Revolutionizing Agriculture: How Precision Farming Technologies Boost Crop Productivity and Empower Farmers

“Precision farming technologies can increase crop yields by up to 30% while reducing water usage by 20-50%, revolutionizing agricultural productivity.”
In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, we find ourselves at the cusp of a technological revolution that is transforming the way we grow food and manage our farms. As we delve into the realm of precision farming technologies and online agriculture solutions, we’re witnessing a paradigm shift in crop productivity and sustainable farming practices. This comprehensive guide will explore how these cutting-edge advancements are empowering farmers, enhancing yields, and paving the way for a more sustainable future in agriculture.
The Dawn of Precision Farming
Precision farming, also known as precision agriculture, is a modern farming management concept that uses digital techniques to monitor and optimize agricultural production processes. By leveraging technologies such as GPS, remote sensing, and IoT (Internet of Things), farmers can now make informed decisions based on real-time data about their crops, soil, and environmental conditions.
- GPS-guided equipment for accurate planting and harvesting
- Satellite and drone imaging for crop health monitoring
- IoT sensors for soil moisture and nutrient level tracking
- AI-powered crop management systems for predictive analytics
These technologies work in concert to provide farmers with unprecedented levels of control and insight into their operations. For instance, Farmonaut, a pioneering agricultural technology company, offers advanced satellite-based farm management solutions that integrate innovative technology and data-driven insights into traditional farming practices.
Enhancing Crop Productivity with Advanced Technologies
One of the primary goals of precision farming is to boost crop productivity while optimizing resource use. Let’s explore some of the key technologies that are making this possible:
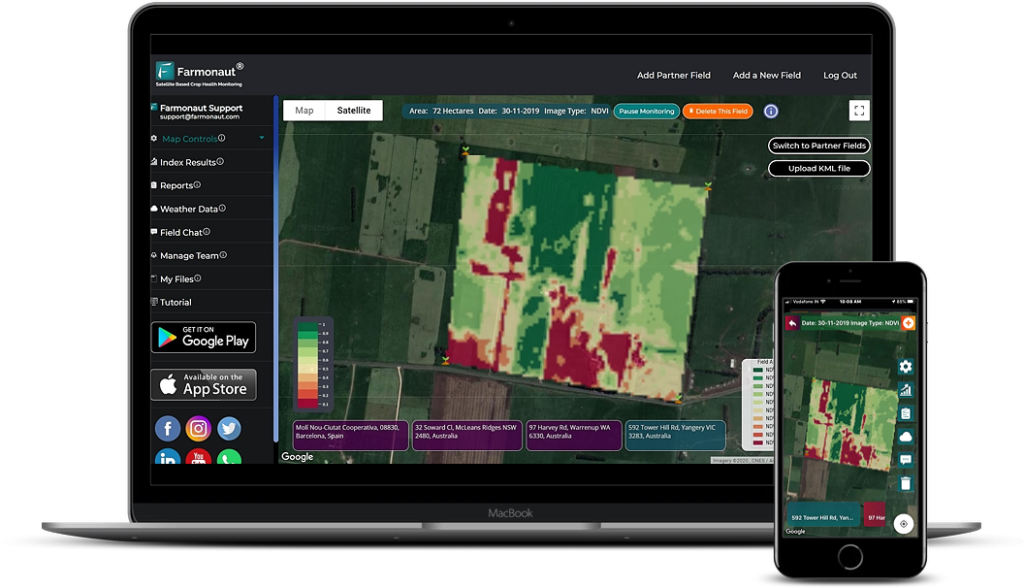
1. Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Satellite imagery has revolutionized the way we monitor crop health. Companies like Farmonaut use multispectral satellite images to provide farmers with vital insights into vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This data allows farmers to:
- Identify problem areas in fields quickly
- Make informed decisions about irrigation and fertilizer application
- Detect pest infestations and diseases early
- Optimize crop yields by addressing issues promptly
2. AI-Powered Advisory Systems
Artificial Intelligence is transforming agronomic advice, making it more personalized and accurate than ever before. Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System, for example, analyzes satellite data and other inputs to generate customized advice for farmers. This technology provides:
- Real-time insights into crop conditions
- Accurate weather forecasts for better planning
- Expert crop management strategies tailored to specific fields
- Recommendations for optimizing resource use
By leveraging AI, farmers can make data-driven decisions that lead to improved farm productivity and efficiency.
3. Precision Irrigation Systems
Water is a precious resource in agriculture, and precision irrigation systems are helping farmers use it more efficiently. These systems use a combination of soil sensors, weather data, and crop models to determine exactly when and how much water crops need. Benefits include:
- Reduced water waste
- Improved crop quality and yield
- Lower energy costs for pumping water
- Minimized risk of over-irrigation and related issues like root diseases
Drip irrigation systems, in particular, have gained popularity for their ability to deliver water directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff.
Organic Farming Solutions in the Digital Age
The precision farming revolution isn’t limited to conventional agriculture. Organic farming solutions are also benefiting from these technological advancements. Here’s how digital tools are supporting sustainable and organic practices:
1. Micronutrient Management
Precision farming technologies allow organic farmers to manage micronutrients more effectively. By using soil sensors and spectral imaging, farmers can:
- Identify specific nutrient deficiencies
- Apply organic micronutrient-rich fertilizers precisely where needed
- Monitor the effectiveness of organic amendments over time
This targeted approach ensures that crops receive the right nutrients without over-application, which is crucial for maintaining organic certification.
2. Bio-Based Pest Control
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a cornerstone of organic farming, and precision technologies are making it more effective than ever. Advanced monitoring systems help farmers:
- Detect pest populations early
- Identify beneficial insects
- Time the release of biological control agents precisely
- Apply organic pesticides like neem-based products only when necessary
These precision approaches reduce the need for broad-spectrum pesticides, preserving beneficial insects and maintaining ecological balance.
3. Crop Rotation and Intercropping Optimization
Digital tools are helping organic farmers optimize their crop rotation and intercropping strategies. By analyzing historical data, soil conditions, and market trends, farmers can:
- Plan more effective crop rotations to manage soil fertility
- Identify ideal companion plants for intercropping
- Maximize land use efficiency
- Enhance natural pest control through strategic planting
These data-driven approaches help organic farmers increase biodiversity and improve overall farm health.
“Modern seedling trays can improve germination rates by 15-25% and reduce transplant shock, enhancing overall crop success rates.”
Empowering Farmers with Cutting-Edge Agricultural Equipment
The revolution in precision farming isn’t just about digital technologies; it’s also about innovative agricultural equipment and tools that help farmers implement these advanced strategies. Let’s explore some of the equipment that’s changing the game:
1. GPS-Guided Machinery
GPS-guided tractors, sprayers, and harvesters are becoming increasingly common on modern farms. These machines offer:
- Precise navigation for reduced overlap and skips
- Automatic steering for reduced operator fatigue
- Variable rate application of seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides
- Improved fuel efficiency and reduced soil compaction
By using these advanced machines, farmers can achieve higher levels of precision in their operations, leading to improved yields and reduced input costs.
2. Smart Seeders and Transplanters
Modern seeding and transplanting equipment is designed to work in harmony with precision farming data. These machines can:
- Adjust seeding rates based on soil conditions and yield potential maps
- Plant seeds at precise depths and spacing for optimal growth
- Record planting data for future analysis and traceability
- Integrate with seedling tray systems for efficient transplanting
Smart seeders and transplanters not only improve planting precision but also contribute to better stand establishment and early crop development.
3. Advanced Spraying Systems
Precision sprayers are revolutionizing the application of crop protection products and liquid fertilizers. These systems offer:
- Variable rate application based on prescription maps
- Automatic nozzle control to maintain optimal droplet size
- Drift reduction technologies for improved target accuracy
- Integration with weather stations to ensure ideal application conditions
By using these advanced sprayers, farmers can reduce chemical use, minimize environmental impact, and improve the efficacy of their crop protection strategies.
Innovative Seed Varieties and Their Role in Precision Farming
The success of precision farming relies not only on technology but also on the quality of inputs, particularly seeds. Modern breeding techniques have led to the development of seed varieties that are specifically designed to thrive in precision farming systems. These innovative seeds offer:
- Enhanced genetic traits for improved yield potential
- Better resistance to pests and diseases
- Improved tolerance to environmental stresses
- Optimized nutrient use efficiency
When combined with precision farming techniques, these advanced seed varieties can significantly boost crop productivity and sustainability.
1. Hybrid Seeds in Precision Agriculture
Hybrid seeds play a crucial role in modern precision farming. These seeds are developed through careful cross-breeding to combine desirable traits from different parent plants. In the context of precision agriculture, hybrid seeds offer:
- Uniform growth patterns that respond well to precision management
- Improved vigor and stress tolerance
- Higher yield potential when provided with optimal conditions
- Better adaptability to specific environmental conditions
By using hybrid seeds in conjunction with precision farming technologies, farmers can maximize the genetic potential of their crops and achieve higher yields.
2. Precision Breeding for Specific Traits
Seed companies are now using advanced breeding techniques to develop varieties tailored for specific precision farming applications. These include:
- Drought-tolerant varieties that thrive with precise irrigation management
- Nutrient-efficient varieties that respond well to variable rate fertilization
- Short-stature varieties optimized for machine harvesting
- Varieties with improved spectral signatures for easier satellite monitoring
These specialized varieties allow farmers to fully leverage the capabilities of their precision farming systems, leading to more efficient and productive operations.
The Role of Data in Modern Agriculture
At the heart of precision farming lies data. The ability to collect, analyze, and act on vast amounts of agricultural data is transforming farming from an art into a data-driven science. Here’s how data is revolutionizing agriculture:
1. Big Data Analytics in Farming
Big data analytics is helping farmers make sense of the vast amounts of information generated by precision farming technologies. This includes:
- Historical yield data
- Soil test results
- Weather patterns
- Market trends
- Equipment performance metrics
By analyzing this data, farmers can identify patterns, predict outcomes, and make more informed decisions about their operations.
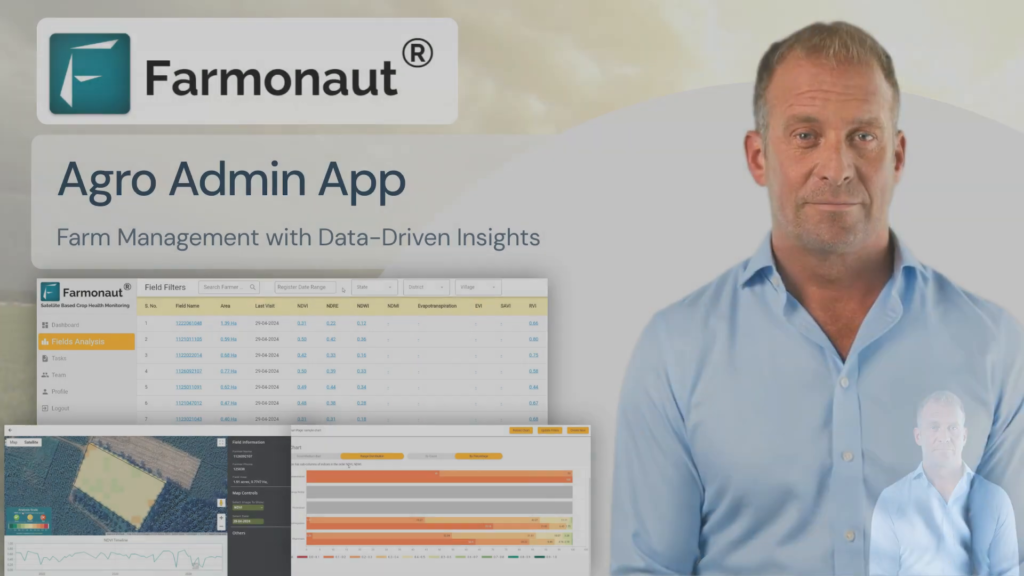
2. Farm Management Information Systems (FMIS)
FMIS platforms like Farmonaut’s web and mobile apps are essential tools for modern farmers. These systems help:
- Centralize and organize farm data
- Generate reports and visualizations for easy interpretation
- Integrate data from various sources (e.g., sensors, machinery, satellites)
- Provide decision support based on AI analysis
With a robust FMIS, farmers can streamline their operations and make data-driven decisions more efficiently.
3. Blockchain for Traceability and Transparency
Blockchain technology is adding a new dimension to agricultural data management. Farmonaut’s blockchain-based product traceability solution offers:
- Secure and transparent record-keeping
- Enhanced traceability from farm to consumer
- Improved food safety and quality assurance
- Potential for premium pricing for verified sustainable practices
By leveraging blockchain, farmers can build trust with consumers and differentiate their products in the marketplace.
Sustainable Agriculture: The Intersection of Technology and Ecology
Precision farming technologies are not just about increasing yields; they’re also crucial for promoting sustainable agriculture. Here’s how these technologies are contributing to more environmentally friendly farming practices:
1. Reduced Environmental Impact
Precision farming techniques help minimize the environmental footprint of agriculture by:
- Reducing chemical runoff through targeted application
- Minimizing soil erosion with precision tillage
- Decreasing greenhouse gas emissions through optimized machinery use
- Conserving water resources with smart irrigation
These practices not only benefit the environment but also help farmers comply with increasingly stringent regulations.
2. Carbon Footprint Tracking
Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting feature is an example of how technology is helping agribusinesses monitor and reduce their environmental impact. This tool provides:
- Real-time data on emissions from various farm activities
- Insights for implementing carbon reduction strategies
- Documentation for carbon credit programs and sustainability certifications
- Benchmarking capabilities to compare performance with industry standards
By tracking their carbon footprint, farmers can identify areas for improvement and potentially access new markets that value sustainable production methods.
3. Biodiversity Conservation
Precision farming technologies can support biodiversity conservation efforts by:
- Identifying and protecting sensitive habitats within farmland
- Optimizing the use of field margins and buffer zones
- Reducing pesticide use through targeted application
- Supporting integrated pest management strategies
By promoting biodiversity, farmers can enhance ecosystem services like pollination and natural pest control, leading to more resilient and sustainable farming systems.
The Economic Impact of Precision Farming
While the environmental benefits of precision farming are clear, it’s also important to consider the economic impact on farmers and the broader agricultural industry:
1. Improved Profitability
Precision farming technologies can significantly improve farm profitability by:
- Increasing yields through optimized crop management
- Reducing input costs with targeted resource use
- Minimizing crop losses due to pests, diseases, and weather events
- Creating opportunities for premium pricing through improved quality and traceability
These economic benefits make precision farming an attractive investment for farmers of all scales.
2. Access to New Markets
The data generated by precision farming technologies can open doors to new markets and opportunities:
- Certification for sustainable or organic production
- Participation in carbon credit markets
- Access to premium markets that demand traceability
- Opportunities for direct-to-consumer sales based on transparency
By leveraging these opportunities, farmers can diversify their income streams and build more resilient businesses.
3. Workforce Development
The adoption of precision farming technologies is creating new job opportunities and changing the skill sets required in agriculture:
- Demand for data analysts and agronomic consultants
- Need for technicians to maintain and repair advanced equipment
- Opportunities for software developers to create agricultural applications
- Training programs for farmers to effectively use new technologies
This shift is helping to attract a new generation of tech-savvy professionals to the agricultural sector.
Overcoming Challenges in Precision Farming Adoption
While the benefits of precision farming are numerous, there are still challenges to widespread adoption. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for the continued growth of precision agriculture:
1. Initial Investment Costs
The upfront costs of precision farming technologies can be a significant barrier for many farmers. To address this:
- Government subsidies and grants for technology adoption
- Leasing and financing options for equipment
- Collaborative purchasing through farmer cooperatives
- Tiered service models like those offered by Farmonaut to suit different farm sizes and budgets
By making these technologies more accessible, we can accelerate their adoption and impact.
2. Technical Skills and Training
The complexity of precision farming systems requires new skills and knowledge. To bridge this gap:
- Comprehensive training programs for farmers and farm workers
- User-friendly interfaces for technology platforms
- Ongoing support and consulting services
- Integration of precision farming concepts in agricultural education curricula
Investing in education and support will ensure that farmers can fully leverage the potential of these technologies.
3. Data Privacy and Security
As farming becomes more data-driven, concerns about data ownership, privacy, and security arise. To address these concerns:
- Clear data ownership and usage policies
- Robust cybersecurity measures for farm management systems
- Transparency in data collection and analysis processes
- Compliance with data protection regulations
Building trust in data management practices is essential for the continued growth of precision farming.
The Future of Precision Farming
As we look to the future, several emerging trends and technologies promise to further revolutionize precision farming:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning will play an increasingly important role in agriculture, offering:
- More accurate predictive models for crop yield and disease outbreaks
- Automated decision-making for routine farm operations
- Advanced image recognition for pest and disease identification
- Personalized crop management recommendations based on vast datasets
These technologies will enable farmers to make even more precise and timely decisions.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G Connectivity
The proliferation of IoT devices and the rollout of 5G networks will enhance connectivity on farms, allowing for:
- Real-time data collection and analysis from multiple sources
- Improved communication between farm equipment and management systems
- Enhanced remote monitoring and control capabilities
- Seamless integration of various precision farming technologies
This increased connectivity will create more responsive and efficient farming systems.
3. Robotics and Automation
Advancements in robotics and automation will continue to transform farm labor, with developments such as:
- Autonomous tractors and harvesters
- Robotic systems for pruning, weeding, and harvesting
- Drone swarms for crop monitoring and precise chemical application
- Automated sorting and packaging systems
These technologies will help address labor shortages and increase operational efficiency.
Conclusion: Embracing the Precision Farming Revolution
As we’ve explored throughout this article, precision farming technologies are revolutionizing agriculture, boosting crop productivity, and empowering farmers in unprecedented ways. From satellite-based crop monitoring to AI-powered advisory systems, from advanced equipment to innovative seed varieties, the tools available to modern farmers are transforming agriculture into a high-tech, data-driven industry.
Companies like Farmonaut are at the forefront of this revolution, making precision agriculture more accessible and affordable for farmers worldwide. By leveraging these technologies, farmers can not only increase their yields and profitability but also contribute to more sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural practices.
As we look to the future, the continued development and adoption of precision farming technologies will be crucial in addressing global challenges such as food security, climate change, and resource conservation. By embracing these innovations, we can create a more resilient, productive, and sustainable agricultural sector that benefits farmers, consumers, and the planet alike.
The precision farming revolution is here, and it’s transforming the way we grow food. Are you ready to be part of this exciting future?
Explore Farmonaut’s precision farming solutions:
Web App | API | API Developer Docs
Precision Farming Technologies Impact Comparison
| Technology Name | Primary Function | Estimated Crop Yield Increase (%) | Estimated Resource Savings (%) | Environmental Impact | Farmer Adoption Difficulty | Initial Investment Level | Long-term Cost Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS-guided equipment | Precise navigation and application | 10-15% | 15-20% | Medium | Moderate | High | High |
| Drone imaging | Crop health monitoring | 5-10% | 10-15% | Low | Moderate | Medium | Medium |
| IoT sensors | Real-time data collection | 8-12% | 20-30% | Low | Easy | Medium | High |
| AI-powered crop management | Decision support and optimization | 15-25% | 25-35% | Medium | Complex | High | High |
| Smart irrigation | Water use optimization | 20-30% | 30-50% | High | Moderate | Medium | High |
| Precision fertilizer application | Targeted nutrient management | 10-20% | 20-30% | High | Moderate | Medium | Medium |
Farmonaut Subscriptions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is precision farming?
A1: Precision farming is a management strategy that uses detailed, site-specific information to precisely manage production inputs. It involves the use of technologies such as GPS guidance, control systems, sensors, robotics, drones, autonomous vehicles, variable rate technology, GPS-based soil sampling, and automated hardware to achieve this precision.
Q2: How does satellite-based crop monitoring work?
A2: Satellite-based crop monitoring uses multispectral imagery from satellites to assess crop health, growth, and potential issues. It analyzes various spectral bands to create indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) that indicate crop vigor, stress, and other conditions. This information helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest management.
Q3: What are the main benefits of using precision farming technologies?
A3: The main benefits include increased crop yields, reduced input costs (such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides), improved environmental sustainability, better decision-making through data-driven insights, and enhanced farm management efficiency.
Q4: How can small-scale farmers adopt precision farming techniques?
A4: Small-scale farmers can start with affordable solutions like smartphone apps for crop monitoring, simple soil sensors, and basic GPS guidance systems. They can also utilize services like Farmonaut that offer scalable solutions suitable for smaller operations. Joining farmer cooperatives or sharing equipment can also make adoption more feasible.
Q5: What role does AI play in precision agriculture?
A5: AI in precision agriculture helps analyze vast amounts of data from various sources (satellites, sensors, weather