Optimizing Alfalfa Yield and Quality: Sustainable Forage Solutions for Wisconsin Livestock Producers
“Reduced-lignin alfalfa can increase feed efficiency by up to 15% in dairy cows, boosting milk production.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on revolutionizing livestock nutrition and sustainable forage production through the power of reduced-lignin alfalfa. As experts in agricultural technology and farm management, we at Farmonaut are excited to share our insights on this game-changing crop that’s transforming the landscape of livestock feed in Wisconsin and beyond.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of high-quality hay crops, exploring how reduced-lignin alfalfa is setting new standards for ruminant nutrition, enhancing feed efficiency, and boosting dairy herd productivity. We’ll uncover innovative strategies for optimizing alfalfa yield and quality throughout the growing season, all while maintaining the flexibility that modern farmers need in their forage management practices.
The Rise of Reduced-Lignin Alfalfa: A Game-Changer for Wisconsin Livestock Producers
Alfalfa has long been a staple in livestock nutrition, particularly for dairy cows and other ruminants. However, the introduction of reduced-lignin alfalfa varieties has taken this forage crop to new heights. Let’s explore why this innovative variety is causing such a stir in the agricultural community, especially here in Fort Atkinson, WI, and surrounding areas.
Understanding Lignin: The Key to Digestibility
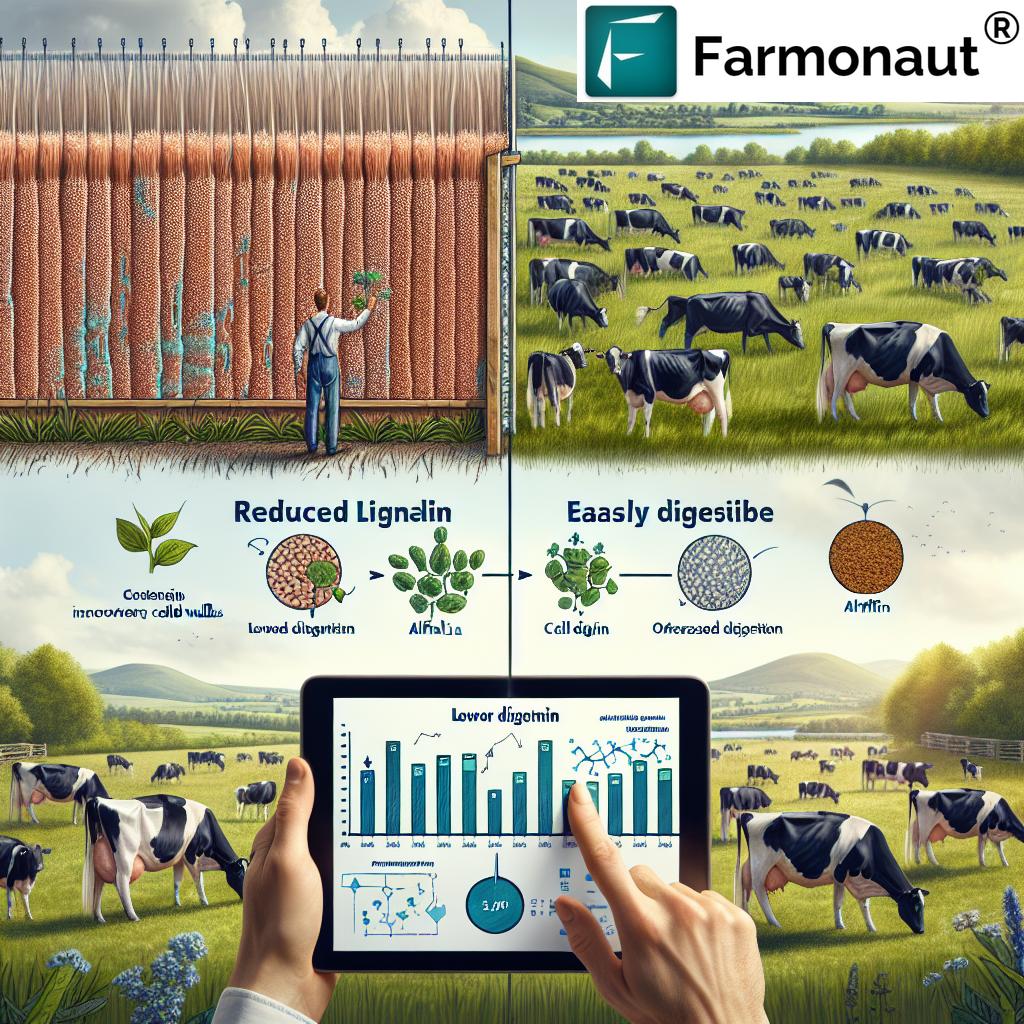
Before we dive into the benefits of reduced-lignin alfalfa, it’s crucial to understand what lignin is and its role in plant structure. Lignin is a complex organic polymer found in the cell walls of many plants, including alfalfa. While it provides structural support and helps plants stand upright, lignin is indigestible for animals. This means that the higher the lignin content in forage, the lower its digestibility and nutritional value for livestock.
The Reduced-Lignin Advantage
Reduced-lignin alfalfa varieties have been developed through careful breeding to contain less lignin than traditional varieties. This simple yet profound change offers several significant advantages:
- Improved Digestibility: With less lignin, more of the plant material can be digested by ruminants, leading to better nutrient absorption.
- Higher Feed Efficiency: As animals can digest more of the forage, they require less feed to meet their nutritional needs, improving overall feed efficiency.
- Increased Milk Production: For dairy producers, this translates to higher milk yields from the same amount of feed.
- Flexibility in Harvest Timing: Reduced-lignin alfalfa maintains its quality for longer periods, allowing farmers more leeway in harvest schedules.
These benefits align perfectly with our mission at Farmonaut to enhance farm productivity and sustainability through innovative solutions. While we focus on providing cutting-edge satellite-based farm management tools, we recognize the importance of crop selection in achieving optimal results.

Comparative Analysis: Reduced-Lignin vs. Traditional Alfalfa
To better understand the advantages of reduced-lignin alfalfa, let’s take a closer look at how it compares to traditional varieties:
| Characteristics | Reduced-Lignin Alfalfa | Traditional Alfalfa |
|---|---|---|
| Lignin Content (%) | 6-7% | 8-9% |
| Digestibility (%) | 65-70% | 55-60% |
| Crude Protein (%) | 18-22% | 16-20% |
| Yield (tons/acre) | 4-6 | 3.5-5.5 |
| Weather Resistance (1-10 scale) | 8 | 7 |
| Harvest Flexibility (days) | 7-10 | 3-5 |
| Estimated Feed Efficiency Improvement (%) | 10-15% | Baseline |
As the table illustrates, reduced-lignin alfalfa offers substantial improvements across several key metrics. These advantages contribute to its growing popularity among Wisconsin livestock producers who are looking to optimize their forage production and animal nutrition strategies.
Optimizing Alfalfa Yield and Quality: Best Practices for Wisconsin Farmers
Now that we’ve established the benefits of reduced-lignin alfalfa, let’s explore how farmers can maximize its potential through optimal management practices. At Farmonaut, we believe that combining innovative crop varieties with data-driven farming techniques is key to achieving sustainable and profitable agriculture.
1. Soil Preparation and Nutrient Management
The foundation of a successful alfalfa crop lies in proper soil preparation and nutrient management. Here are some key points to consider:
- Soil Testing: Conduct regular soil tests to determine pH levels and nutrient content. Alfalfa thrives in soil with a pH between 6.5 and 7.0.
- Lime Application: If soil pH is low, apply lime as recommended by soil test results. This should be done several months before planting to allow time for the lime to react with the soil.
- Nutrient Balance: Ensure adequate levels of phosphorus, potassium, and other essential nutrients. Alfalfa is particularly demanding of potassium, so pay close attention to K levels.
- Organic Matter: Incorporate organic matter into the soil to improve structure, water retention, and nutrient availability.
By leveraging Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring, farmers can gain valuable insights into soil moisture levels and vegetation health, allowing for more precise nutrient management throughout the growing season.
2. Variety Selection and Planting Techniques
Choosing the right reduced-lignin alfalfa variety and employing proper planting techniques are crucial steps in establishing a productive stand:
- Select Adapted Varieties: Choose varieties that are well-suited to Wisconsin’s climate and have demonstrated good performance in local trials.
- Seeding Rate: Aim for a seeding rate of 15-20 pounds per acre for optimal stand establishment.
- Planting Date: In Wisconsin, spring planting (April to early May) or late summer planting (August) are typically recommended.
- Seed Bed Preparation: Ensure a firm, smooth seedbed for good seed-to-soil contact.
- Planting Depth: Plant seeds at a depth of 1/4 to 1/2 inch in medium to heavy soils, and slightly deeper in sandy soils.
Farmonaut’s AI-driven advisory system, Jeevn AI, can provide personalized recommendations on optimal planting times based on local weather forecasts and historical data, helping farmers make informed decisions.
3. Irrigation and Water Management
Proper water management is essential for maximizing alfalfa yield and quality, especially in areas prone to drought or during dry spells:
- Monitor Soil Moisture: Use soil moisture sensors or Farmonaut’s satellite-based moisture monitoring to track water levels in the root zone.
- Irrigation Timing: Water deeply but infrequently to encourage deep root growth. Avoid over-irrigation, which can lead to root diseases and nutrient leaching.
- Consider Growth Stage: Alfalfa has higher water requirements during rapid growth phases and immediately after cutting.
- Drought Tolerance: While reduced-lignin alfalfa is generally more drought-tolerant than traditional varieties, proper irrigation is still crucial for optimal performance.
By integrating Farmonaut’s real-time crop health monitoring with irrigation management, farmers can optimize water use efficiency and maintain crop health even under challenging conditions.
4. Pest and Disease Management
Effective pest and disease control is critical for maintaining high-quality alfalfa stands:
- Regular Scouting: Implement a routine scouting program to detect pest and disease issues early.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Utilize a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical control methods as needed.
- Weed Control: Manage weeds through proper stand establishment, timely cutting, and targeted herbicide applications when necessary.
- Disease Resistance: Choose varieties with resistance to common diseases in your area, such as Phytophthora root rot or Aphanomyces root rot.
Farmonaut’s satellite imagery can help detect early signs of pest infestations or disease outbreaks, allowing for timely interventions and minimizing crop losses.
5. Harvesting Strategies for Optimal Quality
One of the key advantages of reduced-lignin alfalfa is the extended harvest window. However, proper harvesting techniques are still crucial for maximizing forage quality:
- Timing: Harvest at early bloom stage for an optimal balance between yield and quality. Reduced-lignin varieties allow for a 7-10 day delay in harvest without significant quality loss.
- Cutting Height: Maintain a cutting height of 3-4 inches to promote rapid regrowth and stand longevity.
- Moisture Content: For hay production, aim for 15-20% moisture content. For silage, target 60-70% moisture.
- Leaf Retention: Use proper equipment and techniques to minimize leaf loss during harvesting and handling, as leaves contain the highest nutritional value.
Farmonaut’s fleet and resource management tools can help optimize harvesting operations, ensuring timely and efficient crop collection.
Sustainable Forage Production: Environmental Benefits of Reduced-Lignin Alfalfa
“Wisconsin farmers using optimized alfalfa management techniques have reported yield increases of 20-30% over traditional varieties.”
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to promoting sustainable agricultural practices that benefit both farmers and the environment. Reduced-lignin alfalfa aligns perfectly with this mission, offering several environmental advantages:
- Improved Nitrogen Fixation: Like all legumes, alfalfa fixes nitrogen in the soil, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and improving soil health.
- Enhanced Soil Structure: Alfalfa’s deep root system helps improve soil structure, reduce erosion, and increase water infiltration.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Higher digestibility means less feed is required to produce the same amount of milk or meat, potentially reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions from livestock operations.
- Biodiversity Support: Alfalfa fields can provide habitat for pollinators and other beneficial insects when managed properly.
By incorporating reduced-lignin alfalfa into crop rotations and leveraging Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tools, farmers can contribute to more sustainable agricultural systems while potentially qualifying for carbon credit programs.
Economic Advantages for Wisconsin Livestock Producers
The adoption of reduced-lignin alfalfa offers significant economic benefits for livestock producers in Wisconsin:
- Increased Milk Production: Dairy cows fed high-quality reduced-lignin alfalfa can produce more milk per unit of feed consumed, improving overall profitability.
- Reduced Feed Costs: The improved digestibility of reduced-lignin alfalfa means that farmers may be able to reduce the amount of concentrate feed in their animals’ diets, potentially lowering overall feed costs.
- Extended Harvest Window: The flexibility in harvest timing can help farmers better manage their workload and potentially reduce weather-related risks.
- Higher Market Value: High-quality alfalfa hay or silage can command premium prices in the forage market, providing an additional income stream for producers.
By combining these economic advantages with Farmonaut’s data-driven farm management solutions, Wisconsin livestock producers can optimize their operations for maximum profitability and sustainability.
Integrating Reduced-Lignin Alfalfa into Your Farm Management Strategy
To fully leverage the benefits of reduced-lignin alfalfa, consider integrating it into a comprehensive farm management strategy. Here are some key steps:
- Assess Your Current Forage Program: Evaluate your existing forage production and identify areas where reduced-lignin alfalfa could provide the most significant improvements.
- Gradual Implementation: Start by incorporating reduced-lignin alfalfa into a portion of your acreage to gain experience and assess its performance under your specific conditions.
- Adjust Feeding Programs: Work with a nutritionist to optimize your livestock feeding programs to take full advantage of the improved digestibility of reduced-lignin alfalfa.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly assess crop performance, animal productivity, and economic outcomes to fine-tune your management approach.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring and AI-driven advisory services to optimize your alfalfa production and overall farm management.
By taking a holistic approach to integrating reduced-lignin alfalfa into your farming operations, you can maximize its benefits while ensuring sustainable and profitable production.
The Future of Forage: Ongoing Research and Development
The development of reduced-lignin alfalfa is just one example of the ongoing innovation in forage crop breeding and management. Researchers and agricultural scientists continue to explore new ways to improve alfalfa and other forage crops:
- Gene Editing: Advances in gene editing technologies may lead to further improvements in alfalfa digestibility, yield, and stress tolerance.
- Precision Breeding: The use of molecular markers and genomic selection techniques is accelerating the development of new alfalfa varieties with enhanced traits.
- Climate Resilience: Ongoing research aims to develop alfalfa varieties that can better withstand extreme weather events and changing climate conditions.
- Ecosystem Services: Scientists are exploring ways to enhance alfalfa’s role in providing ecosystem services, such as carbon sequestration and pollinator support.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these developments, continuously updating our satellite-based monitoring and AI advisory systems to help farmers make the most of emerging forage technologies.
Conclusion: Embracing Sustainable Forage Solutions for a Thriving Agricultural Future
Reduced-lignin alfalfa represents a significant leap forward in sustainable forage production for Wisconsin livestock producers. By offering improved digestibility, enhanced feed efficiency, and greater management flexibility, this innovative crop variety has the potential to transform dairy and livestock operations across the state and beyond.
As we’ve explored in this comprehensive guide, the key to success lies not just in adopting new crop varieties, but in implementing holistic management strategies that optimize yield, quality, and sustainability. By combining the power of reduced-lignin alfalfa with advanced farm management tools like those offered by Farmonaut, Wisconsin farmers can position themselves at the forefront of efficient, profitable, and environmentally responsible livestock production.
We encourage you to consider incorporating reduced-lignin alfalfa into your forage program and to explore how Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions can help you take your agricultural operations to the next level. Together, we can build a more sustainable and productive future for Wisconsin agriculture.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the main advantage of reduced-lignin alfalfa over traditional varieties?
A: The main advantage is improved digestibility due to lower lignin content, leading to better feed efficiency and potentially higher milk production in dairy cows.
Q: How does reduced-lignin alfalfa impact harvest timing?
A: It provides greater flexibility in harvest timing, allowing farmers to delay cutting by 7-10 days without significant quality loss compared to traditional varieties.
Q: Can reduced-lignin alfalfa help reduce feed costs?
A: Yes, its higher digestibility may allow farmers to reduce the amount of concentrate feed in animal diets, potentially lowering overall feed costs.
Q: Is reduced-lignin alfalfa suitable for all types of livestock?
A: While particularly beneficial for dairy cows, reduced-lignin alfalfa can be valuable for other ruminants like beef cattle, sheep, and goats.
Q: How does Farmonaut’s technology complement reduced-lignin alfalfa production?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring and AI advisory services can help optimize alfalfa production by providing real-time insights on crop health, soil moisture, and weather patterns.
Ready to revolutionize your forage production with cutting-edge farm management tools? Explore Farmonaut’s solutions today: