Sustainable Dairy Farming Practices: 10 Shocking Secrets
Discover how integrating renewable energy, manure management, water conservation, and leading-edge technologies can revolutionize the sustainability and resilience of dairy farming worldwide. As global demand for dairy products accelerates, adopting sustainable dairy farming practices has never been more urgent for minimizing environmental impact and ensuring the industry’s long-term success.
Table of Contents
- Summary: Why Sustainable Dairy Farming Is Vital
- Trivia: Dairy Sustainability Fact #1
- 1. Manure Management and Renewable Energy
- 2. Water Conservation Techniques Dairy Farms Use
- 3. Soil Health and Nutrient Management in Dairy
- 4. Renewable Energy in Dairy Farming
- 5. Precision Dairy Farming Technology
- 6. Sustainable Grazing Practices
- 7. Waste Reduction and the Circular Economy
- 8. Climate Change Adaptation Dairy Farms Employ
- 9. Pollinator-Friendly Dairy Practices
- 10. Community Engagement & Education
- Comparison Table: Environmental Impact of Sustainable Dairy Practices
- Trivia: Dairy Sustainability Fact #2
- Farmonaut: Making Sustainable Dairy Farming Accessible with Technology
- FAQs: Sustainable Dairy Farming Practices
- Conclusion: Creating a Sustainable Dairy Future
Summary: Why Sustainable Dairy Farming Is Vital
Sustainable dairy farming integrates practices that promote environmental stewardship, economic viability, and social responsibility. Our industry is at a crossroads: with rising global demand for dairy products, it is essential to adopt methods that offer long-term success while minimizing our ecological footprint. From renewable energy in dairy farming to advanced precision technology, responsible innovation is enabling both large-scale and smallholder farmers to produce safe, high-quality milk—while restoring our natural systems and communities.
“Over 50% of sustainable dairy farms now use renewable energy sources to power daily operations.”
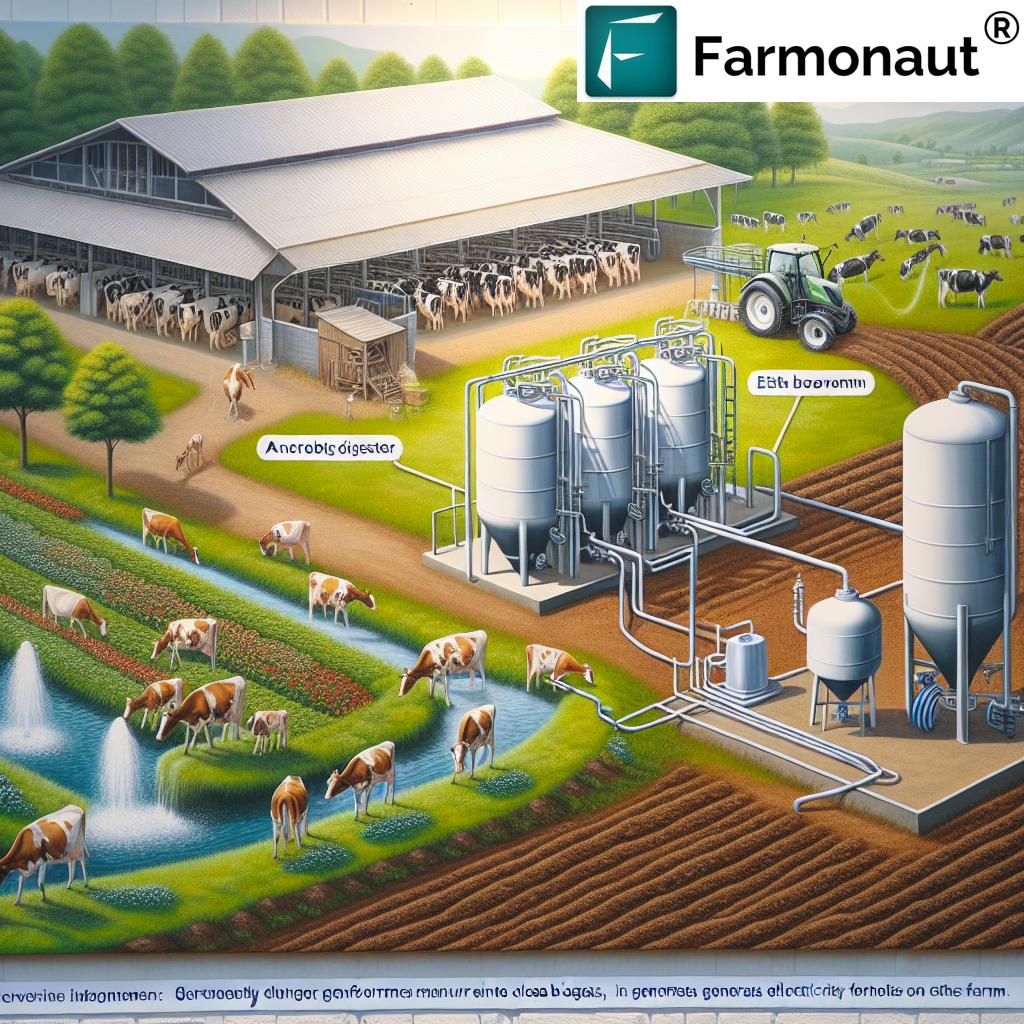
1. Manure Management and Renewable Energy: Turning Waste Into Wealth
Manure management practices are pivotal in transforming waste into valuable resources, making it a cornerstone of sustainable dairy farming. Traditionally, manure disposal posed challenges—producing both odor and methane (a potent greenhouse gas). Today, by composting manure or utilizing anaerobic digesters, we can reduce emissions and convert organic matter into multiple benefits for the environment and our operations.
- Composting: This natural technique stabilizes manure by breaking it down aerobically. The resulting solids serve as nutrient-rich fertilizer, perfect for fields and pastures. By using manure as fertilizer, we decrease dependence on chemical inputs and return nutrients to the soil, promoting soil health in dairy farming.
- Anaerobic Digesters: These enclosed systems break down manure in an oxygen-free environment, producing biogas. Biogas can be used for electricity, heat, or as a natural replacement for pipeline-quality gas. The process also yields nutrient-rich solids for use as fertilizer or bedding, further closing the resource loop.
By adopting these methods, we not only contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions dairy operations can produce, but we also tap into additional revenue streams and decrease operational costs.
Example: Farms in both North America and Europe have shown that effective manure management can cut GHG emissions by up to 30%, while providing energy to power facilities.
Discover more about environmental stewardship through advanced farm management solutions and precision agriculture tools on the Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting page.
2. Water Conservation Techniques Dairy Farms Use
Water is essential, not just for animal hydration, but for feed crop irrigation and facility cleaning. Traditional water-intensive practices are unsustainable as freshwater supplies dwindle. Through water conservation techniques, such as drip irrigation, recycling, and multiple use cycles, we can significantly reduce water consumption while optimizing farm performance.
- Drip Irrigation: By delivering water directly to plant roots, we minimize waste and evaporative loss—saving thousands of liters per year.
- Water Reuse: After milk cooling, water can be reused for drinking by cows or for cleaning machinery and stalls. Rainwater harvesting also supplements non-potable needs, further decreasing consumption.
- Recycling Systems: Closed-loop cleaning systems recycle greywater for non-hygienic purposes, conserving more freshwater for critical uses.
It’s estimated that precision water management could save up to 40% of annual water use in sustainable dairy farming operations. To adopt data-driven water management strategies, harness solutions like those described on the Farmonaut Large-Scale Farm Management resource hub.
3. Soil Health in Dairy Farming: Building a Fertile Foundation
Maintaining robust soil health is fundamental to sustainable dairy farming. Practices like planting cover crops (e.g., rye), no-till methods, and nutrient cycling via manure management not only protect soil from erosion, but also enhance fertility and support carbon sequestration.
- Cover Crops: Species like rye and clover decompose to release nutrients, boosting soil organic matter and fertility.
- Manure as Fertilizer: Applying manure safely replaces chemical fertilizers, minimizing synthetic runoff and maximizing natural nutrient cycling.
- Soil Monitoring: Platforms like Farmonaut offer real-time satellite-based crop health monitoring (NDVI), helping us track soil moisture and nutrient status for more responsive practices.
Implementing these approaches results in healthier soils, high-yield feed crops, and a more resilient ecosystem—all critical for the economic viability of dairy operations. Want to monitor soil health remotely and precisely? Try Farmonaut’s Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory tools.
4. Renewable Energy in Dairy Farming: Powering a Greener Future
The shift towards renewable energy in dairy farming is a game-changer for reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. Modern farms leverage solar panels, wind turbines, and biogas generators (from anaerobic digesters) to provide substantial portions of their electricity.
- Solar Panels: By installing solar arrays, dairy operations offset on-site electricity usage and reduce utility bills, often generating more power than required during peak sunlight.
- Wind Power: Where feasible, wind turbines augment on-farm energy generation, further reducing GHG emissions.
- Biogas: As described earlier, anaerobic digesters not only handle manure but also produce renewable biogas used for heating and power.
Adopting renewable energy technologies reduces costs, creates new income streams (via energy sales or credits), and dramatically improves the sustainability score of any dairy operation. To measure and understand your farm’s emissions, explore Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tools.
5. Precision Dairy Farming Technology: Optimizing Every Input
Advances in precision dairy farming technology empower us to manage resources with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency. By integrating sensors, AI, drones, and satellite monitoring, we can gather data on water use, animal health, and feed needs in real time—making our management both smart and sustainable.
- Sensors & Drones: Automated sensors track cow health, milk yield, and feed intake, helping us spot issues early and personalize care. Drones assess field conditions, mapping crop vigor for precision irrigation or fertilization.
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Farmonaut’s platform provides actionable insights into crop health (NDVI) and soil moisture by harnessing multispectral satellite imagery—optimizing decisions around irrigation, fertilizer use, and pest management.
- Automated Milking Systems: Robots allow cows to be milked at their own pace, improving their well-being and reducing labor costs.
Utilizing precision farming technologies can result in water, feed, and fertilizer reductions of up to 30%—amazing for both economic viability and environmental stewardship. Take control of your data-driven precision strategy with the Farmonaut API and API Documentation.
For large operators, Fleet Management tools by Farmonaut can optimize vehicle use and resource allocation—further supporting cost savings and sustainability.
“Precision technology can reduce water usage in dairy farming by up to 30%, promoting environmental sustainability.”
6. Sustainable Grazing Practices: Regenerating Pastures and Biodiversity
Implementing sustainable grazing practices is crucial to maintaining soil health, preventing overgrazing, and ensuring long-term ecosystem viability on our dairy farms. Rotational grazing (alternating sections to allow recovery) and proper stocking rates (keeping animal numbers in balance with pasture productivity) are foundational.
- Rotational Grazing: Dividing pastures into smaller paddocks and rotating cows allows vegetation to recover, boosting both biomass production and carbon sequestration.
- Stocking Rate Management: Too many animals stress land, while too few can underutilize resources. Balancing is key.
- Riparian Buffer Zones: Keeping livestock out of waterways with fencing preserves water quality.
These methods support both animal welfare and the environmental performance of our dairy operations, making grazing a win-win for sustainability and productivity. Precision tools like those from Farmonaut help us monitor pasture vigor, optimizing regrowth and soil cover while minimizing soil erosion.
7. Waste Reduction and the Circular Economy in Agriculture
Adopting a circular economy in agriculture—where waste is minimized and by-products are continuously repurposed—is transforming dairy’s environmental footprint. In sustainable dairy farming, we close nutrient and energy loops while gaining economic and social benefits.
- Turning Dairy Waste Into Fertilizer: Nutrient-rich by-products from digesters and separated manure solids become valuable fertilizers, boosting soil health and decreasing landfill use.
- Biogas for Heat and Power: Digesters transform farm by-products into energy, reducing reliance on the grid and on-site fuel costs.
- Resource Recycling: Water and organic matter are reused across multiple systems, lowering operational costs and environmental impact.
This waste reduction approach creates new revenue streams for farms, decreases operating expenses, and results in environmentally sustainable dairy farming systems.
Learn more about optimizing every resource and input through the Farmonaut Large-Scale Farm Management app.
8. Climate Change Adaptation Dairy Farms Employ
With climate change intensifying extreme weather, droughts, and disease risks, dairy farmers must proactively incorporate climate change adaptation strategies. Sustainable dairy farming is about resilience as much as productivity.
- Drought-Resistant Crops: Planting hybrids and varieties needing less water shields us from erratic rainfall and severe droughts.
- Climate-Controlled Facilities: Modern barns with advanced ventilation and insulation help cows thrive even during heatwaves or cold snaps.
- Diversified Income Streams: On-farm energy, agritourism, and direct-to-consumer models cushion volatility in dairy prices and weather-driven losses.
Precision monitoring tools such as Farmonaut’s real-time satellite imagery alert us to crop health or weather anomalies, empowering informed and timely responses to climate threats.
Need reliable weather data and risk management for your farm’s financing? Explore Crop Loan and Insurance solutions backed by satellite verification.
9. Pollinator-Friendly Dairy Practices: Safeguarding Nature’s Workforce
Pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, are integral to our ecosystem and directly support crop productivity. Sustainable dairy farming increasingly integrates pollinator-friendly practices to replenish biodiversity and bolster food security.
- Planting Native Flowers and Buffer Strips: By establishing wildflower borders and hedgerows, we provide foraging grounds and shelter, increasing pollinator activity.
- Maintaining Natural Habitats: Preserving wooded patches, wetlands, and uncultivated spaces sustains diverse insect populations essential for pollination.
- Reducing Chemical Use: Limiting pesticides and herbicides protects beneficial insects.
These actions enhance biodiversity and resilience, directly aligning with our environmental and social responsibility objectives. Discover how you can map and protect such biodiversity features with platforms like Farmonaut.
10. Community Engagement and Education: Growing Trust & Responsibility
Effective community engagement and education are vital for the credibility and social acceptance of sustainable dairy farming. Connecting with neighbors, consumers, and local organizations helps us:
- Share Sustainability Initiatives: Transparently reporting on waste reduction, renewable energy adoption, and other environmental efforts.
- Host Farm Tours & Open Houses: Demonstrating our sustainable practices firsthand builds public trust and appreciation for agriculture’s role in environmental stewardship.
- Provide Educational Resources: Empowering schools and civic groups to learn about nutrient cycling, soil conservation, and water management.
- Promote Responsible Consumption: Helping consumers understand the impact of their choices and the benefits of supporting sustainable dairy.
Social responsibility and community integration are the heart of resilient, thriving dairy sectors globally.
For traceable, transparent supply chains—from farm to consumer—see how blockchain solutions are shaping the industry on Farmonaut’s Product Traceability page.
Comparison Table of Sustainable Dairy Farming Practices and Their Estimated Environmental Impact
| Practice Name | Brief Description | Estimated Annual Water Savings (liters) | Estimated GHG Emission Reduction (%) | Estimated Cost Savings (%) | Sustainability Score (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manure Management (Anaerobic Digesters) | Converts manure to biogas and fertilizer, reducing methane. | 50,000–80,000 | 25–35 | 15–25 | 9 |
| Water Conservation Techniques | Drip irrigation, reuse, and recycling systems. | 40,000–70,000 | 8–12 | 12–18 | 8 |
| Soil Health & Nutrient Management | Cover crops, manure, composting. | 10,000–25,000 | 6–9 | 10–15 | 8 |
| Renewable Energy Adoption | Solar panels, wind, and biogas production. | 8,000–16,000 | 18–40 | 15–30 | 9 |
| Precision Dairy Farming Technology | Sensors, satellite monitoring, and data-driven decisions. | 25,000–50,000 | 11–25 | 20–30 | 10 |
| Sustainable Grazing | Rotational systems, proper stocking. | 10,000–22,000 | 10–17 | 6–13 | 7 |
| Circular Economy & Waste Reduction | Recycling nutrients, energy, and materials. | 5,000–12,000 | 10–25 | 10–18 | 8 |
Farmonaut: Making Sustainable Dairy Farming Accessible with Technology
True sustainability requires real-time data, precision tools, and a comprehensive approach to resource management. Farmonaut is leading the transformation by combining satellite imagery, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and machine learning to deliver actionable insights for dairy and crop farmers globally.
- Crop Monitoring and Soil Health: Farmonaut’s NDVI-based crop health monitoring helps us maximize field productivity, detect stress, and plan targeted interventions—optimizing water, fertilizer, and pesticide use for sustainability.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: This personalizes tips and warnings for dairy and crop management, integrating weather forecasts and expert strategies—boosting economic viability and risk resilience.
-
Blockchain Traceability: By ensuring every step is recorded and verifiable, Farmonaut strengthens consumer trust while reducing fraud in dairy and agriculture value chains.
Learn more: Product Traceability -
Carbon Footprinting Tools: Quantifies and helps reduce environmental footprint, aligning with sustainability goals.
Learn more: Carbon Footprinting - Resource & Fleet Management: Efficiently allocate labor, machinery, and vehicles for minimized emissions and costs. Details: Fleet Management
- Scalable and Accessible: As a subscription-based system via web, Android, iOS, and APIs, Farmonaut allows individual farmers, large agribusinesses, and government organizations to embrace sustainable innovation.
Ready to get started with game-changing precision and sustainability insights? Try Farmonaut’s solutions with flexible plans for crops, dairy farms, and supply chains:
FAQs: Sustainable Dairy Farming Practices
What is sustainable dairy farming?
Sustainable dairy farming refers to integrating environmental stewardship, economic viability, and social responsibility into dairy operations. This means using renewable energy, smart manure management, water conservation techniques, and minimizing waste for a low-impact, high-quality dairy supply.
How does manure management reduce farm emissions?
Modern manure management practices (like composting and anaerobic digestion) capture methane and convert it into biogas for electricity or heat. This reduces atmospheric GHGs and provides a renewable energy source.
What role does technology play in sustainable dairy?
Precision dairy farming technology (sensors, drones, satellite imagery) enables informed, efficient resource management: reducing water, feed, and fuel usage; optimizing animal health; and increasing yields.
How can dairy farms conserve water?
By implementing water conservation techniques such as drip irrigation, water reuse, recycling, and rainwater harvesting, dairy farms minimize consumption and protect freshwater ecosystems.
Does adopting these practices affect dairy product quality?
Yes—sustainable practices often improve milk quality by ensuring healthy soils, well-fed cows, and a clean environment, meeting consumer and regulatory standards.
Conclusion: Creating a Sustainable Dairy Future
Sustainable dairy farming is not a passing trend but an absolute necessity for the health of our planet and the long-term viability of our industry. By adopting effective manure management, leveraging renewable energy in dairy farming, using precision dairy farming technology, conserving water, and supporting healthy soils and communities, we can produce more with less, meet global demand, and uphold our environmental and social responsibility.
As technology, data, and wisdom from successful farms continue to evolve, so too will our ability to reduce waste, implement circular practices, and adapt to climate change—preserving our cherished industry for generations to come.
Ready to lead in modern, sustainable dairy agriculture? Start today with precision, innovation, and stewardship—powering a future that’s greener, fairer, and more profitable for all.