Farming Tech Breakthroughs: 7 Mind-Blowing Innovations Transforming Agriculture
“AI-powered precision agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 30% compared to traditional farming methods.”
Summary: The Rise of Farming Tech
The integration of technology into agriculture, farming, and forestry—collectively dubbed “farming tech“—has revolutionized our industries. These agricultural technology advancements are not just about introducing gadgets to fields, but fundamentally transforming how we monitor, manage, and optimize yields, resources, and costs. Today, thanks to AI in agriculture, precision systems, remote sensors, and sustainable practices, we stand at a new frontier of food production that emphasizes efficiency, sustainability, and traceability.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore seven mind-blowing farming innovations—from satellite-based precision agriculture and smart irrigation systems to blockchain in agricultural supply chain—unpacking their key components, real-world impact, and future potential. We incorporate the latest data, AI-driven insights, and breakthrough technologies, with practical examples and applications.
1. Precision Agriculture: Data-Driven Farming for Optimal Yields
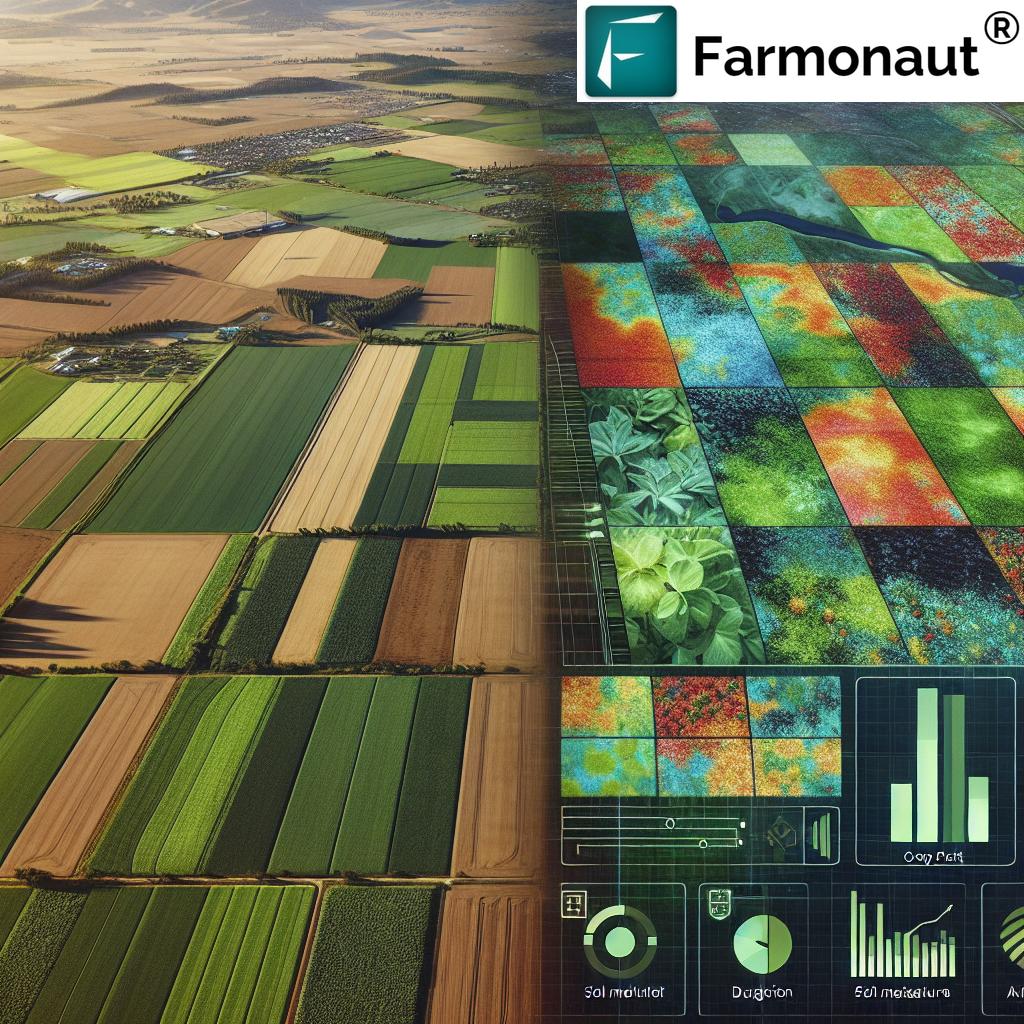
Precision agriculture is at the forefront of the farming revolution. By using a suite of technologies—from satellite imagery to drones and automated systems—we can optimize every phase of the farming cycle. This deliberate, data-driven approach ensures we use just enough water, fertilizer, and pesticide, precisely where and when needed. By managing field variability, we achieve higher yields, lower costs, and improved environmental sustainability.
Key Components of Precision Agriculture
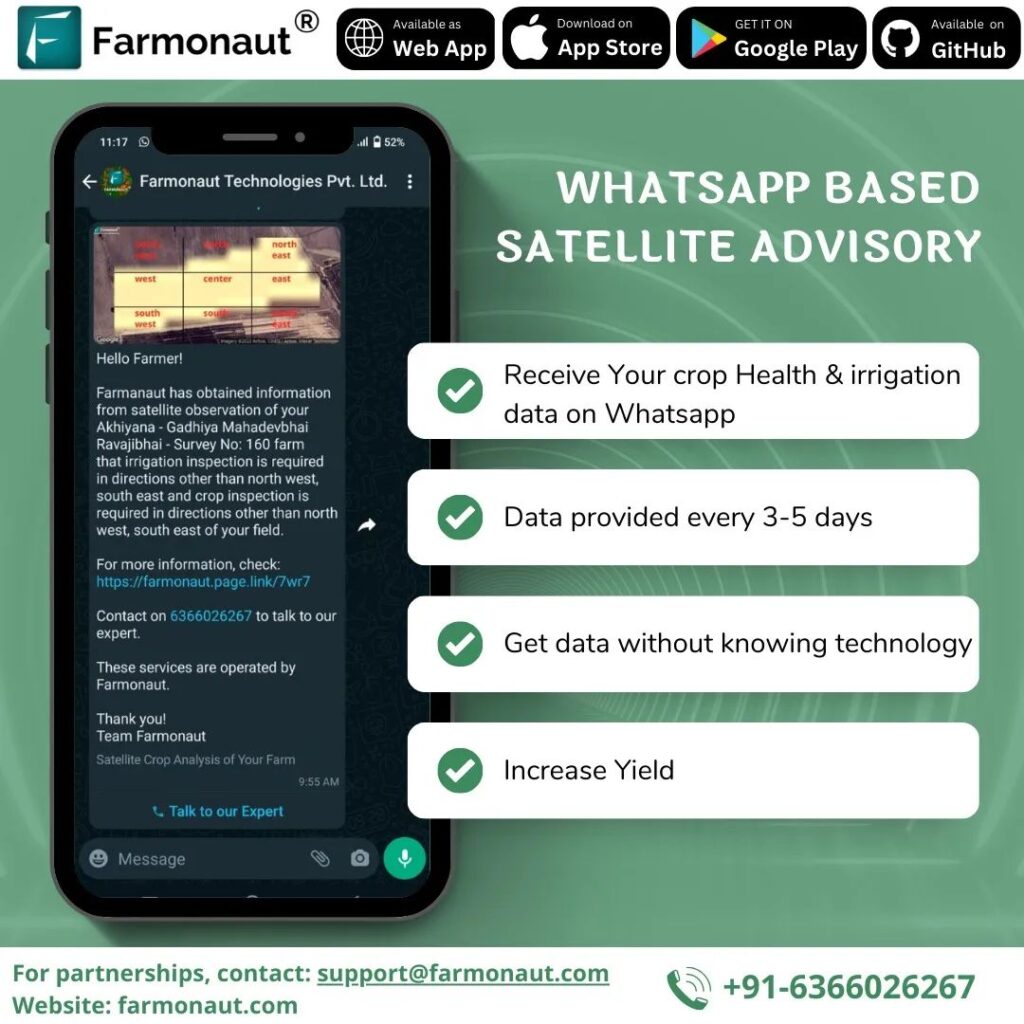
- Satellite Data and Remote Sensing: We utilize satellite imagery to monitor crop health, soil moisture, and identify areas of concern early, from nutrient deficiencies to pest infestations. For example, in India, satellite data has enabled farmers to enhance yields and profits by revealing insights into optimal sowing times and resource management. Such sensing technologies have rapidly improved the accuracy and efficiency of assessment. (Reuters)
- Automated Irrigation Systems: Smart irrigation systems use sensors to assess soil moisture levels and deliver water precisely when and where it’s needed, thereby conserving water and cutting costs. Solar-powered automated irrigation is seeing widespread adoption for its ability to rely on renewable sources and further reduce resource waste. (AP News)
- Drone Crop Monitoring (UAVs): Drones and UAVs deliver real-time aerial imagery, helping us monitor crop growth, assess soil health, and detect issues such as pest and disease outbreaks. With their ability to gather data over large areas efficiently and cost-effectively, drones are essential for precision agriculture and targeted pesticide application.
We at Farmonaut are passionate about making precision farming accessible. Our satellite-based platform leverages multispectral imagery to provide real-time crop health monitoring, soil moisture detection, and actionable AI-based advisory systems—all accessible via Android, iOS, and web apps.
Curious about how this technology works in practice? Explore our advanced fleet and resource management solutions to further increase efficiency and reduce operational costs:
Learn about Fleet Management
Benefits of Precision Agriculture:
- Optimized resource utilization – water, fertilizer, and pesticide are applied only where needed
- Increased yields and profits by improving every variable in the field
- Reduced costs through efficient resource allocation and reduced input wastage
- Improved environmental health and sustainability
- Enables small and large-scale farmers alike to manage fields remotely and make data-driven decisions
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Smarter Decisions for Modern Farming
AI in agriculture is catalyzing a new era of automation and efficiency. Leveraging vast datasets—from satellite imagery to real-time sensors—AI and machine learning algorithms predict threats, optimize planting and harvesting, and automate tedious tasks. Our farms are becoming smarter and more resilient, ready to face modern challenges.
Key Innovations in AI and Machine Learning for Agriculture
- Predictive Analytics: With AI, we model complex variables—weather, soil conditions, past diseases—and predict the best planting times, likely pest infestations, or optimal yields. By enabling proactive management, farmers can respond weeks in advance of a potential crisis. For instance, recent AI applications now alert us to infestations well ahead of visible signs, slashing both pesticide use and crop loss. (Agrilynk)
- Robotics and Automation: Robotics are revolutionizing field operations—automated equipment can efficiently plant, weed, and harvest with minimal human intervention, rapidly increasing farm efficiency and reducing labor costs. Modern agricultural machinery now includes autonomous pesticide sprayers and AI-driven fertilizer dispensers. (AP News)
- AI-Based Farm Advisory Systems: AI assistants, such as Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System, offer personalized recommendations to farmers, blending satellite data and local weather insights to maximize productivity.
How AI & Machine Learning Address Core Farming Challenges
- Early disease and pest detection through image analysis from satellites and UAVs
- Real-time crop health monitoring for quick interventions
- Smart farm resource management – for fertilizer, water, and labor
- Yield forecasting and supply-chain planning
- Efficient field management at scale with minimal human error
Interested in leveraging the power of AI for farm management? With Farmonaut, you receive AI-powered, data-driven recommendations to boost farm productivity, minimize environmental impact, and ensure sustainability.
Learn how our large-scale farm management tools can help you run smarter, AI-optimized operations:
Explore Large-Scale Farm Management
3. Controlled-Environment Agriculture: Maximizing Yields in Any Setting
Controlled-environment agriculture (CEA) is redefining how, where, and when we can grow crops. By cultivating plants in settings where all growth variables—light, temperature, humidity, and nutrients—are precisely managed, CEA enables year-round production and high-density farming, especially in urban environments or harsh climates.
Vertical Farming and Smart Greenhouses
- Vertical Farming: Crops are grown in stacked layers using hydroponics or aeroponics. This maximizes land usage—perfect for densely populated cities. By optimizing resource use (like water and energy), vertical farms can yield up to 10 times more produce per acre than traditional fields. (Wikipedia)
- Smart Greenhouses: Our smart greenhouses are equipped with sensors and automated systems that constantly adjust conditions (light, CO2, humidity) for optimal plant growth. This minimizes water and energy use while extending the growing season. (Sanjeevani Farms)
Key Advantages of Controlled-Environment Agriculture
- Consistent, year-round crop production—even in limited or non-arable land
- Significant resource savings—using up to 90% less water in hydroponic setups
- Reduced risk of pest, disease, and weather-related losses
- Enables urban agriculture and supports local food systems
For regions with unpredictable weather or high population density, these solutions promise food security and enhanced sustainability. Interested in precision agriculture solutions for any environment? Visit our crop cultivation and plantation advisory tool:
Access Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory
“Advanced farming tech has helped reduce fertilizer use by nearly 20% while maintaining optimal plant health.”
4. Sustainable Practices: Enhancing Efficiency and Protecting the Environment
Sustainable farming practices are crucial in ensuring our agriculture is productive today and for future generations. Modern technology helps drive sustainability by reducing resource use, revitalizing soil health, and minimizing the environmental impact of farming.
Key Sustainable Agriculture Innovations
- No-Till Farming: By limiting soil disturbance, no-till methods reduce erosion, improve water retention, and promote beneficial soil organisms. This practice is gaining adoption worldwide, especially in the United States and South America. (Wikipedia)
- Agroecology and Bio-Fertilizers: Blending traditional knowledge and modern science, agroecology utilizes bio-fertilizers to restore soil health, reduce chemical input reliance, and increase food production sustainably. Large-scale initiatives in Africa demonstrate promising results for health and yield improvements. (Reuters)
Through advanced data-driven monitoring and tools like Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting, we can accurately track and reduce the carbon emissions of agricultural operations—aligning with environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
How Technology Drives Sustainable Practices:
- Reduction in chemical and water usage through smart monitoring systems
- Renewal of soil fertility with organic inputs and cover cropping
- Real-time environmental impact assessment through satellite and on-field sensors
- Improved resource efficiency, reduced emissions, and greater biodiversity
5. Nanotechnology in Agriculture: Microscopic Solutions, Macro Impact
Nanotechnology in agriculture is delivering remarkable solutions to some of our most persistent challenges. By engineering substances at the nanoscale, we can create new ways to monitor, protect, and nurture our crops.
Applications of Nanotechnology
- Nanofertilizers: These formulations deliver nutrients in a more efficient and targeted manner. Their small size allows them to penetrate plant cell walls and facilitate better uptake—minimizing environmental losses and maximizing growth. (Wikipedia)
- Nanosensors: Nanosensors are compact devices that detect pathogens, monitor soil health, moisture, and environmental conditions—delivering instant data to our farm management platforms. These sensors can even identify plant diseases before visible symptoms appear, enabling earlier, more effective intervention.
By integrating nanoscale technologies, we enhance precision, resource savings, and environmental safety. This microscopic revolution is rapidly scaling up, enabling farms of all sizes to run greener, leaner, and smarter.
6. Integrating Renewable Energy in Farming: Sustainable Power, Sustainable Growth
The adoption of renewable energy is reducing our farms’ reliance on fossil fuels, lowering operational costs, and driving sustainability in agriculture.
Key Renewable Energy Innovations in Agriculture
- Solar Energy: Solar panels now power irrigation systems, cold storage facilities, and off-grid machinery. Smart irrigation systems that rely on solar power can operate autonomously—empowering farming even in remote regions with unreliable electricity. (Sanjeevani Farms)
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines are increasingly used for large-scale farm operations, further bolstering sustainability and energy independence.
Integrating renewable energy in farming is crucial as regulatory pressures grow and climate volatility increases. Precision systems allow us to optimize energy use, pairing renewable sources with demand-side management technology.
7. Blockchain in Agricultural Supply Chain: Traceability & Trust
The emergence of blockchain technology brings unmatched transparency and security to the agricultural supply chain. Every step—from field to table—is recorded immutably, enhancing trust between farmers, suppliers, retailers, and consumers.
Blockchain Applications in Farming
- Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain-based traceability systems provide a tamper-resistant record of a crop’s journey, enabling stakeholders to verify origin, quality, and sustainability practices. This is vital for combating food fraud and ensuring fair trade. (Agrilynk)
- Enhanced Security: Ensures data privacy, security, and reduces the risk of tampering or fraud in agriculture.
Blockchain empowers farmers and corporate clients alike to demonstrate transparency and accountability. Discover how Farmonaut’s traceability solution provides absolute confidence in product authenticty and sustainability—all built into one seamless platform:
Explore Product Traceability
Comparative Innovations Table: 7 Farming Tech Breakthroughs
| Innovation Name | Brief Description | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Estimated Cost Reduction (%) | Sustainability Impact | Key Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture | Data-driven resource optimization using satellites, drones, & sensors | 15–30 | 10–20 | Water, fertilizer savings; emission reduction | Yield boost, resource conservation, improved decision-making |
| AI & Machine Learning | Predictive analytics, robotics, and AI-based advisory systems | 20–30 | 15–25 | Reduced chemical/pesticide use | Smart planning, automated labor, targeted protection |
| Controlled-Environment Agriculture | Vertical farming and smart greenhouses with controlled variables | 15–25 | 10–20 | Year-round, water savings, reduced land use | Urban farming, food security, resource efficiency |
| Sustainable Practices | No-till, agroecology, bio-fertilizers and real-time carbon tracking | 10–18 | 8–15 | Soil restoration, emission reduction | Erosion control, higher resilience, sustainable food systems |
| Nanotechnology | Nanofertilizers and nanosensors optimize inputs and detect threats | 12–20 | 8–12 | Reduced runoff, early disease detection | Nutrient delivery, disease management, real-time soil assessment |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Solar/wind power for irrigation, storage, and machinery | 5–10 | 15–25 | Lower emissions, resilience, reduced costs | Remote area operations, energy independence |
| Blockchain Supply Chain | Blockchain-based ledger for traceability and transparency | Indirect | 6–12 | Prevents fraud, builds trust, ensures compliance | Product traceability, fair trade, consumer confidence |
Farmonaut: Making Farming Tech Affordable, Accessible, and Actionable
At Farmonaut, we believe in empowering farmers worldwide through innovative, accessible, and cost-effective precision agriculture tools. Our agricultural technology advancements are designed to democratize data, ensuring even smallholder farmers can benefit from the latest in satellite monitoring, AI-based advisory, resource management, and blockchain traceability.
Farmonaut’s Technology Stack Includes:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Real-time, multispectral data for crop health and soil moisture assessment—helping optimize irrigation, fertilizer use, and yields.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Personalized, real-time AI recommendations and weather forecasts—improving efficiency and yield outcomes.
- Blockchain Traceability Solutions: Supply chain transparency and product authenticity, fully integrated for agricultural, textile, and food sectors.
- Fleet & Resource Management Tools: For efficient logistics, equipment utilization, and operational cost reduction.
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Real-time emissions data and actionable sustainability guidance to support responsible, climate-friendly farming operations.
- API and Developer Tools: Seamless integration via Farmonaut API and Developer Docs—expand your software stack with cutting-edge agri-data.
We offer flexible subscription packages for individual farmers, agribusinesses, and organizations—scalable for any field size or operation, delivered on your device of choice.
Challenges & Considerations in Adopting Advanced Farming Tech
While the impact of farming tech is profound, the journey isn’t without its challenges. We must address these factors to ensure equitable access, sustainability, and long-term benefit.
Key Implementation Challenges:
- High Initial Investment: Many advanced solutions require upfront costs that can be prohibitive for smallholder farmers.
- Skill and Knowledge Gaps: Effective adoption demands training, technical support, and continuous learning.
- Data Privacy & Security: As we collect and share more data, reliable safeguards and clear policies are needed to protect farmers’ and enterprises’ interests.
- Labor Market Impacts: Automation may lead to reduced demand for manual labor, necessitating new roles and skill development in rural areas.
- Scalability & Infrastructure: Reliable connectivity, device access, and regional support systems are vital for smooth integration of these technologies everywhere.
At Farmonaut, we offer simple, subscription-based precision agriculture solutions—drastically lowering the cost barrier and providing intuitive mobile/web tools. Our vision is a world where advanced farming tech is accessible to all, regardless of geography or operation size.
Conclusion: The Future of Agricultural Technology Is Here
The past decade has marked an unprecedented acceleration in farming tech. From precision agriculture and AI-led decision making to resource-conserving irrigation, renewable energy integration, and blockchain-enabled transparency, our fields and food systems have been transformed for the better. These innovations make farms more productive, sustainable, and resilient to climate and market volatility.
The journey doesn’t end here. New breakthroughs in robotics, satellite sensing, and nano-agrochemicals are continuously emerging, promising increased yields, reduced costs, and enhanced environmental stewardship. By addressing adoption barriers, investing in training, and choosing scalable solutions—like those offered by Farmonaut—we can collectively usher in a smarter, more sustainable agricultural future.
To see how Farmonaut can make a real difference in your operations, access our platform via browser, Android, or iOS. Transform your approach to farming today!
Frequently Asked Questions: Farming Tech & Innovations
- What is precision agriculture and why is it important?
-
Precision agriculture employs data-driven technologies—like satellites, sensors, and AI—to monitor and manage variability in the field. By applying resources (water, fertilizer, pesticide) precisely where needed, it optimizes yields, reduces costs, and minimizes environmental impact. This approach is revolutionizing efficiency and sustainability in farming.
- How does AI in agriculture increase efficiency?
-
AI in agriculture analyzes vast amounts of data—weather, soil, satellite imagery—to predict crop needs, pest infestations, and optimal planting times. AI-powered robotics automate repetitive tasks such as planting, weeding, and harvesting, allowing farmers to maximize productivity while reducing labor requirements.
- What are the main benefits of drone crop monitoring?
-
Drone crop monitoring provides detailed aerial imagery for assessing crop health, growth patterns, and detecting pests or diseases early. Drones can efficiently cover large areas, identify field variability, and even apply inputs selectively, boosting yields and reducing costs.
- How does blockchain improve transparency in the agricultural supply chain?
-
Blockchain creates an immutable ledger that records every step of an agricultural product’s journey from field to consumer. This transparency helps verify authenticity, quality, and sustainability practices, building trust among all supply chain stakeholders and consumers alike.
- What role does nanotechnology play in agriculture?
-
Nanotechnology enables the creation of nanofertilizers and nanosensors. Nanofertilizers deliver nutrients more efficiently to plants, reducing environmental loss. Nanosensors provide real-time monitoring of soil health, pests, and diseases—allowing for early intervention and optimized farm management.
- How does Farmonaut make advanced farming tech accessible?
-
Farmonaut offers affordable precision agriculture solutions via web, Android, and iOS applications, bringing real-time crop health data, AI-based advisory services, and blockchain traceability to farmers of all scales. Subscription-based pricing, mobile accessibility, and modular tools ensure that everyone can benefit from cutting-edge innovation, regardless of operation size or location.