Breaking News: Europe’s Bird Flu Outbreak 2023 – Delayed Migration, Rising Risks, and Global Impact
“In 2023, warm autumn weather delayed wild bird migration patterns, affecting HPAI virus transmission across Europe.”
As we delve into the latest developments of the bird flu outbreak 2023, we find ourselves facing an unprecedented situation in Europe. The warm autumn weather has set the stage for a complex interplay between climate, wildlife, and disease transmission, creating a unique challenge for farmers, policymakers, and the global agricultural community. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the multifaceted impacts of this evolving crisis and its implications for the future of farming and food security.
The Unexpected Turn: Delayed Avian Influenza Spread in Europe
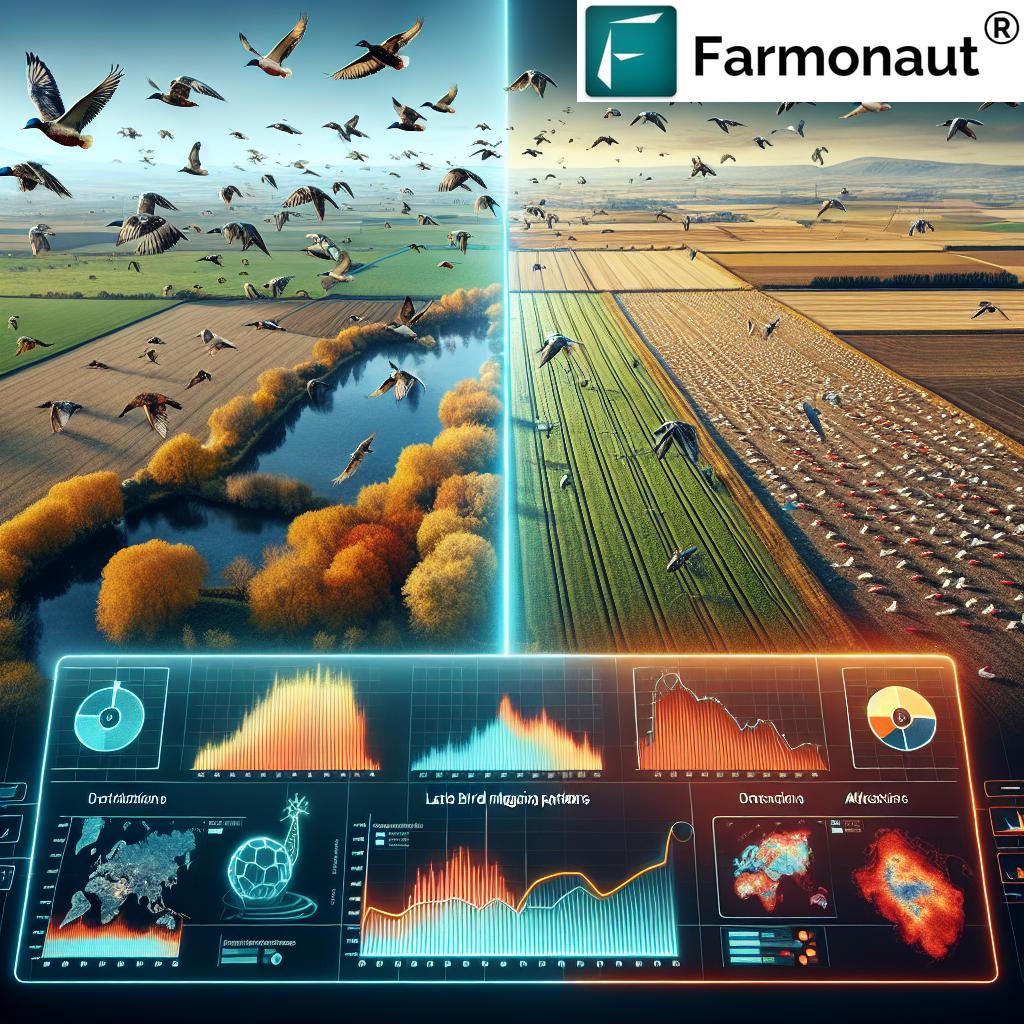
The avian influenza in Europe has taken an unexpected turn in 2023. Typically, we’d expect to see a surge in cases as migratory birds begin their seasonal journeys. However, this year’s unusually warm autumn weather has disrupted the normal patterns, leading to a delayed spread of the highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) virus.
This delay has created a false sense of security among some farmers and industry professionals. However, experts warn that this could potentially lead to a more severe outbreak later in the season, as the virus may have more time to mutate and spread among resident bird populations.
Wild Bird Migration Patterns and HPAI Virus Transmission
The relationship between wild bird migration patterns and HPAI virus spread is crucial to understanding the current situation. Migratory birds are known vectors for avian influenza, capable of carrying the virus across vast distances. The delayed migration we’re witnessing in 2023 has several implications:
- Extended presence of potential virus carriers in their summer habitats
- Increased interaction between migratory and resident bird populations
- Potential for virus mutation due to prolonged circulation in wild populations
- Unpredictable patterns of virus introduction into new areas
These factors combine to create a complex and potentially volatile situation for avian influenza in Europe and beyond.
Climate Change: A Game-Changer in Disease Management
The warm autumn weather we’ve experienced in 2023 is not an isolated incident but part of a larger trend of climate change. This shift in global temperatures is having far-reaching effects on bird migration routes and timing, which in turn impacts the spread of diseases like avian influenza.
As climate patterns become more unpredictable, so too does the behavior of migratory birds. This unpredictability poses significant challenges for:
- Agricultural disease management strategies
- Timing of preventive measures in poultry farms
- Prediction and modeling of potential outbreak patterns
- Resource allocation for disease control and prevention
Farmers and agricultural professionals must now adapt to a new reality where traditional calendars for disease prevention may no longer apply.
The Antarctic Connection: A New Frontier for Bird Flu
“Bird flu detection in Antarctic mammals marks a significant expansion of the virus’s global reach, impacting agriculture worldwide.”
In a startling development, bird flu has been detected in Antarctic mammals, signaling a significant expansion of the virus’s reach. This discovery has sent shockwaves through the scientific community and raised alarming questions about the virus’s ability to adapt to new hosts and environments.
The implications of this discovery are far-reaching:
- Potential for the virus to establish itself in new ecosystems
- Increased risk of genetic reassortment with other influenza strains
- Challenges in monitoring and controlling the virus in remote locations
- Possible impacts on Antarctic wildlife and biodiversity
This development underscores the global nature of the avian influenza threat and the need for international cooperation in disease surveillance and control.
Poultry Industry Under Pressure: Biosecurity Measures and Economic Impact
The poultry industry stands at the forefront of the bird flu outbreak 2023, facing significant challenges and economic pressures. Poultry industry biosecurity measures have become more critical than ever in light of the evolving threat landscape.
Key biosecurity measures being implemented or reinforced include:
- Enhanced cleaning and disinfection protocols
- Restricted access to poultry facilities
- Improved ventilation systems to reduce airborne transmission
- Strict quarantine procedures for new birds
- Regular testing and surveillance of flocks
These measures, while necessary, come at a significant cost to farmers and the industry as a whole. The economic impact is being felt across the supply chain, from small family farms to large-scale commercial operations.

Global Market Responses: Europe and US React
The bird flu outbreak 2023 has sent ripples through global agricultural markets, with both European and US markets showing significant responses. Here’s a breakdown of the key market reactions:
European Markets:
- Increased volatility in poultry and egg prices
- Growing demand for alternative protein sources
- Shifts in trade patterns as countries implement import restrictions
- Rising costs for biosecurity equipment and services
US Markets:
- Heightened surveillance and preventive measures in poultry farms
- Increased investment in vaccine research and development
- Adjustments in export strategies to mitigate potential trade disruptions
- Growing interest in technologies for remote monitoring of flock health
These market responses highlight the interconnected nature of global agriculture and the far-reaching impacts of localized disease outbreaks.
Technology’s Role in Combating Avian Influenza
In the face of this evolving threat, technology is playing an increasingly crucial role in monitoring, predicting, and managing avian influenza outbreaks. Advanced solutions are helping farmers and authorities stay ahead of the curve.
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of this technological revolution in agriculture. Our satellite-based farm management solutions offer valuable tools for monitoring crop health and managing resources effectively, which can be crucial in times of crisis. While our primary focus is on crop management, the principles of data-driven decision-making apply across the agricultural spectrum.
Some key technological advancements in avian influenza management include:
- Satellite-based monitoring of wild bird migration patterns
- AI-powered predictive models for outbreak risk assessment
- IoT devices for real-time monitoring of poultry farm conditions
- Blockchain-based traceability systems for poultry products
- Remote sensing technologies for early detection of stress in poultry flocks
These technologies are helping to create a more resilient and responsive agricultural sector in the face of disease threats.
Explore Farmonaut’s advanced agricultural solutions:
Looking Ahead: Projections and Preparedness for 2024
As we look towards 2024, the agricultural sector must remain vigilant and prepared for the ongoing challenges posed by avian influenza. Based on current trends and expert analyses, here are some key projections and preparedness strategies:
- Continued unpredictability in wild bird migration patterns due to climate change
- Potential for more frequent and severe outbreaks in previously unaffected regions
- Increased focus on developing universal influenza vaccines for poultry
- Greater emphasis on international cooperation in disease surveillance and control
- Integration of advanced technologies in routine farm management practices
Farmers and agricultural professionals should stay informed about the latest developments and be prepared to adapt their practices accordingly.
Timeline of Bird Flu Outbreak 2023-2024
| Date/Month | Event/Development | Impact on Migration | Agricultural Consequences | Policy/Industry Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early 2023 | Initial outbreak detection in Europe | Normal migration patterns observed | Localized impacts on poultry farms | Heightened surveillance measures implemented |
| Autumn 2023 | Unusually warm weather across Europe | Delayed wild bird migration | Extended presence of potential virus carriers | Revision of seasonal risk assessments |
| Late 2023 | Bird flu detected in Antarctic mammals | Concerns over new transmission routes | Increased global vigilance in poultry industry | International task force formation |
| Winter 2023-2024 | Delayed but intensified HPAI spread | Disrupted migration patterns | Significant outbreaks in multiple countries | Emergency biosecurity measures enacted |
| Spring 2024 | Assessment of winter outbreak impacts | Monitoring of spring migration patterns | Economic analysis of poultry industry losses | Review and update of long-term strategies |
The Role of Weather Monitoring in Disease Management
Understanding and predicting weather patterns has become increasingly crucial in managing the spread of avian influenza. The unusual weather conditions we’ve seen in 2023 have highlighted the need for robust weather monitoring systems in agricultural disease management.
At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of accurate weather data in farm management. While our primary focus is on crop health, the principles of weather monitoring apply equally to livestock management and disease control. Our platform provides farmers with access to detailed weather forecasts and historical data, which can be invaluable in planning farm operations and assessing risk.
Key aspects of weather monitoring for avian influenza management include:
- Tracking temperature trends that may affect bird migration timing
- Monitoring humidity levels, which can impact virus survival in the environment
- Assessing wind patterns that could influence the spread of airborne pathogens
- Predicting extreme weather events that may stress poultry and increase susceptibility to disease
By integrating weather data with other farm management practices, farmers can make more informed decisions to protect their flocks and livelihoods.
Explore Farmonaut’s weather monitoring capabilities:
Global Collaboration: The Key to Effective Disease Control
The bird flu outbreak 2023 has underscored the importance of global collaboration in effectively managing and controlling the spread of avian influenza. As the virus knows no borders, neither should our efforts to combat it.
Key aspects of global collaboration include:
- Sharing of real-time outbreak data and genetic sequencing information
- Coordinated research efforts for vaccine development
- Harmonization of biosecurity protocols across countries
- Joint monitoring of migratory bird populations
- Collaborative efforts in developing and implementing early warning systems
By working together, the international community can more effectively respond to the challenges posed by avian influenza and other zoonotic diseases.
FAQs: Bird Flu Outbreak 2023
- Q: How has the warm autumn weather affected the spread of bird flu in Europe?
A: The unusually warm autumn in 2023 has delayed wild bird migration patterns, potentially leading to a later but more severe outbreak of avian influenza. - Q: What are the main risks associated with the delayed migration of wild birds?
A: Delayed migration can lead to prolonged interaction between migratory and resident bird populations, increasing the risk of virus transmission and mutation. - Q: How is climate change impacting the management of avian influenza?
A: Climate change is altering bird migration patterns and timing, making it more challenging to predict and manage the spread of avian influenza. - Q: What does the detection of bird flu in Antarctic mammals mean for global agriculture?
A: This discovery indicates a significant expansion of the virus’s reach, potentially increasing the risk of new mutations and transmission routes that could affect global poultry production. - Q: How are poultry farmers adapting to the evolving bird flu threat?
A: Farmers are implementing enhanced biosecurity measures, increasing surveillance, and adopting new technologies for early detection and prevention of outbreaks. - Q: What role does technology play in combating avian influenza?
A: Advanced technologies like satellite monitoring, AI-powered predictive models, and IoT devices are being used for early detection, risk assessment, and management of avian influenza outbreaks. - Q: How are global markets responding to the bird flu situation in Europe?
A: Markets are experiencing increased volatility in poultry and egg prices, shifts in trade patterns, and growing investment in alternative protein sources and disease prevention technologies. - Q: What can we expect in terms of avian influenza management in 2024?
A: 2024 is likely to see continued unpredictability in outbreak patterns, increased focus on vaccine development, and greater emphasis on international cooperation in disease surveillance and control.
Conclusion: Navigating the Challenges Ahead
The bird flu outbreak 2023 has presented unique challenges to the global agricultural community. The interplay of climate change, altered migration patterns, and the virus’s expanding reach has created a complex landscape that requires adaptive and innovative approaches.
As we move forward, the key to effective management of avian influenza lies in:
- Embracing technology for improved monitoring and prediction
- Enhancing global collaboration and data sharing
- Implementing flexible and robust biosecurity measures
- Continuing research into vaccines and treatment options
- Adapting agricultural practices to account for changing climate patterns
By staying informed, prepared, and adaptable, farmers and agricultural professionals can navigate the challenges posed by avian influenza and work towards a more resilient and secure food system.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing farmers with the tools and insights they need to make informed decisions in these challenging times. While our focus is on crop management, the principles of data-driven agriculture apply across the board, helping to create a more resilient and responsive agricultural sector.
Stay tuned for more updates and insights as we continue to monitor the evolving situation of avian influenza in Europe and its global impacts.