Washington’s Biosolids Dilemma: Balancing Agricultural Benefits with PFAS Contamination Concerns
In the lush agricultural lands of Washington state, a complex and contentious issue is brewing. It’s a dilemma that pits the promise of sustainable farming practices against growing concerns over potential health risks. At the heart of this debate lies biosolids – fertilizers made from human waste – and their use in agriculture. As we delve into this multifaceted topic, we’ll explore the delicate balance between harnessing a valuable resource and safeguarding public health and the environment.

“Washington state’s biosolids debate involves over 120,000 tons of sewage sludge applied to farmland annually.”
The Biosolids Landscape in Washington
Across the verdant fields of Washington, farmers have been spreading thousands of tons of fertilizer derived from human waste on their crops each year. This practice, while not unique to the Evergreen State, has become a focal point of environmental and health discussions. The term “biosolids” – a euphemism for treated sewage sludge – has become both a beacon of agricultural innovation and a source of growing concern.
In counties like King and Pierce, the use of biosolids in agriculture has been particularly prevalent. These nutrient-rich materials offer a sustainable solution to waste management and soil fertilization. However, as we peel back the layers of this practice, a more complex picture emerges – one that involves potential contamination and long-term environmental impacts.
The PFAS Problem: A Growing Concern
At the forefront of the biosolids debate is a group of chemicals known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS. These “forever chemicals” have earned their ominous nickname due to their persistence in the environment and the human body. PFAS are linked to a host of health issues, including cancer, thyroid problems, and developmental delays in children.
The presence of PFAS in biosolids has raised red flags among scientists, policymakers, and the public. While experts in Washington state, particularly in King and Pierce counties, suggest that the PFAS problem isn’t as pronounced as in some other regions, the lack of comprehensive testing leaves many questions unanswered.
Legislative Action: A Step Towards Transparency
In response to growing concerns, Washington state Senator Jeff Wilson has introduced a bill aimed at addressing the PFAS issue in biosolids. This legislative effort would require the state Department of Ecology to establish sampling and testing requirements for PFAS in biosolids by July 2025. The bill represents a critical step towards understanding the extent of PFAS contamination and developing appropriate management strategies.
Key points of the proposed legislation include:
- Mandatory PFAS testing for biosolids producers
- Analysis of PFAS levels in Washington-produced biosolids by 2026
- Recommendations to the Legislature on how to proceed by the end of 2027
This initiative reflects a growing awareness of the need for rigorous scientific assessment and transparent reporting in the use of biosolids in agriculture.
The Balancing Act: Benefits vs. Risks
The use of biosolids in agriculture presents a classic case of balancing benefits against potential risks. On one side of the scale, we have the advantages:
- Sustainable waste management solution
- Rich source of nutrients for crops
- Reduction in the need for synthetic fertilizers
- Improvement of soil structure and water retention
On the other side, we must consider the concerns:
- Potential PFAS contamination
- Presence of other contaminants like heavy metals
- Risk of pathogen spread
- Long-term accumulation of pollutants in soil
“PFAS contamination in biosolids can persist for decades, with some compounds having half-lives exceeding 1,000 years.”

The Role of Technology in Monitoring and Management
As we grapple with the complexities of biosolids use in agriculture, technology emerges as a crucial ally. Advanced monitoring systems and data-driven approaches can play a significant role in ensuring the safe and effective use of biosolids while mitigating potential risks.
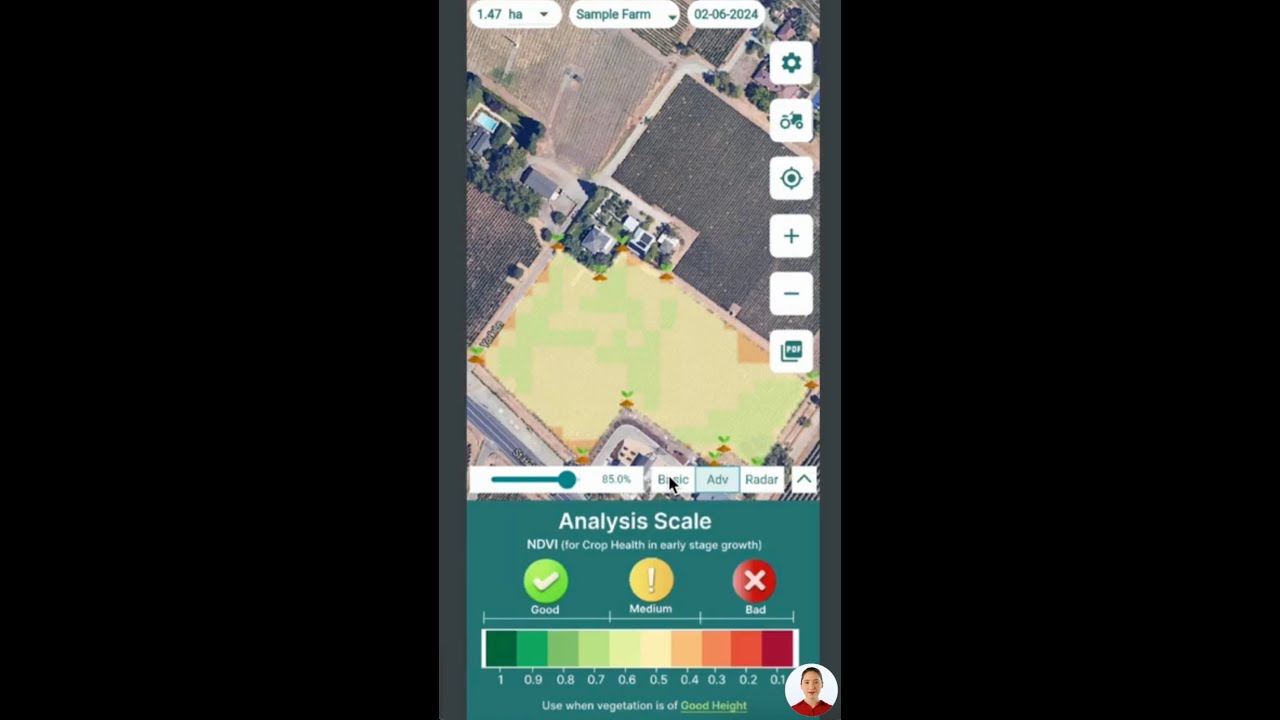
At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of leveraging technology to address agricultural challenges. While our focus is not specifically on biosolids management, our satellite-based crop health monitoring and AI-driven advisory systems can provide valuable insights into soil health and crop performance. These tools can be instrumental in detecting anomalies and optimizing resource management in fields where biosolids are applied.
Our API and API Developer Docs provide access to cutting-edge satellite and weather data, enabling researchers and policymakers to make informed decisions about land use and agricultural practices.
Community Perspectives and Public Health Concerns
The biosolids debate has sparked intense discussions within Washington communities. While some farmers advocate for the continued use of biosolids, citing their agricultural benefits and cost-effectiveness, others express deep concerns about potential health risks and environmental contamination.
Public health experts emphasize the need for comprehensive studies on the long-term effects of biosolids use, particularly regarding PFAS exposure. The persistence of these chemicals in the environment raises questions about their potential accumulation in the food chain and subsequent impact on human health.
Regulatory Landscape and Future Directions
As Washington grapples with its biosolids dilemma, it’s important to note that other states have taken more drastic measures. Connecticut and Maine, for instance, have banned the use of biosolids on agricultural lands due to PFAS concerns. These actions highlight the growing awareness of the potential risks associated with biosolids and the need for robust regulatory frameworks.
The proposed legislation in Washington represents a middle ground – an attempt to gather crucial data while maintaining the option to use biosolids in agriculture. This approach aligns with the state’s commitment to sustainable practices while acknowledging the need for careful monitoring and management.
The Role of Precision Agriculture in Addressing Biosolids Concerns
As we navigate the complex landscape of biosolids use in agriculture, precision farming techniques offer promising solutions for monitoring and managing potential risks. Advanced technologies can play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and effective application of biosolids while minimizing environmental impact.
At Farmonaut, we specialize in satellite-based crop health monitoring and AI-driven advisory systems. While our focus is not specifically on biosolids management, our technologies can provide valuable insights for farmers and researchers dealing with biosolids-related issues:
- Real-time crop health monitoring to detect anomalies that might be related to soil contamination
- Soil moisture analysis to optimize biosolids application and prevent runoff
- AI-powered recommendations for balanced nutrient management
- Data-driven insights to support long-term studies on the effects of biosolids use
Comparative Analysis: Biosolids Benefits and Concerns
| Aspect | Benefits | Concerns | Estimated Impact | Regulatory Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Content | Rich in nitrogen and phosphorus | Potential for over-fertilization | High | Regulated under EPA guidelines |
| Soil Health | Improves soil structure and water retention | Long-term accumulation of contaminants | Medium | Monitored, but regulations vary by state |
| PFAS Contamination | N/A | Persistent environmental pollutant | High | Emerging regulations, varies by state |
| Heavy Metal Presence | Some metals beneficial in trace amounts | Potential toxicity at high levels | Medium | EPA regulated with specific limits |
| Pathogen Risks | N/A | Potential spread of harmful organisms | Low (with proper treatment) | Strictly regulated by EPA |
| Economic Factors | Cost-effective fertilizer alternative | Potential long-term environmental costs | Medium | Not directly regulated, market-driven |
The Path Forward: Balancing Innovation and Caution
As Washington state grapples with its biosolids dilemma, the path forward requires a delicate balance between leveraging agricultural innovations and exercising caution to protect public health and the environment. The proposed legislation for mandatory PFAS testing is a crucial step towards transparency and informed decision-making.
Moving forward, a multi-faceted approach is necessary:
- Continued research into the long-term effects of biosolids use on soil and human health
- Development of advanced treatment technologies to reduce contaminants in biosolids
- Implementation of precision agriculture techniques for optimal biosolids management
- Regular monitoring and testing of soils and crops where biosolids are applied
- Public education and engagement to foster informed discussions on biosolids use
Conclusion: A Call for Balanced Action
Washington’s biosolids dilemma encapsulates the broader challenges facing modern agriculture – the need to balance productivity, sustainability, and safety. As we navigate this complex issue, it’s crucial to embrace a science-based approach that leverages technological innovations while prioritizing public health and environmental protection.
The debate surrounding biosolids use in agriculture is far from over. However, by fostering open dialogue, supporting rigorous research, and implementing advanced monitoring technologies, Washington can lead the way in developing responsible and sustainable practices for biosolids management.
As we continue to monitor this evolving situation, tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring and AI advisory systems can play a vital role in providing data-driven insights to support informed decision-making. By combining innovative technologies with thoughtful policy-making, we can work towards a future where agricultural productivity and environmental stewardship go hand in hand.
Earn With Farmonaut: Join our affiliate program and earn 20% recurring commission by helping farmers save 10% with your promo code. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
FAQ Section
- What are biosolids?
Biosolids are nutrient-rich organic materials resulting from the treatment of domestic sewage in a wastewater treatment facility. They are often used as fertilizer in agriculture. - Why are biosolids used in agriculture?
Biosolids are rich in nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, making them an effective and sustainable alternative to synthetic fertilizers. They also improve soil structure and water retention. - What are PFAS, and why are they a concern in biosolids?
PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) are a group of man-made chemicals that persist in the environment and can accumulate in the human body. They are found in many consumer products and can end up in wastewater, potentially contaminating biosolids. - How is Washington addressing the biosolids issue?
Washington is considering legislation that would require mandatory testing for PFAS in biosolids and comprehensive analysis of PFAS levels in state-produced biosolids. - Are biosolids safe to use in agriculture?
When properly treated and applied, biosolids can be safe and beneficial. However, concerns about contaminants like PFAS have led to increased scrutiny and calls for more rigorous testing and regulation.

















Nothing is listed in the comparative analysis of the contamination of sewage sludge, for pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors, and household cleaning products that don’t degrade in the digesting process.
Also pesticide residues can be a source of PFAS chemicals. There are 30 different pesticides that contain PFAS materials as part of their formulation ingredients.