Revolutionizing Brazil’s Coffee Farms: Precision Agriculture and Sustainable Practices for Climate-Resilient Production
“Brazil’s coffee farms have reduced water usage by up to 30% through precision agriculture and smart irrigation systems.”
In the heart of Brazil’s Cerrado region, a revolution is brewing – not just in coffee cups, but across vast plantations that have long been the lifeblood of the country’s agricultural economy. As we delve into the transformative world of sustainable coffee farming, we find ourselves at the forefront of an exciting era where precision agriculture technologies and climate-resilient production methods are reshaping the landscape of Brazil’s coffee industry.
The Dawn of a New Era in Coffee Farming
Brazil, the world’s largest coffee producer, is facing unprecedented challenges due to climate change, evolving consumer preferences, and the need for more sustainable practices. However, these challenges have sparked innovation and adaptation, leading to a coffee farming revolution that promises to secure the future of this vital industry.
At Farmonaut, we’re excited to be part of this transformation. Our cutting-edge solutions support coffee farmers in their journey towards more sustainable and efficient production methods. By integrating digital platforms and big data analytics, we’re helping optimize resource management and reduce carbon footprints across Brazil’s coffee farms.

Precision Agriculture: The Game-Changer for Coffee Farms
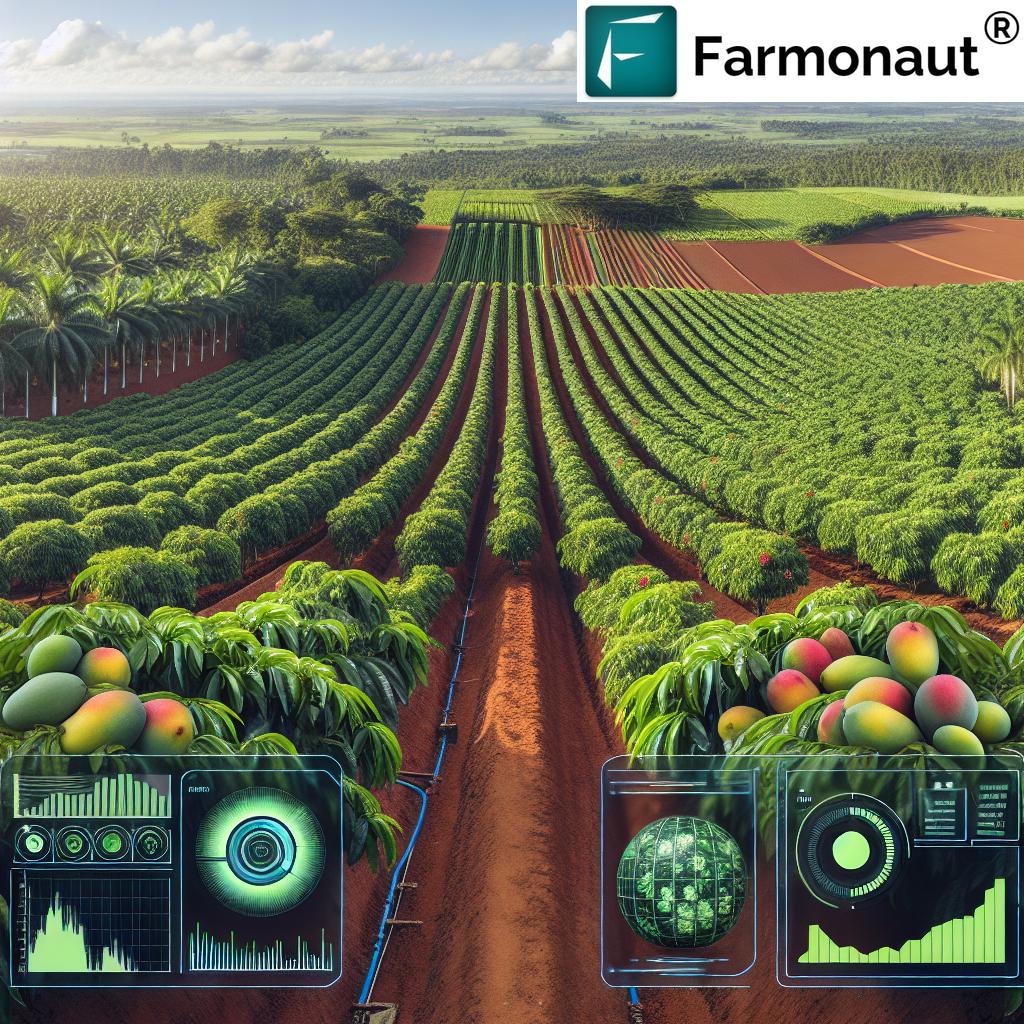
Precision agriculture is at the heart of this revolution. By leveraging advanced technologies, coffee farmers can now make data-driven decisions that were once based on intuition and experience alone. Let’s explore how these innovations are transforming coffee production:
- Drone Monitoring: Unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with multispectral cameras provide real-time insights into crop health, enabling early detection of issues like pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies.
- Soil Sensors: Advanced sensors analyze soil health, moisture levels, and nutrient content, allowing for precise irrigation and fertilization strategies.
- Smart Irrigation Systems: AI-powered irrigation systems optimize water usage, reducing waste and ensuring crops receive exactly what they need, when they need it.
- Big Data Analytics: By collecting and analyzing vast amounts of data, farmers can identify patterns and make predictive decisions to improve yields and quality.
These technologies are not just improving efficiency; they’re fundamentally changing how coffee is grown in Brazil. By adopting precision agriculture, farmers are seeing significant improvements in crop yields, quality, and sustainability.
Climate-Resilient Coffee Production: Adapting to a Changing World
As climate change continues to pose significant challenges to coffee production, developing climate-resilient practices has become crucial. Here’s how Brazilian coffee farms are adapting:
- Drought-Resistant Varieties: Research into developing coffee plant varieties that can withstand higher temperatures and reduced rainfall is ongoing.
- Agroforestry Systems: Integrating trees and shrubs into coffee plantations helps create microclimates that protect coffee plants from extreme weather events.
- Water Conservation: Implementing rainwater harvesting systems and efficient irrigation methods to combat water scarcity.
- Soil Management: Adopting practices like cover cropping and minimal tillage to improve soil health and water retention.
These climate-resilient strategies are not just about survival; they’re about thriving in the face of environmental challenges. By embracing these practices, Brazilian coffee farms are setting a global standard for sustainable production.
Regenerative Coffee Growing Practices: Nurturing the Land
Regenerative agriculture goes beyond sustainability; it aims to improve the land’s health while producing crops. In Brazil’s coffee sector, this approach is gaining traction:
- Soil Health Restoration: Using organic matter and cover crops to enhance soil structure and biodiversity.
- Carbon Sequestration: Implementing practices that capture carbon in the soil, reducing the farm’s overall carbon footprint.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Creating habitats for beneficial insects and wildlife, promoting a balanced ecosystem on the farm.
- Minimal Chemical Use: Relying on natural pest control methods and organic fertilizers to reduce chemical inputs.
These regenerative practices not only benefit the environment but also result in healthier, more resilient coffee plants that produce higher quality beans. It’s a win-win for farmers and consumers alike.
“Sustainable coffee production methods can decrease carbon footprints by up to 25% compared to traditional farming practices.”
Smart Irrigation Systems: Precision Water Management
Water scarcity is a growing concern in many coffee-producing regions of Brazil. Smart irrigation systems are proving to be a game-changer in addressing this challenge:
- Soil Moisture Sensors: These devices provide real-time data on soil moisture levels, enabling precise irrigation scheduling.
- Weather-Based Irrigation Controllers: By integrating local weather data, these systems adjust irrigation based on rainfall and evapotranspiration rates.
- Drip Irrigation: This method delivers water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
- AI-Powered Optimization: Machine learning algorithms analyze historical data and current conditions to predict water needs with high accuracy.
At Farmonaut, we’re proud to offer solutions that support these smart irrigation systems. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring and AI advisory system help farmers make informed decisions about water management, contributing to significant water savings across Brazil’s coffee farms.
Digital Platforms in Agriculture: Connecting the Coffee Value Chain
Digital platforms are revolutionizing how coffee farms operate and connect with the global market:
- Farm Management Software: These platforms help farmers track everything from planting schedules to harvest yields, streamlining operations.
- Supply Chain Traceability: Blockchain-based systems ensure transparency from farm to cup, meeting consumer demands for ethical sourcing.
- Market Access: Digital marketplaces connect farmers directly with buyers, potentially increasing profits and reducing intermediaries.
- Knowledge Sharing: Online forums and educational resources allow farmers to exchange best practices and stay updated on industry trends.
These digital tools are empowering Brazilian coffee farmers to make data-driven decisions and connect with a global market that values sustainability and quality.

Big Data Analytics for Coffee Farms: Harnessing the Power of Information
Big data analytics is transforming coffee farming from an art into a science. Here’s how:
- Yield Prediction: By analyzing historical data and current conditions, farmers can accurately forecast their harvest volumes.
- Quality Optimization: Data on factors like soil composition, weather patterns, and processing methods help produce consistently high-quality beans.
- Resource Allocation: Analytics guide decisions on where to allocate resources for maximum efficiency and profitability.
- Risk Management: Predictive models help farmers prepare for potential challenges like pest outbreaks or adverse weather events.
Farmonaut’s platform leverages big data analytics to provide actionable insights to coffee farmers. Our API and API Developer Docs enable seamless integration of these powerful analytics tools into existing farm management systems.
Traceable Coffee Supply Chain: From Farm to Cup
Traceability has become a key concern for coffee consumers worldwide. Brazilian coffee farms are responding to this demand by implementing comprehensive traceability systems:
- Blockchain Technology: Immutable ledgers record every step of the coffee’s journey, ensuring transparency and authenticity.
- QR Codes: Consumers can scan codes on packaging to access detailed information about the coffee’s origin and production methods.
- IoT Sensors: These devices track environmental conditions during transportation, ensuring quality is maintained from farm to roaster.
- Digital Certifications: Online platforms verify and display various sustainability and quality certifications.
By embracing these traceability measures, Brazilian coffee farms are not only meeting consumer demands but also differentiating themselves in a competitive global market.
Carbon Footprint Reduction in Agriculture: A Sustainable Approach
Reducing the carbon footprint of coffee production is a priority for Brazil’s forward-thinking farms. Here’s how they’re achieving this:
- Energy-Efficient Processing: Implementing solar-powered drying systems and energy-efficient pulping machines.
- Waste Management: Converting coffee pulp and other organic waste into compost or biofuel.
- Reforestation: Planting trees on degraded land to offset carbon emissions and improve biodiversity.
- Transportation Optimization: Using route planning software to reduce fuel consumption during coffee transport.
These efforts not only reduce environmental impact but also often lead to cost savings and improved farm efficiency.
Autonomous Farming Vehicles: The Future of Coffee Cultivation
While still in the early stages of adoption, autonomous farming vehicles are poised to revolutionize coffee production in Brazil:
- Robotic Harvesters: These machines can selectively pick ripe coffee cherries, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
- Autonomous Tractors: Self-driving tractors can perform tasks like planting and fertilizing with high precision.
- Drone Sprayers: Unmanned aerial vehicles can apply fertilizers or pest control products with minimal environmental impact.
- Automated Irrigation Systems: Self-adjusting sprinklers optimize water usage based on real-time soil and weather data.
As these technologies mature, they promise to address labor shortages and further improve the sustainability and efficiency of Brazil’s coffee farms.
Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs. Precision Agriculture Methods
To better understand the impact of these technological advancements, let’s compare traditional coffee farming methods with precision agriculture approaches:
| Farming Aspect | Traditional Method | Precision Agriculture Method |
|---|---|---|
| Irrigation | Scheduled watering based on general observations | Smart irrigation systems using soil moisture sensors and weather data |
| Pest Management | Blanket application of pesticides | Targeted pest control using drone surveillance and AI-powered diagnostics |
| Soil Health Monitoring | Annual soil testing | Real-time soil analysis using IoT sensors |
| Yield Prediction | Estimates based on historical data and visual inspection | AI-powered yield forecasting using satellite imagery and big data analytics |
| Resource Efficiency | Generalized approach leading to potential overuse | Optimized resource use with up to 30% reduction in water and fertilizer consumption |
| Carbon Footprint | Higher due to inefficiencies | Up to 25% reduction through precision techniques and sustainable practices |
This comparison clearly illustrates the significant advantages that precision agriculture brings to coffee farming in Brazil, particularly in terms of resource efficiency and environmental impact.
The Circular Economy in Coffee Production
The concept of a circular economy is gaining traction in Brazil’s coffee sector, focusing on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency:
- Coffee Husk Utilization: Using coffee husks as biomass fuel or as a component in construction materials.
- Wastewater Treatment: Implementing systems to purify and reuse water from coffee processing.
- Biodegradable Packaging: Developing packaging materials from coffee by-products.
- Spent Coffee Grounds: Using grounds as organic fertilizer or in the production of biofuels.
These circular economy principles not only reduce waste but also create new value streams for coffee farmers, enhancing the overall sustainability and profitability of their operations.
The Role of Education and Training
As Brazil’s coffee farms embrace these new technologies and practices, education and training become crucial:
- Digital Literacy Programs: Helping farmers become proficient in using digital tools and platforms.
- Sustainable Farming Workshops: Offering hands-on training in regenerative and climate-resilient practices.
- Technology Adoption Support: Providing guidance on implementing and maximizing the benefits of precision agriculture tools.
- Continuous Learning Platforms: Developing online resources for ongoing education and knowledge sharing among farmers.
By investing in education, Brazil is ensuring that its coffee farmers are well-equipped to lead the global transition to more sustainable and technologically advanced coffee production methods.
The Future of Brazilian Coffee: A Sustainable Vision
As we look to the future, the trajectory of Brazil’s coffee industry is clear. By embracing precision agriculture, sustainable practices, and innovative technologies, Brazilian coffee farms are positioning themselves at the forefront of a global movement towards more responsible and efficient food production.
The integration of digital platforms, big data analytics, and AI-driven decision-making tools, such as those offered by Farmonaut, will continue to play a crucial role in this transformation. These technologies not only enhance productivity and sustainability but also empower farmers to adapt to the challenges posed by climate change and evolving market demands.
As consumers increasingly seek out sustainably sourced, high-quality coffee, Brazil’s commitment to innovation and sustainability will likely strengthen its position as a leader in the global coffee market. The revolution in Brazilian coffee farms is not just about preserving an industry; it’s about reimagining it for a more sustainable and prosperous future.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How is precision agriculture improving coffee farming in Brazil?
Precision agriculture is enhancing coffee farming through technologies like drone monitoring, soil sensors, and smart irrigation systems, leading to improved crop yields, better resource management, and reduced environmental impact. - What are some climate-resilient practices being adopted by Brazilian coffee farms?
Climate-resilient practices include developing drought-resistant coffee varieties, implementing agroforestry systems, improving water conservation methods, and adopting advanced soil management techniques. - How are digital platforms transforming the coffee supply chain in Brazil?
Digital platforms are enhancing traceability, improving farm management, facilitating direct market access, and enabling knowledge sharing among coffee farmers and stakeholders across the supply chain. - What role does big data analytics play in modern coffee farming?
Big data analytics helps in yield prediction, quality optimization, resource allocation, and risk management, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions for more efficient and profitable operations. - How are Brazilian coffee farms reducing their carbon footprint?
Farms are reducing their carbon footprint through energy-efficient processing, waste management, reforestation efforts, and optimized transportation methods, often resulting in cost savings and improved efficiency.