Grapevine Leafroll Disease: Symptoms, Transmission, and Control in Infected Vines

In the world of viticulture, grapevine leafroll disease (GLD) stands as one of the most significant challenges faced by vineyard owners and wine producers. This complex viral disease affects grapevines worldwide, causing substantial economic losses and compromising the quality of grapes and wine. At Farmonaut, we understand the critical importance of early detection and effective management of this disease to maintain healthy vineyards and ensure the production of high-quality grapes.
Understanding Grapevine Leafroll Disease
Grapevine leafroll disease is caused by a group of viruses known as Grapevine Leafroll-associated Viruses (GLRaVs). These viruses belong to the family Closteroviridae and can significantly impact the health and productivity of grapevines. There are several varieties of GLRaVs, with GLRaV-1, GLRaV-2, and GLRaV-3 being the most prevalent and economically important.
Impact on Vineyards and Wine Production
The effects of grapevine leafroll disease on vines and wine production are far-reaching:
- Reduced grape yield (up to 40% in severely infected vines)
- Delayed fruit ripening
- Reduced sugar content in grapes
- Alterations in grape and wine color
- Negative impact on overall wine quality
These consequences underscore the importance of effective disease management strategies in vineyards.
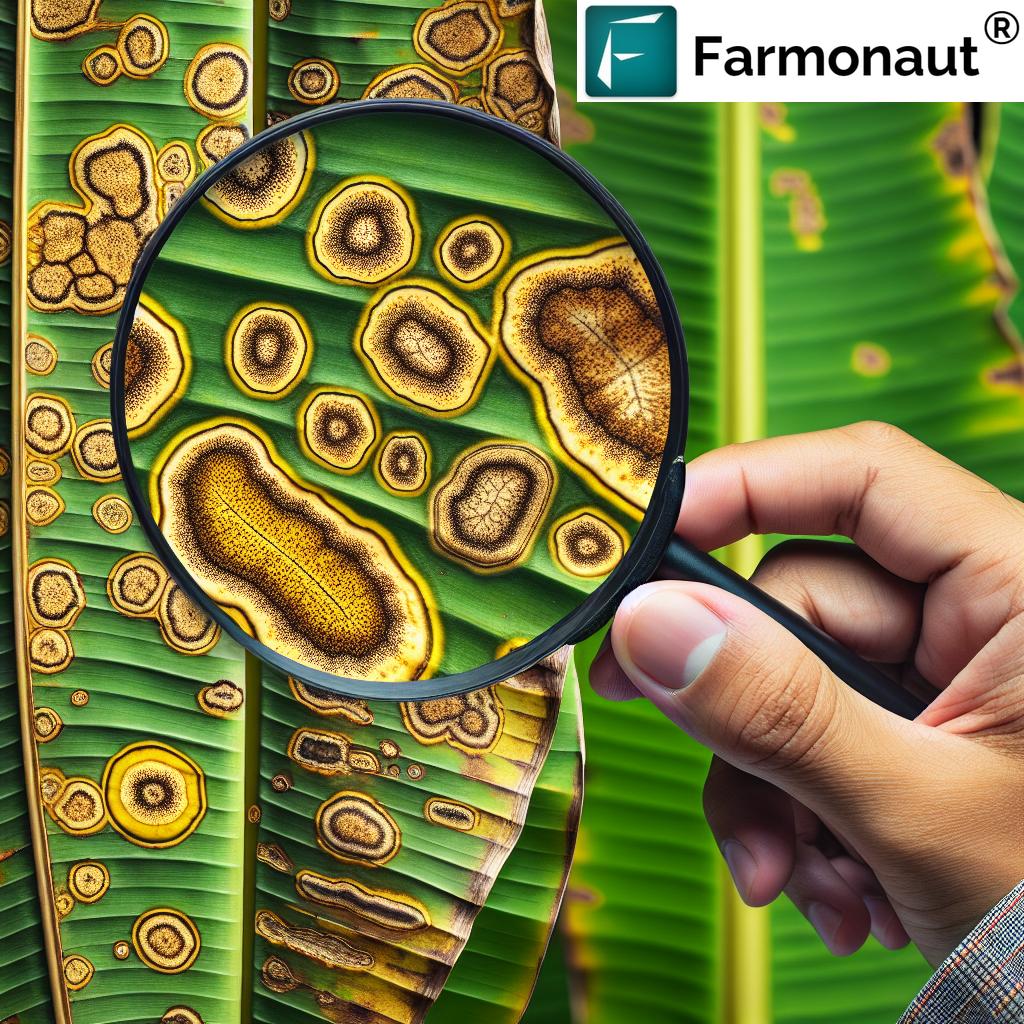
Recognizing the Symptoms of Grapevine Leafroll Disease
Early identification of grapevine leafroll disease is crucial for implementing timely control measures. The symptoms can vary depending on the grape variety, virus strain, and environmental conditions. However, some common signs to look out for include:
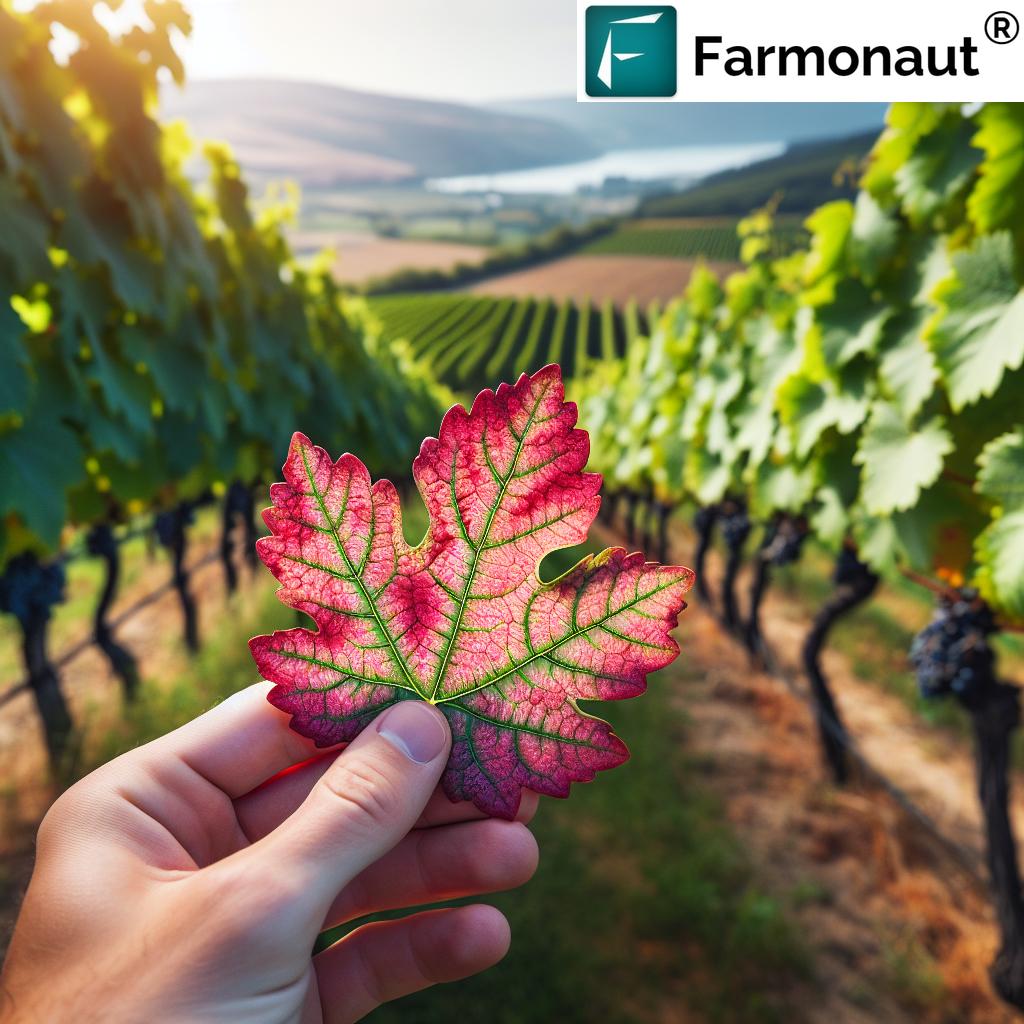
Leaf Symptoms
- Leaves rolling downward, particularly in red grape varieties
- Reddening of leaves in red grape varieties, often starting from the leaf edges
- Yellowing of leaves in white grape varieties
- Premature leaf fall in severe cases
Vine and Fruit Symptoms
- Stunted growth of infected vines
- Delayed fruit ripening
- Reduced berry size and cluster weight
- Uneven coloration of grape berries
It’s important to note that symptoms may not be immediately visible in newly infected vines, making regular monitoring and advanced detection methods crucial.
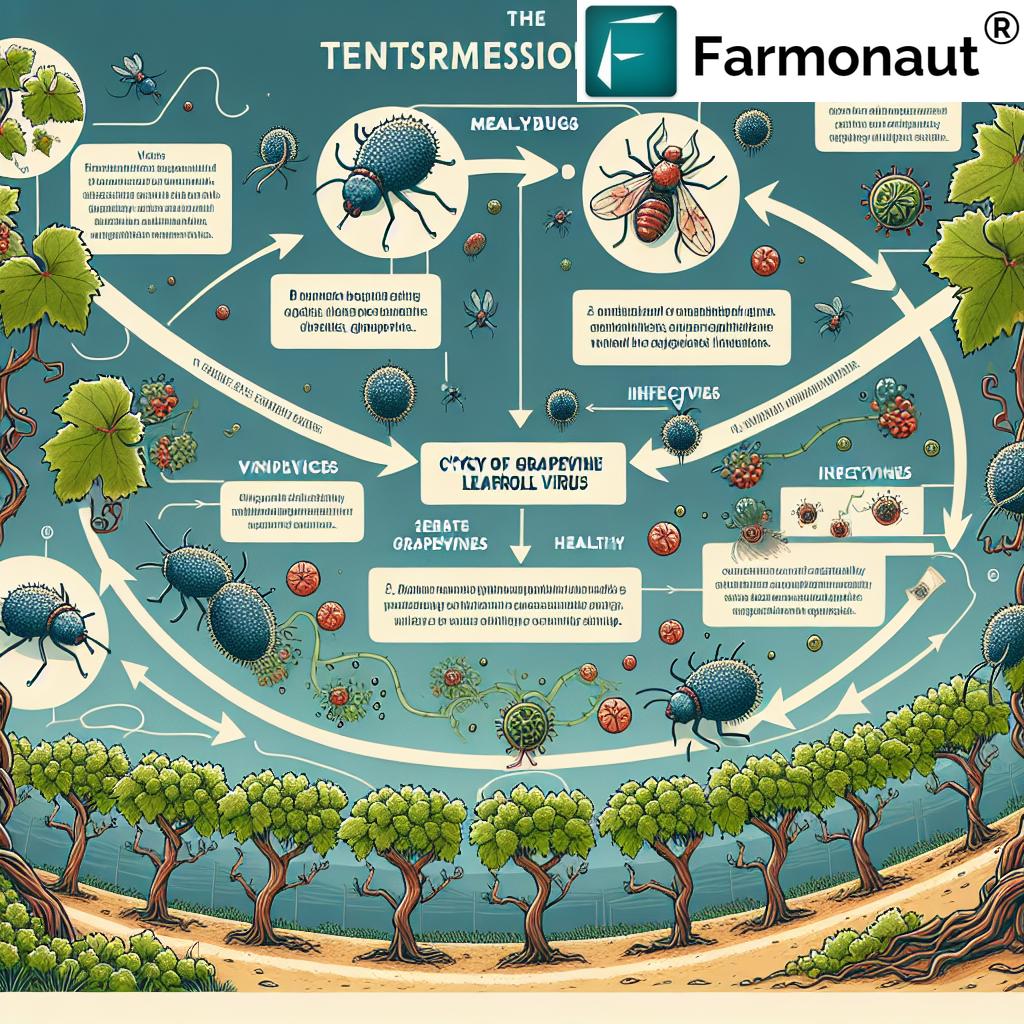
Transmission of Grapevine Leafroll Disease
Understanding how grapevine leafroll disease spreads is essential for developing effective control strategies. The virus can be transmitted through various means:
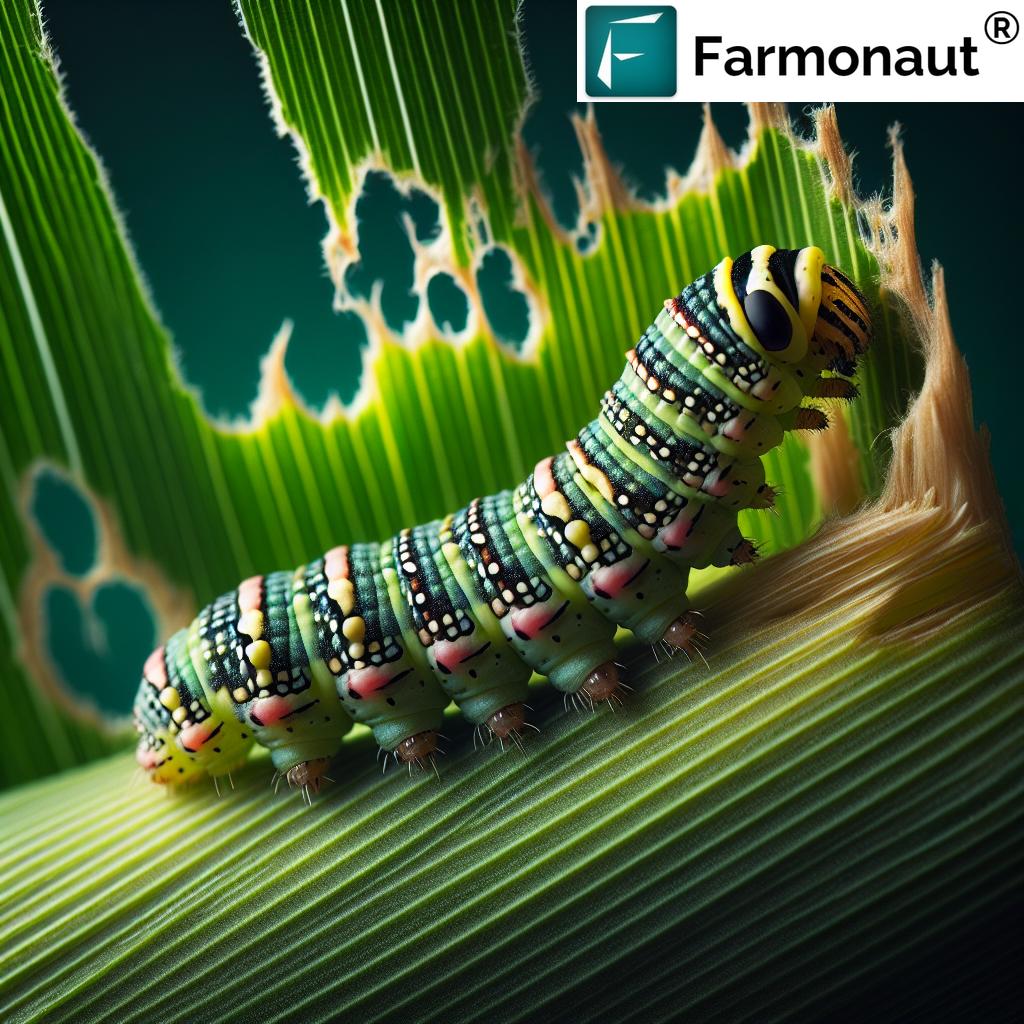
Vector Transmission
The primary vectors for grapevine leafroll disease are mealybugs and soft scale insects. These pests feed on the phloem of infected vines and can transmit the virus to healthy plants. The most common mealybug species involved in GLRaV transmission include:
- Planococcus ficus (vine mealybug)
- Pseudococcus longispinus (longtailed mealybug)
- Pseudococcus calceolariae (citrophilus mealybug)
These mealybugs can acquire the virus from infected vines and retain it for several days, potentially spreading it to multiple plants.
Grafting and Propagation
Grapevine leafroll disease can also be spread through the use of infected plant material in grafting and propagation. This highlights the importance of using certified virus-free rootstock and scion material when establishing new vineyards or replacing vines.
Mechanical Transmission
While less common, mechanical transmission through pruning tools and other vineyard equipment is possible. Proper sanitation practices are essential to minimize this risk.
Control and Management Strategies
Effectively managing grapevine leafroll disease requires a multifaceted approach. At Farmonaut, we recommend a combination of preventive measures and active control strategies:
1. Vector Control
Controlling mealybug populations is crucial in preventing the spread of GLRaVs. Integrated pest management (IPM) strategies include:
- Regular monitoring of mealybug populations
- Use of biological control agents such as parasitic wasps
- Targeted application of insecticides when necessary
- Removal of alternative host plants that may harbor mealybugs
2. Vineyard Sanitation
Maintaining a clean vineyard environment can significantly reduce the risk of disease spread:
- Remove and destroy infected vines
- Properly dispose of pruning debris
- Clean and disinfect pruning tools between vines
3. Use of Virus-Free Planting Material
When establishing new vineyards or replacing infected vines, always use certified virus-free rootstock and scion material. This practice is fundamental in preventing the introduction of GLRaVs into clean vineyards.
4. Regular Monitoring and Early Detection
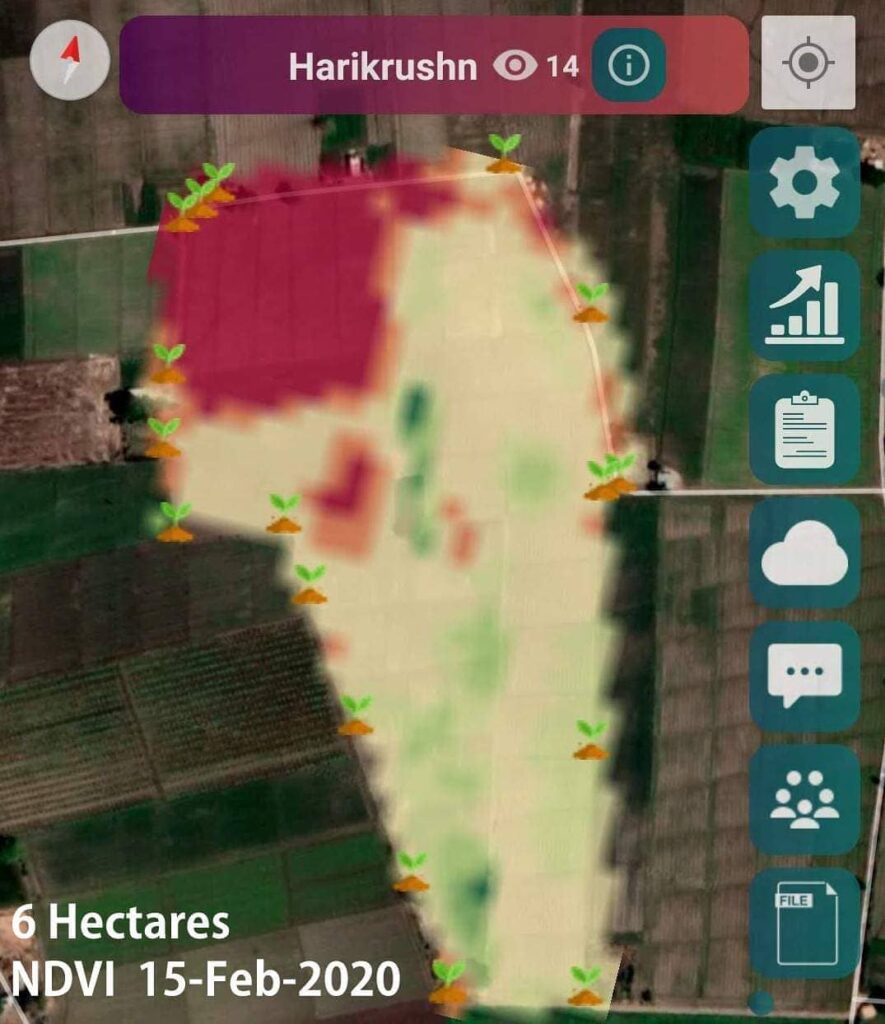
Implementing a robust monitoring program is essential for early detection of grapevine leafroll disease. This is where Farmonaut’s advanced satellite monitoring technology comes into play, offering vineyard owners a powerful tool for large-scale, efficient monitoring of vine health.
| Aspect | Traditional Monitoring | Farmonaut Satellite Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Early Detection | Limited to visual inspection, may miss early stages | Advanced spectral analysis can detect subtle changes in vine health |
| Coverage Area | Limited to manual inspection capabilities | Large-scale coverage of entire vineyards |
| Labor Requirements | High, requires trained personnel for regular field inspections | Low, automated analysis with minimal human intervention |
| Cost-effectiveness | Costly for large vineyards due to labor and time requirements | Highly cost-effective, especially for large-scale operations |
Our satellite monitoring service offers several advantages over traditional monitoring methods:
- Comprehensive coverage of large vineyard areas
- Early detection of stress patterns that may indicate disease presence
- Regular, automated monitoring without the need for extensive manual labor
- Data-driven insights to support decision-making in disease management
To learn more about how Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring can enhance your vineyard management, visit our app page or explore our API services.
5. Roguing and Replanting
In cases of severe infection, removing (roguing) infected vines and replanting with virus-free material may be necessary. This practice helps prevent the spread of the disease to healthy vines.
The Role of Technology in Disease Management
At Farmonaut, we believe that integrating advanced technology into vineyard management practices is key to effectively combating grapevine leafroll disease and other viticultural challenges. Our suite of tools and services is designed to support vineyard owners and managers in their disease management efforts:
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Our satellite monitoring technology provides regular updates on vine health, allowing for the early detection of stress patterns that may indicate disease presence. This technology enables vineyard managers to:
- Monitor large areas efficiently
- Detect anomalies in vine health before they become visible to the naked eye
- Track the spread of disease over time
- Identify hotspots for targeted intervention
To start using our satellite monitoring service, download our app from the Google Play Store or the Apple App Store.
AI-Powered Advisory System
Our Jeevn AI advisory system integrates satellite data with other relevant information to provide personalized recommendations for disease management. This system can help vineyard managers:
- Optimize timing for pest control measures
- Plan targeted interventions based on disease risk assessments
- Receive alerts for potential disease outbreaks
Weather Monitoring and Forecasting
Environmental conditions play a crucial role in the development and spread of grapevine leafroll disease. Our weather monitoring and forecasting services provide valuable data to support disease management decisions. For developers interested in integrating our weather data into their own applications, check out our Weather API documentation.
The Economic Impact of Grapevine Leafroll Disease
The economic consequences of grapevine leafroll disease on the wine industry are significant and multifaceted. Understanding these impacts underscores the importance of effective disease management:
Reduced Yield and Quality
Infected vines typically produce fewer and lower-quality grapes, leading to:
- Decreased grape yield, often by 15-40% in severely affected vines
- Lower sugar content in berries, affecting wine quality and alcohol content
- Altered grape and wine color, particularly in red varieties
- Reduced overall wine quality, potentially affecting market value
Increased Production Costs
Managing grapevine leafroll disease incurs additional costs for vineyard owners:
- Expenses related to vector control measures
- Costs associated with roguing and replanting infected vines
- Increased labor requirements for monitoring and management
- Investment in disease detection and prevention technologies
Long-term Vineyard Viability
Persistent infection can have long-lasting effects on vineyard sustainability:
- Reduced lifespan of infected vines, necessitating earlier replanting
- Potential loss of valuable old-vine vineyards
- Impact on the terroir expression, affecting wine uniqueness and marketability
Research and Future Perspectives
The fight against grapevine leafroll disease is an ongoing effort, with researchers and industry professionals continually working to develop new strategies and technologies for disease management. Some promising areas of research include:
Genetic Resistance
Scientists are exploring the potential for developing grapevine varieties with natural resistance to GLRaVs. This could provide a long-term solution to the disease, reducing reliance on chemical controls and minimizing economic losses.
Advanced Detection Methods
Ongoing research into more sensitive and efficient detection methods, including molecular techniques and remote sensing technologies, could revolutionize early disease detection and management strategies.
Biological Control Agents
The development of more effective biological control agents for mealybugs and other vectors could provide environmentally friendly alternatives to chemical pesticides.
Precision Viticulture
The integration of technologies like those offered by Farmonaut into precision viticulture practices holds great promise for more targeted and effective disease management strategies.
Conclusion
Grapevine leafroll disease presents a significant challenge to the global wine industry, affecting both the quantity and quality of grape production. However, with a comprehensive understanding of the disease, its transmission mechanisms, and available management strategies, vineyard owners and managers can effectively mitigate its impact.
At Farmonaut, we are committed to supporting the viticulture industry in its fight against grapevine leafroll disease and other challenges. By leveraging advanced satellite technology, AI-driven insights, and comprehensive data analysis, we provide vineyard managers with the tools they need to monitor vine health, detect disease early, and implement targeted management strategies.
The future of viticulture lies in the integration of traditional knowledge with cutting-edge technology. By embracing these advancements, we can work towards more resilient, productive, and sustainable vineyards, ensuring the continued production of high-quality wines for generations to come.
FAQs
- Q: Can grapevine leafroll disease be cured?
A: Currently, there is no cure for grapevine leafroll disease once a vine is infected. Management focuses on prevention, control of vectors, and removal of infected vines. - Q: How long can a mealybug transmit the leafroll virus after feeding on an infected vine?
A: Mealybugs can retain and transmit the virus for several days after feeding on an infected vine, potentially spreading it to multiple healthy plants. - Q: Are all grape varieties equally susceptible to grapevine leafroll disease?
A: While all grape varieties can be affected, some may show more severe symptoms or be more susceptible to infection. Red grape varieties often show more visible symptoms than white varieties. - Q: How does Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring help in managing grapevine leafroll disease?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring provides early detection of stress patterns in vines that may indicate disease presence, allowing for timely intervention and more efficient management of large vineyard areas. - Q: Can grapevine leafroll disease spread through soil or water?
A: No, grapevine leafroll viruses are not known to spread through soil or water. The primary modes of transmission are through infected plant material and insect vectors like mealybugs.
For more information on how Farmonaut can help you manage your vineyard health and productivity, visit our website or contact our team of experts. Together, we can work towards healthier vines and better wines.