Drought Solutions: 7 Powerful Ways Arizona Farmers Restore Arid Land
“Arizona farmers use over 7 climate-resilient crops to combat drought and restore soil health in arid regions.”
Understanding Drought and Desertification in Arizona
Around the globe, drought and desertification have increasingly become a crisis affecting our food systems, agriculture, and the very land we rely on. In the United States, and especially Arizona, we are at the scientific and ecological frontier of facing persistent drought conditions, increased temperatures, and soil degradation.
According to the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), drought has affected more people than any other natural disaster in the past forty years. The phenomenon is closely tied to the process of desertification—a gradual decline in productive land caused by climate extremes and unsustainable practices.
As residents of the Southwest and stewards of the Arizona landscape, it is our collective responsibility to combat environmental decline and work toward restoring degraded landscapes for future generations.
The Impact of Extreme Weather on Arid Land
Higher temperatures and drier climates are making regions like Arizona, New Mexico, and surrounding arid areas more vulnerable to drought, resource scarcity, and severe land degradation. The past decade, according to meteorological data, has been the hottest on record globally. Combined with reduced rainfall and erratic weather, we are witnessing a silent but severe risk to food security, water access, and the health of our soil.
Nearly 2 billion people worldwide live in dryland areas, with a growing percentage directly affected by these environmental effects. The crisis is as much about community well-being as it is about ecosystems. Without comprehensive solutions, entire regions could face increased hunger, declining health, and a loss of biodiversity in the ecosystem.
“Dryland farming techniques can increase soil moisture retention by up to 50% in desertified areas.”
Introduction: The Need for Drought Solutions
Is all lost? Absolutely not. We have a path forward through science, technology, and collective willpower. Arizona farmers are combining traditional wisdom with innovative solutions to transform arid landscapes into productive, thriving farm systems.
With the right crops, advanced monitoring, and sustainable practices, we can adapt to extreme weather in agriculture, improve soil health in arid regions, and ensure resilient food security in drought affected areas.
Let us explore seven core strategies—proven, scalable, and actionable—that any farming community can use to safeguard our shared future.
Comparative Solutions Table: Drought Restoration Methods in Arizona
For a quick overview, here’s a comparative table of the seven proven drought solutions utilized by skilled Arizona farmers to restore arid land and secure our food future. Estimated quantitative impacts provide clearer insight into each solution’s benefits.
| Solution Name | Description | Est. Impact on Soil Health (%) | Est. Water Savings (%) | Climate Resilience Score (1-5) | Example Crop Supported |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adoption of Climate Resilient Crops | Planting native or drought-tolerant crops for improved adaptation | 35-50 | 30-45 | 5 | Tepary Beans |
| Water Conservation in Agriculture | Employing drip irrigation, mulching, and water harvesting | 20-30 | 40-55 | 4 | Prickly Pear Cactus |
| Improving Soil Health in Arid Regions | Using compost, cover crops, and amendments to increase fertility | 45-60 | 20-25 | 5 | Millet |
| Innovative Dryland Farming Practices | Reduced tillage, crop rotation, and microclimate management | 35-45 | 30-40 | 4 | Sorghum |
| Harnessing Soil Microbes | Utilizing beneficial microbes to enhance nutrient cycling and disease resistance | 50-65 | 15-20 | 5 | Cowpea |
| Restoration of Degraded Landscapes | Reforestation, grass strips, and riparian buffers for land rehabilitation | 60-75 | 10-20 | 5 | Mesquite |
| Advanced Land Monitoring & Data-Driven Decision Making | Applying satellite, AI, and digital tools for precision agriculture | 40-60 | 35-50 | 5 | Sesame |
7 Powerful Drought Solutions for Arizona’s Arid Land
Each solution below is tailored to improve the unique challenges we face in the Southwest. These strategies have broad applications—from individual smallholder farms to large-scale agriculture systems across the world.
1. Adoption of Climate Resilient Crops
Climate resilient crops are the foundation for any successful adaptation to arid conditions. In Arizona, we utilize crops naturally adapted to dryland farming—from ancient grains to indigenous food plants.
- Indigenous crops for arid climates like Tepary Beans, Prickly Pear, Millet, and Amaranth thrive under minimal water and high heat.
- Modern options include drought-tolerant varieties of corn, chickpeas, and cowpea, supporting food security while requiring less water than conventional staples.
- Our reliance on these crops has been strengthened by organizations such as Native Seeds/SEARCH and the Arizona Alliance for Climate-Smart Crops. These groups preserve and promote seeds that can sustain both food systems and community health in the Southwest.
- The increased adoption of such climate-resilient crops reduces risk, improves soil health, and diversifies our agricultural output, making us less vulnerable to drought and desertification.
2. Water Conservation in Agriculture
Water conservation in agriculture is critical on our arid lands. By deploying water-saving techniques, we can combat water shortages and improve the sustainability of dry land farming.
- Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation losses by up to 50% compared to open-field irrigation.
- Mulching and ground covers help retain soil moisture and suppress weed competition for precious water.
- Rainwater harvesting, cisterns, and contour bunding channel scarce rainfall for beneficial use, especially during critical crop stages.
- We are also experimenting with technologies that optimize the timing and amount of water application through farm management systems—such as those provided by Farmonaut (see below for more details).
3. Improving Soil Health in Arid Regions
Healthy soils = healthy crops. Soil health is a cornerstone for restoring degraded landscapes in Arizona and other arid regions.
- We boost soil organic matter through composting, strategic application of manure, and growing cover crops such as cowpea or clover.
- Cover crops protect soil from erosion and scorching heat, fostering soil microbes that fix nitrogen and decompose organic material.
- Reducing tillage conserves soil structure, moisture, and prevents wind- and water-driven erosion.
- Smart use of organic and mineral amendments fosters crop yields and resilience against drought.
4. Innovative Dryland Farming Practices
Solutions for dryland farming emphasize innovation within natural limitations. Arizona farmers apply proven techniques to make every drop of moisture count.
- Cropping systems: Strategic rotation, intercropping, and agroforestry increase biodiversity and reduce soil-borne diseases.
- Minimal tillage: Maintaining protective residue on the soil surface curbs degradation and locks in precious moisture.
- Contour farming on slopes slows water run-off, promoting deeper infiltration and shielding soils from flash erosion.
- Agro-ecological approaches build bridges between traditional wisdom and 21st-century science for maximum ecosystem resilience.
5. Harnessing Soil Microbes for Yield and Health
Soil microbes are nature’s hidden warriors against drought and desertification.
Utilizing their power is a fundamental solution for improving soil health in arid regions.
- Certain microbes (including nitrogen-fixing bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi) enhance nutrient availability for crops, leading to enhanced growth and food security in drought affected areas.
- Microbial treatments help break down organic matter, recycle nutrients, and suppress plant pathogens.
- Recent international research has linked the use of specific beneficial microbes with up to 65% improvement in soil health metrics in arid and degraded lands.
6. Restoration of Degraded Landscapes
Restoring degraded landscapes is vital for ensuring that our ecosystems provide food security, water regulation, and habitat for native species. Reforestation, planting grass barriers, and establishing riparian buffers can incrementally rebuild lost fertility and riverbed stability.
- Great Green Wall style initiatives are being adopted at a local scale, with targeted tree plantings, native shrub reintroductions, and erosion control projects.
- Establishing grass strips and rain gardens decreases surface runoff and rebuilds the soil’s organic layer.
- Riparian buffers and check dams can catch and slowly release scarce water, invigorating both wild and cultivated zones.
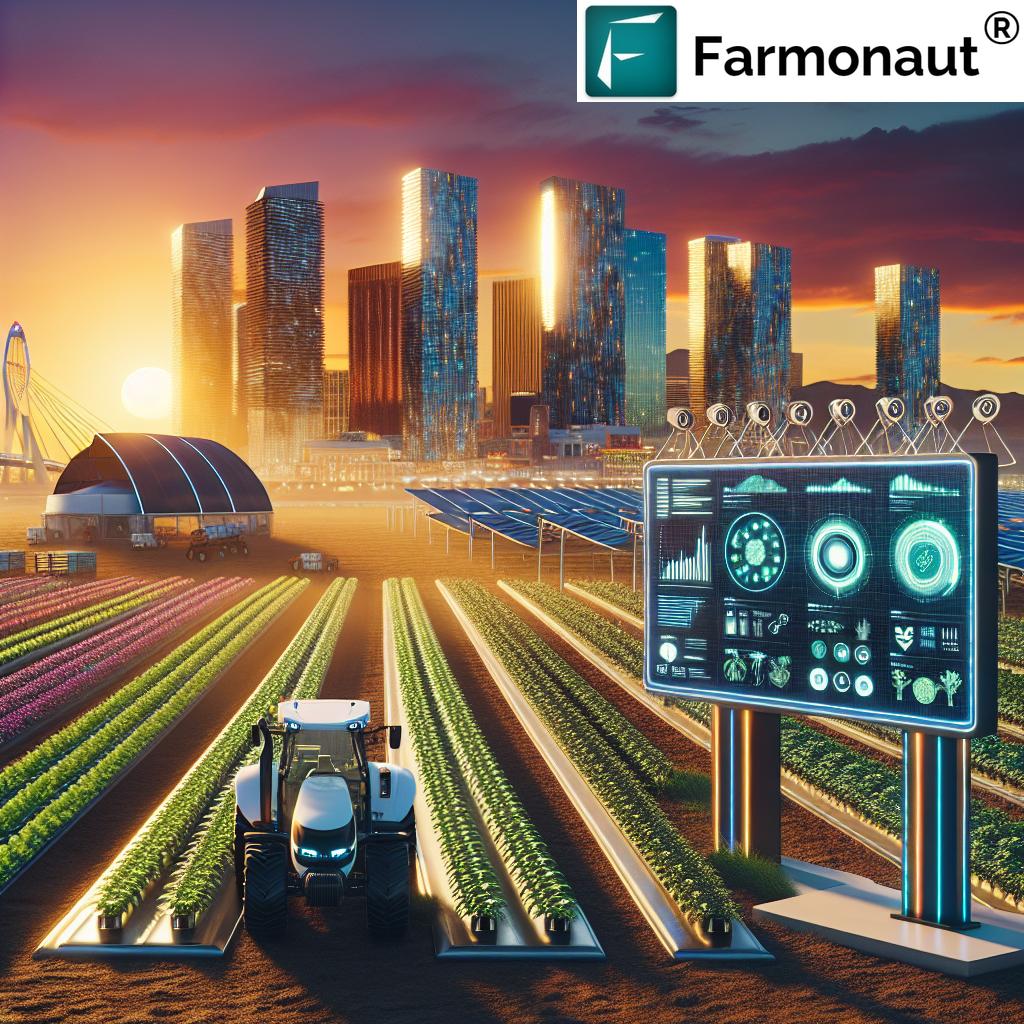
7. Advanced Land Monitoring & Data-Driven Decision Making
The frontier of modern agriculture is data-driven and digitally connected. Arizona farmers, like many around the world, implement precision techniques that use satellite data, AI advisory systems, and mobile technology to amplify the effectiveness of all previous solutions.
- By leveraging satellite-based monitoring (as provided by Farmonaut), we can track crop health, spot soil moisture deficiencies, and optimize irrigation or fertilizer use in real time.
- AI analytics and digital advisory platforms supply tailored drought and crop management strategies that adapt with shifting weather conditions.
- Digital traceability—thanks to blockchain—reinforces transparency and trust in the food system, letting us track every step from land to plate.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for custom agricultural solutions. Integrate real-time satellite and weather data into your own platforms for scalable, location-specific monitoring and restoration of arid lands.
|
View API Developer Docs for seamless integration.
Farmonaut Technology for Arid Land Restoration
Farmonaut empowers farmers, researchers, and organizations globally—especially in drought affected areas like Arizona—through real-time data, advanced analytics, and accessible technology.
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring: Track NDVI, soil moisture, and vegetation indices to support climate resilient crop management and restore arid land.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Receives customized, data-driven management insights for adaptation to extreme weather in agriculture.
- Blockchain traceability: Ensures transparent, fraud-resistant supply chains from farm to marketplace.
- Resource & fleet management: Cuts input waste and improves efficiency from day one.
- Carbon footprint tracking: Move toward sustainable farming and environmental compliance.
Farmonaut solutions are cost-effective, scalable, and easy to deploy via web and mobile app. From Baltimore, Maryland to Arizona and beyond, our technologies address food security as well as environmental risk reduction at a global scale.
Farmonaut Access and Subscriptions
Farmonaut provides flexible subscription packages for individual farmers, agribusinesses, and government agencies seeking precision agriculture solutions. From small plots to large tracts of arid land, our systems scale for any need.
Sign up for Farmonaut today and join the global movement to nourish your community and restore arid land for future generations.
FAQ: Drought & Arid Land Restoration
What are the main causes of drought and desertification in Arizona?
The primary causes are sustained higher temperatures, inconsistent rainfall, poor agricultural practices, overgrazing, and climate change. These factors combine to decrease soil moisture, reduce plant growth, and eventually transform fertile areas into arid or desert-like land.
How can Arizona farmers adapt to extreme weather in agriculture?
We adapt by selecting climate resilient crops, improving soil health, embracing innovative water conservation strategies, and leveraging digital farm management tools. Community-level action and adoption of indigenous knowledge are also key.
Which crops are best for dryland farming in Arizona?
Tepary Beans, Prickly Pear, Sorghum, Millet, Cowpea, Amaranth, and Mesquite are among the top choices for dryland farming in Arizona’s arid climate due to their drought resistance and historical success in local systems.
What technology helps with water conservation in agriculture?
Modern drip irrigation, soil moisture sensors, and satellite-based crop health monitoring (such as Farmonaut) all help track water use and optimize irrigation. These tools are accessible via web and mobile applications.
How does improving soil health help fight drought?
Healthier soils retain more water, resist erosion, support more robust microbial communities, and foster climate resilience—ensuring productive crops even in times of water scarcity.
Where can I learn more about Farmonaut’s solutions?
Visit the official Farmonaut website or access our blog for detailed product roadmaps, support, and user guides to sustainable arid land restoration.
Conclusion: Our Path Forward
Arizona’s farmers are uniquely positioned—at the intersection of innovation and tradition—to tackle the real and rising threats of drought and desertification. With climate resilient crops, data-powered platforms like Farmonaut, and a commitment to soil and community health, we are building a food future that is both secure and sustainable.
As we continue to restore degraded landscapes and adapt to extreme weather in agriculture, let us share knowledge, invest in science, and honor the resilience of our land—together.