Organic Aphid Control: Integrated Pest Management for Effective Crop Protection
In the world of agriculture, one of the most persistent challenges farmers face is the control of pests, particularly aphids. These tiny insects can cause significant damage to a wide variety of crops, leading to reduced yields and economic losses. At Farmonaut, we understand the importance of effective pest management strategies that not only protect crops but also maintain the delicate balance of our ecosystem. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the world of organic aphid control and how Integrated Pest Management (IPM) can provide an effective solution for crop protection.
Understanding Aphids: The Green Menace
Aphids are small, soft-bodied insects that feed on the sap of plants. They come in various colors, including green, yellow, black, or red, depending on the species and the plants they infest. These pests can reproduce rapidly, leading to quick infestations that can severely damage crops if left unchecked.
Some common crops affected by aphids include:
- Cabbage and other brassicas
- Peach trees and other stone fruits
- Leafy greens
- Tomatoes
- Peppers
- Beans
The damage caused by aphids can manifest in several ways:
- Stunted growth of plants
- Curled or distorted leaves
- Yellowing of foliage
- Reduced crop yields
- Transmission of plant viruses
The Limitations of Conventional Pest Control
Traditionally, farmers have relied heavily on chemical insecticides to control aphid populations. While these conventional methods can be effective in the short term, they come with several drawbacks:
- Environmental pollution
- Harm to beneficial insects and pollinators
- Development of pesticide resistance in aphid populations
- Potential health risks for farmers and consumers
- High costs associated with frequent applications
As we at Farmonaut advocate for sustainable farming practices, we believe it’s crucial to explore alternative methods that are both effective and environmentally friendly.
Integrated Pest Management: A Holistic Approach
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive approach to pest control that combines various strategies to manage pest populations effectively while minimizing environmental impact. IPM focuses on long-term prevention and sustainable solutions rather than relying solely on chemical treatments.
The key components of IPM include:
- Monitoring and identification of pests
- Setting action thresholds
- Prevention methods
- Cultural controls
- Biological controls
- Chemical controls (as a last resort)
By implementing IPM strategies, farmers can effectively manage aphid populations while promoting a healthier ecosystem on their farms.
Organic Aphid Control Strategies
When it comes to organic aphid control, there are numerous effective methods that align with IPM principles. Let’s explore some of these strategies in detail:
1. Cultural Controls
Cultural controls involve modifying the growing environment to make it less favorable for aphids. Some effective cultural control methods include:
- Crop rotation: Planting different crops in successive seasons can disrupt aphid life cycles.
- Companion planting: Growing plants that repel aphids or attract beneficial insects near vulnerable crops.
- Proper irrigation: Avoiding over-watering, which can create conditions favorable for aphid growth.
- Pruning and removing infested plant parts: This can help reduce aphid populations and prevent their spread.
2. Biological Controls
Biological control involves using natural predators and parasites to manage aphid populations. Some beneficial organisms that can help control aphids include:
- Ladybugs
- Lacewings
- Hoverflies
- Parasitic wasps
Encouraging these beneficial insects by providing habitat and food sources can help maintain a natural balance in your fields.
3. Organic Insecticides
When other methods are insufficient, organic insecticides can be used as part of an IPM strategy. Some effective organic options include:
- Neem oil: A natural insecticide derived from the neem tree
- Insecticidal soaps: Specially formulated soaps that disrupt the cell membranes of soft-bodied insects
- Pyrethrin: A natural insecticide extracted from chrysanthemum flowers
These organic insecticides are generally less harmful to beneficial insects and the environment compared to synthetic chemicals.
4. Entomopathogenic Fungi
Certain fungi can be used as natural pest control agents. Species such as Beauveria bassiana, Isaria fumosorosea, and Lecanicillium lecanii are known to be effective against aphids. These fungi infect and kill the pests without harming beneficial insects or the environment.
The Role of Technology in Modern IPM
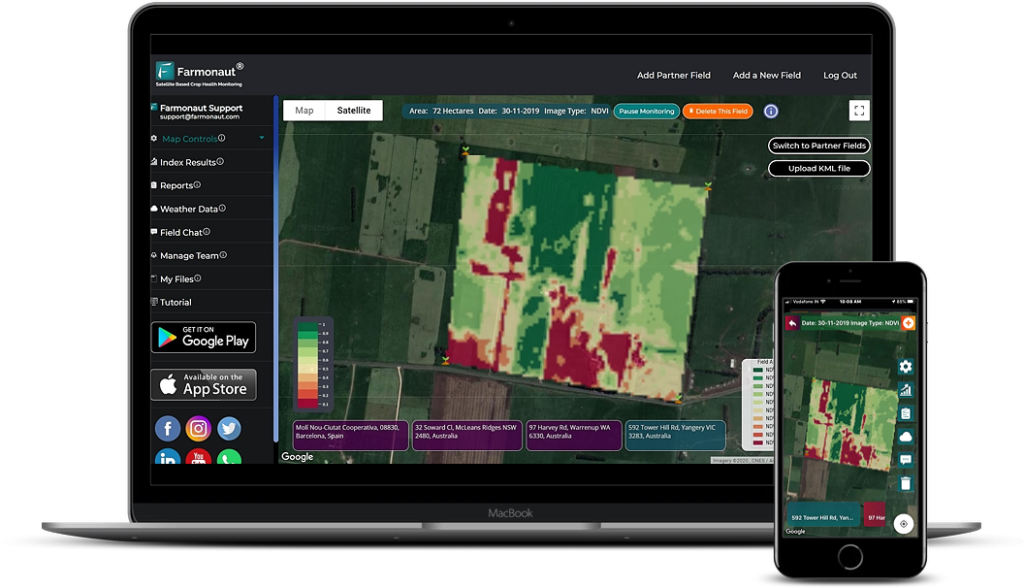
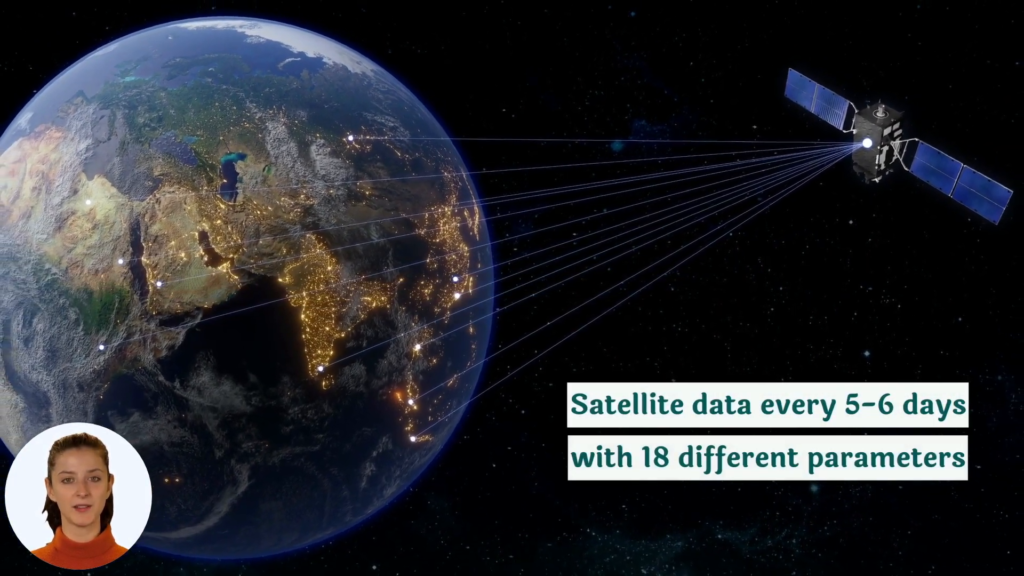
At Farmonaut, we believe that technology plays a crucial role in enhancing IPM strategies. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system can help farmers detect early signs of aphid infestations, enabling timely intervention and reducing the need for chemical treatments.
Here’s how our technology supports IPM:
- Early detection: Our satellite imagery can identify changes in crop health that may indicate aphid infestations before they become visible to the naked eye.
- Precision targeting: By pinpointing affected areas, farmers can apply treatments more precisely, reducing overall pesticide use.
- Monitoring effectiveness: Our system allows farmers to track the effectiveness of their IPM strategies over time, enabling continuous improvement.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can support your IPM efforts, visit our app or explore our API documentation.
Comparing Traditional and IPM Approaches
To better understand the benefits of organic IPM strategies over conventional chemical control methods, let’s compare the two approaches:
| Aspect | Traditional Chemical Control | Organic IPM Strategies | Farmonaut’s Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | High – Potential pollution and harm to non-target species | Low – Minimal environmental disruption | Supports eco-friendly practices through precise monitoring |
| Long-term Effectiveness | Decreases over time due to pest resistance | Improves as natural balance is established | Enables continuous monitoring for sustained effectiveness |
| Cost | High recurring costs for chemicals | Initial investment, but lower long-term costs | Reduces costs through early detection and targeted interventions |
| Biodiversity | Reduces biodiversity | Promotes biodiversity | Helps maintain biodiversity through minimized chemical use |
| Resistance Development | High risk of pests developing resistance | Low risk due to diverse control methods | Aids in rotating strategies to prevent resistance |
| Worker Safety | Potential health risks from chemical exposure | Safer for farm workers | Reduces need for chemical applications, enhancing worker safety |
Implementing IPM on Your Farm
Implementing an effective IPM strategy for aphid control requires careful planning and execution. Here are some steps to get started:
- Monitor and identify: Regularly inspect your crops for signs of aphid infestation. Use Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring tools to detect early warning signs.
- Set action thresholds: Determine the level of infestation at which control measures need to be implemented.
- Implement preventive measures: Use cultural controls and encourage beneficial insects in your fields.
- Choose appropriate treatments: When action thresholds are reached, select the most suitable organic control method based on the severity of the infestation.
- Evaluate and adjust: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your IPM strategy and make adjustments as needed.
Remember, successful IPM is an ongoing process that requires patience and adaptability. By leveraging Farmonaut’s technology and following these principles, you can develop a robust aphid control strategy that protects your crops while promoting environmental sustainability.
Case Studies: Successful Organic Aphid Control
While we don’t include specific case studies or success stories, it’s worth noting that many farmers around the world have successfully implemented organic IPM strategies to control aphid populations. These farmers have reported benefits such as:
- Reduced crop damage
- Lower pest control costs
- Improved overall crop health
- Increased biodiversity on their farms
- Better compliance with organic certification standards
These success stories demonstrate the potential of organic IPM strategies when implemented correctly and consistently.
The Future of Aphid Control: Emerging Technologies and Research
As we continue to face challenges in pest management, researchers and agricultural technology companies are working on innovative solutions for aphid control. Some exciting developments include:
- RNA interference (RNAi) technology: This emerging technique could potentially target specific pest species without affecting beneficial insects.
- Advanced pheromone traps: These traps use species-specific pheromones to lure and trap aphids, providing both monitoring and control capabilities.
- Precision agriculture tools: Technologies like drones and AI-powered image analysis are enhancing our ability to detect and respond to pest infestations quickly.
- Plant breeding for resistance: Ongoing research is focused on developing crop varieties with enhanced natural resistance to aphids.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these developments and integrating new technologies into our platform to support more effective and sustainable pest management strategies.
Challenges and Considerations in Organic Aphid Control
While organic IPM strategies offer numerous benefits, it’s important to acknowledge some of the challenges farmers may face when transitioning from conventional pest control methods:
- Longer implementation time: Establishing a balanced ecosystem that naturally suppresses pest populations can take time.
- Initial learning curve: Farmers may need to invest time in learning new monitoring and control techniques.
- Weather dependence: Some organic treatments may be less effective in certain weather conditions.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensuring all methods and products used comply with organic certification standards can be complex.
Despite these challenges, the long-term benefits of organic IPM often outweigh the initial difficulties. With proper planning, education, and support, farmers can successfully overcome these obstacles.
The Economic Impact of Organic Aphid Control
Implementing organic aphid control strategies can have significant economic implications for farmers:
- Reduced input costs: Over time, reliance on expensive chemical pesticides decreases.
- Premium pricing: Organically grown produce often commands higher prices in the market.
- Improved crop resilience: Healthier plants are better able to withstand other stresses, potentially leading to more consistent yields.
- Long-term sustainability: Preserving beneficial insects and soil health can lead to more stable and productive farming systems over time.
By leveraging Farmonaut’s technology to implement precise and timely IPM strategies, farmers can maximize these economic benefits while minimizing risks.
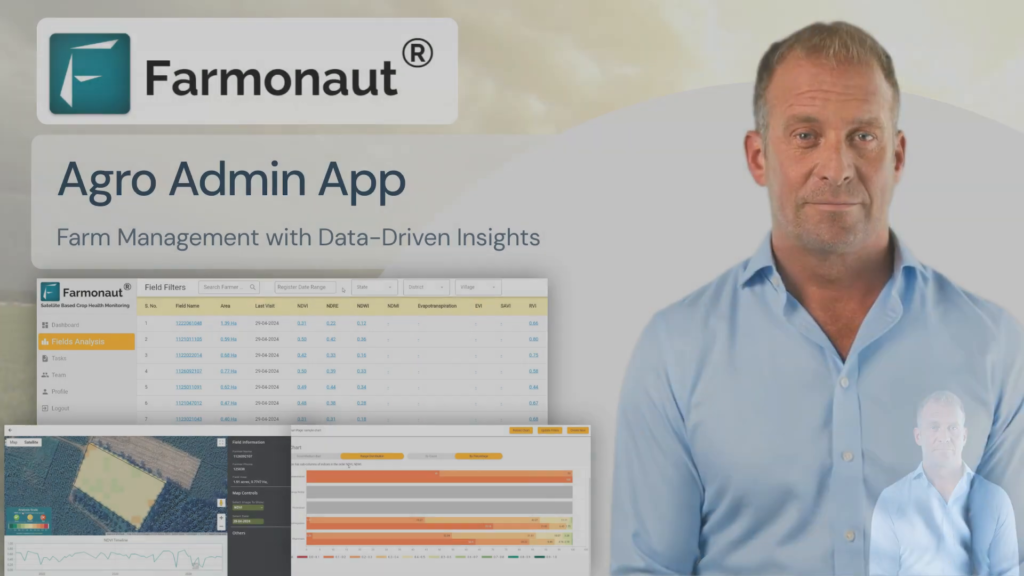
Farmonaut’s Commitment to Sustainable Agriculture
At Farmonaut, we’re dedicated to supporting farmers in their transition to more sustainable and effective pest management practices. Our satellite-based monitoring system is just one of the many tools we offer to help farmers implement successful IPM strategies.
We encourage farmers to explore our range of services, including:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- AI-powered pest detection
- Customized treatment recommendations
- Integration with other farm management tools
To learn more about how Farmonaut can support your organic aphid control efforts, visit our website or download our app:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What are the most common signs of aphid infestation?
A1: Common signs include curled or distorted leaves, sticky residue on leaves (honeydew), presence of ants, yellowing of foliage, and visible clusters of small insects on plant stems and undersides of leaves.
Q2: How quickly can aphids reproduce?
A2: Aphids can reproduce extremely quickly. Under optimal conditions, they can complete a generation in as little as 7-10 days, with each adult female capable of producing 40-100 offspring.
Q3: Are there any plants that naturally repel aphids?
A3: Yes, several plants are known to repel aphids, including marigolds, nasturtiums, garlic, chives, and catnip. Planting these near susceptible crops can help deter aphids.
Q4: How does Farmonaut’s technology detect aphid infestations?
A4: Our satellite imagery analyzes changes in plant health indicators, such as chlorophyll content and leaf structure, which can indicate stress caused by aphid feeding. This allows for early detection before visible symptoms appear.
Q5: Is it possible to completely eliminate aphids from my crops?
A5: Complete elimination is rarely possible or necessary. The goal of IPM is to manage aphid populations below economically damaging levels while maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
Q6: How long does it take to see results from organic aphid control methods?
A6: Results can vary depending on the methods used and the severity of the infestation. Some treatments, like insecticidal soaps, can show immediate effects, while others, like encouraging beneficial insects, may take several weeks to establish effective control.
Q7: Can I use organic aphid control methods in greenhouse settings?
A7: Yes, many organic control methods are suitable for greenhouse use. In fact, controlled environments can make some strategies, like the introduction of beneficial insects, even more effective.
Q8: How does weather affect aphid populations?
A8: Weather can significantly impact aphid populations. Mild temperatures and high humidity generally favor aphid reproduction, while extreme heat, cold, or heavy rainfall can reduce their numbers.
Q9: Are organic aphid control methods effective against all aphid species?
A9: While many organic methods are broadly effective, some aphid species may be more resistant to certain treatments. It’s important to identify the specific aphid species and tailor your approach accordingly.
Q10: How can I integrate Farmonaut’s technology with my existing pest management practices?
A10: Farmonaut’s platform is designed to complement existing farm management practices. Our API and mobile apps allow for easy integration with your current systems, enhancing your ability to monitor and respond to pest pressures effectively.
Conclusion
Organic aphid control through Integrated Pest Management offers a sustainable and effective approach to protecting crops from these persistent pests. By combining cultural, biological, and organic chemical controls with advanced monitoring technologies like those offered by Farmonaut, farmers can achieve long-term success in managing aphid populations while promoting environmental health and biodiversity.
As we continue to face challenges in agriculture, including climate change and increasing pest pressures, the importance of sustainable pest management strategies cannot be overstated. By embracing IPM and leveraging cutting-edge technologies, we can work towards a future where productive agriculture and environmental stewardship go hand in hand.
We invite you to explore how Farmonaut can support your journey towards more sustainable and effective pest management. Together, we can cultivate a healthier, more resilient agricultural landscape for generations to come.
Ready to take your pest management to the next level? Subscribe to Farmonaut today:
For more information on our API and developer resources, visit our API documentation.