Vermont’s Act 181: Revolutionizing Land Use Planning in Manchester and Bennington County
“Act 181 introduces a tiered system of exemptions, potentially affecting development in over 250 Vermont municipalities.”
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of Vermont’s groundbreaking Act 181 and its profound impact on land use planning, particularly in Manchester and Bennington County. As we delve into this transformative legislation, we’ll uncover how it’s reshaping the landscape of agricultural land use planning and opening new avenues for sustainable development.
Understanding Act 181: A New Era for Vermont’s Land Use
In January 2024, the Manchester Planning Commission embarked on a journey to adapt to the sweeping changes brought about by Vermont’s Act 181. This legislative milestone represents a significant shift in the state’s approach to land use planning, particularly in its relation to the long-standing Act 250.
Act 181 aims to streamline development processes in designated growth areas while preserving rural conservation zones. This delicate balance is crucial for towns like Manchester, Bennington, and Landgrove, which are currently in the midst of updating their Town Plans as part of a mandated eight-year review process.

The Tiered System: A New Approach to Development
At the heart of Act 181 is the introduction of a tiered system of exemptions. This innovative approach aims to simplify development processes in designated areas, providing a more nuanced and flexible framework for land use planning. Let’s break down this system:
| Tier Level | Area Description | Exemption Status | Potential Impact on Agriculture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1A: Urban Centers | Downtown and village centers with adequate infrastructure | Highest level of exemption from Act 250 requirements | Minimal direct impact; may reduce pressure on agricultural lands |
| Tier 1B: Planned Growth Areas | Areas adjacent to urban centers, slated for development | Significant exemptions, but more oversight than Tier 1A | Moderate impact; may include some conversion of farmland |
| Tier 2: Village Centers | Smaller community centers with some infrastructure | Moderate exemptions, focused on maintaining character | Potential for integration of small-scale agriculture |
| Tier 3: Rural Conservation Zones | Agricultural lands and natural areas | Limited exemptions; focus on preservation | High protection for existing agricultural activities |
This tiered system offers municipalities like Manchester the opportunity to obtain Tier 1A status, potentially easing the pathway for future developments. For towns with designated village centers, this presents a favorable position for streamlined growth.
Regional Collaboration: A Key to Success
The implementation of Act 181 has sparked a collaborative effort between local municipalities and regional planning bodies. In Manchester, this collaboration is exemplified by the work of the Bennington County Regional Commission (BCRC).
- Creation of unified regional land use maps
- Standardization of terminology across Vermont’s 11 regional planning bodies
- Development of comprehensive categories for future planning
These efforts aim to ensure clarity and consistency in future planning endeavors, creating a robust framework for sustainable development across the state.
Precision Agriculture: A Game-Changer in Land Use Planning
As Vermont adapts to these new planning frameworks, the role of precision agriculture becomes increasingly significant. This is where Farmonaut’s innovative technologies come into play.
“Vermont’s new land use planning could impact approximately 625,000 acres of agricultural land in the state.”
Farmonaut’s precision farming techniques and smart irrigation systems offer invaluable tools for optimizing crop yields within these newly defined regions. By leveraging satellite-based farm management solutions, farmers can make data-driven decisions that align with the goals of Act 181.
Smart Irrigation: Conserving Resources in a Changing Landscape
One of the key challenges in adapting to new land use regulations is the efficient use of resources, particularly water. Farmonaut’s smart irrigation systems provide a solution by:
- Analyzing soil moisture levels through satellite imagery
- Providing real-time data on crop water needs
- Optimizing irrigation schedules to reduce water waste
This technology not only helps farmers comply with new regulations but also contributes to overall water conservation efforts in Vermont.
GIS for Farm Management: Adapting to New Zoning Regulations
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a crucial role in adapting to the new zoning regulations introduced by Act 181. Farmonaut’s GIS capabilities allow farmers and planners to:
- Visualize land use changes in real-time
- Identify optimal areas for different types of agricultural activities
- Comply with new zoning requirements while maximizing productivity
By integrating GIS data with precision farming techniques, we can ensure that agricultural practices align seamlessly with the new tiered system of land use planning.
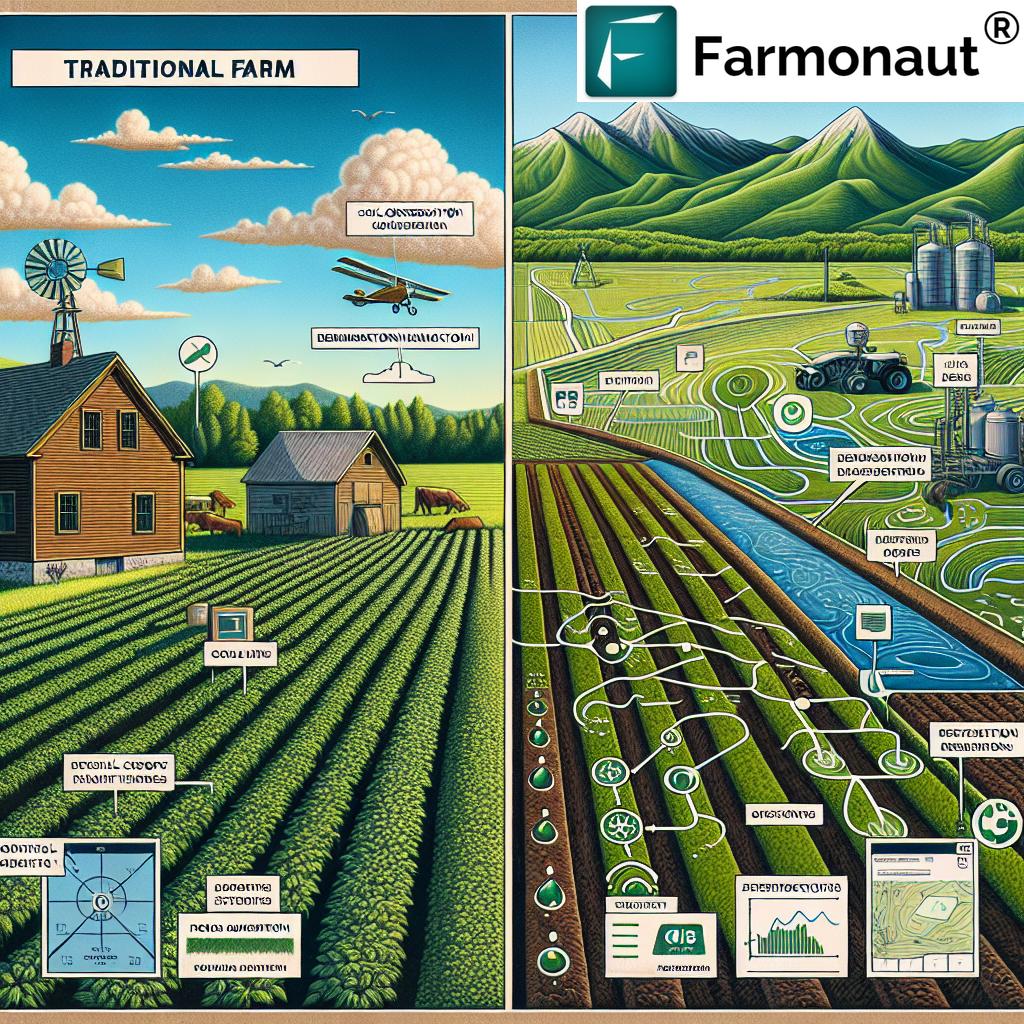
Remote Sensing: A Tool for Sustainable Agriculture
Remote sensing technology is at the forefront of adapting to Vermont’s evolving agricultural landscape. Farmonaut’s advanced remote sensing capabilities offer:
- Regular monitoring of crop health and growth patterns
- Early detection of potential issues like pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies
- Assistance in making informed decisions about resource allocation
These capabilities are particularly valuable in areas designated as rural conservation zones under Act 181, where sustainable agriculture practices are paramount.
Soil Conservation Methods: Aligning with Act 181’s Goals
Act 181’s emphasis on preserving rural conservation zones highlights the importance of soil conservation methods. Farmonaut’s technology supports these efforts by:
- Providing data on soil health and composition
- Recommending crop rotation strategies to maintain soil fertility
- Monitoring erosion risks and suggesting mitigation measures
By implementing these methods, farmers can ensure long-term sustainability while complying with new land use regulations.
Crop Yield Optimization: Balancing Growth and Conservation
As Vermont strives to balance development with conservation, optimizing crop yields becomes crucial. Farmonaut’s AI-driven advisory system, Jeevn AI, offers personalized recommendations for:
- Optimal planting times based on local climate data
- Fertilizer application schedules to maximize yield while minimizing environmental impact
- Pest management strategies that align with conservation goals
These insights help farmers adapt to the new land use categories while maintaining or even improving their agricultural output.
The Role of Technology in Implementing Act 181
As we navigate the complexities of Act 181, technology plays a pivotal role in ensuring its successful implementation. Farmonaut’s suite of tools, including our API and API Developer Docs, provide the necessary infrastructure for:
- Real-time monitoring of land use changes
- Data-driven decision-making in agricultural planning
- Seamless integration of farming practices with new zoning regulations
Economic Implications of Act 181 for Vermont Agriculture
The implementation of Act 181 brings significant economic implications for Vermont’s agricultural sector. By streamlining development in designated areas, the Act aims to:
- Encourage economic growth in urban and village centers
- Preserve valuable agricultural lands
- Create new opportunities for sustainable farming practices
Farmonaut’s technology can help farmers navigate these changes by providing tools for efficient resource management and crop optimization, potentially leading to increased profitability even within new land use constraints.
Community Engagement and Act 181
The success of Act 181 heavily relies on community engagement and understanding. In Manchester and Bennington County, this involves:
- Public feedback sessions on proposed land use maps
- Educational initiatives on the benefits of precision agriculture
- Collaboration between farmers, planners, and technology providers
Farmonaut supports these efforts by offering user-friendly tools that make advanced agricultural technology accessible to all stakeholders.
The Future of Vermont Agriculture Under Act 181
As we look to the future, Act 181 sets the stage for a more sustainable and efficient agricultural sector in Vermont. The integration of precision farming techniques, smart irrigation systems, and advanced GIS tools will be crucial in realizing this vision. Farmonaut is committed to supporting this transition by continually innovating and adapting our technologies to meet the evolving needs of Vermont’s farmers and planners.
Conclusion: Embracing Change for a Sustainable Future
Vermont’s Act 181 represents a bold step towards modernizing land use planning and agricultural practices. By embracing precision agriculture technologies and sustainable farming methods, we can ensure that Vermont’s agricultural sector not only survives but thrives in this new regulatory environment. As we continue to navigate these changes, Farmonaut remains dedicated to providing the tools and insights necessary for success in this evolving landscape.
FAQ Section
Q: How does Act 181 affect small farmers in Vermont?
A: Act 181 aims to protect rural conservation zones, which can benefit small farmers by preserving agricultural lands. Additionally, the tiered system may provide opportunities for small-scale agriculture in village centers.
Q: Can Farmonaut’s technology help in complying with new zoning regulations?
A: Yes, Farmonaut’s GIS and remote sensing capabilities can assist farmers in understanding and adhering to new zoning regulations by providing detailed land use data and crop management insights.
Q: How does precision agriculture contribute to sustainable farming under Act 181?
A: Precision agriculture techniques, such as those offered by Farmonaut, help optimize resource use, reduce environmental impact, and improve crop yields – all of which align with Act 181’s goals of sustainable development and conservation.
Q: What role do smart irrigation systems play in the context of Act 181?
A: Smart irrigation systems are crucial for water conservation, which is an important aspect of sustainable agriculture under Act 181. These systems help farmers use water more efficiently, especially in areas designated for agricultural preservation.
Q: How can communities get involved in the implementation of Act 181?
A: Communities can participate in public feedback sessions, engage with local planning commissions, and stay informed about changes in land use planning. They can also explore how technologies like Farmonaut can support sustainable agriculture in their area.
For more information on how Farmonaut can support your agricultural needs in light of Act 181, explore our web app, Android app, and iOS app.
Interested in partnering with us? Check out our Earn With Farmonaut program and start growing your income today!
















