Best Practices for Lemon Tree Planting in Florida: The Ultimate Guide to Soil, Watering, Pruning, Pests & Healthy Yields
- Introduction
- Site Selection
- Soil Preparation: Best Soil for Lemon Trees
- Planting Techniques
- Spacing for Lemon Orchards
- Lemon Tree Watering Schedule
- Fertilizing Lemon Trees
- Pruning Lemon Trees
- Pest Management in Lemon Orchards
- Mulching for Citrus Trees
- Growing Lemon Trees in Cold Climates
- Lemon Tree Planting & Care Schedule Table
- How Farmonaut Supports Lemon Tree Growers
- FAQ: Lemon Trees in Florida
- Conclusion: Achieving Success in Florida Lemon Orchards
Introduction
Florida’s abundant sunshine, rich soils, and favorable climate make it an ideal backdrop for planting lemon trees. Whether you’re an experienced grower or a passionate beginner, the prospect of cultivating a thriving lemon orchard is both enticing and rewarding. However, establishing healthy lemon trees with high fruit yields requires careful attention to several critical factors: site selection, soil preparation, planting techniques, watering schedules, pruning methods, pest management, and ongoing lemon tree care.
This comprehensive guide is specifically crafted for Florida growers seeking expert lemon tree care tips and the latest best practices. Throughout, we’ll incorporate tried-and-tested strategies for the region, practical step-by-step instructions, and important seasonal actions based on the latest research (University of Florida IFAS Extension).
Let’s explore how to maximize your lemon orchard’s productivity and success.
Site Selection: Choosing the Perfect Location for Lemon Trees in Florida
The cornerstone of successful lemon tree planting is selecting the right site. The correct location not only determines the tree’s long-term growth and fruit production but also minimizes exposure to pest and disease problems. Let’s break down what makes an optimal planting site:
Key Factors for Lemon Tree Site Selection
- Full Sunlight Exposure: Lemon trees require at least 6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily for healthy foliage, strong root development, and abundant fruiting.
- Air Circulation: Choose a spot away from dense trees, buildings, or power lines to ensure good air circulation. Proper airflow helps prevent fungal plant disease and reduces pest infestations—a best practice in lemon tree care.
- Well-Drained Soils: Avoid low-lying and poorly-drained spots that can accumulate water during the heavy Florida rains. Persistent wetness can cause root rot, one of the leading causes of tree failure.
- Protection from Cold Winds: Lemon trees are highly sensitive to frost. In Florida, select an area protected from chilling north winds or plant on the south/southeast sides of windbreaks or buildings (but always adhere to spacing recommendations for full sun).
- Distance from Structures: Maintain at least 15 to 25 feet distance from houses, fences, and sheds to prevent shading and allow for future canopy expansion.
Florida Tip: As per UF IFAS guidelines, never plant lemon trees where they’ll shade each other or be shaded by large structures, as this leads to weak growth and poor fruit yields.
Soil Preparation: Best Soil for Lemon Trees
Proper soil preparation is fundamental for nurturing healthy roots and supporting vigorous tree growth and fruit production. The key is to create fertile, well-draining, slightly acidic soils tailored to the needs of lemon trees in Florida’s diverse environments.
Soil Testing & Modification
- Soil pH: Optimal range is 5.5 to 6.5 (UF IFAS), ensuring high nutrient availability and healthy growth.
- Testing: Conduct a comprehensive soil test before planting to assess pH and nutrient levels. Your results will determine whether you need to amend the soil (e.g., adding sulfur to lower pH or lime to raise pH).
Amending the Soil for Lemon Trees
- Sandy Soils: Common in Florida, sand drains quickly but can lack nutrients and organic matter. Remove a 3- to 10-foot diameter ring of grass sod before planting, and dig the hole 3x the depth and 3–4x the width of the root container.
- Soil Mix: Blend topsoil or compost with the excavated soil (never pure compost—aim for a 50/50 ratio). This mixture fosters strong root establishment while avoiding waterlogging.
- Avoid Heavy or Clay Soils: If clay is present, amend with sand and organic matter, or consider constructing raised beds to improve water drainage and air penetration.
Key Practice: Always check for the right soil moisture before planting: soil should be moist but not waterlogged.
Steps for Soil Preparation in Florida
- Remove sod and grass in a circular area around the intended planting spot.
- Dig a large, deep hole as described above for proper root expansion.
- Assess soil structure and drainage: Fill the hole with water and observe drainage. If water pools for 12+ hours, further amendments or raised beds are needed.
- Incorporate organic materials (compost, well-rotted manure) with native soils for improved fertility and structure.
- Avoid chemical fertilizers at planting: these can burn new roots. Focus on organic amendments first.
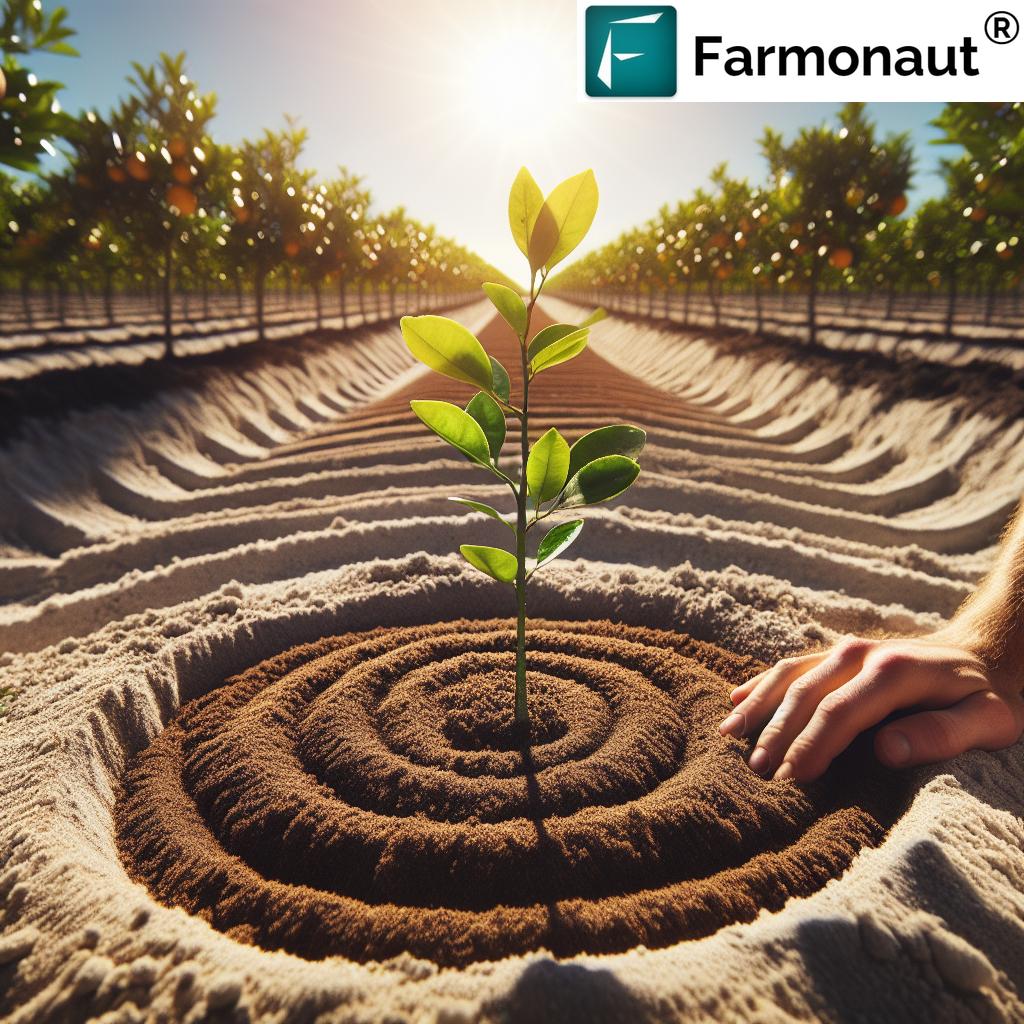
Planting Techniques: How to Plant Lemon Trees for Healthy Growth
Timing, technique, and initial setup determine your lemon tree’s ability to thrive in the unique climate of Florida. Let’s explore the best planting techniques to ensure a robust start for your orchard.
Best Time to Plant Lemon Trees
- Spring or Early Summer: Ideal for planting as temperatures are consistently warm and the tree has a full growing season to establish roots.
- Winter Planting: Avoid unless you can fully protect trees from frost or cold snaps.
How to Plant Lemon Trees Step-By-Step
- Dig the Hole: Make it twice as wide and as deep as the root ball for optimal root expansion.
- Position the Tree: Place the tree in the center so the top of the root ball is level with or slightly above ground. This keeps the trunk base protected from rot.
- Backfill Carefully: Refill the hole with your amended soil blend, gently tamping down to remove air pockets. Water halfway through backfilling to settle the soil.
- Water Thoroughly: After planting, water deeply to ensure full contact of soil with roots.
-
Mulch and Stake:
- Apply mulch, keeping it several inches from the trunk.
- Staking is optional—use cotton or natural fiber ties to avoid trunk injury.
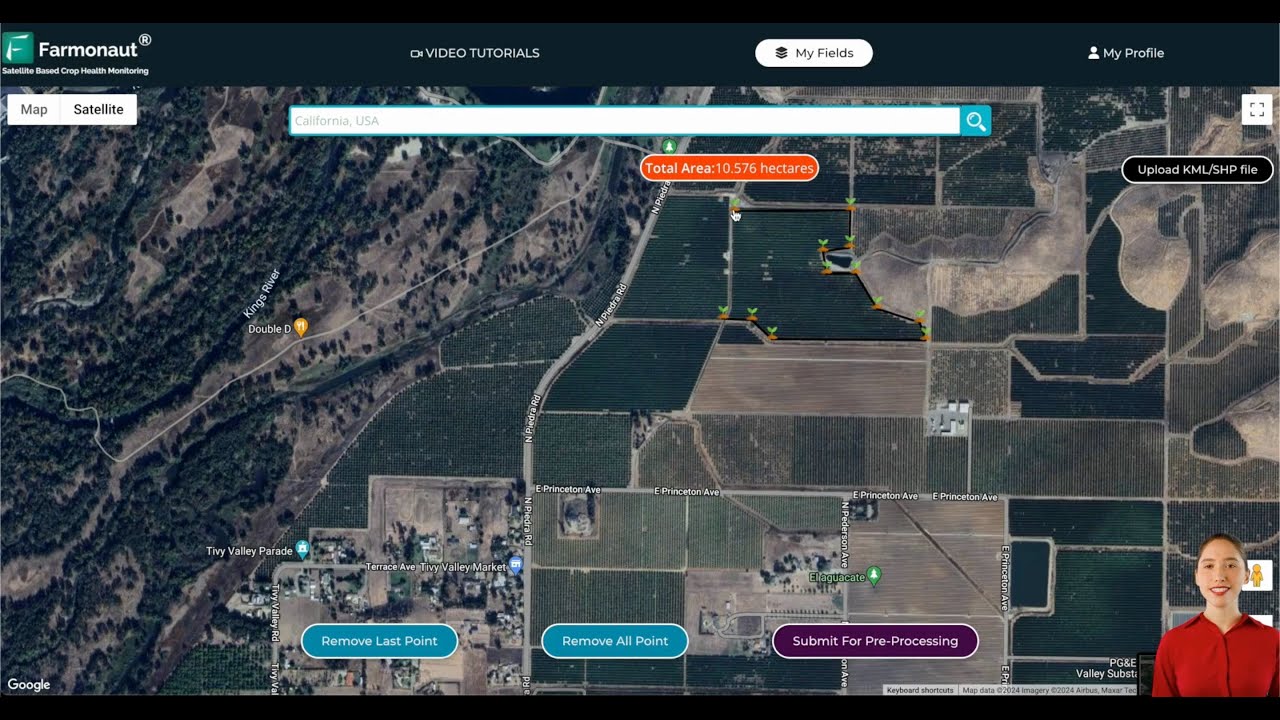
Farmonaut Tip: After planting, leverage satellite-based monitoring to assess real-time moisture levels and soil condition (read more about Farmonaut’s API for developers).
Spacing for Lemon Orchards: Maximizing Air Circulation and Fruit Production
Correct spacing is more important than many realize. It’s essential not only for light and air circulation but also for disease prevention and maximizing fruit yields.
How Far Apart to Plant Lemon Trees?
- Follow a 15 to 25 foot spacing between trees, depending on the variety and anticipated mature canopy size.
- Always measure from trunk to trunk for accuracy.
- Rows should also be at least 15 feet apart for equipment and maintenance access.
- Maintain spacing from fences, buildings, and power lines to avoid root competition and shading.
This spacing for lemon orchards encourages disease-free growth, easy access for pruning and harvesting, and optimal exposure to full sunlight.
Lemon Tree Watering Schedule: Ensuring Consistent Moisture for Healthy Growth
Consistent soil moisture is critical for strong root systems, leafy growth, and fruit set. However, overwatering can be just as harmful as drought, leading to root rot, fungal diseases, and even fruit drop.
Watering Best Practices
- Spring & Summer: Water deeply every 7 days (about 1–2 inches of water at root zone per session).
- Fall & Winter: Shift to every 10–14 days as trees slow down and rainfall may increase.
- Soil Check: Feel the soil; it should be moist up to 6 inches deep but never soggy.
- Avoid Overhead Watering: Always irrigate at the base to minimize the risk of leaf and fruit diseases (like fungal blights).
Pro Tip: Using mulching for citrus trees helps regulate moisture and minimizes water loss.
For larger orchards or commercial growers, precision irrigation management is essential. Our large-scale farm management platform can help you monitor soil moisture efficiently with real-time satellite data, ensuring optimized lemon tree watering schedules.
Fertilizing Lemon Trees: Best Nutrient Practices for Fruit Production
Lemon trees are among the most nutrient-hungry citrus crops. Regular and balanced fertilization ensures lush foliage, robust growth, and heavy fruit yields.
Fertilization Guidelines
- Balanced Citrus Fertilizer: Choose a mix high in nitrogen—the most important element for lemon trees. Use products labeled specifically for citrus.
- Spring Initiation: Apply your first dose as new growth emerges in spring.
- Regular Feeding: Continue fertilizing every 4–6 weeks through the growing season (spring through summer).
- Reduce in Fall/Winter: Scale back frequency and quantity as trees approach dormancy.
- Avoid Over-Fertilization: Always follow package directions—too much can “burn” roots and reduce yields.
Typical application methods include granular broadcast around the drip line, gentle raking in, and deep watering to activate the nutrients.
Farmonaut Feature: For high-value or organic systems, use carbon footprinting technologies to analyze fertilizer usage sustainability and environmental impact.
Pruning Lemon Trees for Health and High Yields
Pruning is essential for controlling shape, increasing air circulation, removing disease and dead wood, and ultimately boosting fruit production.
How and When to Prune Lemon Trees
- Initial Years (1–5): Focus only on removing suckers below the graft and eliminating upward-growing “water sprouts.”
- Mature Trees: Annually remove dead, diseased, or crossing branches. Thin the canopy just enough to allow light and air to penetrate.
- Timing: Best time is late winter or very early spring, just before new growth begins.
- Techniques: Use open-center or espalier methods for maximizing space in limited areas. Always use sharp, sterilized pruning shears.
Tip: Dispose of diseased branches far away from your orchard to prevent the spread of pests and pathogens.
For more advanced management, our plantation and forest advisory tools provide tailored AI-based pruning alerts by monitoring crop health and canopy structure from space!
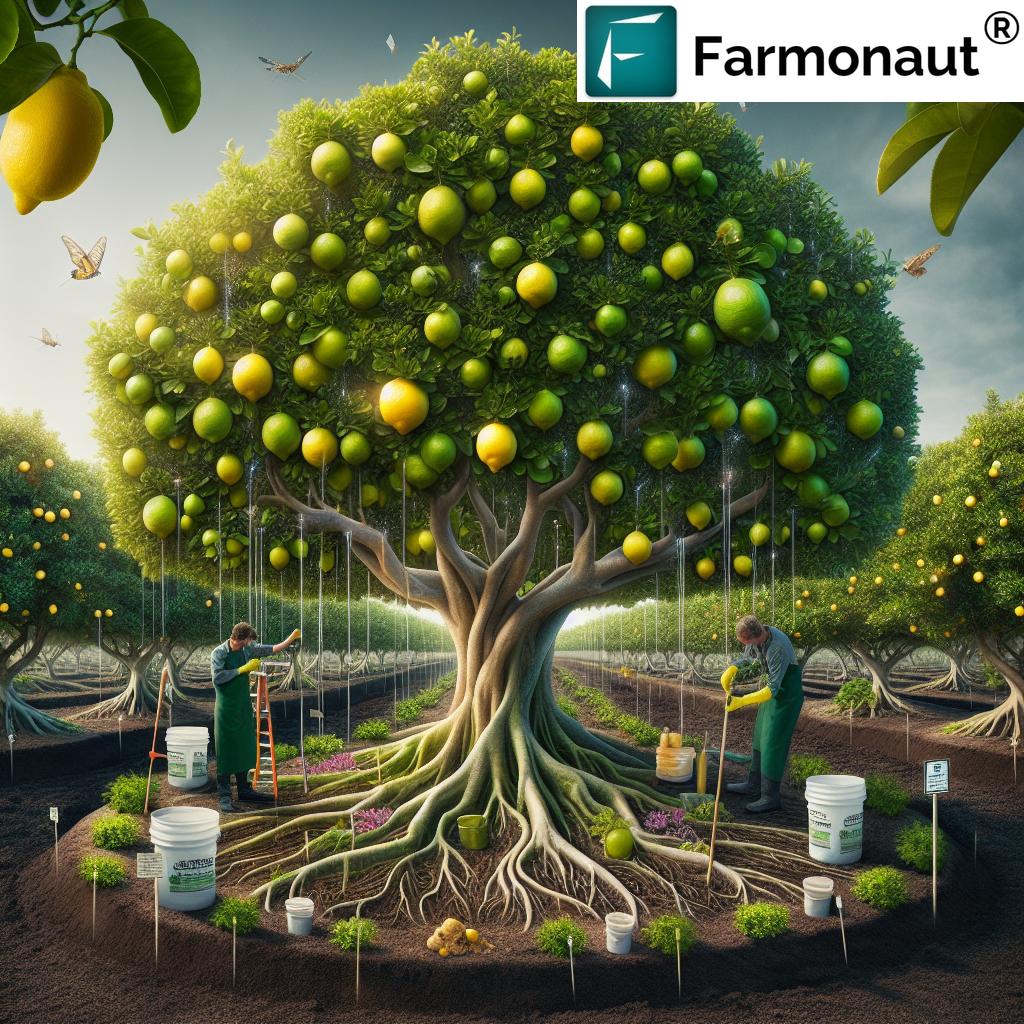
Pest Management in Lemon Orchards: Keeping Your Citrus Trees Healthy
Lemon trees in Florida may face threats from a variety of pests and diseases—from leaf miners, scale insects, and mites to fungal infections and viral disease.
Common Lemon Tree Pests in Florida
- Citrus Leaf Miner: Causes leaf curling and limits tree vigor.
- Aphids, Red Spiders, and Mealybugs: Damage leaves, attract ants, and spread disease.
- Scale Insects: Sap feeders that weaken the tree and can cause sooty mold.
- Phytophthora (root rot): Thrives in poorly-drained soils; rapid root decay.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Lemons
- Regular Inspection: Check trees weekly for pest or disease signs.
- Natural Predators: Encourage ladybugs and lacewings—nature’s pest controllers.
- Organic Controls: Use neem oil, horticultural oils, or insecticidal soaps as a first defense.
- Cultural Practices: Avoid overwatering or overly dense foliage that boosts pest and rot outbreaks.
- Remove Debris: Keep the area beneath trees clear of fallen fruit and leaves.
For precision detection and targeted response, real-time crop health monitoring—leveraged through Farmonaut’s satellite data API—can pinpoint early pest/disease outbreaks, saving your crop and reducing chemical interventions.
Mulching for Citrus Trees: Protect Roots and Improve Soil
A proper mulching regimen offers many advantages:
- Retains Soil Moisture: Reduces evaporation and supports regular lemon tree watering schedules.
- Regulates Temperature: Keeps root zones cool in summer, insulated in winter.
- Suppresses Weeds: Reduces competition for vital soil nutrients.
- Feeds the Soil: As organic mulch (wood chips, straw, compost) decomposes, it naturally nourishes the soil.
Proper Mulching Practices
- Apply a 2–4 inch layer in a wide circle, extending to the drip line.
- Keep mulch 3–6 inches from the trunk to avoid collar rot and pest nesting.
- Replenish annually or after heavy rainfall breaks down materials.
This “mulching for citrus trees” approach helps Florida growers maintain stable, healthy orchards year-round.
Growing Lemon Trees in Cold Climates: Climate Considerations and Variety Selection
While Florida’s warm weather is a boon, occasional cold spells and frost present challenges. Here’s how to safeguard your investment:
Frost Protection & Heat Management
- Choose Cold-Hardy Varieties: Some types tolerate occasional light frost (e.g., ‘Improved Meyer’).
- Frost Covers & Microclimates: Use cloths or protective wraps during unexpected winter dips below 32°F.
- Planting on Mounds or Raised Beds: Encourages faster drainage and reduces risk of cold-sink damage.
- Summer Heat: During extreme heatwaves, ensure ample mulch and supplemental irrigation to prevent heat stress and fruit drop.
With wise site selection and choosing appropriate varieties, you can minimize weather-related losses and establish a resilient orchard.
Lemon Tree Planting & Care Schedule Table
| Step/Activity | Description | Recommended Timing/Season | Estimated Effort/Duration | Outcome/Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site Selection | Identify sunny, well-drained, protected area with windbreak | Winter–Early Spring (before planting) | 1–3 hours | Healthy initial root and canopy growth |
| Soil Preparation | Test and amend soil, remove grass, blend organic matter | Winter–Spring | 2–3 hours | Optimal soil pH and fertility |
| Planting Tree | Dig hole, position tree, backfill, water, mulch | Spring/Early Summer | 30–45 minutes per tree | Strong root establishment |
| Watering | Deep watering at regular intervals; adjust by season | Year Round | 20–30 min/irrigation; every 7–14 days | Consistent growth, minimized stress |
| Fertilization | Apply balanced citrus fertilizer as per schedule | Spring start; every 4–6 weeks in season | 10–20 min/application | High vigor and fruit production |
| Pruning | Remove dead/sick branches, shape canopy | Late Winter/Early Spring; as needed | 30–45 min/tree yearly | Improved yields & air circulation |
| Pest Management | Monitor for pests/disease; apply IPM/organic controls | Throughout growing season | 10–15 min/tree weekly | Minimized loss, healthier trees |
Planning a large orchard or monitoring tree health over time? Consider our fleet management and resource tools to efficiently deploy staff and equipment across your farm, or product traceability for full lifecycle tracking of your fruit to market.
How Farmonaut Supports Lemon Tree Growers in Florida
At Farmonaut, our mission is to empower Florida’s citrus growers—from backyard enthusiasts to commercial orchard managers—with advanced, affordable, and intuitive precision agriculture solutions.
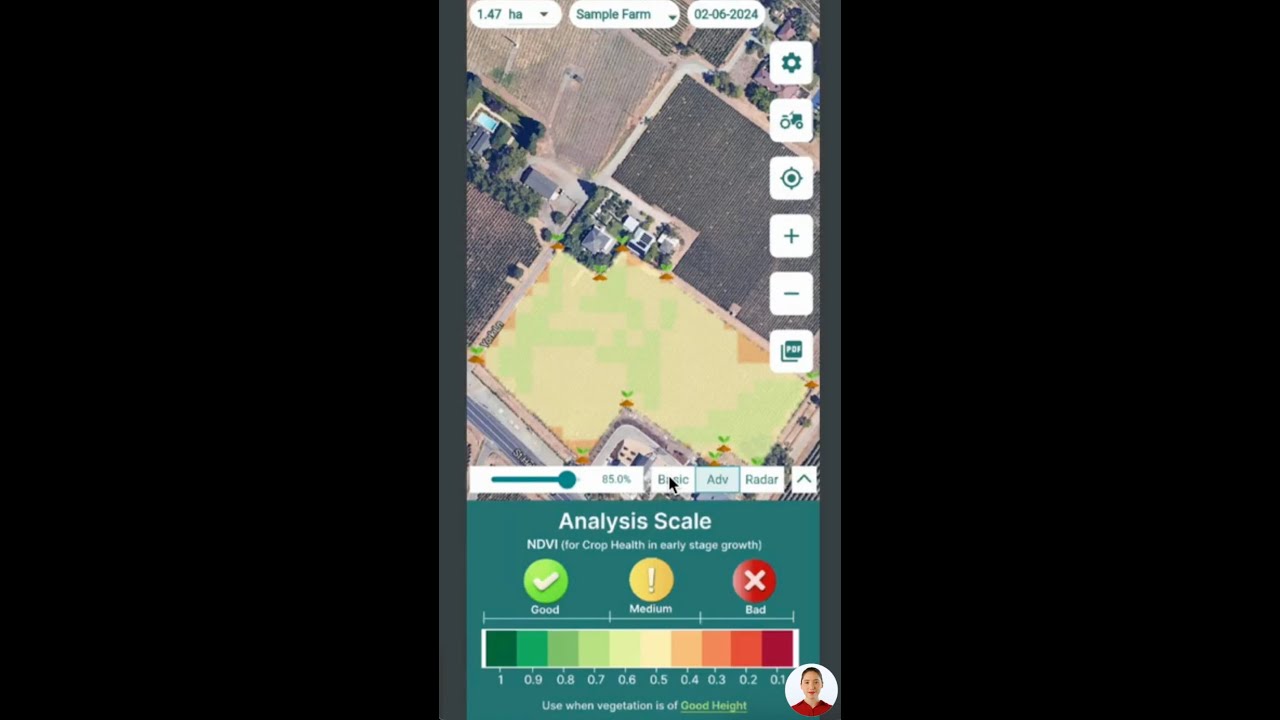
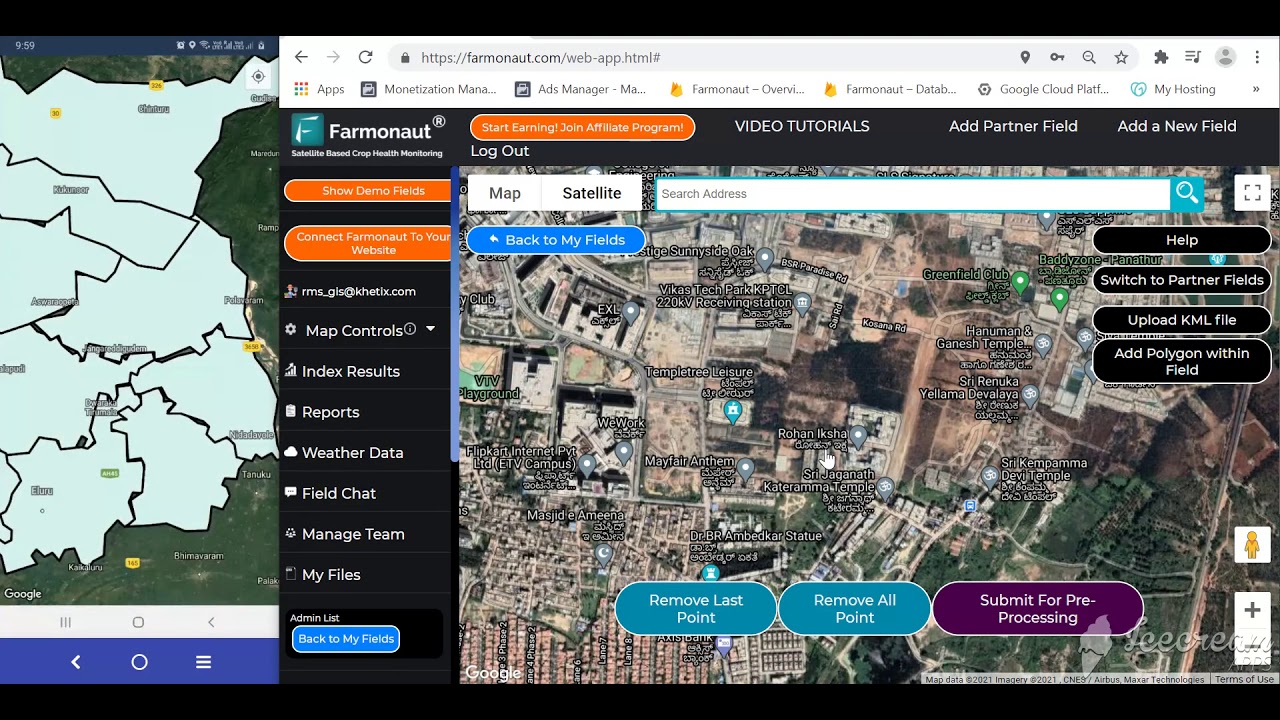
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Receive real-time, field-level insights on vegetation health, soil moisture, and disease risks. Early detection of irrigation needs or pest/disease stress is crucial for proactive care.
- AI-Based Advisory: Our Jeevn AI system offers personalized crop management advice—from watering alerts to pruning lemon trees and fertilizer recommendations—direct to your mobile device.
- Blockchain Traceability: Lemon growers can ensure quality and consumer trust by tracking every stage of their fruit’s journey using secure, tamper-proof records.
- Fleet, Resource, and Carbon Management: Maximize efficiency of labor and machinery while minimizing environmental impact.
- Easy Access: Available on web, Android, and iOS—our tools let you monitor, analyze, and act on your orchard’s data from anywhere!
FAQ: Lemon Trees in Florida
-
Q: How deep should I plant my lemon tree?
A: Set the top of the root ball level with or a little above the existing soil line to prevent trunk rot and ensure healthy root expansion. -
Q: What’s the ideal soil pH for lemon trees, and how can I test it?
A: The best pH is 5.5–6.5. Use a reliable, local soil testing kit or send samples to your extension service and amend as needed. -
Q: When and how often should I water my lemon trees?
A: Water every 7 days in spring/summer and every 10–14 days in fall/winter, ensuring 1–2 inches per session. Adjust frequency based on rain and soil moisture. -
Q: Do lemon trees need to be fertilized?
A: Yes. Start at spring bud break, use a balanced citrus fertilizer, and repeat every 4–6 weeks through the growing season. -
Q: What’s the most common pest for lemon trees in Florida?
A: The citrus leaf miner is prevalent, but aphids, scale, and root rot are also threats—monitor regularly and use integrated management strategies. -
Q: Should I mulch my lemon tree?
A: Yes! A 2–4 inch layer of organic mulch conserves water, suppresses weeds, and stabilizes soil temperatures. -
Q: Are there cold-hardy lemon varieties for north Florida?
A: ‘Improved Meyer Lemon’ is the common choice for areas with light winter frost. Still, ensure protection in freezes!
Conclusion: Achieving Success in Florida Lemon Orchards
Planting lemon trees in Florida is a rewarding journey—one that blends careful preparation, seasonal discipline, and modern planting techniques. By following best practices in site selection, soil preparation, spacing, watering, fertilization, pruning, and proactive pest management, you’re setting the foundation for years of bountiful harvests.
For advanced, data-driven orchard management, our Farmonaut platform equips you with tools to monitor crop health, soil moisture, and optimize inputs, empowering both traditional and progressive citrus growers. Our focus is always to provide reliable, actionable agricultural insights—not to serve as a seller of farm inputs or machinery.
Ready to transform your lemon orchard? Download Farmonaut’s app on web, Android, or iOS and access precision agriculture solutions from planting to harvest.
Let’s make each season your best for healthy trees, abundant yields, and sustainable Florida lemon production!