Revolutionizing Agriculture: How LULC Mapping and GIS Drive Sustainable Farming Practices
“LULC mapping techniques can identify up to 30 different land cover classes, enabling precise agricultural planning.”
In an era where global food demands are soaring and environmental concerns are paramount, the agricultural sector is undergoing a profound transformation. At the forefront of this revolution is the innovative use of Land Use Land Cover (LULC) mapping and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in sustainable farming practices. These cutting-edge technologies are reshaping how we approach agriculture, offering unprecedented insights into land management and resource allocation.
As we delve into this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how LULC mapping and GIS are not just buzzwords but powerful tools driving the future of agriculture. From enhancing food security to mitigating climate change impacts, these technologies are proving instrumental in creating a more sustainable and efficient farming landscape.
Understanding LULC Mapping in Agriculture
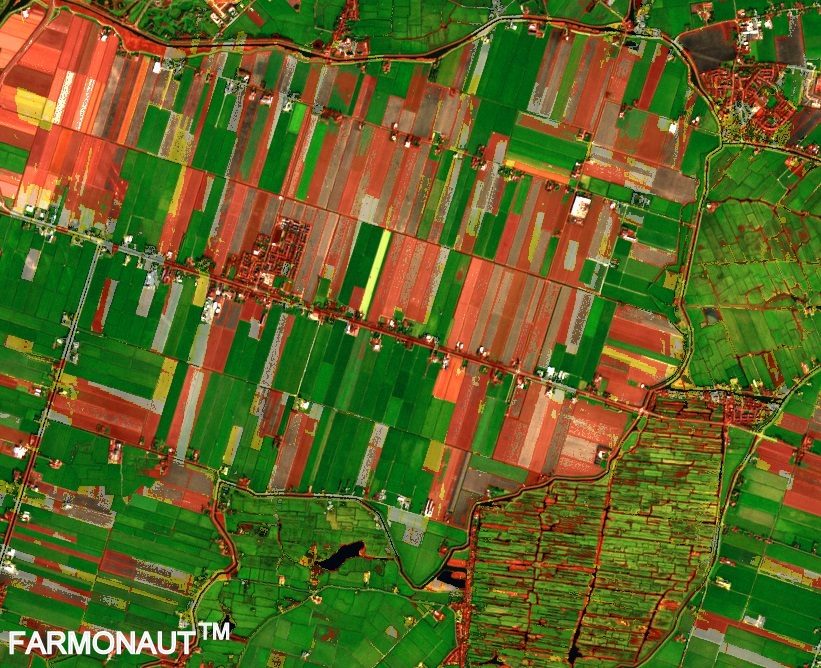
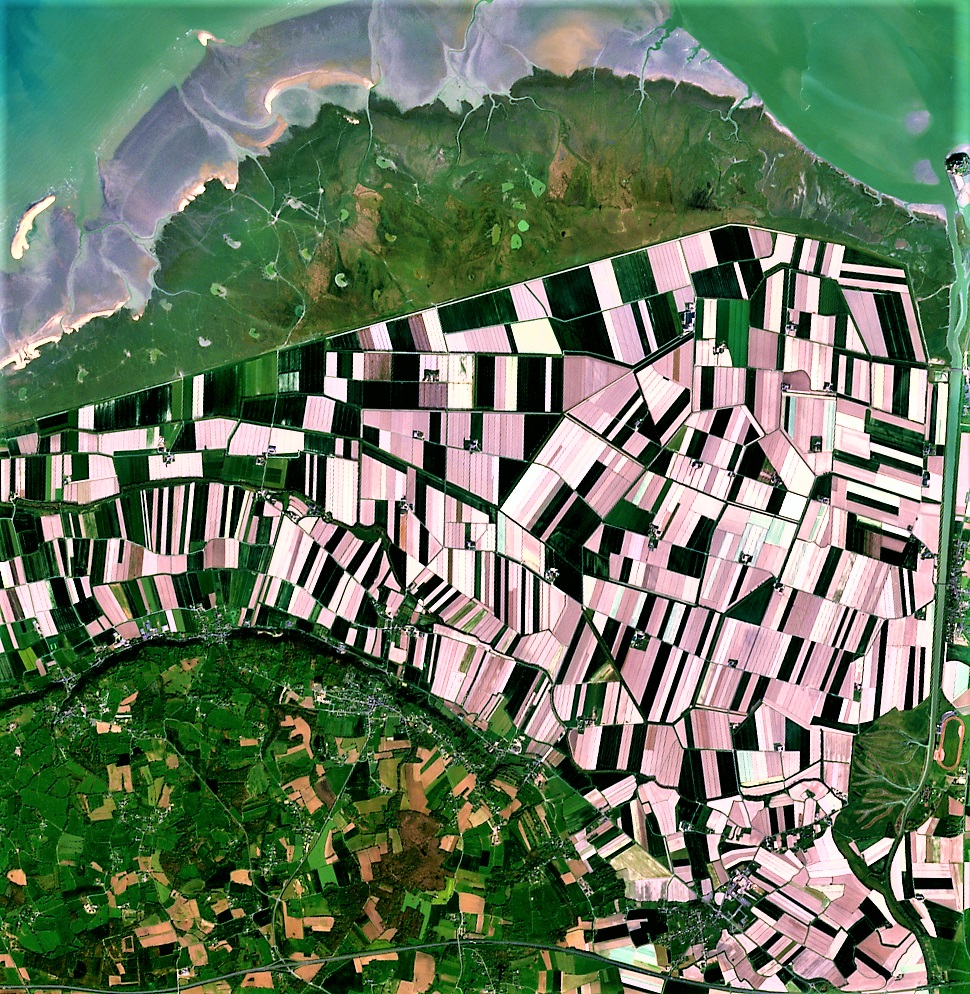
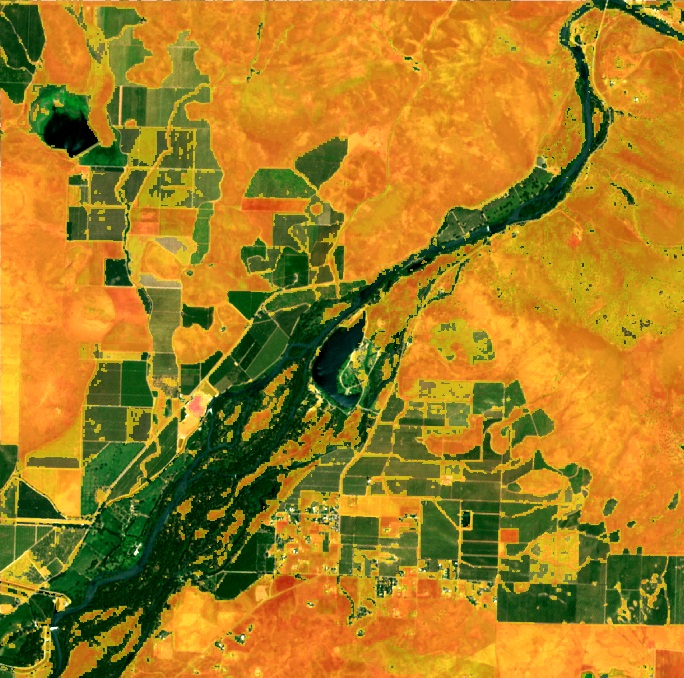
Land Use Land Cover (LULC) mapping is a sophisticated process that involves classifying and categorizing the Earth’s surface based on both its natural and man-made features. In the context of agriculture, LULC mapping provides invaluable information about:
- Cropland distribution and health
- Soil characteristics and quality
- Water resources and irrigation patterns
- Forest cover and deforestation rates
- Urban encroachment on arable land
By leveraging remote sensing technologies and satellite imagery, LULC mapping offers a bird’s-eye view of agricultural landscapes, enabling farmers and policymakers to make informed decisions about land use and resource management.
The Role of GIS in Modern Agriculture
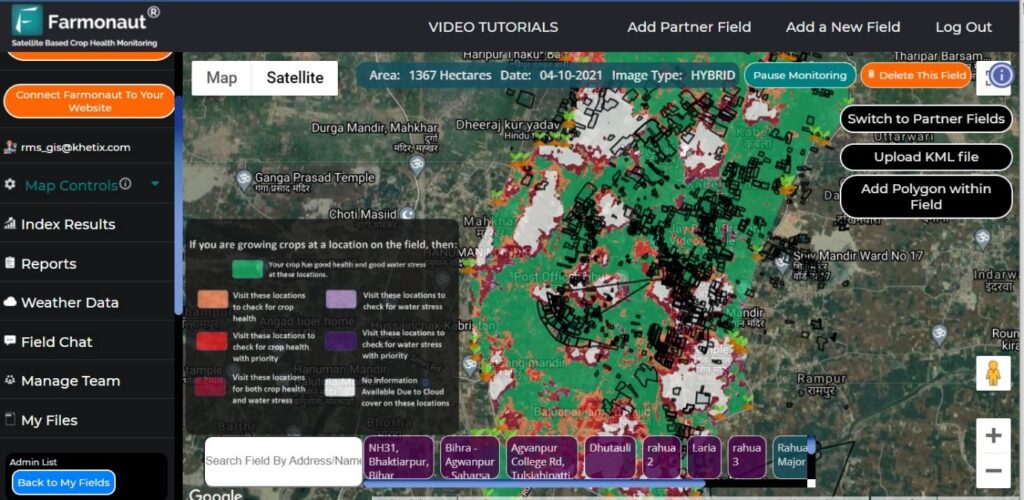
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) complement LULC mapping by providing a framework for analyzing and visualizing spatial data. In agriculture, GIS plays a crucial role in:
- Precision agriculture and site-specific crop management
- Yield mapping and forecasting
- Pest and disease monitoring
- Soil erosion prevention strategies
- Optimizing irrigation systems
By integrating LULC data with GIS tools, farmers can create detailed maps of their fields, track changes over time, and make data-driven decisions to improve crop yields while minimizing environmental impact.
LULC Classification: A Key to Sustainable Land Management
One of the fundamental aspects of LULC mapping is the classification of land into distinct categories. This process is crucial for sustainable land management in agriculture. Let’s explore how different LULC classes impact farming practices:
| LULC Class | Description | Agricultural Applications | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | Areas used for cultivation of crops | Crop rotation planning, yield optimization | Efficient use of arable land, reduced chemical inputs |
| Grassland | Natural or managed grassy areas | Pasture management, livestock grazing | Carbon sequestration, biodiversity preservation |
| Forest | Areas covered with trees and woody vegetation | Agroforestry, ecosystem services | Climate regulation, soil conservation |
| Urban | Built-up areas and infrastructure | Urban agriculture planning, land use zoning | Balancing development with agricultural needs |
| Water Bodies | Rivers, lakes, and other water features | Irrigation planning, aquaculture | Water resource management, flood control |
Understanding these classifications allows for more targeted and effective agricultural strategies, ensuring that each land type is utilized optimally while preserving its ecological function.
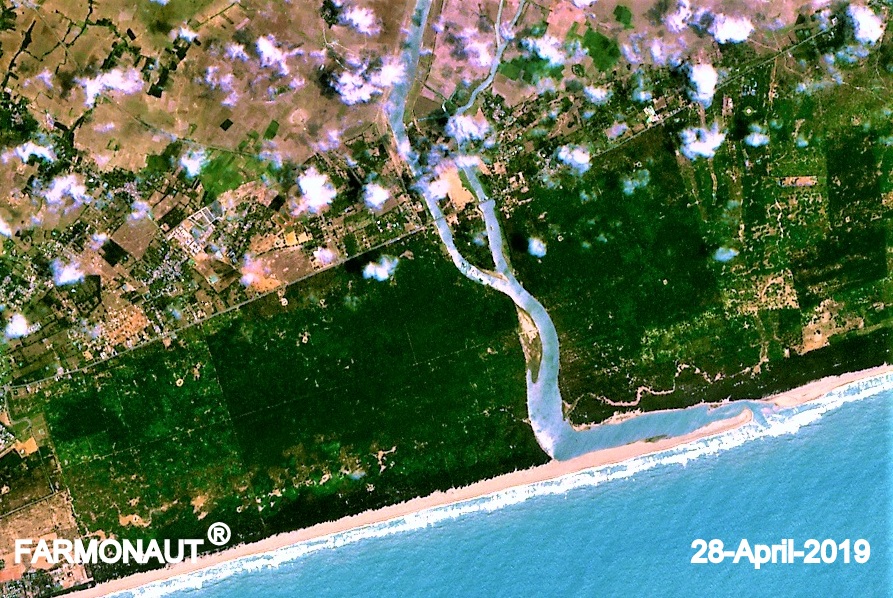
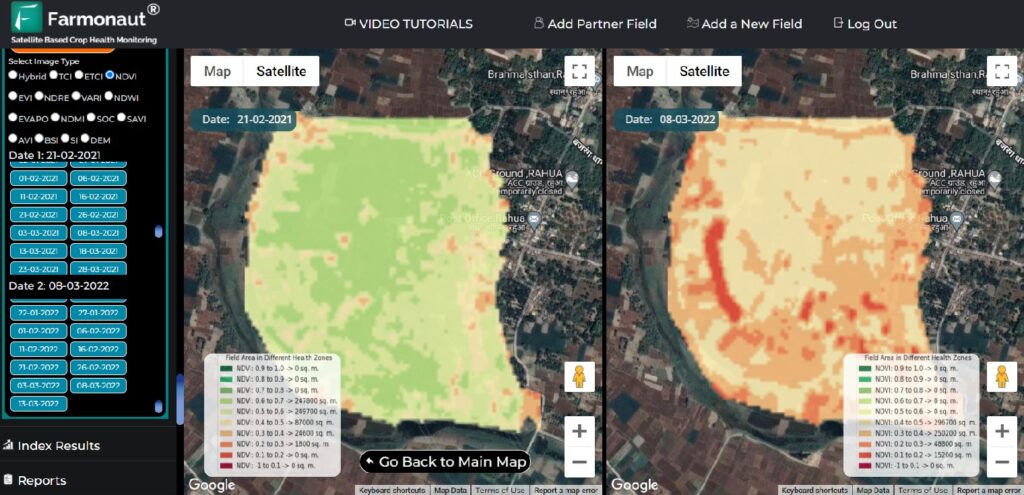
Remote Sensing: The Eye in the Sky for Crop Monitoring
Remote sensing technology has revolutionized the way we monitor and manage crops. By using satellites and other airborne sensors, we can gather crucial data about crop health, soil moisture, and even predict yields with remarkable accuracy. Here’s how remote sensing is transforming crop monitoring:
- Vegetation Indices: Metrics like the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) help assess crop health and vigor.
- Thermal Imaging: Detects water stress in crops, allowing for timely irrigation interventions.
- Multispectral Analysis: Identifies nutrient deficiencies and pest infestations before they become visible to the naked eye.
- Crop Yield Forecasting: Combines historical data with current observations to predict harvest outcomes.
These remote sensing applications enable farmers to make proactive decisions, optimize resource use, and minimize crop losses.
Precision Agriculture: Where LULC and GIS Converge
Precision agriculture represents the pinnacle of technological integration in farming. By combining LULC data with GIS analysis, farmers can implement highly targeted management practices. This approach offers numerous benefits:
- Reduced input costs through optimized resource application
- Improved crop quality and yield consistency
- Minimized environmental impact from over-application of chemicals
- Enhanced traceability in the food supply chain
Precision agriculture technologies, such as variable rate application systems and GPS-guided machinery, rely heavily on the accurate spatial data provided by LULC mapping and GIS analysis.
“Satellite-based LULC analysis can monitor changes in agricultural land use with 85% accuracy over vast areas.”
Soil Erosion Prevention: Safeguarding Our Most Precious Resource
Soil erosion is a critical issue in agriculture, threatening food security and ecosystem health. LULC mapping and GIS play a vital role in combating this problem by:
- Identifying areas at high risk of erosion
- Designing targeted conservation measures
- Monitoring the effectiveness of erosion control strategies
- Predicting future erosion patterns based on land use changes
By integrating topographical data with land cover information, we can create sophisticated models that guide sustainable land management practices and protect our soil resources for future generations.
Deforestation Monitoring: Balancing Agriculture and Conservation
As agricultural expansion continues to be a leading cause of deforestation, monitoring forest cover changes has become crucial for sustainable land management. LULC mapping and GIS provide powerful tools for:
- Detecting illegal deforestation activities
- Assessing the impact of agricultural expansion on forest ecosystems
- Planning sustainable agroforestry initiatives
- Supporting reforestation and afforestation projects
By leveraging these technologies, we can strike a balance between agricultural productivity and forest conservation, ensuring food security without compromising vital ecosystem services.
Climate Change Adaptation: LULC’s Role in Building Resilience
Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture, from shifting growing seasons to increased frequency of extreme weather events. LULC mapping and GIS are instrumental in developing adaptation strategies:
- Identifying areas vulnerable to climate impacts
- Modeling future scenarios to guide crop selection and land use planning
- Monitoring changes in vegetation patterns and water availability
- Supporting the development of climate-resilient farming systems
By providing detailed spatial information on land use trends and environmental conditions, these technologies enable farmers and policymakers to make informed decisions in the face of climate uncertainty.
Smart Farming Applications: Bringing LULC Data to the Field
The integration of LULC mapping and GIS into smart farming applications is revolutionizing on-farm decision-making. These applications offer:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- Precision irrigation management
- Automated pest and disease detection
- Yield prediction and harvest planning tools
By putting the power of LULC analysis in the hands of farmers through user-friendly apps and interfaces, we’re democratizing access to advanced agricultural technologies.
Explore Farmonaut’s innovative solutions:
The Future of LULC in Agriculture: AI and Machine Learning
As we look to the future, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning with LULC mapping promises even greater advancements in sustainable agriculture:
- Automated land cover classification with higher accuracy
- Predictive modeling for crop yields and market demands
- Real-time optimization of farming practices based on LULC data
- Enhanced detection of subtle land use changes and environmental impacts
These technologies will enable more responsive and adaptive agricultural systems, capable of meeting the challenges of food security in a changing world.
Challenges and Opportunities in LULC-Based Agriculture
While the potential of LULC mapping and GIS in agriculture is immense, there are challenges to overcome:
- Ensuring data accuracy and reliability
- Addressing privacy concerns related to high-resolution imagery
- Bridging the digital divide to make technologies accessible to all farmers
- Integrating LULC data with other agricultural information systems
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration across the agricultural sector.
Conclusion: Embracing LULC for a Sustainable Agricultural Future
As we’ve explored throughout this article, LULC mapping and GIS are not just technological innovations; they’re essential tools for building a sustainable and resilient agricultural system. By providing unprecedented insights into land use patterns, crop health, and environmental impacts, these technologies empower farmers, researchers, and policymakers to make informed decisions that balance productivity with conservation.
The future of agriculture lies in our ability to harness these tools effectively, creating farming practices that are not only productive but also environmentally sustainable and socially responsible. As we continue to face global challenges such as climate change, population growth, and resource scarcity, the role of LULC mapping and GIS in shaping our agricultural landscape will only grow in importance.
We invite you to explore how these technologies can transform your approach to farming and land management. Whether you’re a small-scale farmer, a large agricultural enterprise, or a policymaker, embracing LULC-based solutions can help you contribute to a more sustainable and food-secure world.
FAQs
- What is LULC mapping, and how does it benefit agriculture?
LULC mapping is the process of classifying land based on its use and cover. In agriculture, it helps in understanding crop distribution, soil quality, and resource allocation, leading to more efficient and sustainable farming practices. - How does GIS contribute to sustainable farming?
GIS allows for the analysis and visualization of spatial data, enabling precision agriculture, yield forecasting, and targeted resource management, all of which contribute to more sustainable farming practices. - What role does remote sensing play in LULC mapping for agriculture?
Remote sensing provides high-resolution imagery and data on crop health, soil moisture, and land use changes, allowing for accurate and up-to-date LULC mapping without the need for extensive ground surveys. - How can LULC mapping help in preventing soil erosion?
By identifying areas at risk of erosion and monitoring land use changes, LULC mapping helps in designing targeted conservation measures and assessing their effectiveness over time. - What are the challenges in implementing LULC-based agricultural practices?
Challenges include ensuring data accuracy, addressing privacy concerns, making the technology accessible to all farmers, and integrating LULC data with existing agricultural systems.
Explore Farmonaut’s API and developer documentation: