Mastering Sustainable Agriculture: A Comprehensive Guide to Precision Farming Technologies and Crop Disease Management
“Precision farming can reduce water usage by up to 30% compared to traditional irrigation methods.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on sustainable agriculture practices and precision farming technologies. In this extensive resource, we’ll explore the cutting-edge world of modern crop cultivation, covering everything from seed selection to postharvest management. Our goal is to provide you with valuable insights into crop disease management, organic farming techniques, and water-efficient methods that can revolutionize your farming practices.
As we delve into this topic, we’ll be focusing on innovative approaches like bio-fertilizers and drone technology in agriculture, which are changing the landscape of both crop and livestock production. We’ll also explore practical aspects such as agricultural land measurement, mushroom cultivation, and strategies to minimize storage losses for various crops like potato, onion, and basmati rice.
Let’s begin our journey into the world of efficient and sustainable farming for improved yields and quality produce.
1. The Foundation of Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is at the heart of modern farming practices. It’s an approach that focuses on meeting society’s present food and textile needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Here are some key aspects of sustainable agriculture:
- Resource Conservation: Minimizing water usage, preserving soil health, and reducing reliance on synthetic inputs.
- Biodiversity Promotion: Encouraging diverse ecosystems within farmlands to support natural pest control and pollination.
- Economic Viability: Ensuring farming practices are profitable and support local communities.
- Social Responsibility: Providing fair working conditions and supporting rural development.
By adopting sustainable agriculture practices, we can address many of the challenges facing modern farming, including climate change, water scarcity, and soil degradation.
2. Precision Farming Technologies: A Game-Changer
Precision farming technologies are revolutionizing the agricultural sector by enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions. These technologies allow for more efficient use of resources, resulting in higher yields and reduced environmental impact. Let’s explore some of the key precision farming technologies:
2.1 Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
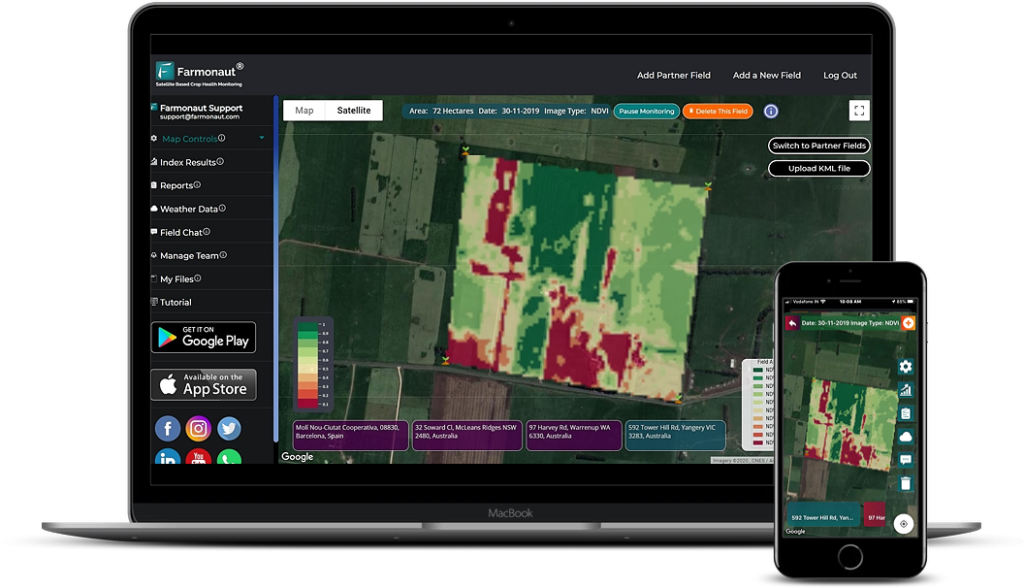
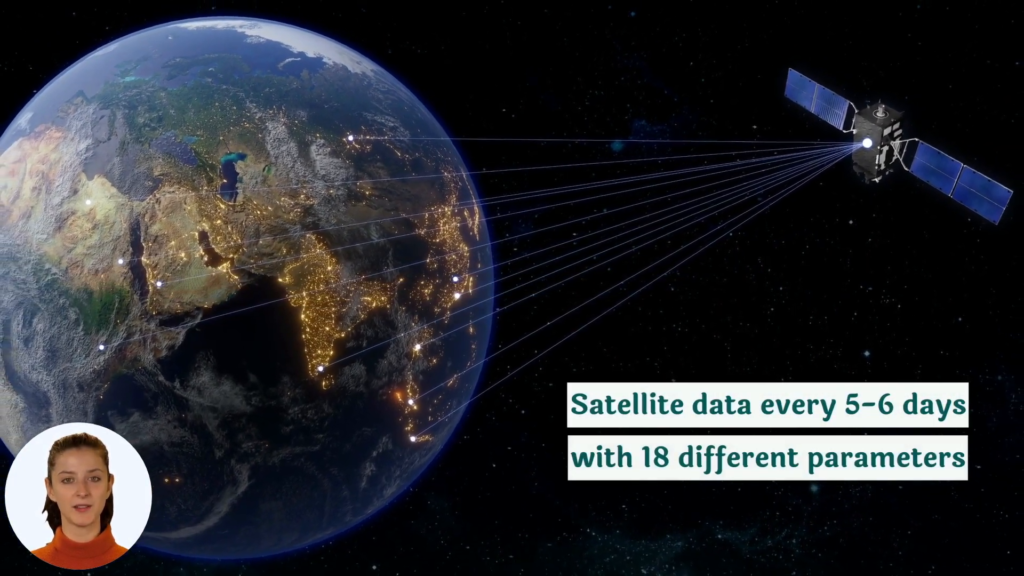
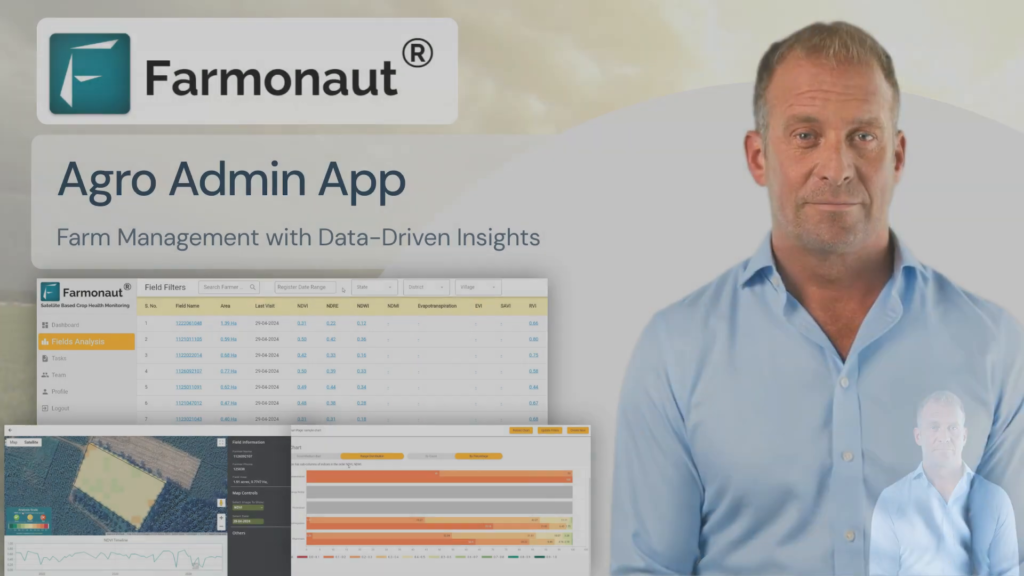
Satellite-based crop monitoring is a powerful tool that provides farmers with real-time insights into their fields. Companies like Farmonaut offer advanced satellite-based farm management solutions that can transform the way we approach agriculture.
Benefits of satellite-based crop monitoring:
- Real-time crop health assessment
- Early detection of pest and disease outbreaks
- Optimization of irrigation and fertilizer application
- Improved yield predictions
To learn more about how satellite-based crop monitoring works, check out this informative video:
For those interested in implementing satellite-based crop monitoring, Farmonaut offers various solutions:
Web App | Android App | iOS App

2.2 Drone Technology in Agriculture
Drones have become an invaluable tool in modern agriculture. They offer a bird’s-eye view of fields, allowing farmers to quickly assess crop health, identify problem areas, and make informed decisions.
Applications of drones in agriculture:
- Crop mapping and surveying
- Precision spraying of pesticides and fertilizers
- Monitoring irrigation systems
- Assessing crop damage after extreme weather events
2.3 IoT Sensors and Smart Farming
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors are transforming farms into smart, connected environments. These sensors can monitor various parameters such as soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels in real-time.
Benefits of IoT in agriculture:
- Precise irrigation management
- Optimal fertilizer application
- Early detection of plant stress
- Improved livestock monitoring and management
3. Crop Disease Management: A Critical Aspect of Sustainable Farming
Effective crop disease management is crucial for ensuring high yields and quality produce. By implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, farmers can reduce their reliance on chemical pesticides while maintaining healthy crops.
3.1 Early Detection and Prevention
Early detection of crop diseases is key to preventing widespread outbreaks. Satellite-based crop monitoring systems, like those offered by Farmonaut, can help identify potential disease hotspots before they become major problems.
Steps for early disease detection:
- Regular field scouting
- Monitoring of weather conditions
- Use of remote sensing technologies
- Soil and plant tissue testing
3.2 Biological Control Methods
Biological control methods involve using natural enemies of pests and pathogens to manage crop diseases. This approach is environmentally friendly and can be highly effective when implemented correctly.
Examples of biological control methods:
- Introduction of beneficial insects
- Use of microbial antagonists
- Planting of trap crops
- Application of biopesticides
3.3 Cultural Practices for Disease Management
Cultural practices play a crucial role in preventing and managing crop diseases. These practices focus on creating an environment that is less favorable for disease development.
Effective cultural practices include:
- Crop rotation
- Proper plant spacing
- Adequate drainage
- Timely planting and harvesting
- Use of disease-resistant varieties
“Implementing proper storage techniques can reduce post-harvest losses of crops like potatoes and onions by 15-20%.”
4. Organic Farming Techniques: Nurturing Soil Health
Organic farming techniques focus on building and maintaining soil health, which is fundamental to sustainable agriculture. These methods rely on natural processes and avoid the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
4.1 Composting and Green Manuring
Composting and green manuring are essential practices in organic farming that help improve soil structure and fertility.
Benefits of composting and green manuring:
- Increased soil organic matter
- Improved water retention capacity
- Enhanced soil microbial activity
- Reduced dependency on synthetic fertilizers
4.2 Crop Rotation and Intercropping
Crop rotation and intercropping are age-old practices that have proven benefits for soil health and pest management.
Advantages of crop rotation and intercropping:
- Improved soil fertility
- Reduced pest and disease pressure
- Increased biodiversity
- Optimized use of soil nutrients
4.3 Bio-fertilizers in Crop Production
Bio-fertilizers are microorganisms that enhance nutrient availability to plants. They are an eco-friendly alternative to chemical fertilizers and play a crucial role in organic farming.
Types of bio-fertilizers:
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g., Rhizobium)
- Phosphate solubilizing bacteria
- Mycorrhizal fungi
- Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR)
5. Water-Efficient Farming Methods
Water scarcity is a growing concern in agriculture. Implementing water-efficient farming methods is crucial for sustainable crop production.
5.1 Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient water delivery system that minimizes water loss through evaporation and runoff.
Benefits of drip irrigation:
- Water savings of up to 50-70%
- Reduced weed growth
- Improved crop yields
- Decreased soil erosion
5.2 Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is an ancient practice that’s gaining renewed importance in modern agriculture. It involves collecting and storing rainwater for later use in irrigation.
Advantages of rainwater harvesting:
- Reduced dependence on groundwater
- Improved water availability during dry periods
- Decreased soil erosion
- Flood mitigation
5.3 Mulching Techniques
Mulching involves covering the soil surface with organic or inorganic materials to conserve moisture and suppress weed growth.
Benefits of mulching:
- Reduced water evaporation
- Weed control
- Regulation of soil temperature
- Improved soil structure
6. Agricultural Land Measurement and Management
Accurate land measurement is crucial for effective farm management, resource allocation, and yield estimation. Modern technologies have made this process more precise and efficient.
6.1 Satellite-Based Land Measurement
Satellite technology has revolutionized agricultural land measurement. Platforms like Farmonaut offer precise land area calculation using satellite imagery.
Advantages of satellite-based land measurement:
- High accuracy
- Time and cost-efficient
- Ability to measure large areas quickly
- Historical data comparison
To see how satellite-based land measurement works in practice, watch this informative video:
6.2 GPS-Based Field Mapping
GPS technology allows farmers to create detailed maps of their fields, including information on soil types, crop varieties, and yield data.
Applications of GPS in field mapping:
- Precise boundary demarcation
- Creation of elevation maps
- Identification of problem areas
- Planning for variable rate applications
7. Optimizing Livestock Production
Sustainable agriculture isn’t just about crops; it also involves optimizing livestock production. Modern technologies and management practices can significantly improve animal husbandry.
7.1 Precision Livestock Farming
Precision livestock farming uses sensors and data analytics to monitor individual animals’ health, behavior, and productivity.
Benefits of precision livestock farming:
- Early disease detection
- Optimized feeding strategies
- Improved reproductive management
- Enhanced animal welfare
7.2 Sustainable Feed Production
Producing livestock feed sustainably is crucial for reducing the environmental impact of animal husbandry.
Strategies for sustainable feed production:
- Use of crop residues and by-products
- Cultivation of fodder crops
- Implementation of rotational grazing
- Adoption of agroforestry systems
8. Minimizing Storage Losses
Post-harvest losses can significantly impact farm profitability. Implementing proper storage techniques is essential for preserving crop quality and reducing waste.
8.1 Storage Techniques for Potato and Onion
Potatoes and onions are staple crops that require specific storage conditions to maintain quality.
Best practices for potato and onion storage:
- Proper curing before storage
- Temperature and humidity control
- Adequate ventilation
- Regular monitoring for signs of spoilage
8.2 Basmati Rice Storage
Basmati rice, known for its distinct aroma and flavor, requires careful storage to maintain its quality.
Tips for storing basmati rice:
- Use of airtight containers
- Storage in cool, dry places
- Protection from pests
- Regular quality checks
9. The Role of Multipurpose Trees in Farming Systems
Multipurpose trees, such as neem, play a vital role in sustainable farming systems. They provide multiple benefits to farmers and the environment.
9.1 Benefits of Neem in Agriculture
Neem is a versatile tree with numerous applications in agriculture.
Uses of neem in farming:
- Natural pesticide
- Soil amendment
- Livestock feed supplement
- Windbreak and shade
9.2 Agroforestry Systems
Agroforestry integrates trees with crops or livestock, creating diverse and resilient farming systems.
Benefits of agroforestry:
- Improved soil fertility
- Enhanced biodiversity
- Diversified income sources
- Carbon sequestration
10. Advanced Cropping Systems
Advanced cropping systems combine traditional knowledge with modern technologies to maximize productivity and sustainability.
10.1 Conservation Agriculture
Conservation agriculture focuses on minimizing soil disturbance, maintaining soil cover, and diversifying crop rotations.
Principles of conservation agriculture:
- Minimal tillage
- Permanent soil cover
- Crop rotation
- Integrated pest management
10.2 Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is an innovative approach to agriculture that maximizes space utilization and resource efficiency.
Advantages of vertical farming:
- Year-round crop production
- Reduced water usage
- Minimal pesticide use
- Optimized space utilization

11. Precision Farming Technologies Comparison
To help you better understand the various precision farming technologies available, we’ve compiled a comparison table:
| Technology Name | Primary Function | Crop Type Suitability | Environmental Impact | Implementation Cost ($/hectare) | Potential Yield Increase (%) | Water Efficiency Improvement (%) | Labor Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drone Mapping | Crop health assessment, precision spraying | All types | Low | 50-100 | 10-15 | 20-30 | 30-40 |
| Soil Sensors | Soil moisture and nutrient monitoring | All types | Low | 100-200 | 15-20 | 25-35 | 20-30 |
| GPS-guided Machinery | Precise planting, fertilizing, harvesting | Row crops | Medium | 200-300 | 5-10 | 10-15 | 40-50 |
| Automated Irrigation Systems | Water management | All types | Low | 300-500 | 20-30 | 30-50 | 50-60 |
| Crop Monitoring Satellites | Large-scale crop health monitoring | All types | Low | 10-50 | 10-20 | 15-25 | 30-40 |
This table provides a comprehensive overview of various precision farming technologies, allowing you to compare their benefits and applications easily. It’s important to note that the actual figures may vary depending on specific implementations and local conditions.
12. The Future of Sustainable Agriculture
As we look to the future, sustainable agriculture will continue to evolve, incorporating new technologies and practices to meet the growing global demand for food while minimizing environmental impact.
12.1 Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture
AI is set to play an increasingly important role in agriculture, from crop prediction to autonomous farming equipment.
Potential applications of AI in agriculture:
- Predictive analytics for crop yields
- Automated pest and disease detection
- Robotic harvesting
- Precision resource management
12.2 Biotechnology and Crop Improvement
Advances in biotechnology are opening new possibilities for crop improvement, focusing on traits like drought resistance and nutritional content.
Areas of focus in crop biotechnology:
- Drought-tolerant varieties
- Biofortified crops
- Pest-resistant cultivars
- Climate-resilient crop varieties
13. Implementing Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Transitioning to sustainable agriculture practices requires careful planning and implementation. Here are some steps to get started:
- Assess your current practices: Evaluate your current farming methods and identify areas for improvement.
- Set clear goals: Define specific, measurable objectives for sustainability improvements.
- Educate yourself and your team: Stay informed about the latest sustainable farming practices and technologies.
- Start small: Begin with pilot projects to test new methods before scaling up.
- Monitor and adjust: Regularly assess the impact of new practices and make adjustments as needed.
- Collaborate and share knowledge: Connect with other farmers and experts to exchange ideas and experiences.
For those looking to implement satellite-based crop monitoring as part of their sustainable agriculture strategy, Farmonaut offers comprehensive solutions. Learn more about their services:
Farmonaut Web App | API Services | API Developer Docs
14. Conclusion
Mastering sustainable agriculture is a journey that requires continuous learning and adaptation. By embracing precision farming technologies, implementing effective crop disease management strategies, and adopting water-efficient methods, we can create a more resilient and productive agricultural system.
Remember, the key to success lies in balancing traditional farming wisdom with modern innovations. As we move forward, let’s continue to explore new ways to optimize our farming practices, minimize our environmental impact, and ensure food security for future generations.
FAQs
- What is precision farming?
Precision farming is an approach that uses technology to optimize crop management, allowing farmers to apply the right treatments in the right place at the right time. - How does satellite-based crop monitoring work?
Satellite-based crop monitoring uses multispectral imagery to assess crop health, soil moisture, and other key parameters, providing farmers with real-time insights into their fields. - What are the benefits of organic farming?
Organic farming promotes soil health, reduces chemical exposure, enhances biodiversity, and often results in higher-quality produce. - How can I reduce water usage in agriculture?
Implement water-efficient irrigation systems like drip irrigation, practice mulching, and use drought-resistant crop varieties. - What role does AI play in sustainable agriculture?
AI can help in various aspects of farming, including predictive analytics for crop yields, automated pest detection, and precision resource management.