Mastering Nitrogen Management: A Comprehensive Guide to Boosting Crop Yield and Soil Health with Precision Agriculture

“Precision agriculture techniques can increase nitrogen use efficiency by up to 30%, significantly reducing fertilizer waste and costs.“
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on mastering nitrogen management in agriculture. In this blog post, we’ll explore the critical role of nitrogen in plant growth and provide practical solutions for sustainable agriculture practices. As we delve into the world of precision agriculture and cutting-edge technologies, we’ll show you how to optimize your crop yield while maintaining soil health.
The Importance of Nitrogen in Agriculture
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth and development. It plays a crucial role in various plant processes, including:
- Chlorophyll production for photosynthesis
- Protein synthesis
- Cell structure formation
- Energy transfer within the plant
Without adequate nitrogen, plants struggle to grow, leading to reduced yields and poor crop quality. However, managing nitrogen effectively can be challenging due to its dynamic nature in the soil and its susceptibility to loss through various mechanisms.
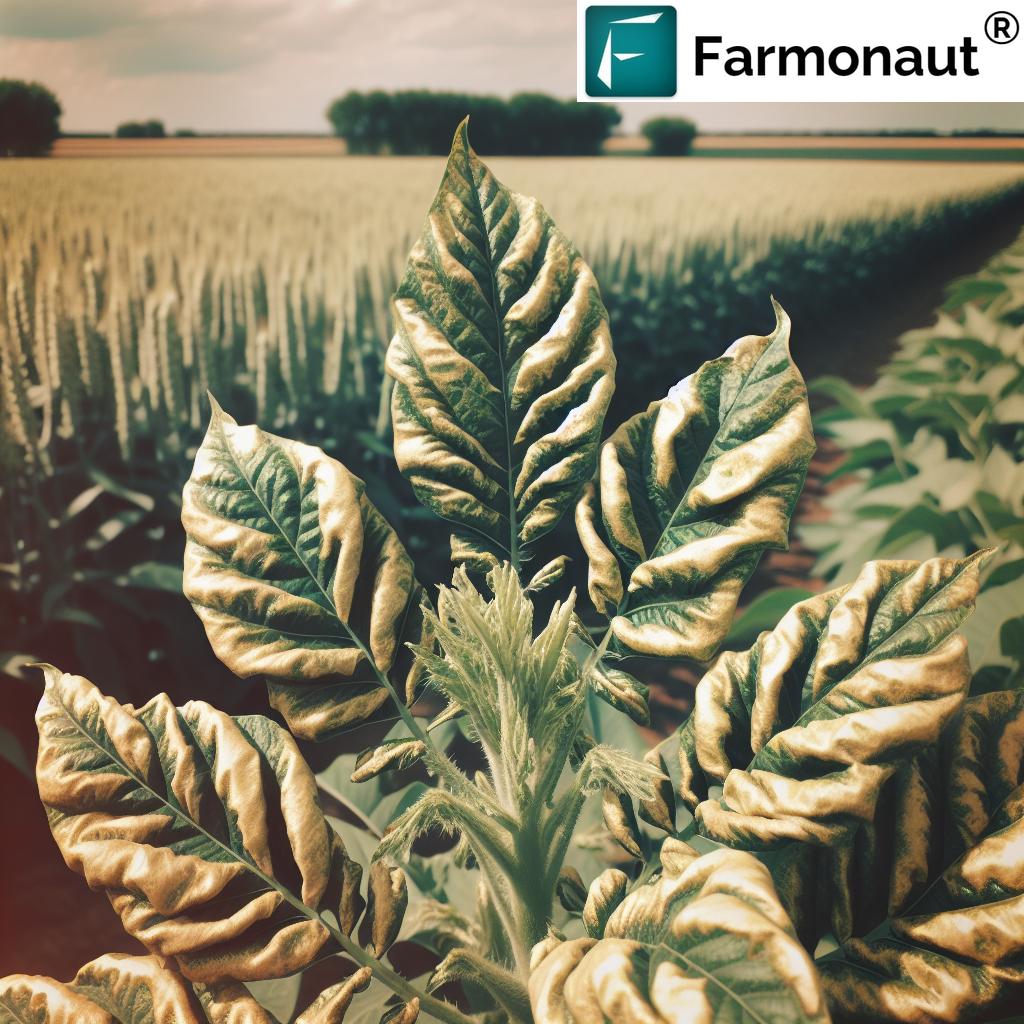
Identifying Nitrogen Deficiency in Plants
Recognizing the symptoms of nitrogen deficiency is crucial for timely intervention. Here are some common signs to look out for:
- Yellowing of older leaves (chlorosis), starting from the tip and moving towards the base
- Stunted growth and reduced plant vigor
- Smaller leaves and thinner stems
- Premature leaf senescence
- Reduced fruit or grain size and quality
To help you better understand and address nitrogen deficiency, we’ve prepared a comprehensive table outlining symptoms and management solutions:
| Plant Part | Deficiency Symptoms | Management Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Leaves |
– Yellowing (chlorosis) of older leaves – V-shaped yellowing pattern on corn leaves – Smaller leaf size |
– Apply nitrogen-rich fertilizers – Use foliar sprays for quick uptake – Implement split application of nitrogen |
| Stems |
– Thin, weak stems – Reduced branching – Purpling of stems in some crops |
– Adjust planting density – Improve overall soil fertility – Use slow-release nitrogen sources |
| Roots |
– Reduced root system – Stunted root growth – Fewer root hairs |
– Enhance soil structure for better root growth – Apply nitrogen near the root zone – Use cover crops to improve soil nitrogen content |
| Fruits/Grains |
– Smaller fruit or grain size – Reduced yield – Poor kernel fill in corn |
– Time nitrogen applications to match crop demand – Use precision agriculture for targeted application – Implement tissue testing for accurate nutrient management |
Sustainable Nitrogen Management Strategies
Implementing sustainable nitrogen management practices is essential for long-term soil health and crop productivity. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Soil Testing and Analysis
Regular soil testing is the foundation of effective nitrogen management. By analyzing soil samples, we can determine:
- Current nitrogen levels in the soil
- Soil pH and organic matter content
- Presence of other nutrients that may affect nitrogen uptake
With this information, we can make informed decisions about fertilizer application rates and timing.
2. Precision Agriculture Technologies
Precision agriculture tools revolutionize nitrogen management by enabling targeted and efficient application. Some key technologies include:
- Variable Rate Nitrogen Application (VRA): This technology allows for customized nitrogen application based on soil variability and crop needs within a field.
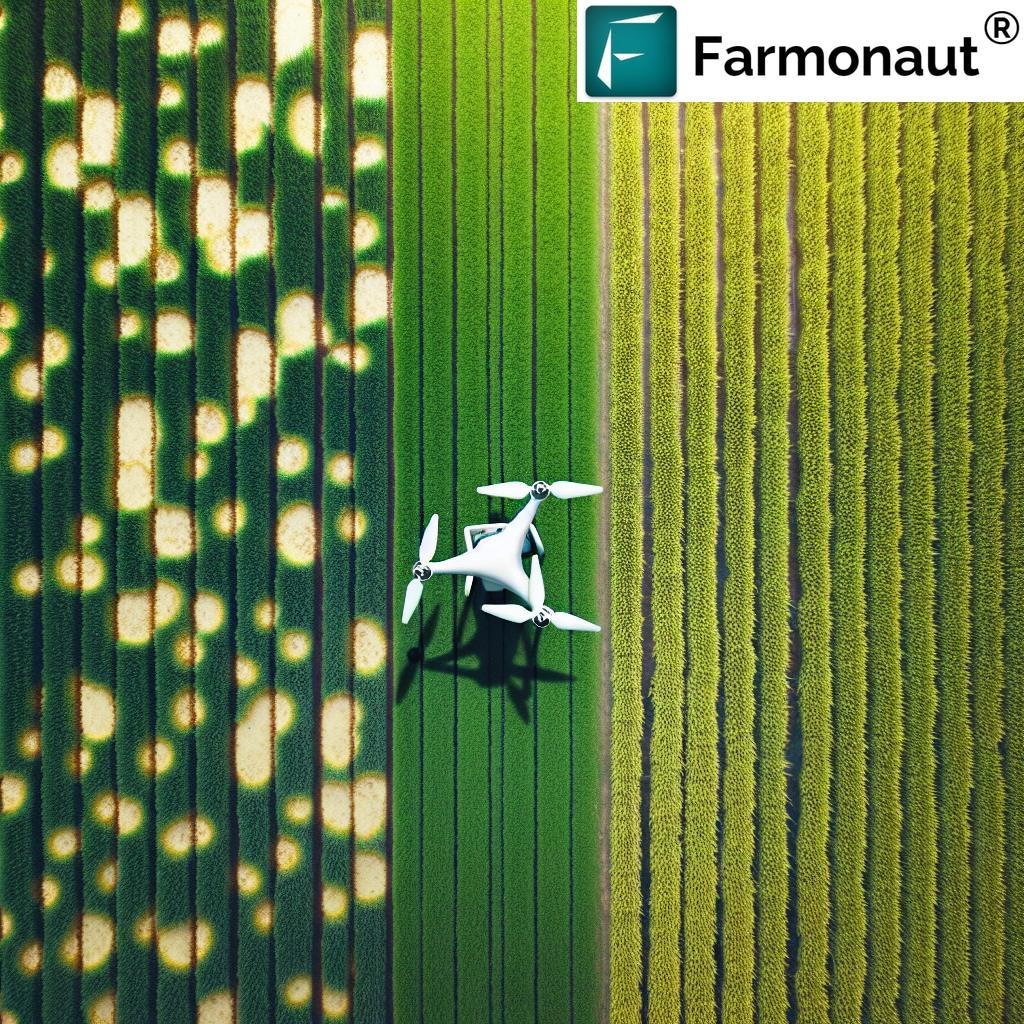
- Remote Sensing: Satellite and drone imagery provide valuable insights into crop health and nitrogen status across large areas.
- Soil Mapping: Creating detailed soil maps helps identify areas with different nitrogen requirements.
Farmonaut’s platform offers innovative tools for agricultural data analysis, prescription mapping, and crop monitoring, enabling farmers to make informed decisions for improved yields. Our satellite-based solutions provide real-time insights into crop health and soil conditions, supporting precision agriculture practices.
3. Organic Fertilization Methods
Incorporating organic fertilization methods can improve soil health and provide a sustainable source of nitrogen. Some effective organic approaches include:
- Composting: Using well-decomposed organic matter as a slow-release nitrogen source
- Green Manures: Growing and incorporating nitrogen-fixing cover crops into the soil
- Animal Manure: Applying properly composted animal manure to enrich soil nitrogen content
4. Cover Crops and Crop Rotation
Implementing cover crops and diverse crop rotations can significantly improve nitrogen management:
- Leguminous Cover Crops: Plants like clover, vetch, and peas fix atmospheric nitrogen, enriching the soil
- Non-Leguminous Cover Crops: Grasses and brassicas can scavenge residual nitrogen, preventing leaching
- Crop Rotation: Alternating between high and low nitrogen-demanding crops helps balance soil nutrient levels
Optimizing Nitrogen Use Efficiency
Improving nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) is crucial for maximizing crop yields while minimizing environmental impact. Here are some strategies to enhance NUE:
1. Timing of Nitrogen Application
Synchronizing nitrogen application with crop demand is essential. Consider the following approaches:
- Split Applications: Divide nitrogen fertilizer into multiple applications throughout the growing season
- Growth Stage-Based Timing: Apply nitrogen at critical growth stages when crop demand is highest
- Weather-Informed Decisions: Avoid applying nitrogen before heavy rainfall to prevent leaching
2. Placement of Nitrogen Fertilizers
Proper placement of nitrogen fertilizers can significantly improve uptake efficiency:
- Band Application: Place fertilizer in concentrated bands near plant roots
- Fertigation: Apply nitrogen through irrigation systems for precise delivery
- Foliar Application: Use foliar sprays for quick nitrogen uptake during critical growth stages
3. Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizers (EEFs)
EEFs are designed to improve nitrogen use efficiency and reduce losses:
- Slow-Release Fertilizers: Gradually release nitrogen over an extended period
- Controlled-Release Fertilizers: Release nitrogen based on soil temperature and moisture
- Nitrification Inhibitors: Slow down the conversion of ammonium to nitrate, reducing leaching potential
“Legumes can fix up to 200 kg of nitrogen per hectare annually, naturally improving soil fertility for subsequent crops.“
Leveraging Precision Agriculture for Nitrogen Management
Precision agriculture technologies offer powerful tools for optimizing nitrogen management. Here’s how we can leverage these innovations:
1. Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
Satellite imagery provides valuable insights into crop health and nitrogen status across large areas. Farmonaut’s platform utilizes advanced satellite data to offer:
- Vegetation health indices (e.g., NDVI) for early detection of nitrogen stress
- Temporal analysis to track crop development and nitrogen uptake over time
- Field variability maps to identify areas requiring targeted nitrogen management
2. Prescription Mapping
Prescription maps combine multiple data layers to create customized nitrogen application plans:
- Soil type and fertility maps
- Historical yield data
- Topography and drainage information
- In-season crop health imagery
Using Farmonaut’s platform, farmers can generate precise prescription maps for variable rate nitrogen application, optimizing input use and maximizing yield potential.
3. Real-Time Crop Monitoring
Continuous monitoring throughout the growing season allows for adaptive nitrogen management:
- Regular satellite imagery updates to track crop progress
- Integration with weather data for informed decision-making
- AI-powered crop health analysis for early detection of nitrogen deficiencies
Balancing Nitrogen Application with Environmental Concerns
While nitrogen is essential for crop production, excessive application can lead to environmental issues. Here’s how we can strike a balance:
1. Minimizing Nitrogen Runoff
Implementing practices to reduce nitrogen runoff protects water quality:
- Establish buffer zones near water bodies
- Use cover crops to capture excess nitrogen
- Implement conservation tillage to reduce soil erosion
2. Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Optimizing nitrogen use can help mitigate agriculture’s contribution to climate change:
- Use nitrification inhibitors to reduce nitrous oxide emissions
- Implement precision agriculture to minimize over-application
- Incorporate legumes into crop rotations to reduce synthetic nitrogen use
3. Promoting Soil Health
Balanced nitrogen management supports long-term soil health:
- Maintain soil organic matter through crop residue management
- Encourage microbial activity with diverse crop rotations
- Use soil tests to avoid excessive nitrogen accumulation
The Role of Data in Nitrogen Management
Effective nitrogen management relies heavily on data-driven decision-making. Here’s how we can leverage agricultural data:
1. Historical Data Analysis
Analyzing past performance helps inform future nitrogen management strategies:
- Review previous years’ yield data and nitrogen application rates
- Identify trends in crop response to different nitrogen management practices
- Use historical weather data to understand nitrogen loss patterns
2. Real-Time Data Integration
Incorporating real-time data allows for adaptive nitrogen management:
- Use soil moisture sensors to optimize nitrogen application timing
- Integrate weather forecasts to avoid applying nitrogen before heavy rainfall
- Utilize crop health imagery to identify areas requiring immediate nitrogen intervention
3. Predictive Modeling
Advanced modeling techniques can help forecast nitrogen requirements:
- Use crop growth models to predict nitrogen uptake throughout the season
- Incorporate soil and weather data to estimate nitrogen mineralization rates
- Develop yield potential maps to guide variable rate nitrogen application
Farmonaut’s platform offers powerful tools for agricultural data analysis, enabling farmers to make informed decisions based on comprehensive, up-to-date information.
The Future of Nitrogen Management in Agriculture
As we look ahead, several emerging technologies and approaches promise to further revolutionize nitrogen management:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML algorithms are being developed to:
- Analyze complex datasets for optimized nitrogen recommendations
- Predict crop nitrogen requirements based on multifactorial inputs
- Automate decision-making processes for precision nitrogen application
2. Sensor Technologies
Advanced sensors are enhancing our ability to monitor nitrogen in real-time:
- In-field nitrate sensors for continuous soil nitrogen monitoring
- Hyperspectral imaging for detailed crop nitrogen status assessment
- IoT-enabled sensor networks for comprehensive field monitoring
3. Biological Nitrogen Fixation
Research is ongoing to enhance biological nitrogen fixation:
- Development of non-legume crops with nitrogen-fixing capabilities
- Enhancing the efficiency of symbiotic nitrogen fixation in legumes
- Exploring the potential of free-living nitrogen-fixing microorganisms
By staying informed about these advancements and leveraging platforms like Farmonaut, farmers can continually improve their nitrogen management practices, boosting crop yields while promoting sustainable agriculture.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced agricultural data integration
Conclusion
Mastering nitrogen management is crucial for optimizing crop yield and maintaining soil health in modern agriculture. By combining traditional agronomic knowledge with cutting-edge precision agriculture technologies, we can achieve sustainable and efficient nitrogen use. Platforms like Farmonaut offer invaluable tools for data-driven decision-making, enabling farmers to implement targeted nitrogen management strategies that benefit both their bottom line and the environment.
As we continue to face challenges such as climate change and increasing food demand, effective nitrogen management will play a pivotal role in ensuring global food security while minimizing agriculture’s environmental footprint. By embracing precision agriculture techniques, leveraging data analytics, and staying informed about the latest research and technologies, we can work towards a more sustainable and productive agricultural future.
FAQ Section
Q: What are the main symptoms of nitrogen deficiency in plants?
A: The main symptoms include yellowing of older leaves (chlorosis), stunted growth, smaller leaves, and reduced fruit or grain size and quality.
Q: How can precision agriculture help in nitrogen management?
A: Precision agriculture technologies like variable rate application, remote sensing, and soil mapping enable targeted and efficient nitrogen application, reducing waste and optimizing crop uptake.
Q: What role do cover crops play in nitrogen management?
A: Cover crops, especially legumes, can fix atmospheric nitrogen, enrich the soil, prevent nitrogen leaching, and improve overall soil health.
Q: How does Farmonaut’s platform contribute to nitrogen management?
A: Farmonaut offers satellite-based crop monitoring, prescription mapping, and data analysis tools that help farmers make informed decisions about nitrogen application timing and rates.
Q: What are some organic methods for improving soil nitrogen content?
A: Organic methods include using compost, green manures, animal manure, and implementing crop rotations with leguminous plants.
Q: How can farmers balance nitrogen application with environmental concerns?
A: Farmers can minimize nitrogen runoff by establishing buffer zones, using cover crops, implementing conservation tillage, and utilizing precision agriculture for targeted application.
Q: What future technologies are being developed for nitrogen management?
A: Emerging technologies include AI and machine learning for optimized recommendations, advanced sensors for real-time monitoring, and research into enhancing biological nitrogen fixation.
Access Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs for integration guidance