5 Top Biological Innovations Boost Soybean Yields in Brazil
Discover how breakthroughs in biological soil treatments revolutionize soybean production in Brazil,
naturally increasing crop yield and reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers.
“Brazilian farmers using biological soil treatments saw soybean yields increase by up to 20% in recent studies.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Growth of Brazilian Agriculture
- Context: Hungria and the Boom in Soybean Production in Brazil
- 5 Top Biological Innovations Boosting Soybean Yields in Brazil
- Comparison Table: Key Biological Innovations and Impact
- Accelerating Sustainable Farming Solutions: The Farmonaut Approach
- Adopting Biological Products for Farming: Benefits & Insights
- Challenges and Future Directions for Biological Soil Treatments
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Introduction: The Rapid Growth of Brazilian Agriculture and Soybean Production
Brazil has long been recognized as a world leader in agricultural innovation, standing out as the top producer and exporter of soybeans. The growth of Brazilian agriculture over the last four decades is nothing less than spectacular; especially notable is soybean production in Brazil, which skyrocketed from 15 million metric tons in the 1980s to over 170 million tons today. This incredible transformation was made possible by a combination of visionary research, cutting-edge technology, and a steadfast commitment to sustainable farming solutions.
At the heart of this green revolution are biological soil treatments—innovations that harness naturally occurring bacteria and microbes to enrich soil nutrients and promote healthy crop growth. These biological products for farming have not only increased crop yield naturally but also helped Brazilian farmers reduce their reliance on commercial chemical fertilizers, decrease production costs, and meet the rising demand from environmentally-conscious consumers for food produced with fewer chemicals.
In this post, we take a closer look at the top five biological innovations driving this revolution, with a particular focus on contributions by renowned Brazilian microbiologist Mariangela Hungria, recipient of the 2025 World Food Prize. We’ll explore how new soil treatments are transforming not only Brazil, but also the global landscape for sustainable soybean agriculture.
Context: Hungria’s Work and the Boom in Soybean Production in Brazil
In 2025, the World Food Prize was awarded to Dr. Mariangela Hungria, a Brazilian microbiologist whose research transformed both the scale and sustainability of soybean production in Brazil. Her pioneering work at Embrapa, Brazil’s leading state-run agricultural center, focused on improving how plants acquire nutrients—particularly through the isolated use of soil bacteria and biological treatments.
Traditionally, soybeans need large inputs of nitrogen to grow robustly. Importing nitrogen-based chemical fertilizers was expensive and left the country heavily dependent on global suppliers. Recognizing this challenge, Hungria isolated potent rhizobia strains, enabling inoculation of soybean seeds with beneficial bacteria that fix nitrogen directly from the atmosphere. The results were revolutionary for Brazilian farmers—a solution both widespread and highly effective, now applied on more than 40 million hectares of Brazilian soybean plantations.
Let us now explore how these innovations—alongside others—are reshaping the landscape for producer nations, exporters, and consumers alike, fulfilling demand for high-yield, low-chemical-sourced food commodities.
5 Top Biological Innovations Boosting Soybean Yields in Brazil
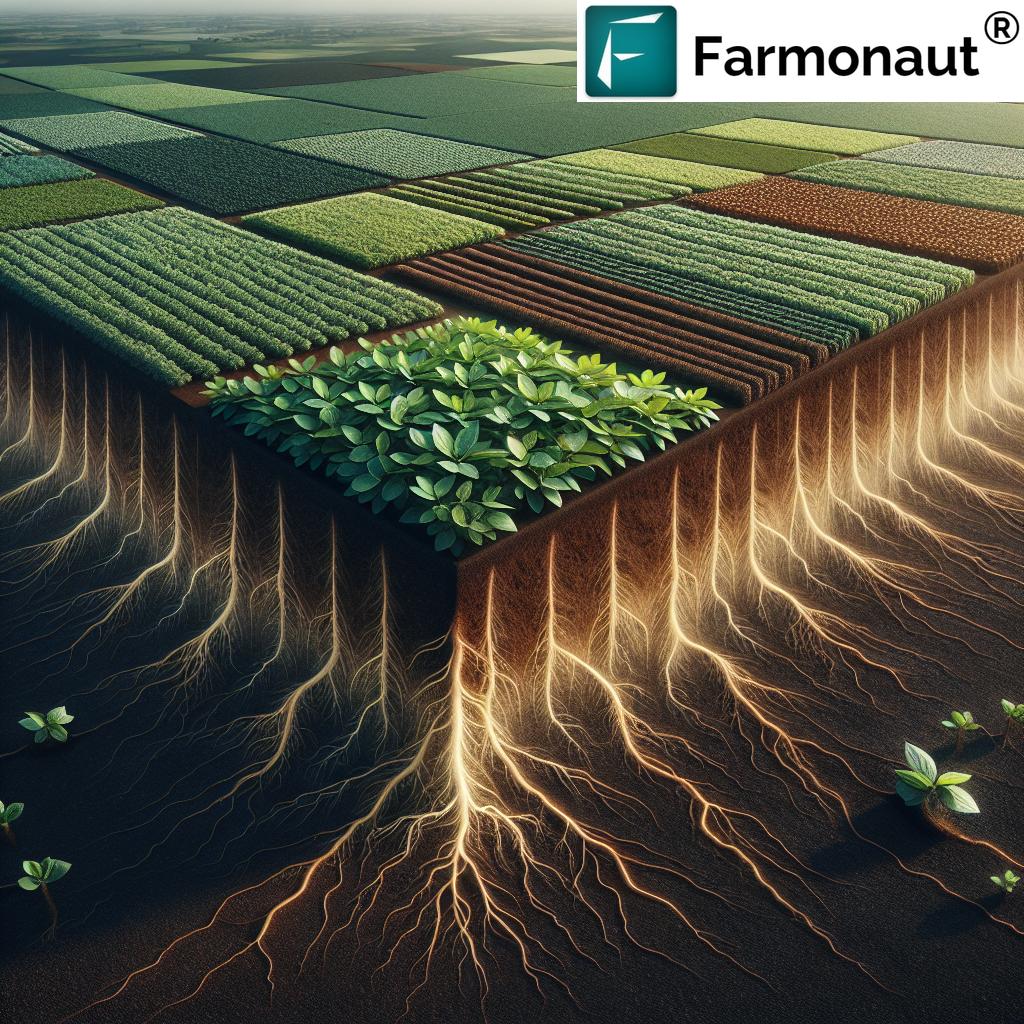
1. Rhizobium Inoculants for Nitrogen Fixation in Agriculture
One of the most transformative innovations in Brazilian soybean production is the use of rhizobia bacteria inoculants. Rhizobia are soil bacteria that enter into a symbiotic relationship with soybean root nodules, enabling the plant to fix atmospheric nitrogen—a process vital for healthy, robust plant growth. By inoculating soybean seeds with these isolated strains before planting, Brazilian farmers have greatly enhanced the natural fertility of their fields.
- Nitrogen fixation in agriculture: This approach reduces or eliminates the need for imported synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, thereby decreasing costs and dependency on foreign sources.
- Increased yield: Fields using rhizobia inoculants have observed yield improvements of up to 20% compared to non-inoculated plots.
- Widespread solution: Today, this practice is used across more than 40 million hectares of Brazilian soybean plantations.
This innovation is attributed directly to Dr. Hungria’s research at Embrapa, highlighting the profound, lasting impact scientific discovery has on commercial agriculture.
2. Azospirillum brasilense: Boosting Root Systems for Larger Yields
The next breakthrough leverages another native bacteria—Azospirillum brasilense. While rhizobia primarily assist with nitrogen, Azospirillum offers a suite of benefits to both soybeans and other crops like corn:
- Bigger roots: Azospirillum brasilense stimulates the development of larger and deeper root systems, enabling plants to access water and nutrients even during periods of low soil humidity.
- Resilience: Crops inoculated with Azospirillum demonstrate enhanced drought resistance, essential for production in Brazil’s Cerrado and other challenging climates.
- Legume synergy: When used in combination with rhizobia, these strains create a synergistic effect that further improves plant growth and overall production.
Such innovations, when implemented en masse, contribute significant yield gains and support the sustainable intensification of agriculture across the country.
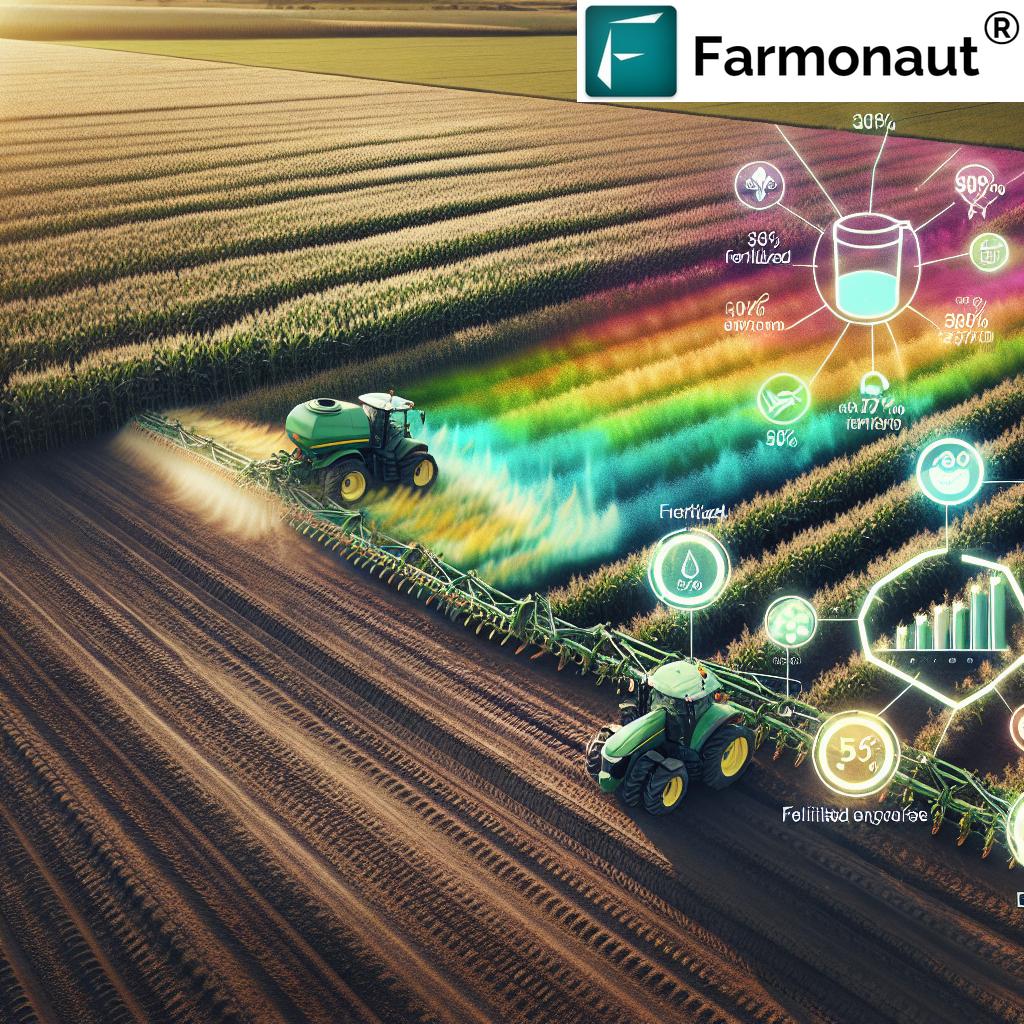
“Biological innovations have reduced chemical fertilizer use in Brazilian soybean fields by approximately 30% since 2020.”
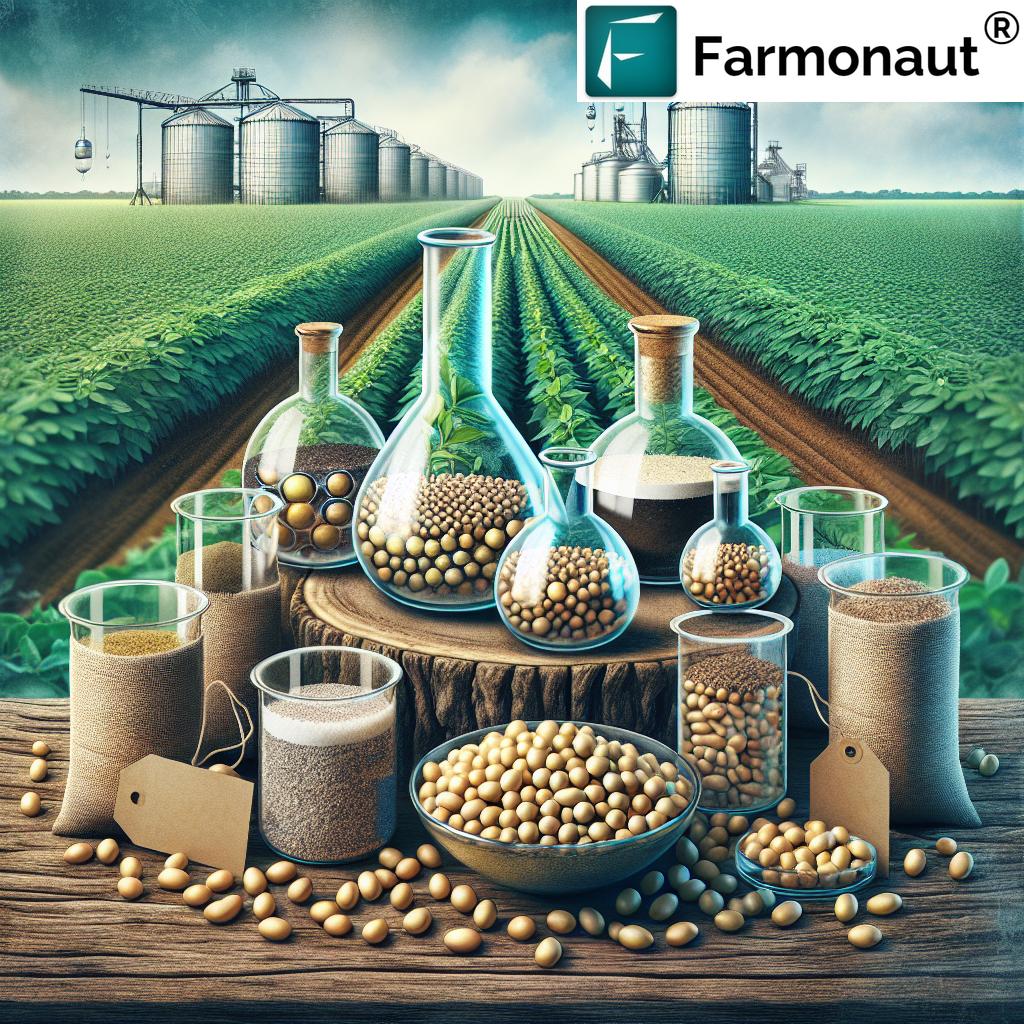
3. Microbial Consortia: Synergistic Soil Health Builders
Another remarkable stride has been made with the development and application of microbial consortia—blends of multiple bacteria and fungi specifically designed to improve soil health and plant growth. These innovative products deliver broad benefits:
- Enhanced nutrient uptake: Multispecies blends catalyze critical nutrient cycles, making phosphorus, potassium, and trace elements more available.
- Greater biological resilience: Diverse strains provide robust defense against a wider range of soil-borne diseases and pests.
- Sustainable yield increase: Trials in Brazil have shown yield boosts of 8-15% using these biological soil treatments.
Microbial consortia serve as potent sustainable farming solutions and mark the industry’s future, as more producers in Brazil and worldwide shift to biological products for farming.
4. Biostimulants and Biofertilizers: Natural Plant Growth Promoters
Brazil is at the forefront in the use of biostimulants and biofertilizers as alternatives to traditional chemical fertilizers. These natural compounds and living organisms work in a variety of complementary ways:
- Stimulating root and shoot growth: By naturally enhancing metabolic processes, plants grow larger and more resilient.
- Improved stress tolerance: Plants treated with biostimulants can withstand environmental stressors such as drought and nutrient-poor soils.
- Reduced chemical fertilizer usage: Some regions have reported up to 30% reductions in synthetic fertilizer dependency thanks to biostimulant applications.
- Boosted yields: Field results show average yield increase of 6-12%.
As consumers increasingly demand food produced with fewer chemicals, these sustainable tools are becoming vital for the future of Brazilian agriculture.
5. Biological Control of Soil-Borne Diseases
Managing diseases without heavy chemical interventions is a cornerstone of sustainable soybean production in Brazil. Biocontrol agents—beneficial microorganisms that suppress harmful pathogens—represent the fifth top innovation:
- Reduced crop loss: Antagonistic bacteria and fungi (like Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma species) outcompete or neutralize disease-causing organisms, protecting root systems and plant health.
- Sustained yields: Consistent biological suppression can keep losses under 7%, a critical figure as more land is cultivated for soy and other commodities.
- Chemical reduction: By relying on biological treatments, farmers have been able to decrease their overall fungicide and pesticide applications, leading to improved soil health and ecosystem balance.
- Meets international food standards: Significant for exporter nations like Brazil, helping growers comply with global food safety standards.
Using biological disease management solutions thus plays a central part in both safeguarding crops and supporting higher yields per hectare.
Comparison Table: Key Biological Innovations and Impact
| Biological Innovation | Mechanism of Action | Estimated Yield Increase (%) | Reduction in Chemical Fertilizer Use (%) | Year of Adoption in Brazil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhizobium Inoculants | Forms symbiosis with soy roots to fix atmospheric nitrogen | 12-20% | Up to 90% (nitrogen fertilization) | 1980s |
| Azospirillum brasilense | Enhances root development for better nutrient and water uptake | 6-11% | 15-25% | 2007 |
| Microbial Consortia | Optimizes nutrient cycling and soil resilience using multiple strains | 8-15% | 15-30% | 2012 |
| Biostimulants/Biofertilizers | Enhances plant metabolism and natural defenses | 6-12% | Up to 30% | 2017 |
| Biological Disease Suppression | Controls pathogens via beneficial microbes | Reduce losses by up to 7% | 10-15% (pesticide reduction) | 2015 |
For plantations and agribusinesses managing large hectares, Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management Tools let you track field health, inputs, and yield history across dozens to thousands of parcels with satellite imagery and advanced analytics. This empowers managers to rapidly detect and respond to variability, reducing risk and maximizing returns.
Integrate satellite crop and weather data directly into your systems with Farmonaut’s API. For developers, see the API Developer Docs for implementation resources and full endpoints.
Strengthen food safety and export compliance: Farmonaut’s Blockchain Product Traceability
provides transparent end-to-end records of a crop’s journey,
helping both producers and exporters meet global standards while enhancing consumer trust.
Accelerating Sustainable Farming Solutions in Brazil: The Farmonaut Approach
Harnessing the full power of biological soil treatments requires precision, monitoring, and data-driven decision-making. This is where Farmonaut, a global agricultural technology pioneer, plays a vital role in the ecosystem.
- Satellite-based Crop Monitoring: By delivering real-time health data on vegetation (such as NDVI), soil moisture, and nutrient status, Farmonaut enables farmers to evaluate the effectiveness of biological treatments across expansive hectares.
- AI-driven Advisory Systems: Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI system provides custom recommendations on crop management, irrigation, and input use. This means growers can increase crop yield naturally and sustainably, leveraging each innovation to its maximum effect.
- Blockchain Traceability: Transparent food supply chains ensure exporter of soybeans can demonstrate compliance with strict international market requirements—a crucial advantage as the world market becomes more competitive.
- Carbon Footprinting: With heightened consumer and regulatory demand for low-carbon, sustainable agriculture, Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tools allow Brazilian farmers and agribusinesses to monitor emissions and reduce their environmental impact when using advanced biological products for farming.
- Scalable Solutions Via Apps and API: Whether a single farmer or a multi-thousand hectare agribusiness, Farmonaut’s platform delivers actionable insights directly to smartphones, web browsers, or integrated APIs.
As one of the most robust, affordable, and accessible systems supporting sustainable innovation, Farmonaut stands out in helping producers adopt and optimize these biological breakthroughs.
Adopting Biological Products for Farming: Benefits, Insights, and Steps Forward
- Environmental benefits: Reduced reliance on imported chemical fertilizers and pesticides directly improves soil, water, and ecosystem health in Brazil’s major agricultural zones.
- Economic gains: Lower input costs, more stable yields, and increased capacity to tackle global market demands for “green” commodities mean sustained profitability for farmers.
- Social and regulatory compliance: Growing consumer and government pressure to increase crop yield naturally, reduce agrochemical residues, and achieve traceable, verifiable food safety is driving broad adoption of these solutions.
- How do we start? Transitioning to biological soil treatments involves training, selecting appropriate inoculants for specific crops and soil types, and periodic monitoring—with digital decision-support platforms like Farmonaut providing unparalleled operational efficiency.
Taken together, these innovations and tools ensure that Brazil continues to grow as a world agricultural powerhouse, setting higher standards for sustainable productivity and responsible stewardship.
Access advanced monitoring for Crop-Loan and Insurance Verification—ensuring smooth claims and financing based on field-verified satellite imagery.
Challenges and Future Directions for Biological Soil Treatments in Brazil
While the impressive gains in soybean production in Brazil stand as testament to the success of these new biological approaches, some hurdles must continually be addressed:
- Quality control: Ensuring mass-produced bio-inoculants remain viable and effective across Brazil’s diverse climates requires robust infrastructure and training.
- Education and outreach: Ongoing engagement with farmers on new strains, techniques, and application timing maximizes results—digital advisory systems are proving especially useful.
- Soil biodiversity: Preserving underlying native microbial diversity is critical for achieving multiple years of improved yields and resilience.
- Metrics and data: Regular field-level monitoring, with support from satellite and AI-based platforms, underpins verification, benchmarking, and continuous improvement.
Looking ahead, the intersection of biological solutions, data-driven technology, and large-scale adoption will define the future of not just Brazilian agricultural development, but also global approaches to food security and sustainable intensification.
For efficient field logistics and machine deployment, explore Farmonaut’s Fleet Management Solutions—minimize downtimes and costly delays by tracking the status and movement of agricultural equipment in real-time.
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
Farmonaut operates on a flexible subscription basis—choose the right plan for satellite monitoring, fleet management, carbon footprinting, and more, scaling from individual fields to national projects:
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What defines “biological soil treatments” in modern Brazilian soybean production?
Biological soil treatments refer to the use of naturally occurring (or specially cultivated) microorganisms such as rhizobia, Azospirillum, and diverse microbial consortia to enhance nutrient cycles, facilitate nitrogen fixation in agriculture, and suppress soil-borne diseases. These are applied as seed coatings, liquid treatments, or granular products at planting.
-
How do these treatments increase yields and decrease fertilizer dependency?
By enhancing the plant’s ability to extract and utilize nitrogen and other nutrients directly from the soil and air, these biological agents replace or supplement expensive, imported chemical fertilizers. The enhanced root growth and plant vigor also translate to higher yields per hectare.
-
Are these solutions only useful in Brazil?
No. While Brazil has led their development and adoption, similar biological products for farming are now in use in soybean, corn, and other commodity crops worldwide. Their application helps producers in diverse climates and soils meet rising demand for “chemical-light” crops and comply with international standards.
-
How can technology platforms like Farmonaut support biological treatments?
By providing continuous satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisories, traceability, and resource management tools, Farmonaut empowers farmers and large agribusinesses to track the specific results of these biological programs, optimize applications, and document sustainability for regulatory or export purposes.
-
Where do I find more resources on integrating biological and digital innovations?
Refer to Farmonaut’s Mobile App for detailed crop management and satellite health data, or review the API documentation for integration into large-scale farm management systems.
Need advice for forest, crop, and plantation management? Tap “Advisory” in the mobile app or start at Farmonaut Crop, Plantation & Forest Advisory for site-specific insights!
Conclusion: Brazil Leads the World in Sustainable Soybean Innovation
The extraordinary story of soybean production in Brazil reflects the power of scientific research, innovation, and the determination of a nation’s farmers. Breakthroughs in biological soil treatments by leaders like Hungria have transformed not only Brazilian farming but have become the new global standard for sustainable agricultural practice.
By reducing chemical fertilizers, building resilient, high-yield crops, and tapping digital tools such as Farmonaut’s monitoring and traceability platforms, Brazil sets an example for balancing productivity with stewardship. As consumers and regulators alike call for transparency, reduced chemical use, and higher standards in food production, the lessons and tools pioneered in Brazil are more relevant than ever across the world.
Farmers, agribusinesses, and policymakers: let’s continue to champion these biological innovations, leverage the best of emerging technology, and secure a thriving, sustainable food future for all.