Revolutionizing Water Reuse: Washington’s Groundbreaking Resource Recovery Center Transforms Food Processing Waste into Sustainable Solutions
“Washington’s resource recovery center transforms 150 million gallons of food processing wastewater annually into renewable resources.”
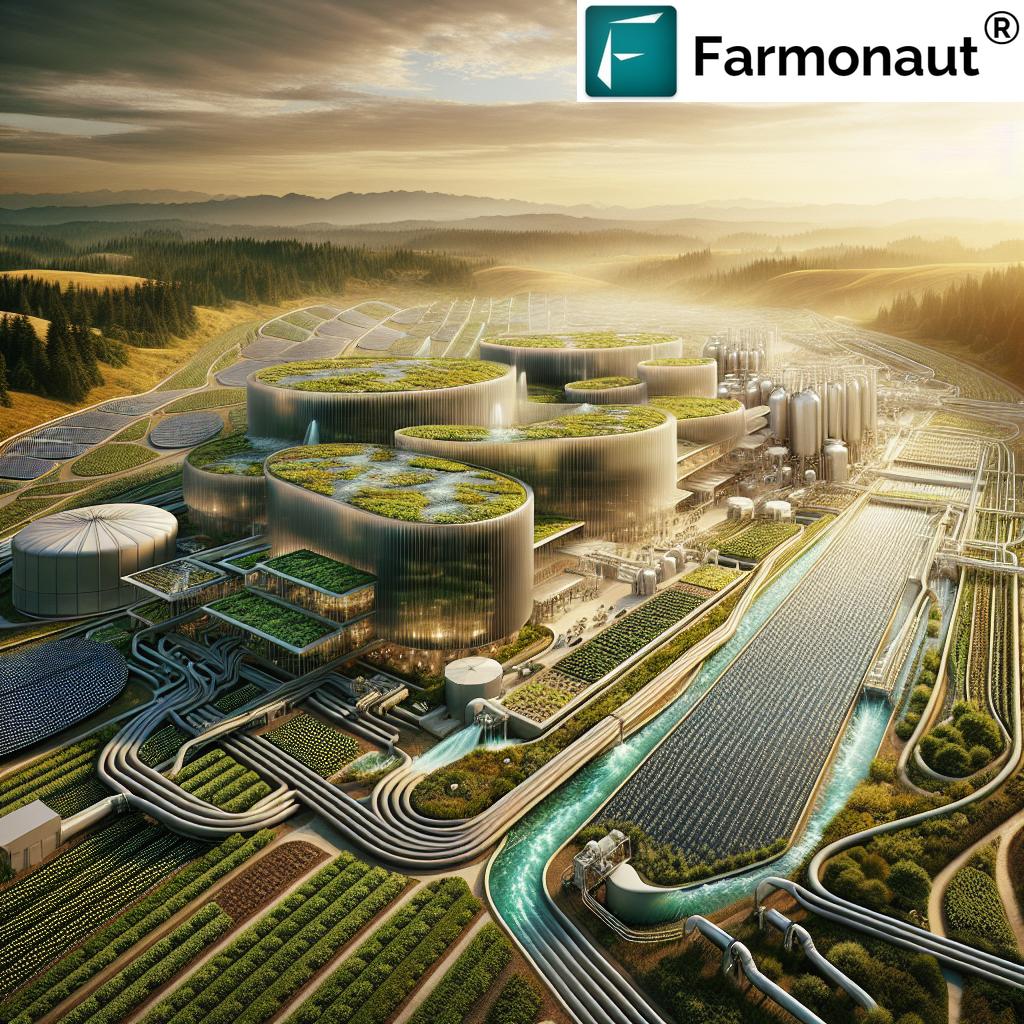
In the heart of Washington state, a groundbreaking initiative is setting new standards for sustainable water management and environmental stewardship. We’re excited to share with you the remarkable story of the Process Water Reuse Facility (PWRF) and Pasco Resource Recovery Center (PRRC) in the City of Pasco, WA. This innovative project is not just transforming waste into valuable resources; it’s reshaping our understanding of what’s possible in the realm of environmental technologies and sustainable solutions.

The Genesis of a Sustainable Revolution
The City of Pasco, in collaboration with Burnham RNG LLC and a host of project partners, has embarked on an ambitious journey to address one of the most pressing challenges of our time: sustainable water management. The PWRF and PRRC represent a leap forward in how we approach food processing waste and water reuse, setting a new benchmark for environmental impact reduction and resource recovery.
At its core, this facility is designed to tackle a significant environmental challenge: the vast amounts of wastewater generated by food processing plants. Instead of viewing this wastewater as a problem, the innovative minds behind this project saw an opportunity. They envisioned a system that could not only treat this water but transform it into valuable resources, creating a closed-loop system that benefits both industry and the environment.
A Closer Look at the Process
The PRRC’s approach to water reuse and resource recovery is nothing short of revolutionary. Let’s break down the process:
- Collection: Process water from seven local food processing plants is collected and brought to the facility.
- Treatment: The water undergoes a series of advanced treatment processes, including biological treatment and filtration.
- Resource Extraction: During treatment, valuable resources are extracted:
- Renewable Natural Gas (RNG): Biogas is produced through anaerobic digestion and upgraded to RNG.
- Soil Amendments: Nutrient-rich byproducts are processed into high-quality soil amendments.
- Algae: Certain treatment processes cultivate algae, which can be used in various bioproducts.
- Water Purification: The treated water is purified to meet stringent quality standards.
- Distribution: Clean water is returned for agricultural irrigation, completing the cycle.
This innovative process not only addresses the issue of wastewater but turns it into an opportunity for sustainable resource generation. It’s a prime example of circular economy principles in action, where waste from one process becomes a valuable input for another.
Environmental Impact and Benefits
The environmental benefits of this facility are multifaceted and far-reaching:
- Water Conservation: By treating and reusing process water, the facility significantly reduces the demand on local water sources.
- Renewable Energy Production: The generation of RNG provides a clean, renewable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Soil Health: The production of nutrient-rich soil amendments supports sustainable agriculture practices.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: The entire process results in a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional waste management methods.
- Ecosystem Protection: By treating wastewater to high standards, the facility helps protect local ecosystems from potential pollutants.
These benefits align perfectly with global sustainability goals and showcase how innovative environmental technologies can make a real difference in our fight against climate change and resource depletion.
For those interested in monitoring and reducing environmental impact in agriculture, Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tools offer valuable insights. These tools help agribusinesses track their emissions and identify areas for improvement, complementing efforts like those seen at the Pasco facility.
Expanding Capacity to Meet Growing Demand
“The facility’s expansion increased its capacity by 50%, enabling it to process more waste and generate additional biogas for energy production.”
The success of the PWRF and PRRC has not gone unnoticed. As demand for process water treatment in the Pasco area grew, including the addition of major players like Darigold, the need for expansion became clear. This growth is a testament to the facility’s effectiveness and the increasing recognition of the importance of sustainable water management practices in the food processing industry.
The expansion project, valued at US$180 million, is set to significantly increase the facility’s treatment capacity. This enhancement will not only allow for the processing of more wastewater but will also boost the production of valuable resources like RNG and soil amendments. It’s a clear indication of the project’s success and the growing demand for sustainable solutions in industrial processes.

Innovative Partnerships Driving Success
The success of the PWRF and PRRC is not just about technology; it’s also about innovative partnerships and collaboration. The City of Pasco’s strategic 30-year public-private partnership with Burnham RNG is a prime example of how such collaborations can drive sustainability initiatives forward.
This partnership model allows for:
- Shared costs and risks
- Access to private sector expertise and innovation
- Long-term planning and investment
- Flexibility to adapt to changing needs and technologies
The involvement of companies like Swinerton Energy as the EPC contractor further ensures that the project is completed on time and within budget, demonstrating the power of bringing together diverse expertise to tackle complex environmental challenges.
Technology at the Heart of Sustainability
The PWRF and PRRC showcase some of the most advanced environmental technologies available today. These include:
- Advanced Anaerobic Digestion: For efficient biogas production
- Membrane Bioreactors: For high-quality water treatment
- Nutrient Recovery Systems: To extract valuable soil amendments
- Biogas Upgrading Technology: To produce pipeline-quality RNG
These technologies work in harmony to create a highly efficient, closed-loop system that maximizes resource recovery while minimizing environmental impact. It’s a testament to what’s possible when we apply cutting-edge science and engineering to environmental challenges.
In the realm of agricultural technology, Farmonaut’s crop plantation and forest advisory services offer similar innovative approaches. By leveraging satellite technology and AI, these services provide valuable insights for sustainable land management, complementing the goals of water conservation and resource optimization seen in the Pasco facility.
Sustainable Water Management: A Model for the Future
The PWRF and PRRC in Pasco, WA, represent more than just a local success story; they offer a model for sustainable water management that could be replicated across the United States and beyond. By demonstrating that it’s possible to turn waste into valuable resources, this facility is paving the way for a new approach to industrial water use and waste management.
Key takeaways from this project include:
- The importance of viewing waste as a resource
- The potential for closed-loop systems in industrial processes
- The value of public-private partnerships in driving innovation
- The role of advanced technology in achieving sustainability goals
As we face increasing water scarcity and environmental challenges globally, projects like this offer hope and a practical roadmap for creating more sustainable, resilient communities.
Resource Recovery: A Closer Look at the Outputs
Let’s delve deeper into the valuable resources recovered at the Pasco facility and their applications:
| Resource Recovered | Production Process | Environmental Benefits | Agricultural Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) | Anaerobic digestion of organic waste, followed by biogas upgrading | Reduces greenhouse gas emissions, replaces fossil fuels | Powers farm equipment, heats greenhouses |
| Soil Amendments | Extraction of nutrients from wastewater, processing of organic solids | Reduces need for synthetic fertilizers, improves soil health | Enhances crop yields, improves soil structure |
| Clean Water for Irrigation | Advanced treatment and purification of process water | Conserves freshwater resources, reduces strain on local water supplies | Provides reliable water source for crop irrigation |
This table illustrates the circular economy in action, where waste products are transformed into valuable resources that support sustainable agriculture and energy production. It’s a prime example of how innovative environmental technologies can create multiple benefits across different sectors.
For farmers and agricultural businesses looking to optimize their resource use, Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management solutions offer powerful tools. These solutions can help integrate sustainable practices, like those demonstrated at the Pasco facility, into daily farm operations, enhancing efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
While the Pasco facility focuses on water reuse and resource recovery, it’s part of a broader movement towards technology-driven sustainable agriculture. Advanced technologies are playing an increasingly crucial role in helping farmers and agribusinesses optimize their operations and reduce their environmental footprint.
Some key areas where technology is making a difference include:
- Precision Agriculture: Using satellite imagery and AI to optimize crop management
- Smart Irrigation: Employing sensors and data analytics to improve water use efficiency
- Soil Health Monitoring: Utilizing advanced testing methods to maintain optimal soil conditions
- Crop Traceability: Implementing blockchain and other technologies to ensure food safety and transparency
These technologies complement the work being done at facilities like the PWRF and PRRC, creating a more holistic approach to sustainable agriculture and food production.
The Future of Sustainable Water Management
As we look to the future, the success of the Pasco facility points to several exciting possibilities:
- Expanded Application: Similar resource recovery centers could be implemented in other food processing hubs across the country.
- Technological Advancements: Continued innovation in treatment technologies could further improve efficiency and resource recovery.
- Integration with Smart City Initiatives: Resource recovery centers could become key components of broader smart city and sustainable urban planning efforts.
- Policy Support: The success of such projects could lead to more supportive policies and incentives for sustainable water management practices.
The journey towards truly sustainable water management is ongoing, but projects like the PWRF and PRRC in Pasco are lighting the way forward. They demonstrate that with innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to sustainability, we can transform our approach to resource use and environmental stewardship.
For those interested in staying at the forefront of agricultural innovation, Farmonaut’s suite of digital farming tools offers cutting-edge solutions. From satellite-based crop monitoring to AI-driven insights, these tools empower farmers to make data-driven decisions that align with sustainable practices.
Conclusion: A Model for Sustainable Innovation
The Process Water Reuse Facility and Pasco Resource Recovery Center in Washington state stand as a shining example of what’s possible when we reimagine our approach to waste and resource management. By transforming food processing waste into valuable resources, this facility is not just solving a local environmental challenge; it’s providing a blueprint for sustainable water management that could be replicated across the globe.
Key takeaways from this groundbreaking project include:
- The power of viewing waste as a resource rather than a problem
- The importance of innovative partnerships in driving sustainable solutions
- The critical role of advanced environmental technologies in achieving sustainability goals
- The potential for significant environmental and economic benefits through resource recovery
As we face increasing environmental challenges, from water scarcity to climate change, initiatives like the PWRF and PRRC offer hope and practical solutions. They demonstrate that with creativity, collaboration, and commitment, we can create systems that not only reduce our environmental impact but also generate value and support sustainable growth.
The success of this facility should inspire us all to think differently about our resources and waste streams. Whether you’re a policymaker, an industry leader, or an individual concerned about sustainability, there are lessons to be learned and applied from this innovative project.
As we move forward, let’s continue to support and invest in such innovative solutions. By doing so, we can create a more sustainable, resilient future for generations to come.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the main purpose of the Process Water Reuse Facility (PWRF) and Pasco Resource Recovery Center (PRRC)?
A: The main purpose is to transform process water from food processing plants into valuable resources like renewable natural gas, soil amendments, and clean water for irrigation, while reducing environmental impact.
Q: How does the facility generate renewable natural gas?
A: The facility uses anaerobic digestion to break down organic waste in the process water, producing biogas which is then upgraded to renewable natural gas.
Q: What are the environmental benefits of this project?
A: The project reduces water waste, generates clean energy, produces sustainable soil amendments, and significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional waste management methods.
Q: How does this facility impact local agriculture?
A: It provides clean water for irrigation and nutrient-rich soil amendments, supporting sustainable agricultural practices in the region.
Q: Can this model be replicated in other areas?
A: Yes, this model could potentially be adapted and implemented in other food processing hubs, offering a sustainable solution for water management and resource recovery.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
For developers interested in integrating agricultural data into their applications, check out the Farmonaut API and the comprehensive API Developer Docs.