, forestry, and even urban landscapes—because they rely on ecological principles that are universal to plants and pests.
How does crop rotation help in pest control?
Crop rotation disrupts the life cycles of pests and pathogens by removing consistent food sources and hosts. This practice can reduce root and soil-borne pests by up to 80% and also maintains soil fertility and structure.
Are preventive pest control methods cost-effective?
While some strategies require initial investment (like purchasing beneficial insects or implementing monitoring tools), the long-term savings from reduced pesticide use, healthy soil, and stable yields usually outweigh initial costs.
What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
IPM is a holistic framework combining cultural, mechanical, biological, and, as a last resort, chemical measures. The goal is to maintain pest populations at manageable levels while minimizing environmental impact and supporting sustainable agriculture practices.
How does Farmonaut support preventive pest control?
Farmonaut’s satellite and AI-driven farm management tools help in early pest detection, ongoing crop health monitoring, decision support, and optimized resource use, empowering farmers and agribusinesses to implement effective, data-driven preventive strategies.
Conclusion
As we strive for more resilient, productive, and environmentally sustainable food systems, preventive pest control stands as a pillar of modern agriculture and forestry. By strategically integrating cultural practices, biological pest control methods, physical interventions, soil management for healthy crops, monitoring and early detection of pests, and advanced analytical tools, we cultivate healthier crops, safeguard our soils, and nurture ecosystem biodiversity.
The adoption of these crop-saving hacks not only protects our farms from pests and diseases but also aligns with global goals of reducing chemical input, minimizing environmental harm, and improving the long-term viability of agricultural livelihoods. With innovative platforms like Farmonaut, farmers, foresters, and agribusiness leaders have unprecedented access to affordable, actionable intelligence—ushering in a new era of sustainable agriculture practices, productivity, and stewardship.
Let us take a preventive stance together—adapting, innovating, and succeeding for generations to come.