Farmonaut’s Guide: Harnessing GIS and Remote Sensing for Climate-Smart Agriculture in America

“USDA’s Disaster Resource Center offers over 20 different assistance programs for farmers affected by natural disasters.”
In the ever-evolving landscape of American agriculture, the integration of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing technologies has become increasingly crucial for implementing climate-smart farming practices. As we navigate the challenges posed by climate change and unpredictable weather patterns, it’s essential for farmers, ranchers, and agricultural stakeholders to embrace innovative solutions that enhance productivity while promoting sustainability. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how Farmonaut’s cutting-edge technology complements the United States Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) efforts in disaster preparedness and farm risk management, ultimately contributing to the resilience of rural communities across America.
The Importance of Agricultural Disaster Preparedness
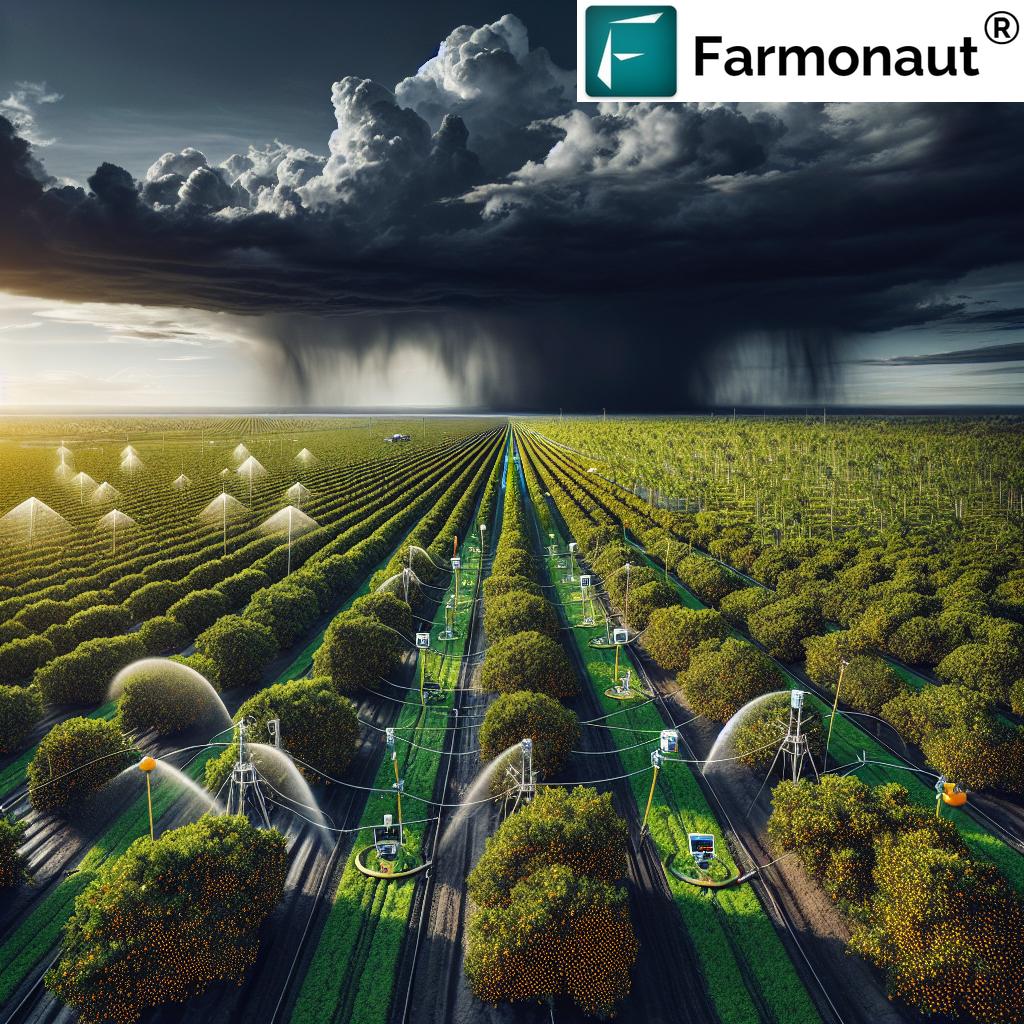
Agricultural disaster preparedness is a critical aspect of modern farming that can’t be overlooked. With the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters, it’s more important than ever for farmers and ranchers to have robust risk management strategies in place. The USDA has developed a comprehensive approach to disaster preparedness, which we’ll explore in detail throughout this guide.
- Proactive planning for potential disasters
- Implementation of risk mitigation strategies
- Access to resources and support systems
- Rapid response and recovery mechanisms
By focusing on these key areas, we can build more resilient agricultural systems that can withstand and recover from various types of disasters, including storms, droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures.
USDA’s Disaster Resource Center: A Vital Tool for Farmers
The USDA’s Disaster Resource Center serves as a central hub for farmers and ranchers seeking assistance during times of crisis. This comprehensive platform offers a wealth of information and resources to help agricultural producers navigate the challenges posed by natural disasters.
Key features of the Disaster Resource Center include:
- A disaster assistance discovery tool
- Detailed information on various USDA disaster assistance programs
- Guidelines for food safety during emergencies
- Resources for developing livestock evacuation plans
- Instructions for reporting crop damage
By utilizing these resources, farmers can better prepare for potential disasters and access the support they need when faced with challenging situations.
Tropical Storm Nicholas: A Case Study in Disaster Response
To illustrate the importance of disaster preparedness and the effectiveness of USDA’s resources, let’s examine the impact of Tropical Storm Nicholas, which affected large areas of agricultural land across Texas, Louisiana, and Mississippi in 2021.
“Tropical Storm Nicholas in 2021 impacted over 500,000 acres of agricultural land across Texas, Louisiana, and Mississippi.”
This significant weather event highlighted the need for robust disaster response mechanisms and the value of USDA’s comprehensive approach to supporting affected farmers and ranchers.
Essential Resources for Farmers and Ranchers
In addition to the Disaster Resource Center, the USDA offers a range of tools and programs designed to support agricultural producers in times of need. These resources are crucial for maintaining the stability and resilience of America’s food production systems.
- Noninsured Crop Disaster Assistance Program (NAP)
- Emergency Conservation Program
- Livestock Forage Disaster Program
- Emergency Assistance for Livestock, Honeybees, and Farm-Raised Fish Program
Each of these programs addresses specific needs within the agricultural sector, providing targeted support to help farmers and ranchers recover from various types of disasters.
Implementing Effective Farm Risk Management Strategies
Proactive farm risk management is essential for building resilient agricultural operations. By implementing comprehensive strategies, farmers can minimize potential losses and ensure the long-term sustainability of their businesses.
Key components of effective farm risk management include:
- Diversification of crops and livestock
- Implementation of conservation practices
- Utilization of crop insurance and other financial protection mechanisms
- Adoption of precision agriculture technologies
- Regular monitoring and assessment of farm operations
By incorporating these elements into their management practices, farmers can better withstand the challenges posed by natural disasters and market fluctuations.
Farmonaut: Enhancing Climate-Smart Agriculture with Advanced Technology
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting farmers in their journey towards more sustainable and resilient agricultural practices. Our advanced remote sensing and GIS capabilities provide valuable insights that complement USDA’s efforts in disaster preparedness and farm risk management.
Some of the key features offered by Farmonaut include:
- Real-time crop health monitoring using satellite imagery
- AI-driven advisory systems for personalized farm management
- Blockchain-based traceability solutions for supply chain transparency
- Resource management tools for optimizing farm operations
By leveraging these innovative technologies, farmers can make more informed decisions, improve productivity, and enhance their overall resilience to climate-related challenges.
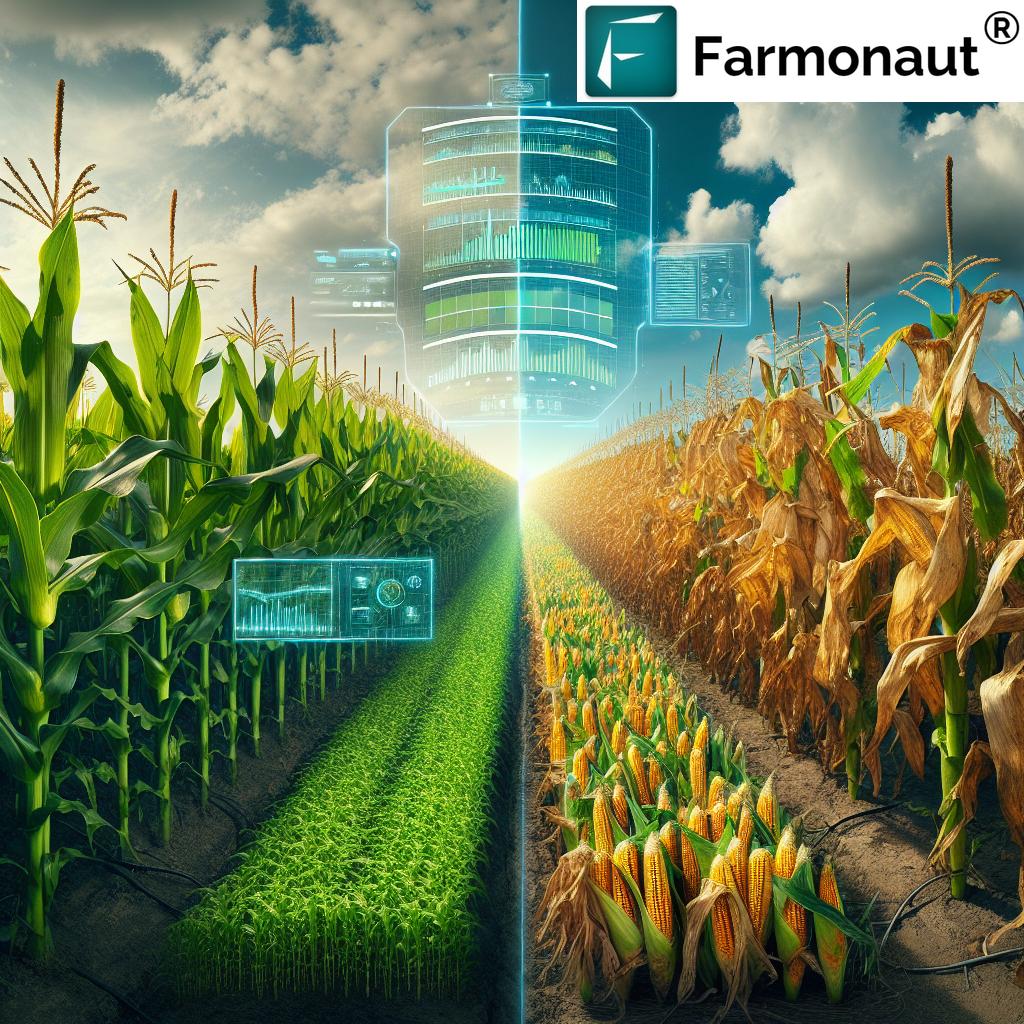
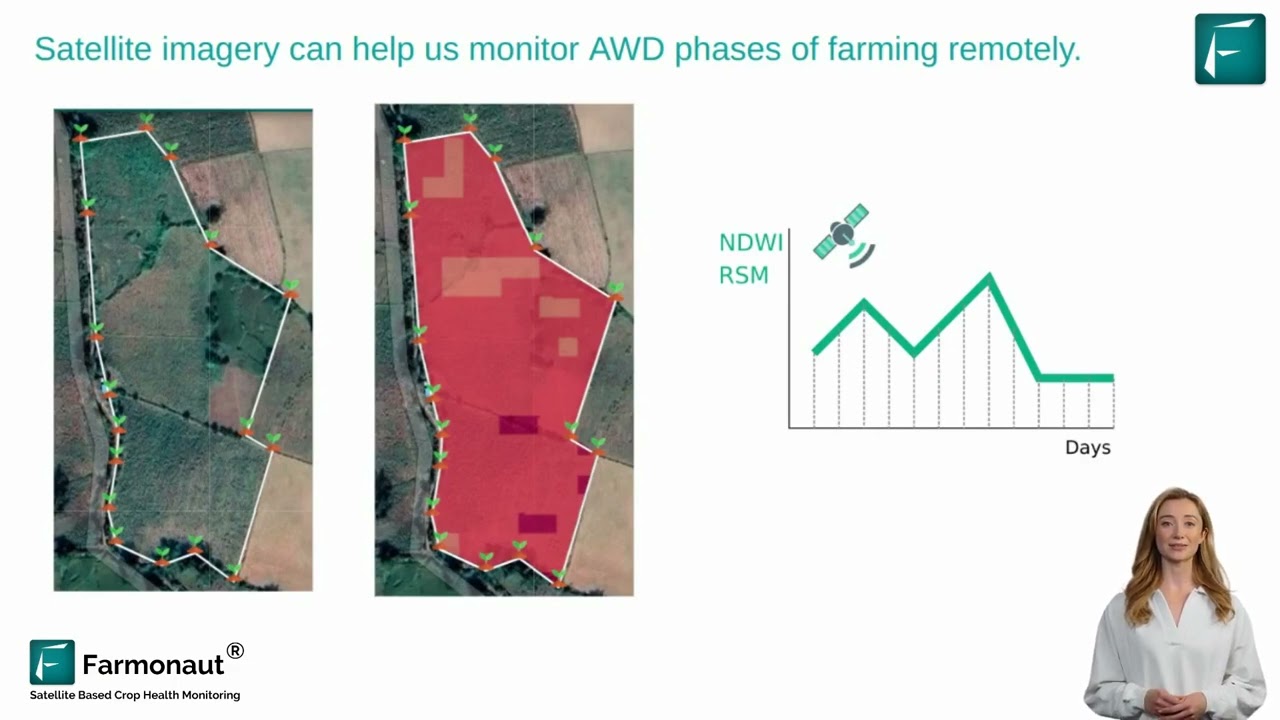
The Role of GIS and Remote Sensing in Climate-Smart Agriculture
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing technologies play a crucial role in advancing climate-smart agriculture practices. These tools provide farmers with valuable data and insights that can inform decision-making and improve overall farm management.
Benefits of GIS and remote sensing in agriculture include:
- Precise mapping of farm boundaries and crop areas
- Monitoring of crop health and growth patterns
- Early detection of pest infestations and diseases
- Optimization of irrigation and fertilizer application
- Assessment of soil quality and moisture levels
By harnessing these technologies, farmers can implement more targeted and efficient management practices, ultimately leading to increased productivity and reduced environmental impact.
Sustainable Farming Practices for a Resilient Future
Adopting sustainable farming practices is essential for building resilient agricultural systems that can withstand the challenges posed by climate change. These practices not only help to mitigate environmental impacts but also contribute to long-term farm productivity and profitability.
Key sustainable farming practices include:
- Conservation tillage and no-till farming
- Cover cropping and crop rotation
- Integrated pest management
- Precision agriculture techniques
- Water conservation and efficient irrigation systems
By implementing these practices, farmers can improve soil health, reduce erosion, conserve water resources, and minimize the use of chemical inputs, all while maintaining or even increasing crop yields.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced agricultural data management
Precision Agriculture Technology: A Game-Changer for American Farmers
Precision agriculture technology has revolutionized the way farmers approach crop management and resource allocation. By leveraging data-driven insights and advanced tools, farmers can optimize their operations for maximum efficiency and productivity.
Key components of precision agriculture include:
- GPS-guided machinery for precise planting and harvesting
- Variable rate technology for optimized input application
- Yield mapping and analysis
- Soil sampling and mapping
- Remote sensing for crop health monitoring
Farmonaut’s advanced remote sensing capabilities complement these precision agriculture technologies, providing farmers with real-time data on crop health, soil moisture, and other critical parameters.
Building Rural Community Resilience Through Agriculture
The resilience of rural communities is closely tied to the health and sustainability of local agricultural systems. By implementing climate-smart farming practices and leveraging advanced technologies, we can strengthen these communities and ensure their long-term viability.
Key factors contributing to rural community resilience include:
- Diversification of agricultural production
- Development of local food systems
- Investment in agricultural education and training
- Support for small and medium-sized farms
- Promotion of sustainable resource management
By focusing on these areas, we can create more resilient rural communities that are better equipped to face the challenges of a changing climate and evolving agricultural landscape.
Access Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs for integration guidance
USDA Disaster Assistance Programs: A Comprehensive Overview
The USDA offers a range of disaster assistance programs designed to support farmers and ranchers in times of need. Understanding these programs is crucial for effective farm risk management and disaster preparedness.
| Program Name | Purpose | Eligibility Criteria | Application Process | Estimated Funding Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noninsured Crop Disaster Assistance Program (NAP) | Provides financial assistance to producers of non-insurable crops when low yields, loss of inventory, or prevented planting occur due to natural disasters | Producers of crops not eligible for crop insurance | Apply at local FSA office before the application closing date for the crop | Varies based on crop and loss |
| Emergency Conservation Program | Provides emergency funding and technical assistance to farmers and ranchers to rehabilitate farmland damaged by natural disasters | Farmers and ranchers with conservation problems caused by natural disasters | Contact local FSA office to report damage and request assistance | Up to 75% of the cost to implement approved emergency conservation practices |
| Livestock Forage Disaster Program | Provides compensation to eligible livestock producers who have suffered grazing losses due to drought or fire | Livestock producers who own or lease grazing land physically located in a county affected by drought | Apply at local FSA office within 30 days after the end of the calendar year in which the grazing loss occurred | Payment rates vary based on type and number of livestock |
| Emergency Assistance for Livestock, Honeybees, and Farm-Raised Fish Program | Provides emergency assistance to eligible producers of livestock, honeybees, and farm-raised fish for losses due to disease, adverse weather, or other conditions not covered by other disaster programs | Producers of livestock, honeybees, and farm-raised fish who have suffered eligible losses | File a notice of loss within 30 calendar days of when the loss is first apparent | Payment limitations apply, consult FSA for details |
These programs provide critical support to agricultural producers facing various types of disasters, helping to ensure the continuity of food production and the stability of rural communities.
Farmonaut’s Role in Agricultural Data Management
Effective agricultural data management is essential for implementing climate-smart farming practices and improving overall farm productivity. Farmonaut’s advanced technology platform offers a range of tools and services designed to help farmers collect, analyze, and utilize data for better decision-making.
Key features of Farmonaut’s agricultural data management solutions include:
- Satellite-based crop monitoring for real-time insights
- AI-powered analytics for predictive modeling
- Integration with weather data for improved forecasting
- User-friendly mobile and web applications for easy access to data
- Secure data storage and management
By leveraging these tools, farmers can gain valuable insights into their operations, optimize resource use, and make more informed decisions to improve overall farm performance.
The Future of Climate-Smart Agriculture in America
As we look to the future, it’s clear that climate-smart agriculture will play an increasingly important role in ensuring food security and environmental sustainability. By combining the efforts of organizations like the USDA with innovative technologies provided by companies like Farmonaut, we can create a more resilient and productive agricultural sector.
Key trends shaping the future of climate-smart agriculture include:
- Increased adoption of precision agriculture technologies
- Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in farm management
- Development of climate-resilient crop varieties
- Expansion of regenerative agriculture practices
- Enhanced focus on water conservation and management
By staying ahead of these trends and continuously innovating, we can build a more sustainable and productive agricultural system that benefits farmers, communities, and the environment.
Conclusion: Embracing Innovation for a Sustainable Agricultural Future
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, the integration of GIS and remote sensing technologies, coupled with USDA’s comprehensive disaster preparedness and assistance programs, is crucial for building a more resilient and sustainable agricultural sector in America. By leveraging these tools and resources, farmers and ranchers can better prepare for and respond to the challenges posed by climate change and natural disasters.
Farmonaut’s innovative solutions complement these efforts by providing advanced agricultural data management capabilities, real-time crop monitoring, and AI-driven insights. By embracing these technologies and adopting climate-smart farming practices, we can create a more productive, sustainable, and resilient food system that benefits farmers, rural communities, and consumers alike.
As we move forward, it’s essential that we continue to innovate, collaborate, and adapt to the changing agricultural landscape. By doing so, we can ensure a bright and sustainable future for American agriculture, one that meets the needs of today while preserving resources for generations to come.
FAQ Section
Q: What is climate-smart agriculture?
A: Climate-smart agriculture is an approach that helps guide actions to transform agricultural systems to effectively support development and ensure food security in a changing climate. It aims to sustainably increase agricultural productivity and incomes, adapt and build resilience to climate change, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions where possible.
Q: How does GIS contribute to agricultural disaster preparedness?
A: GIS helps in agricultural disaster preparedness by providing tools for mapping and analyzing potential hazards, assessing risk, and planning response strategies. It allows for the creation of detailed maps showing vulnerable areas, crop distributions, and infrastructure, which are crucial for effective disaster management and response.
Q: What are some key USDA disaster assistance programs for farmers?
A: Key USDA disaster assistance programs include the Noninsured Crop Disaster Assistance Program (NAP), Emergency Conservation Program, Livestock Forage Disaster Program, and Emergency Assistance for Livestock, Honeybees, and Farm-Raised Fish Program. These programs provide financial and technical assistance to farmers and ranchers affected by various types of disasters.
Q: How can Farmonaut’s technology help in implementing climate-smart agriculture practices?
A: Farmonaut’s technology supports climate-smart agriculture by providing real-time crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisory systems, and resource management tools. These features help farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer use, and pest management, leading to more efficient resource utilization and reduced environmental impact.
Q: What are some sustainable farming practices that can improve farm resilience?
A: Sustainable farming practices that can improve farm resilience include conservation tillage, cover cropping, crop rotation, integrated pest management, precision agriculture techniques, and efficient irrigation systems. These practices help improve soil health, conserve water, reduce chemical inputs, and enhance overall farm productivity and sustainability.