Revolutionary Organic Nanozymes: Advancing Sustainable Agriculture and Food Safety Detection in Illinois
“Organic nanozymes can detect histamine in vegetables, glyphosate in crops, and glucose in biological samples within minutes.”
In the heart of Illinois, a groundbreaking revolution is taking place in the world of agricultural sensing and food safety detection. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed sustainable organic nanozymes that are set to transform the way we approach point-of-use testing in agriculture. This innovative technology combines the power of environmentally friendly nanomaterials with enzyme-like catalytic properties, offering a cost-effective and non-toxic alternative to conventional inorganic counterparts.
As we delve into this exciting advancement, we’ll explore how these novel organic nanozymes are paving the way for rapid, on-site molecule detection without the need for complex laboratory equipment. From detecting histamine in vegetables to identifying glyphosate in crops and glucose in biological samples, this integrated system is poised to revolutionize food safety monitoring and agricultural testing.
Understanding Organic Nanozymes: A New Frontier in Agricultural Science
Nanozymes are synthetic materials that exhibit enzyme-like catalytic properties. While they have been widely used in biomedical applications such as disease diagnostics, their potential in agriculture and food safety has been limited due to the toxicity, high cost, and complex production processes associated with inorganic nanozymes.
Enter the next generation of organic nanozymes. Developed by a team of researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, these innovative materials offer a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to their inorganic counterparts. Let’s break down the key features that make these organic nanozymes a game-changer for agricultural and food safety applications:
- Non-toxic composition: Unlike inorganic nanozymes, these organic variants are made from safe, biodegradable materials.
- Cost-effective production: The synthesis process is simpler and more affordable, making large-scale production viable.
- Environmentally friendly: Their organic nature ensures minimal environmental impact, aligning with sustainable agricultural practices.
- Enhanced performance: These nanozymes mimic the catalytic activity of target enzymes with high efficiency.
The Evolution of Organic Nanozymes: From OC to OA to OM
The journey to develop these revolutionary organic nanozymes has been one of continuous improvement and innovation. Let’s trace the evolution of this technology:
- First-generation OC Nanozymes: The initial organic-compound-based (OC) nanozymes showed promise but had limitations. They required particle stabilizing polymers with repeatable functional groups to maintain stability, resulting in larger particle sizes.
- Second-generation OA Nanozymes: Researchers refined the process, using a core amino acid (L-alanine) and polyethylene glycol as constituent materials. A novel particle synthesis technique allowed them to reduce the particle size to less than 100 nanometers, significantly enhancing performance.
- Latest OM Nanozymes: The most recent iteration, organic-material (OM) nanozymes, represent the pinnacle of this technology. They offer improved catalytic activity and are specifically designed for integration into point-of-use sensing platforms.
This progression demonstrates the rapid advancements in the field and the potential for further improvements in the future.
Applications in Agriculture and Food Safety
The versatility of these organic nanozymes opens up a wide range of applications in agriculture and food safety. Here are some of the key areas where this technology is making a significant impact:
1. Histamine Detection in Vegetables
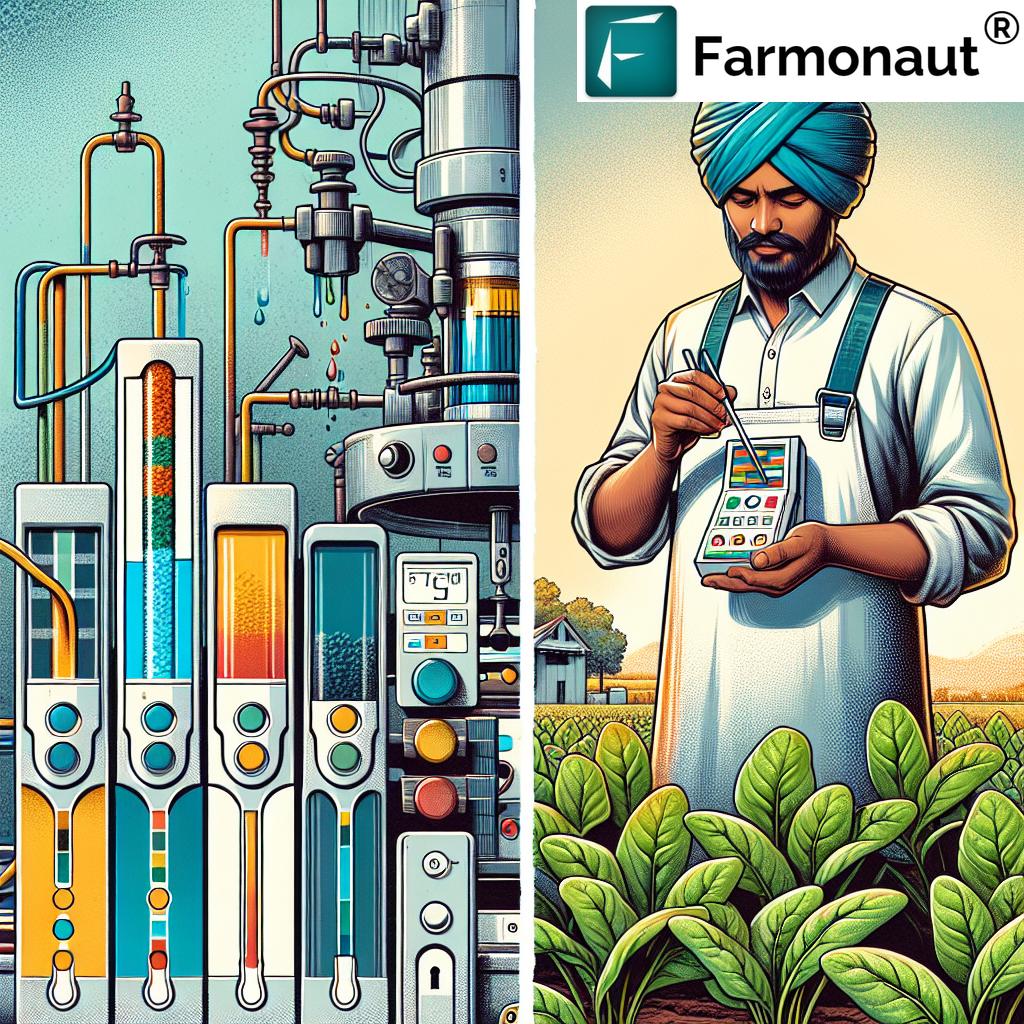
Histamine is a compound that can cause adverse reactions in sensitive individuals when present in high concentrations in food. The research team demonstrated the effectiveness of their OA nanozymes in detecting histamine in vegetables, particularly focusing on spinach and eggplant, which are known to contain higher levels of this compound.
Using a colorimetric sensing platform combined with the OA nanozymes, researchers achieved an affordable and accurate method for histamine detection. This application showcases the potential for real-world use in food safety monitoring, providing a cost-effective solution for both producers and consumers.
2. Glyphosate Detection in Crops
Glyphosate, a common agricultural herbicide, has been a subject of concern due to its potential environmental and health impacts. The OM nanozyme-based system developed by the researchers offers a rapid and sensitive method for detecting glyphosate residues in crops.
This point-of-use testing capability allows farmers and agricultural inspectors to perform on-site assessments of glyphosate levels, ensuring compliance with safety regulations and promoting sustainable farming practices.
3. Glucose Detection in Biological Samples
While primarily focused on agricultural applications, the versatility of the OM nanozymes extends to biological molecule detection as well. The research team successfully demonstrated the system’s ability to detect glucose in biological samples using an enzyme-cascade reaction method.
This application highlights the potential for these organic nanozymes to bridge the gap between agricultural and biomedical sensing technologies, opening up new avenues for integrated health and food safety monitoring.
The Point-of-Use Sensing Platform: Bringing Lab-Quality Results to the Field
“The new colorimetric sensing platform uses a smartphone app and microfluidic strips for rapid, on-site molecule detection.”
One of the most exciting aspects of this research is the development of an integrated, colorimetric point-of-use platform that enables rapid detection of agricultural and biological molecules without the need for a laboratory environment. This system represents a paradigm shift in how we approach agricultural testing and food safety monitoring.
Key Components of the Point-of-Use Platform:
- Microfluidic Strips: These small, portable strips contain the OM nanozymes and serve as the testing surface for sample analysis.
- Smartphone App: A custom-developed app uses image processing algorithms to analyze the colorimetric changes on the microfluidic strips.
- Colorimetric Sensing: The system relies on color changes to indicate the presence and concentration of target molecules.
How It Works:
- Users add food or crop samples to a liquid solution.
- The sample is tested using a small paper microfluidic strip containing the OM nanozymes.
- If the target molecule is present, the strip changes color to green, indicating catalytic activity.
- The intensity of the color correlates with the concentration of the target molecule.
- Users take a picture of the strip using their smartphone.
- The app processes the image and provides an estimated concentration of the target molecule.
This user-friendly system democratizes access to advanced agricultural and food safety testing, allowing farmers, food producers, and even consumers to perform quick and accurate tests without specialized training or equipment.

Advantages Over Conventional Detection Methods
The organic nanozyme-based sensing platform offers several significant advantages over traditional laboratory-based detection methods:
- Rapid Results: Tests can be completed in minutes, compared to hours or days for conventional lab analysis.
- Portability: The entire system is compact and can be used directly in the field or at point of sale.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By eliminating the need for expensive laboratory equipment and trained personnel, the overall cost per test is significantly reduced.
- Environmental Friendliness: The use of organic, biodegradable materials minimizes environmental impact.
- Ease of Use: The intuitive smartphone app and simple testing procedure make it accessible to a wide range of users.
To better illustrate these advantages, let’s compare the organic nanozyme-based method with traditional detection techniques:
| Detection Method | Cost-effectiveness | Testing Time | Portability | Environmental Impact | Accuracy | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Nanozymes | Low ($5-$10 per test) | 2-5 minutes | High (On-site capability) | Low (Biodegradable materials) | 90-95% | High (Smartphone app-based) |
| Traditional Laboratory Tests | High ($50-$100+ per test) | 24-48 hours | Low (Lab-based only) | Moderate (Chemical waste) | 95-99% | Low (Requires trained personnel) |
As we can see, the organic nanozyme-based method offers a compelling alternative to traditional testing, especially in situations where rapid, on-site results are crucial.
Implications for Sustainable Agriculture and Food Safety
The development of these organic nanozymes and their integration into a point-of-use sensing platform has far-reaching implications for sustainable agriculture and food safety:
- Enhanced Food Safety Monitoring: Rapid, on-site testing allows for more frequent and comprehensive food safety checks throughout the supply chain.
- Improved Agricultural Practices: Farmers can quickly test for pesticide residues and adjust their practices accordingly, promoting more sustainable farming methods.
- Reduced Food Waste: Faster detection of spoilage or contamination can help prevent large-scale food recalls and reduce waste.
- Empowered Consumers: As the technology becomes more accessible, consumers may be able to test their own food products, leading to greater awareness and demand for food safety.
- Support for Organic Farming: The environmentally friendly nature of these nanozymes aligns well with organic farming principles, potentially boosting this sector.
The Role of Farmonaut in Advancing Agricultural Technology
While the organic nanozyme technology represents a significant advancement in agricultural sensing and food safety detection, it’s important to note that other innovative companies are also contributing to the evolution of agriculture through technology. One such company is Farmonaut, which offers advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions.
Farmonaut’s platform provides valuable services such as real-time crop health monitoring, AI-based advisory systems, and resource management tools. While not directly involved in nanozyme technology, Farmonaut’s solutions complement advancements in agricultural sensing by offering farmers comprehensive data and insights to improve their operations.
Learn more about Farmonaut’s innovative agricultural solutions:
Future Directions and Potential Applications
The development of organic nanozymes for agricultural and food safety applications is still in its early stages, with vast potential for future advancements and applications. Some exciting areas for future research and development include:
- Expanded Molecule Detection: Researchers are likely to explore the detection of a wider range of agricultural chemicals, contaminants, and nutrients.
- Integration with IoT Systems: Combining nanozyme-based sensors with Internet of Things (IoT) technology could enable real-time, automated monitoring of crop health and food safety.
- Customized Nanozymes: Development of nanozymes tailored to specific crops or agricultural regions could further enhance detection accuracy and relevance.
- Multi-Parameter Sensing: Future iterations might allow for simultaneous detection of multiple parameters from a single sample, providing a more comprehensive analysis.
- Scaling for Industrial Use: Adapting the technology for large-scale industrial applications in food processing and agricultural production could significantly impact food safety practices.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of organic nanozymes in agriculture and food safety is immense, there are several challenges and considerations that need to be addressed:
- Regulatory Approval: As with any new technology in food safety, extensive testing and regulatory approval will be necessary before widespread adoption.
- Standardization: Establishing industry-wide standards for nanozyme-based testing will be crucial for ensuring consistency and reliability across different applications.
- Education and Training: Farmers, food producers, and other stakeholders will need proper education and training to effectively use and interpret results from nanozyme-based sensing platforms.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Ensuring compatibility with current agricultural and food safety practices will be essential for seamless adoption.
- Long-term Environmental Impact: While organic nanozymes are biodegradable, their long-term effects on ecosystems should be carefully studied.
Conclusion: A New Era in Agricultural Science and Food Safety
The development of revolutionary organic nanozymes by researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign marks a significant milestone in the fields of agricultural science and food safety. By offering a sustainable, cost-effective, and user-friendly alternative to traditional detection methods, this technology has the potential to transform how we monitor and ensure the safety of our food supply.
From rapid on-site detection of histamine in vegetables to identifying glyphosate residues in crops and glucose in biological samples, these organic nanozymes demonstrate versatility and efficiency that could revolutionize point-of-use testing in agriculture. The integration of this technology with smartphone apps and microfluidic strips brings advanced laboratory capabilities directly to the field, empowering farmers, food producers, and even consumers with real-time insights.
As we look to the future, the continued development and refinement of organic nanozyme technology promise to play a crucial role in promoting sustainable agriculture, enhancing food safety, and supporting global food security. By embracing these innovative solutions and combining them with other advanced agricultural technologies, we can work towards a more efficient, sustainable, and safer food production system for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What are organic nanozymes?
Organic nanozymes are synthetic materials made from organic compounds that exhibit enzyme-like catalytic properties. They are designed to mimic the function of natural enzymes but offer advantages such as lower cost, improved stability, and environmental friendliness. - How do organic nanozymes differ from traditional inorganic nanozymes?
Organic nanozymes are made from biodegradable, non-toxic materials, making them more environmentally friendly and suitable for agricultural applications. They are also generally less expensive to produce and can be tailored more easily for specific applications. - What are the main applications of organic nanozymes in agriculture?
Organic nanozymes can be used for rapid detection of various compounds in agricultural products, including histamine in vegetables, glyphosate residues in crops, and glucose in biological samples. They offer a fast, cost-effective method for on-site testing. - How does the point-of-use sensing platform work?
The platform combines organic nanozymes with microfluidic strips and a smartphone app. Users apply a sample to the strip, which changes color in the presence of target molecules. The smartphone app then analyzes the color change to determine the concentration of the target compound. - What are the advantages of using organic nanozymes for food safety testing?
Organic nanozymes offer rapid results, portability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use compared to traditional laboratory testing methods. They also have a lower environmental impact due to their biodegradable nature. - Are organic nanozymes safe for use in food testing?
Yes, organic nanozymes are designed to be non-toxic and environmentally friendly. However, as with any new technology in food safety, they will undergo rigorous testing and regulatory approval before widespread adoption. - Can organic nanozymes replace all traditional laboratory testing methods?
While organic nanozymes offer many advantages for rapid, on-site testing, they may not completely replace all traditional laboratory methods, especially for highly complex or specialized analyses. They are best seen as a complementary technology that expands testing capabilities. - How might organic nanozyme technology impact farmers and food producers?
This technology could allow farmers and food producers to perform quick, on-site tests for various compounds, helping them make informed decisions about crop management, harvest timing, and food safety. It could lead to more efficient farming practices and improved food safety monitoring. - What is the future potential of organic nanozyme technology?
Future developments may include expanded detection capabilities for a wider range of compounds, integration with IoT systems for automated monitoring, and customization for specific agricultural applications. The technology has the potential to significantly impact sustainable agriculture and food safety practices. - How does this technology relate to other agricultural innovations like those offered by Farmonaut?
While organic nanozyme technology focuses on point-of-use chemical detection, it complements other agricultural innovations like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring and AI advisory systems. Together, these technologies contribute to a more comprehensive approach to precision agriculture and sustainable farming practices.
Earn With Farmonaut: Join Our Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Explore Farmonaut’s Subscription Options
For developers interested in integrating Farmonaut’s satellite and weather data into their own systems, check out our API and API Developer Docs.