Organic Papaya Protection: Controlling Aphids, Ringspot Virus, and Other Pests for Healthy Crops

In the world of tropical fruit cultivation, papaya stands out as a beloved and nutritious crop. However, papaya growers face numerous challenges, particularly when it comes to pest and disease management. At Farmonaut, we understand the importance of maintaining healthy papaya crops while adhering to organic farming principles. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the most common issues affecting papaya plants, focusing on aphids, ringspot virus, and other pests, as well as effective organic control methods.
Understanding the Papaya Crop
Papaya (Carica papaya) is a fast-growing, short-lived perennial plant that produces delicious, nutrient-rich fruits. Native to tropical America, papaya is now cultivated in many warm regions around the world. The plant is known for its large, palm-like leaves and sweet, juicy fruits that are rich in vitamins A and C, as well as antioxidants.
While papaya trees can grow quite tall, most commercial varieties are bred to remain shorter for easier harvesting. The plants typically begin bearing fruit within their first year of growth and can continue producing for several years under optimal conditions.
Common Pests and Diseases Affecting Papaya
Papaya crops are susceptible to various pests and diseases that can significantly impact yield and fruit quality. Some of the most prevalent issues include:
- Aphids: These small, soft-bodied insects feed on plant sap and can transmit viruses.
- Papaya Ringspot Virus (PRSV): A devastating disease that can cause significant crop losses.
- Spider mites: Tiny arachnids that can cause leaf damage and reduced plant vigor.
- Fruit flies: Insects that lay eggs in ripening fruits, leading to fruit spoilage.
- Powdery mildew: A fungal disease that affects leaves and can reduce photosynthesis.
- Root rot: Caused by various soil-borne pathogens, particularly in poorly drained soils.
In this article, we’ll focus primarily on aphids and the papaya ringspot virus, as these are among the most challenging issues for papaya growers.
Aphids: The Silent Menace
Aphids are small, soft-bodied insects that can cause significant damage to papaya plants. These pests are particularly problematic because they reproduce rapidly and can quickly infest an entire crop if left unchecked.
Identifying Aphid Infestations
To effectively control aphids, it’s crucial to identify them early. Here are some signs to look out for:
- Clusters of small, pear-shaped insects on the undersides of leaves or on new growth
- Curling, yellowing, or distorted leaves
- Sticky residue on leaves or fruits (honeydew excreted by aphids)
- Presence of sooty mold growing on the honeydew
- Stunted plant growth
Damage Caused by Aphids
Aphids can harm papaya plants in several ways:
- Direct feeding damage: Aphids suck sap from plant tissues, weakening the plant and reducing its ability to produce fruit.
- Virus transmission: Aphids can transmit various viruses, including the devastating papaya ringspot virus.
- Honeydew production: The sticky substance excreted by aphids can attract ants and promote the growth of sooty mold, which can interfere with photosynthesis.
- Reduced fruit quality: Heavy infestations can lead to smaller, misshapen fruits with reduced market value.
Organic Control Methods for Aphids
At Farmonaut, we advocate for organic pest control methods whenever possible. Here are some effective strategies for managing aphid populations in papaya orchards:
- Biological control: Encourage natural predators such as ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps by planting diverse, flowering plants nearby.
- Neem oil spray: Apply neem oil solution to affected plants, focusing on the undersides of leaves where aphids tend to cluster.
- Insecticidal soaps: Use organic insecticidal soaps that suffocate aphids without harming beneficial insects.
- Pruning: Remove heavily infested plant parts and dispose of them properly to reduce aphid populations.
- Reflective mulches: Use silver-colored mulches around plants to confuse and repel aphids.
- Companion planting: Grow plants that repel aphids, such as marigolds or nasturtiums, near your papaya trees.
Remember that consistent monitoring and early intervention are key to successful aphid control. Regular inspections of your papaya trees can help you catch infestations before they become severe.
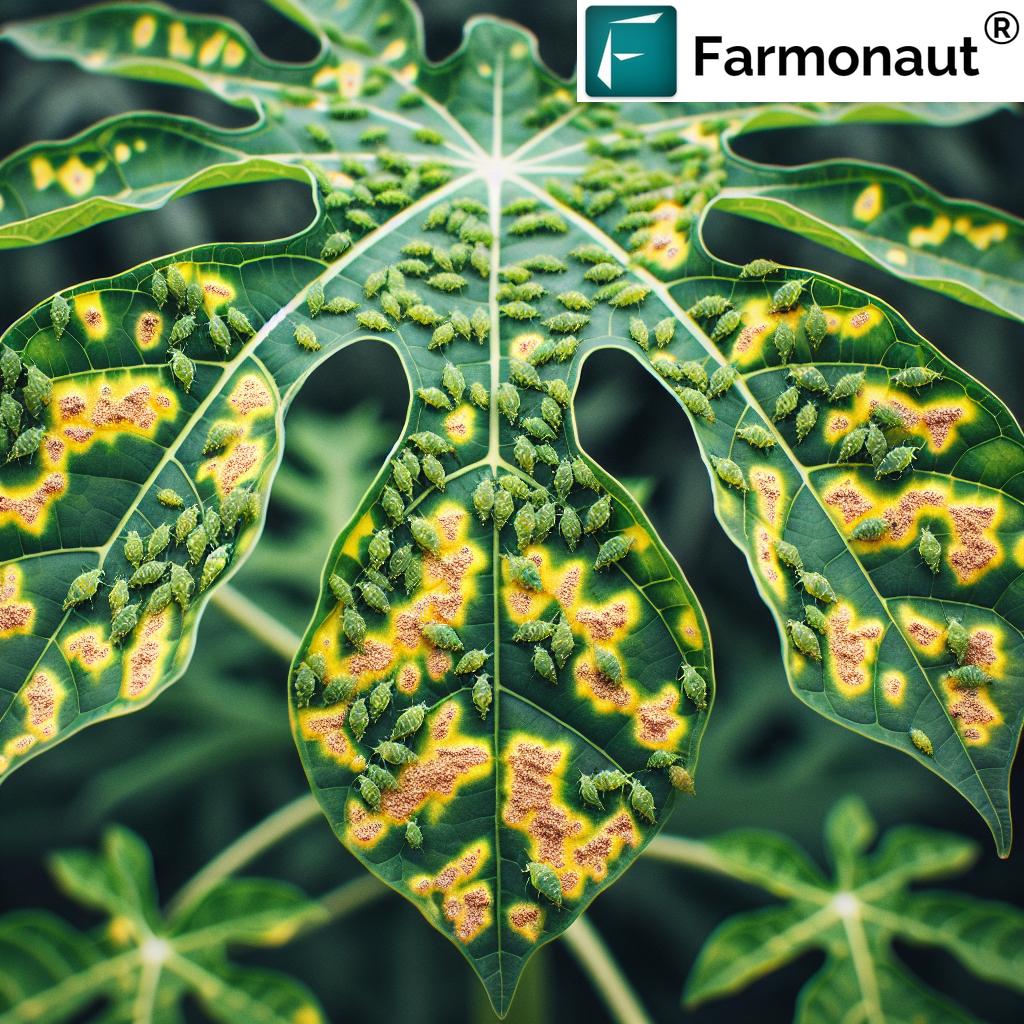
Papaya Ringspot Virus (PRSV): A Major Threat to Papaya Crops
The papaya ringspot virus (PRSV) is one of the most serious diseases affecting papaya production worldwide. This virus belongs to the potyvirus group and can cause devastating losses in papaya orchards.
Understanding PRSV Transmission
PRSV is primarily transmitted by aphids in a non-persistent manner. This means that aphids can acquire the virus quickly from an infected plant and transmit it to healthy plants within minutes. The virus can also spread through:
- Mechanical transmission (e.g., contaminated pruning tools)
- Infected seedlings or rootstocks
- Grafting of infected plant material
It’s important to note that PRSV does not persist in seeds, so seed transmission is not a concern.
Recognizing PRSV Symptoms
Early detection of PRSV is crucial for effective management. The symptoms of PRSV infection can vary depending on the plant’s age and environmental conditions, but typically include:
- Mosaic patterns on leaves, often accompanied by leaf distortion
- Yellowing of leaf veins (vein clearing)
- Stunted growth and reduced fruit production
- Characteristic ringspots on fruits, giving the disease its name
- Water-soaked lesions on leaf petioles and stems
- Distorted or malformed fruits
As the disease progresses, infected trees may produce fewer and smaller fruits, ultimately leading to significant yield losses.
Organic Management Strategies for PRSV
Managing PRSV organically can be challenging, but several strategies can help reduce its impact:
- Aphid control: Since aphids are the primary vectors, implementing effective aphid management (as discussed earlier) is crucial.
- Roguing: Promptly remove and destroy infected plants to prevent the virus from spreading to healthy trees.
- Quarantine measures: Isolate new plants and monitor them for symptoms before introducing them to your orchard.
- Sanitation: Regularly clean and disinfect tools and equipment to prevent mechanical transmission.
- Resistant varieties: Where available, plant PRSV-resistant papaya varieties developed through conventional breeding or genetic engineering.
- Barrier crops: Plant non-host crops around papaya orchards to create a physical barrier against aphid movement.
- Reflective mulches: Use reflective mulches to repel aphids and reduce virus transmission.
It’s important to note that once a plant is infected with PRSV, there is no cure. Therefore, prevention and early detection are key to managing this disease effectively.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Papaya Crops
At Farmonaut, we strongly advocate for an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach to papaya crop protection. IPM combines various control methods to manage pests and diseases effectively while minimizing environmental impact and promoting sustainable agriculture.
Key Components of IPM for Papaya
- Regular monitoring: Consistently inspect your papaya trees for signs of pests, diseases, or nutritional deficiencies.
- Cultural practices: Implement good agricultural practices such as proper irrigation, fertilization, and pruning to maintain plant health.
- Biological control: Encourage natural predators and use biopesticides when necessary.
- Mechanical control: Use physical barriers, traps, or manual removal of pests when appropriate.
- Chemical control: Use organic or synthetic pesticides judiciously and only as a last resort.
- Record keeping: Maintain detailed records of pest populations, treatments applied, and their effectiveness to inform future management decisions.
The Role of Technology in Papaya Crop Management
Advanced technologies can play a crucial role in implementing effective IPM strategies for papaya crops. At Farmonaut, we offer cutting-edge solutions that can help growers monitor and manage their papaya orchards more efficiently:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring: Our satellite imagery analysis can detect early signs of stress in papaya trees, allowing for timely intervention.
- AI-powered advisory system: Our Jeevn AI system provides personalized recommendations based on real-time data and expert knowledge.
- Weather forecasting: Accurate weather predictions help growers plan pest control activities and avoid conditions conducive to disease development.
- Mobile app integration: Our mobile apps allow growers to access crucial information and record observations in the field.
To learn more about how Farmonaut’s technology can enhance your papaya crop management, visit our app page or explore our API offerings.
Comparison: Traditional Monitoring vs. Farmonaut Satellite System for Papaya Crop Health
| Aspect | Traditional Monitoring | Farmonaut Satellite System |
|---|---|---|
| Early pest/disease detection | Limited to visible symptoms, often detected late | Can detect stress before visible symptoms appear |
| Coverage area | Limited to areas physically inspected | Covers entire fields or orchards at once |
| Frequency of monitoring | Depends on labor availability, usually weekly or bi-weekly | Regular updates based on satellite pass frequency |
| Cost-effectiveness | Labor-intensive and time-consuming | Highly cost-effective for large areas |
| Precision in identifying affected areas | Varies based on inspector’s experience | High precision with GPS-tagged data points |
Organic Alternatives to Chemical Pesticides
While chemical pesticides can be effective in controlling pests and diseases, they often come with environmental and health risks. At Farmonaut, we encourage the use of organic alternatives whenever possible. Here are some effective organic options for papaya pest and disease control:
Botanical Insecticides
- Neem oil: Extracted from neem tree seeds, this natural insecticide repels and disrupts the feeding of many pests, including aphids.
- Pyrethrin: Derived from chrysanthemum flowers, pyrethrin is effective against a wide range of insects.
- Garlic and chili spray: A homemade mixture of garlic and chili can repel many pests and even some fungal pathogens.
Microbial Insecticides
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): A naturally occurring bacterium that controls certain caterpillar pests.
- Beauveria bassiana: A fungus that can control a variety of insects, including aphids and whiteflies.
Mineral-based Products
- Diatomaceous earth: A fine powder that can control soft-bodied insects through physical action.
- Kaolin clay: Creates a protective barrier on plants that repels insects and reduces sunburn.
Beneficial Insects
Encouraging or introducing beneficial insects can help control pest populations naturally:
- Ladybugs and lacewings for aphid control
- Parasitic wasps for various pests
- Predatory mites for spider mite control
Cultural Practices for Papaya Disease Prevention
Implementing good cultural practices is essential for maintaining healthy papaya crops and preventing disease outbreaks. Here are some key strategies:
Site Selection and Preparation
- Choose well-drained soils to prevent root rot issues
- Ensure adequate sunlight exposure for optimal plant growth
- Conduct soil tests and amend as necessary to provide optimal nutrition
Plant Spacing and Pruning
- Space plants properly to ensure good air circulation
- Prune regularly to remove dead or diseased plant material
- Maintain a clean orchard floor by removing fallen leaves and fruits
Irrigation Management
- Use drip irrigation to minimize leaf wetness
- Water early in the day to allow foliage to dry before nightfall
- Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root problems and increase disease susceptibility
Crop Rotation and Intercropping
- Practice crop rotation to break disease cycles
- Consider intercropping with companion plants that repel pests or attract beneficial insects
Nutrient Management
- Provide balanced nutrition to promote plant health and disease resistance
- Use organic fertilizers and compost to improve soil health
- Avoid excessive nitrogen, which can make plants more susceptible to pests and diseases
Monitoring and Early Detection Techniques
Regular monitoring is crucial for effective pest and disease management in papaya orchards. Here are some techniques that can help you detect issues early:
Visual Inspections
- Conduct weekly walk-throughs of your orchard
- Check both upper and lower leaf surfaces for signs of pests or disease
- Examine fruits for abnormalities or pest damage
- Look for changes in overall plant vigor and growth patterns
Trapping and Scouting
- Use yellow sticky traps to monitor flying insects like aphids and whiteflies
- Set up pheromone traps for specific pests like fruit flies
- Employ leaf sampling techniques to estimate pest populations
Technology-Assisted Monitoring
At Farmonaut, we offer advanced monitoring solutions that can complement traditional scouting methods:
- Satellite imagery analysis: Our platform uses multispectral satellite images to detect changes in crop health before they’re visible to the naked eye.
- AI-powered image recognition: Upload photos of suspicious symptoms to our app for instant identification and treatment recommendations.
- Weather station integration: Monitor local weather conditions that may influence pest and disease development.
To learn more about our monitoring solutions, visit our Android app or iOS app pages.
Sustainable Weed Management in Papaya Orchards
Effective weed control is essential for maintaining healthy papaya crops. Weeds compete with papaya trees for nutrients, water, and sunlight, and can also harbor pests and diseases. Here are some sustainable weed management strategies:
Mulching
- Apply organic mulch around papaya trees to suppress weed growth
- Use biodegradable materials like straw, wood chips, or shredded leaves
- Maintain a mulch layer of 2-4 inches thick, keeping it away from the tree trunk
Cover Crops
- Plant low-growing cover crops between papaya rows to suppress weeds
- Choose species that fix nitrogen, such as legumes, to improve soil fertility
- Mow or roll cover crops periodically to prevent competition with papaya trees
Mechanical Control
- Use hand weeding or hoeing for small areas or spot treatments
- Employ mechanical cultivators for larger areas, being careful not to damage papaya roots
- Mow or trim weeds regularly to prevent seed production
Thermal Weed Control
- Use flame weeding or steam treatment for non-chemical weed control
- Apply these methods carefully to avoid damaging papaya trees
Precision Weed Management
Farmonaut’s satellite imagery analysis can help identify areas of high weed pressure, allowing for targeted control measures. This precision approach can reduce labor costs and minimize the environmental impact of weed management efforts.
Post-Harvest Handling and Disease Prevention
Proper post-harvest handling is crucial for maintaining fruit quality and preventing the spread of diseases. Here are some best practices:
Harvesting
- Harvest fruits at the appropriate stage of ripeness
- Use clean, sanitized cutting tools to prevent disease transmission
- Handle fruits gently to avoid bruising and damage
Sanitation
- Clean and disinfect harvesting equipment regularly
- Remove and dispose of any diseased or pest-infested fruits promptly
- Maintain a clean packing area to prevent contamination
Storage and Transportation
- Store fruits at appropriate temperatures to slow ripening and prevent decay
- Use clean, sanitized containers for storage and transportation
- Avoid mixing fruits from different harvests or quality grades
Traceability
Implementing a traceability system can help identify and isolate potential sources of contamination or disease outbreaks. Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability solution can provide a secure and transparent way to track papaya fruits from harvest to market.
The Future of Papaya Crop Protection
As we look to the future, several emerging technologies and approaches hold promise for improving papaya crop protection:
Genetic Engineering
While controversial, genetically engineered papaya varieties resistant to PRSV have been successfully developed and deployed in some regions. Ongoing research aims to develop varieties with resistance to other pests and diseases.
Precision Agriculture
Advanced sensors, drones, and satellite imagery are enabling more precise and timely interventions for pest and disease management. Farmonaut is at the forefront of this technology, offering satellite-based crop monitoring and AI-driven advisory services.
Biocontrol Agents
Research into new biological control agents, including beneficial microorganisms and insects, continues to expand the toolkit for organic pest management.
Climate-Resilient Varieties
As climate change impacts agricultural systems, breeding programs are focusing on developing papaya varieties that can withstand extreme weather events and changing pest pressures.
Integrated Data Systems
The integration of various data sources, including weather patterns, pest populations, and crop health indicators, will enable more sophisticated predictive models for pest and disease outbreaks.
Conclusion
Protecting papaya crops from pests and diseases, particularly aphids and the devastating ringspot virus, requires a multifaceted approach. By combining cultural practices, organic control methods, and advanced monitoring technologies, growers can maintain healthy, productive papaya orchards while minimizing environmental impact.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting papaya growers with cutting-edge tools and expertise. Our satellite-based crop monitoring, AI-powered advisory system, and blockchain traceability solutions can help you stay ahead of pest and disease challenges, optimize resource use, and improve overall crop management.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can support your papaya growing operation, visit our website or explore our API documentation for developers.
FAQs
- Q: How often should I monitor my papaya trees for pests and diseases?
A: We recommend weekly visual inspections, supplemented by regular satellite-based monitoring using Farmonaut’s platform. - Q: Can papaya ringspot virus be cured?
A: Unfortunately, there is no cure for PRSV once a plant is infected. Prevention and early detection are key to managing this disease. - Q: Are there any PRSV-resistant papaya varieties available?
A: Yes, some PRSV-resistant varieties have been developed through conventional breeding and genetic engineering. Check with your local agricultural extension office for varieties suitable for your region. - Q: How can I encourage beneficial insects in my papaya orchard?
A: Plant diverse flowering plants near your orchard, avoid broad-spectrum pesticides, and consider releasing commercially available beneficial insects. - Q: Is it safe to use neem oil on papaya fruits?
A: Neem oil is generally considered safe for use on papaya, but always follow label instructions and wash fruits thoroughly before consumption. - Q: How can Farmonaut’s technology help me manage my papaya crop?
A: Farmonaut offers satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-powered advisory services, and weather forecasting to help you detect issues early and make informed management decisions. - Q: Are organic control methods as effective as chemical pesticides?
A: While organic methods may require more consistent application, they can be highly effective when used as part of an integrated pest management strategy. - Q: How can I prevent the spread of diseases in my papaya orchard?
A: Practice good sanitation, remove infected plants promptly, use clean tools, and implement proper cultural practices to maintain plant health. - Q: What’s the best way to control aphids organically?
A: A combination of encouraging natural predators, using insecticidal soaps or neem oil, and practicing good cultural management can effectively control aphid populations. - Q: How can I access Farmonaut’s services for my papaya farm?
A: You can sign up for our services through our website or by downloading our mobile app. We offer various subscription plans to suit different farm sizes and needs.












